Linux进程间通信---管道和有名管道
一、管道
管道:管道是一种半双工的通信方式,数据只能单方向流动,而且只能在具有亲缘关系的进程间使用,因为管道
传递数据的单向性,管道又称为半双工管道。进程的亲缘关系通常是指父子进程关系。
管道的特点决定了其使用的局限性:
- 数据只能由一个进程流向另一个进程(其中一个为写管道,另一个为读管道);如果要进行全双工通信,需要
建立两个管道。
- 管道只能用于父子进程或者兄弟进程间的通信,也就是说管道只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程间的通信,无亲缘
关系的进程不能使用管道。
管道的创建:
Linux下创建管道可以通过函数pipe来完成。该函数如果调用成功则返回0,并且数组中将包含两个新的文件描述符;
如果有错误发生,返回-1,该函数返回两个文件描述符:pipefd[0]和pipefd[1]。前者打开来读,后者打开来写。该函
数的原型为:
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
1. 下面是通过建立管道和创建父子进程间的通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h> int main()
{
int fd[];
pid_t pid;
int ret;
ret= pipe(fd);
if(ret== -)
{
perror("pipe.\n");
exit();
}
pid= fork();
if(pid== -)
{
perror("fork.\n");
exit();
}
else if(pid== )
{
char buff[];
close(fd[]);
read(fd[],buff,);
printf("Form parent say: %s\n",buff);
close(fd[]);
}
else
{
char *say= "Hello Linux.";
close(fd[]);
write(fd[],say,strlen(say)+ );
close(fd[]);
int status;
wait(&status);
}
return ;
}
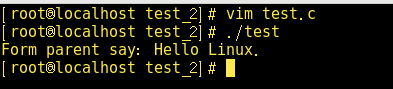
这是父子进程间利用管道进行通信的一个例子。
2. 下面是通过建立两个管道来实现父子进程间全双工通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h> int main()
{
char *parent_talk[]= {"Hello","Can you tell me what time is it?","Ok,I must go,Bye",NULL};
char *child_talk[]= {"Hi","No problem","See you,Bye",NULL};
int fd1[],fd2[];
pid_t pid;
int ret;
ret= pipe(fd1);
if(ret== -)
{
perror("pipe1.\n");
exit();
}
ret= pipe(fd2);
if(ret== -)
{
perror("pipe2.\n");
exit();
}
pid= fork();
if(pid== -)
{
perror("fork.\n");
exit();
}
else if(pid== )
{
char buff[];
close(fd1[]);
close(fd2[]);
int i= ;
char *talk= child_talk[i];
while(talk!= NULL)
{
read(fd1[],buff,);
printf("Parent say: %s\n",buff);
write(fd2[],talk,strlen(talk)+ );
talk= child_talk[++i];
}
close(fd1[]);
close(fd2[]);
}
else
{
char buff[];
close(fd1[]);
close(fd2[]);
int i= ;
char *talk= parent_talk[i];
while(talk!= NULL)
{
write(fd1[],talk,strlen(talk)+ );
read(fd2[],buff,);
printf("Child say: %s\n",buff);
talk= parent_talk[++i];
}
close(fd1[]);
close(fd2[]);
int status;
wait(&status);
}
return ;
}
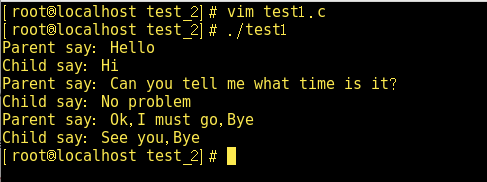
这是通过建立两个管道来实现父子进程间全双工通信的例子。
二、有名管道
管道的有一个不足之处是没有名字,因此,只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程间通信,在有名管道(FIFO)提出后,该
限制得到了克服。FIFO不同于管道之处在于它提供一个路径名与之关联,以FIFO的文件形式存储于文件系统中。有名
管道是一个设备文件,因此,即使进程与创建FIFO的进程不存在亲缘关系,只要可以访问该路径,就能够通过FIFO相
互通信。需要注意的是,FIFO总是按照先进先出的原则工作,第一个被写入的数据将首先从管道中读出。
有名管道的创建:
Linux下有两种方式创建有名管道。一是在Shell下交互地建立一个有名管道,二是在程序中使用系统函数建立有
