3---Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
目录
添加节流
自定义节流的方法
- 限制60s内只能访问3次
(1)API文件夹下面新建throttle.py,代码如下:
# utils/throttle.py from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
import time
VISIT_RECORD = {} #保存访问记录 class VisitThrottle(BaseThrottle):
'''60s内只能访问3次'''
def __init__(self):
self.history = None #初始化访问记录 def allow_request(self,request,view):
#获取用户ip (get_ident)
remote_addr = self.get_ident(request)
ctime = time.time()
#如果当前IP不在访问记录里面,就添加到记录
if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD:
VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime,] #键值对的形式保存
return True #True表示可以访问
#获取当前ip的历史访问记录
history = VISIT_RECORD.get(remote_addr)
#初始化访问记录
self.history = history #如果有历史访问记录,并且最早一次的访问记录离当前时间超过60s,就删除最早的那个访问记录,
#只要为True,就一直循环删除最早的一次访问记录
while history and history[-1] < ctime - 60:
history.pop()
#如果访问记录不超过三次,就把当前的访问记录插到第一个位置(pop删除最后一个)
if len(history) < 3:
history.insert(0,ctime)
return True def wait(self):
'''还需要等多久才能访问'''
ctime = time.time()
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
(2)settings中全局配置节流
#全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
#节流
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":['API.utils.throttle.VisitThrottle'],
}
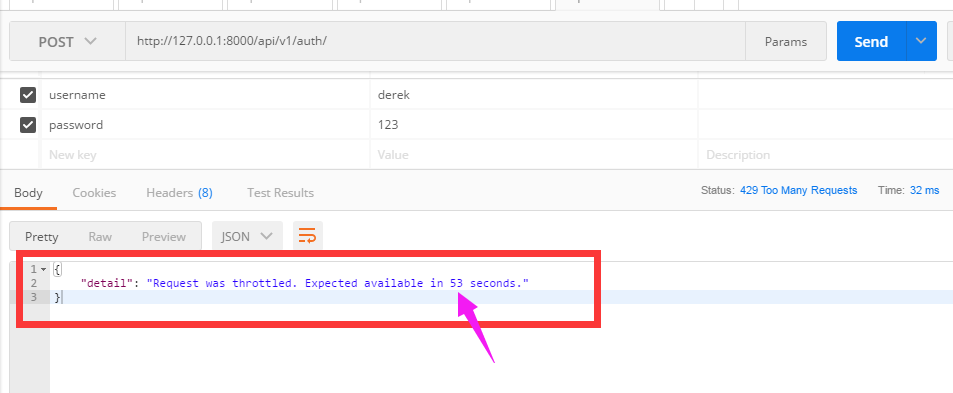
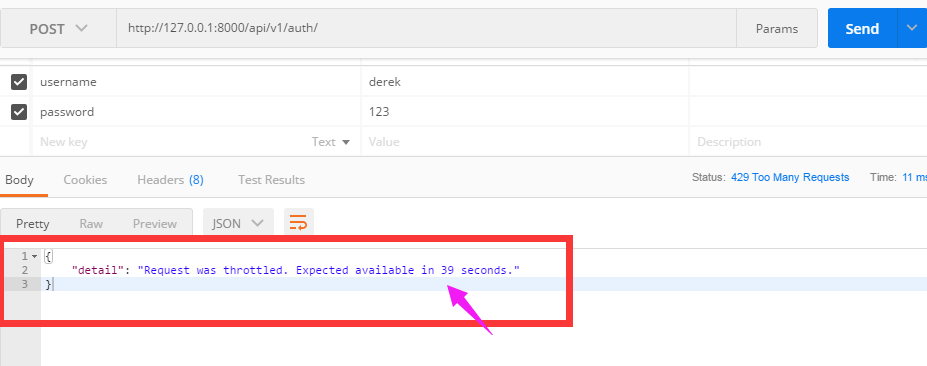
(3)现在访问auth看看结果:
- 60s内访问次数超过三次,会限制访问
- 提示剩余多少时间可以访问
接着访问
节流源码分析
(1)dispatch
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
#对原始request进行加工,丰富了一些功能
#Request(
# request,
# parsers=self.get_parsers(),
# authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
# negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
# parser_context=parser_context
# )
#request(原始request,[BasicAuthentications对象,])
#获取原生request,request._request
#获取认证类的对象,request.authticators
#1.封装request
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try:
#2.认证
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response
(2)initial
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
#4.实现认证
self.perform_authentication(request)
#5.权限判断
self.check_permissions(request)
#6.控制访问频率
self.check_throttles(request)
(3)check_throttles
里面有个allow_request
def check_throttles(self, request):
"""
Check if request should be throttled.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled.
