C++ class without pointer members
- 写在前面
- Object Oriented
class 的分类:带指针的class和不带指针的class,
class 的声明
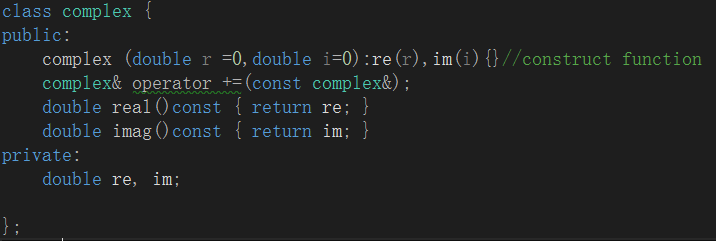
这里有一个inline的概念,写在类里面的默认为inline,写在class外部的只有声明,为inline才有可能编译成Inline,最终编译时是否为inline,由编译器决定。Inline函数速度快.
public:
private:所有数据都应放在private,函数根据是否想要被外界调
使用对象
× 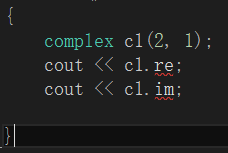 √
√ 
- 构造函数:
想要创建一个对象,会自动调用的函数就是构造函数,如上,构造函数与类同名,没有返回类型,不需要有,因为构造函数就是要来创建对象的,此处对象就是complex,上面定义的构造函数使用了列表初始化,并且这种初始化只有构造函数才有,其它函数是没有的,并且给出了default argument
这里多说一些,一个数值的设定有两个阶段,一个是初始化,一个是后面再赋值(assign),所以列表初始化和在函数体赋值是不同的。
与构造函数对应是析构函数,但是这个例子中不需要写析构函数,前面提到过class的经典分类,不带指针的class多半需用写析构函数
构造函数可以有多个-overloading,但是存在歧义的不可以,如下:
complex() :re(), im() {}//不可以,ambiguous
如下面的对象c2,都没有给参数,编译器发现 可以调用上面的,但是编译器也发现class中的构造函数虽然有参数,但是有默认值,也可以调用,因此编译器就不知调用哪个了
创建对象
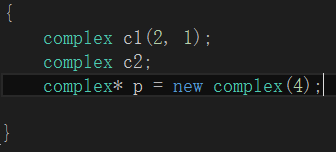
构造函数放在private中,即不允许外界调用构造函数
class A {
public:
static A& getInstance();
private:
A();
A(const A& rhs);
};
A& A::getInstance()
{
static A a;
return a;
}
外界只能用一份A,即static的部分,外界用的时候不能使用传统的调用方式,只能通过getInstance()函数
- 参数传递与返回值
double real()const { return re; }
double imag()const { return im; }
看上面的代码,都是const型的,因为我不需要改变数据,只是将数据拿出来,看下面两种情况
A.  B.
B.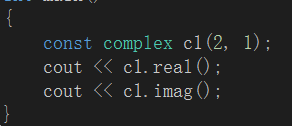
如果我的函数没用定义为const类型,B中的调用就是错误的,使用者本想,我只是返回数据,并不改变,所以创建了一个常对象,但是由于函数没有定义为const,所以就会出现调用错误。
- 参数传递:
pass by value vs pass by reference(to const)
pass by value 就是整包都传过去,数据多大就传多大,传的数据是压到static栈中的,本例中,传的是double,是4个字节,传的就是4个字节,若传的数据很大呢,效率就低,所以尽量不要pass by value, 可以pass by reference ,reference在底部就是指针,
ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const complex& x)
{
return os << '(' << real(x) << ',' << imag(x) << ')';
}
int main()
{
complex c1(, );
complex c2;
c2 += c1;
cout << c2;
}
第7,8行会调用构造函数,通过pass by lalue的方式,第9行会调用1-4行的函数,pass by reference的方式。返回值的传递也尽量pass by reference
friend complex& __doapl(complex*, const complex&);//return value :pass by reference
后面会给出上面函数的detail
下面看一种情况,为什么可以这样使用
int func(const complex& param)
{
return param.re + param.im;
}
//用法
complex c3;
c3.func(c1);
可以这样理解:相同class的各个objects 互为friends
class body外的各种定义什么情况下可以pass by value,什么情况下可以pass by reference
首先看看什么情况不能return by reference
inline complex&
__doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re += r.re;//第一参数将会被改动
ths->im += r.im;//第二参数不会被改动
return *ths;
}
inline complex&
complex::operator+=(const complex& r)
{
return __doapl(this, r);
}
这里,函数将结果放在第一个参数中,有专门的存储的空间,还有一种情况就是函数专门开辟一个空间存放结果,如果只是
return c1 + c2;
这时,是一个临时开辟的local变量存储c1+c2的结果,函数结束,这个临时变量的生命就结束了,这时,就不能返回reference
- 操作符重载(-1,成员函数) this
想象我们在数学中的复数,有哪些操作,比如相加,复数+复数,复数+实数,复数+纯虚数,