名管道。Shell方式下可使用mkfifo或mknod命令。创建有名管道的系统函数有两个:mkfifo和mknod。两个函数均定义
在头文件sys/stat.h中,函数的原型为:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname,mode_t mode);
int mknod(const char *pathname,mode_t mode,dev_t dev);
函数mkfifo参数中pathname为创建的有名管道的全路径名;mode为创建的有名管道的模式,指明其存取权限;函
数mknod参数中pathname为创建的有名管道的全路径名;mode为创建的有名管道的模式,指明其存取权限;dev为设
备值,该值取决于文件创建的种类,它只在创建设备文件时才会用到。这两个函数调用成功都返回0,失败都返回-1。
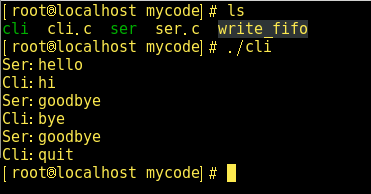
下面是使用有名管道建立一个客户端/服务器的例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 256
const char *write_fifo= "write_fifo";
const char *read_fifo= "read_fifo"; int main()
{
if(access(write_fifo,F_OK))
{
int ret= mkfifo(write_fifo,);
if(ret== -)
{
perror("mkfifo");
exit();
}
}
int write_fd= open(write_fifo,O_WRONLY);
if(write_fd== -)
{
perror("open write_fifo.");
exit();
}
int read_fd;
while()
{
read_fd= open(read_fifo,O_RDONLY);
if(read_fd== -)
{
sleep();
continue;
}
break;
}
char sendbuf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char recvbuf[BUFFER_SIZE];
while()
{
printf("Ser:");
scanf("%s",sendbuf);
if(strcmp(sendbuf,"quit")== )
{
unlink(write_fifo);
break;
}
write(write_fd,sendbuf,strlen(sendbuf)+ );
read(read_fd,recvbuf,BUFFER_SIZE);
printf("Cli:%s\n",recvbuf);
}
close(write_fd);
close(read_fd);
return ;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 256
const char *write_fifo= "write_fifo";
const char *read_fifo= "read_fifo"; int main()
{
int read_fd= open(write_fifo,O_RDONLY);
if(read_fd== -)
{
perror("open write_fifio.");
exit();
}
if(access(read_fifo,F_OK))
{
int ret= mkfifo(read_fifo,);
if(ret== -)
{
perror("mkfifo");
exit();
}
}
int write_fd= open(read_fifo,O_WRONLY);
if(write_fd== -)
{
perror("open read_fifo.");
exit();
}
char sendbuf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char recvbuf[BUFFER_SIZE];
while()
{
read(read_fd,recvbuf,BUFFER_SIZE);
printf("Ser:%s\n",recvbuf);
printf("Cli:");
scanf("%s",sendbuf);
if(strcmp(sendbuf,"quit")== )
{
unlink(read_fifo);
break;
}
write(write_fd,sendbuf,strlen(sendbuf)+ );
}
close(write_fd);
close(read_fd);
return ;
}

Linux进程间通信---管道和有名管道的更多相关文章
- Unix/Linux进程间通信(二):匿名管道、有名管道 pipe()、mkfifo()
1. 管道概述及相关API应用 1.1 管道相关的关键概念 管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一,具有以下特点: 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动:需要双方通信时,需要建立起两个管 ...
- Linux 进程通信(有名管道)
有名管道(FIFO) 有名管道是持久稳定的. 它们存在于文件系统中. FIFO比无名管道作用更大,因为他们能让无关联的进程之间交换数据. 管道文件一般用于交换数据. shell命令创建管道 一个she ...