"""
for throttle in self.get_throttles():
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
(4)get_throttles
def get_throttles(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of throttles that this view uses.
"""
return [throttle() for throttle in self.throttle_classes]
(5)thtottle_classes
内置节流类
上面是写的自定义节流,drf内置了很多节流的类,用起来比较方便。
(1)BaseThrottle
- 自己要写allow_request和wait方法
- get_ident就是获取ip
class BaseThrottle(object):
"""
Rate throttling of requests.
""" def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if the request should be allowed, `False` otherwise.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden') def get_ident(self, request):
"""
Identify the machine making the request by parsing HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR
if present and number of proxies is > 0. If not use all of
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR if it is available, if not use REMOTE_ADDR.
"""
xff = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
num_proxies = api_settings.NUM_PROXIES if num_proxies is not None:
if num_proxies == 0 or xff is None:
return remote_addr
addrs = xff.split(',')
client_addr = addrs[-min(num_proxies, len(addrs))]
return client_addr.strip() return ''.join(xff.split()) if xff else remote_addr def wait(self):
"""
Optionally, return a recommended number of seconds to wait before
the next request.
"""
return None
(2)SimpleRateThrottle
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
"""
A simple cache implementation, that only requires `.get_cache_key()`
to be overridden. The rate (requests / seconds) is set by a `rate` attribute on the View
class. The attribute is a string of the form 'number_of_requests/period'. Period should be one of: ('s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day') Previous request information used for throttling is stored in the cache.
"""
cache = default_cache
timer = time.time
cache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'
scope = None #这个值自定义,写什么都可以
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
self.rate = self.get_rate()
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate) def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden. May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden') def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg) try:
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg) def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
num, period = rate.split('/')
num_requests = int(num)
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration) def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled. On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
if self.rate is None:
return True self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
self.now = self.timer() # Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success() def throttle_success(self):
"""
Inserts the current request's timestamp along with the key
into the cache.
"""
self.history.insert(0, self.now)
self.cache.set(self.key, self.history, self.duration)
return True def throttle_failure(self):
"""
Called when a request to the API has failed due to throttling.
"""
return False def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
我们可以通过继承SimpleRateThrottle类,来实现节流,会更加的简单,因为SimpleRateThrottle里面都帮我们写好了
(1)throttle.py
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
'''匿名用户60s只能访问三次(根据ip)'''
scope = 'NBA' #这里面的值,自己随便定义,settings里面根据这个值配置Rate def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#通过ip限制节流
return self.get_ident(request) class UserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
'''登录用户60s可以访问10次'''
scope = 'NBAUser' #这里面的值,自己随便定义,settings里面根据这个值配置Rate def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return request.user.username
(2)settings.py
#全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
#节流
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":['API.utils.throttle.UserThrottle'], #全局配置,登录用户节流限制(10/m)
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES":{
'NBA':'3/m', #没登录用户3/m,NBA就是scope定义的值
'NBAUser':'10/m', #登录用户10/m,NBAUser就是scope定义的值
}
}
(3)views.py
局部配置方法
class AuthView(APIView):
.
.
.
# 默认的节流是登录用户(10/m),AuthView不需要登录,这里用匿名用户的节流(3/m)
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle,]
.
.
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from API import models
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from API.utils.permission import SVIPPremission,MyPremission
from API.utils.throttle import VisitThrottle ORDER_DICT = {
1:{
'name':'apple',
'price':15
},
2:{
'name':'dog',
'price':100
}
} def md5(user):
import hashlib
import time
#当前时间,相当于生成一个随机的字符串
ctime = str(time.time())
m = hashlib.md5(bytes(user,encoding='utf-8'))
m.update(bytes(ctime,encoding='utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest() class AuthView(APIView):
'''用于用户登录验证''' authentication_classes = [] #里面为空,代表不需要认证
permission_classes = [] #不里面为空,代表不需要权限
# 默认的节流是登录用户(10/m),AuthView不需要登录,这里用匿名用户的节流(3/m)
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle,] def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
#为用户创建token
token = md5(user)
#存在就更新,不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={'token':token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret) class OrderView(APIView):
'''
订单相关业务(只有SVIP用户才能看)
''' def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
self.dispatch
#request.user
#request.auth
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None,'data':None}
try:
ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret) class UserInfoView(APIView):
'''
订单相关业务(普通用户和VIP用户可以看)
'''
permission_classes = [MyPremission,] #不用全局的权限配置的话,这里就要写自己的局部权限
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs): print(request.user)
return HttpResponse('用户信息')
views.py
说明:
- API.utils.throttle.UserThrottle 这个是全局配置(根据ip限制,10/m)
- DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES --->>>设置访问频率的
- throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle,] --->>>局部配置(不适用settings里面默认的全局配置)
总结
基本使用
- 创建类,继承BaseThrottle, 实现:allow_request ,wait
- 创建类,继承SimpleRateThrottle, 实现: get_cache_key, scope='NBA' (配置文件中的key)
全局
#节流
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":['API.utils.throttle.UserThrottle'], #全局配置,登录用户节流限制(10/m)
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES":{
'NBA':'3/m', #没登录用户3/m,NBA就是scope定义的值
'NBAUser':'10/m', #登录用户10/m,NBAUser就是scope定义的值
}
}
局部
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle,]
所有代码
认证、权限和节流
# MyProject/urls.py from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from API.views import AuthView,OrderView,UserInfoView urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('api/v1/auth/',AuthView.as_view()),
path('api/v1/order/',OrderView.as_view()),
path('api/v1/info/',UserInfoView.as_view()),
]
MyProject/urls.py
#全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
#认证
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['API.utils.auth.Authentication',],
#权限
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":['API.utils.permission.SVIPPermission'],
#节流
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":['API.utils.throttle.UserThrottle'], #全局配置,登录用户节流限制(10/m)
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES":{
'NBA':'3/m', #没登录用户3/m,NBA就是scope定义的值
'NBAUser':'10/m', #登录用户10/m,NBAUser就是scope定义的值
}
}
settings.py
# API/models.py from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Model):
USER_TYPE = (
(1,'普通用户'),
(2,'VIP'),
(3,'SVIP')
) user_type = models.IntegerField(choices=USER_TYPE)
username = models.CharField(max_length=32)
password = models.CharField(max_length=64) class UserToken(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField(UserInfo,on_delete=models.CASCADE)
token = models.CharField(max_length=64)
API/models.py
# API/views.py from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from API import models
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from API.utils.permission import SVIPPermission,MyPermission
from API.utils.throttle import VisitThrottle ORDER_DICT = {
1:{
'name':'apple',
'price':15
},
2:{
'name':'dog',
'price':100
}
} def md5(user):
import hashlib
import time
#当前时间,相当于生成一个随机的字符串
ctime = str(time.time())
m = hashlib.md5(bytes(user,encoding='utf-8'))
m.update(bytes(ctime,encoding='utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest() class AuthView(APIView):
'''用于用户登录验证''' authentication_classes = [] #里面为空,代表不需要认证
permission_classes = [] #不里面为空,代表不需要权限
# 默认的节流是登录用户(10/m),AuthView不需要登录,这里用匿名用户的节流(3/m)
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle,] def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
#为用户创建token
token = md5(user)
#存在就更新,不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={'token':token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret) class OrderView(APIView):
'''
订单相关业务(只有SVIP用户才能看)
''' def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
self.dispatch
#request.user
#request.auth
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None,'data':None}
try:
ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret) class UserInfoView(APIView):
'''
订单相关业务(普通用户和VIP用户可以看)
'''
permission_classes = [MyPermission,] #不用全局的权限配置的话,这里就要写自己的局部权限