- Linux进程间通信方式--信号,管道,消息队列,信号量,共享内存
1.概述 通信方法 无法介于内核态与用户态的原因 管道(不包括命名管道) 局限于父子进程间的通信. 消息队列 在硬.软中断中无法无阻塞地接收数据. 信号量 无法介于内核态和用户态使用. 内存共享 需要 ...
- UNIX环境高级编程——无名管道和有名管道
一.进程间通信 每个进程各自有不同的用户地址空间,任何一个进程的全局变量在另一个进程中都看不到,所以进程之间要交换数据必须通过内核,在内核中开辟一块缓冲区,进程1把数据从用户空间拷到内核缓冲区,进程2 ...
- linux进程间通信之一:无名管道
无名管道是linux中管道通信的一种原始方法,有以下特征: 1.单工通信模式,具有固定的读端和写端: 2.管道可以看成是一种特殊的文件,对于它的读写可以使用普通的read(),write()等文件IO ...
- Linux系统编程(11)——进程间通信之有名管道
管道应用的一个重大限制是它没有名字,因此,只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程间通信,在有名管道(named pipe或FIFO)提出后,该限制得到了克服.FIFO不同于管道之处在于它提供一个路径名与之关联,以 ...
- Linux 进程间通信 有名管道(fifo)
有名管道特点: 1)无名管道只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程之间,这就限制了无名管道的使用范围 2)有名管道可以使互不相关的两个进程互相通信. 3)有名管道可以通过路径名来指出,并且在文件系统中可见,但内容 ...
- Linux进程间通信之管道
1,进程间通信 (IPC ) Inter-Process Communication 比较好理解概念的就是进程间通信就是在不同进程之间传播或交换信息. 2,linux下IPC机制的分类:管道.信号.共 ...
- Linux环境进程间通信(一):管道及命名管道
linux下进程间通信的几种主要手段: 管道(Pipe)及有名管道(named pipe):管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的功能外,它还允 ...
随机推荐
- Java 的版本历史与特性
Java SE 8[2014-03-14发行] Lambda表达式 Pipelines和Streams Date和Time API Default方法 Type注解 Nashhorn JavaScri ...
- Git for Android Studio 学习笔记
http://learngitbranching.js.org/ 一个特别好的git学习教程 创建一个project,然后导入github
- java使用commons-fileupload进行文件上传
java中使用文件上传时需要使用特定的类库,这里使用commons-files类库进行文件上传,在http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-fileupload ...
- 对 Vue 的理解(一)
一.什么是 Vue ? 首先,Vue 是一个 MVVM 框架,M -- 模型,就是用来定义驱动的数据,V -- 视图,是经过数据改变后的 html,VM -- 框架视图,就是用来实现双向绑定的中间桥梁 ...
- time&datetime模块
在Python中,和时间处理相关的模块有time,datatime,calendar(不常用)三个. UTCC(Coordinated Universal Time,世界协调时)亦即格林威治天文时间, ...
- html-标题标签、水平线标签和特殊字符
标题标签 <h1></h1> <h2></h2> ...... <h6></h6> 从h1到h6,大小是依次变小,同时会自动换 ...
- 《CSS实现单行、多行文本溢出显示省略号》
如果实现单行文本的溢出显示省略号同学们应该都知道用text-overflow:ellipsis属性来,当然还需要加宽度width属来兼容部分浏览. 实现方式: overflow: hidden; te ...
- Java入门到精通——调错篇之Spring2.5利用aspect实现AOP时报错: error at ::0 can't find referenced pointcut XXX
一.问题描述及原因. 利用Aspect注解实现AOP的时候出现了error at ::0 can't find referenced pointcut XXX.一看我以为注解写错了,结果通过查询相关资 ...
- Mybatis 的多个数据源
主要思路: DataSource --> SqlSessionFactory --> SqlSessionTemplate 第一方式: 定义多套 DataSource --> Sq ...
- 【Linux】Linux 在线安装yum
Linux如何安装软件? 一.RPM安装 优点: 安装过程很简单 缺点: 需要自己寻找和系统版本对应的RPM包 安装过程中需要解决包的依赖问题(例如tftp包) 二.yum在线安装 软件包仓库 仓库的 ...