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs): print(request.user)
return HttpResponse('用户信息')
API/views.py
# API/utils/auth/py from rest_framework import exceptions
from API import models
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication class Authentication(BaseAuthentication):
'''用于用户登录验证'''
def authenticate(self,request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user,token_obj) def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
API/utils/auth/py
# utils/permission.py from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission class SVIPPermission(BasePermission):
message = "必须是SVIP才能访问"
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user.user_type != 3:
return False
return True class MyPermission(BasePermission):
def has_permission(self,request,view):
if request.user.user_type == 3:
return False
return True
utils/permission.py
# utils/throttle.py
#
# from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
# import time
# VISIT_RECORD = {} #保存访问记录
#
# class VisitThrottle(BaseThrottle):
# '''60s内只能访问3次'''
# def __init__(self):
# self.history = None #初始化访问记录
#
# def allow_request(self,request,view):
# #获取用户ip (get_ident)
# remote_addr = self.get_ident(request)
# ctime = time.time()
# #如果当前IP不在访问记录里面,就添加到记录
# if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD:
# VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime,] #键值对的形式保存
# return True #True表示可以访问
# #获取当前ip的历史访问记录
# history = VISIT_RECORD.get(remote_addr)
# #初始化访问记录
# self.history = history
#
# #如果有历史访问记录,并且最早一次的访问记录离当前时间超过60s,就删除最早的那个访问记录,
# #只要为True,就一直循环删除最早的一次访问记录
# while history and history[-1] < ctime - 60:
# history.pop()
# #如果访问记录不超过三次,就把当前的访问记录插到第一个位置(pop删除最后一个)
# if len(history) < 3:
# history.insert(0,ctime)
# return True
#
# def wait(self):
# '''还需要等多久才能访问'''
# ctime = time.time()
# return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1]) from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
'''匿名用户60s只能访问三次(根据ip)'''
scope = 'NBA' #这里面的值,自己随便定义,settings里面根据这个值配置Rate def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#通过ip限制节流
return self.get_ident(request) class UserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
'''登录用户60s可以访问10次'''
scope = 'NBAUser' #这里面的值,自己随便定义,settings里面根据这个值配置Rate def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return request.user.username
utils/throttle.py
end。。。
- 添加节流
- 节流源码分析
- 内置节流类
- (1)BaseThrottle
- (2)SimpleRateThrottle
3---Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流的更多相关文章
- Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(1)----认证
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- Django rest framework 源码分析 (1)----认证
一.基础 django 2.0官方文档 https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ 安装 pip3 install djangorestframework 假如我们想 ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(一) 认证
一.基础 最近正好有机会去写一些可视化的东西,就想着前后端分离,想使用django rest framework写一些,顺便复习一下django rest framework的知识,只是顺便哦,好吧. ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(4)----版本
版本 新建一个工程Myproject和一个app名为api (1)api/models.py from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Mo ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(2)----权限
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- Django之REST framework源码分析
前言: Django REST framework,是1个基于Django搭建 REST风格API的框架: 1.什么是API呢? API就是访问即可获取数据的url地址,下面是一个最简单的 Djang ...
- Django Rest Framework源码剖析(八)-----视图与路由
一.简介 django rest framework 给我们带来了很多组件,除了认证.权限.序列化...其中一个重要组件就是视图,一般视图是和路由配合使用,这种方式给我们提供了更灵活的使用方法,对于使 ...
- Django Rest Framework源码剖析(三)-----频率控制
一.简介 承接上篇文章Django Rest Framework源码剖析(二)-----权限,当服务的接口被频繁调用,导致资源紧张怎么办呢?当然或许有很多解决办法,比如:负载均衡.提高服务器配置.通过 ...
随机推荐
- PS插件开发plugin
Photoshop插件开发 VC++制作Photoshop自动化插件:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_73c52fda0101c7hw.html Photoshop 的扩 ...
- XE StringGrid应用(G1属性触发G2)
unit UnitMain; interface uses System.SysUtils, System.Types, System.UITypes, System.Classes, System. ...
- Js杂谈-单体模式
单体模式的思想:保证一个特定类仅有一个实例,意味着第二次使用同一个类创建新对象的时候,应该得到与第一次所创建对象完全相同的对象. 下面举几个实现的例子 1.new操作符 这种思想在于当使用同一个构造函 ...
- [database] postgresql 外网访问
配置 环境 ubuntu 14.04 LTS 版本 postgresql version 9.3 修改监听地址 编辑 /etc/postgresql/9.3/main/postgresql.conf ...
- c# 根据文件夹或文件名返回(文件夹或文件)的完整路径
c# 根据文件夹或文件名返回(文件夹或文件)的完整路径 一.方案一:(使用windows API) 二.方案二:(扫描全盘)
- 《C#多线程编程实战》2.8 Barrier
不得不说,C#的同步线程的机制是真的多. 各式各样.几乎各种场景下都有可以使用的同步机制. 今天说的,就是比较有意思了. 等待的机制很简单,单纯的等待. 使用的方法我就等. 等待的东西或者内容则是你自 ...
- 【转】C#日期时间格式化
源地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/polk6/p/5465088.html
- JDBC_ResultSet结果集用法_游标原理_关闭连接问题
依次关闭使用对象及连接 ResultSet---Statement--Connectionimport java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManage ...
- php 写入csv时 双引号,逗号及特殊字符
1.双引号 <?php function new_csv($string) { $filename = date('Ymd').'.csv'; //设置文件名 header("Cont ...
- vue模块拖拽效果
正巧在之前面试中遇到问实现拖拽效果 当时面试的时候简单回答了实现的方式与逻辑. 现在闲来无事,把这个东西实现了一下. 原理很简单,写的很方便. 数据驱动,建立一个数组,数组初始长度为1 拖动触发时,添 ...