继续看上面代码,编译器看到c2+=c1,就会把操作符作用到左边c2身上,上面的inline complex& complex::operator+=(const complex& r){}相当于
inline complex& complex::operator(this,const complex& r){}
为什么可以这样呢,这就是上面辩题中写道的操作符重载之成员函数,因为所有成员函数带有一个隐藏的参数this,谁调用这个函数谁就是this,这里this是c2,
Note:this不可以写在参数列表中,用可以像函数体中那样用,return __doapl(this,r);
- return by reference 语法分析
继续看上面的代码,看函数定义时的返回类型是complex&,函数体内返回的却是*ths,这样是正确的,因为,传递者无需知道接收者是以reference形式接收
class body之外的函数定义
operator overloading(操作符重载-2,非成员函数)无this
考虑到用户的行为,定义了三种+ 形式
inline complex
operator +(const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex(real(x) + real(y), imag(x) + imag(y));
} inline complex
operator +(const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex(real(x) + y, imag(y));
} inline complex
operator +(double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex(x + real(y), imag(y));
}
如上,对于上面的操作符重载,没有this pointer,因为是全域函数,不再是成员函数
- temp object (临时对象)tempname()
再看上面的代码,return by value,对于上面的代码,绝不可以return by reference,因为他们返回的一定是local object,因为加的结果是函数临时创建的,函数结束,临时变量死亡,
解释一下:tempname(),此处是complex(),就是创建临时对象,tempname()类似于Int(),
operator +(const complex& x)
{
return x;
} inline complex
operator -(const complex& x)
{
return complex(-real(x), -imag(x));
}
//使用
{
complex c1(, );
complex c2;
cout << -c1;
cout << +c1;
}
这里是return by value,这里可是return by reference,因为,这里结果没有改变,也没有创建新的临时对象,所以是可以return by reference的。
接下来还是操作符重载,考察的东西一样,语法上没有新的了,
inline bool
operator ==(const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return real(x) == real(y) && imag(x) == iamg(y);
}
inline bool
operator ==(const complex& x, double y)
{
return real(x) == y && iamg(x) == ;
} inline bool
operator ==(double x, complex& y)
{
return x == real(y) && iamg(y) == ;
} inline bool
operator !=(const complex& x, complex& y)
{
return real(x) != real(y) || imag(x) != imag(y);
} inline bool
operator !=(const complex& x, double y)
{
return real(x) != y || iamg(x) != ;
} inline bool
operator !=(double x, complex& y)
{
return x != real(y) || iamg(y) != ;
} inline complex
conj(const complex& x)
{
return complex(real(x), -imag(y));
}
ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const complex& x)
{
return os << '(' << real(x) << ',' << imag(x) << ')';
} //使用
{
cout << conj(c1);
cout << c1 << conj(c1);
}
"<<"作用在左边,这里绝不能写成成员函数,必须写成全域函数。os也不可是const的,因为每往cout中放入“东西”的时候都是在改变os中的内容,若将返回类型 ostream& ,改为 void 可以吗?
如果只是输出一个是可以的(上面第一处使用),如果连续输出是不可以的(第二处使用),
下面是完整的代码(还有很多操作没写,但写的已经涵盖了这种类型的class的几乎所有语法,有时间再补全):
#pragma once
#ifndef __COMPLEX__
#define __COMPLEX__ class complex {
public:
complex(double r = , double i = ) :re(r), im(i) {}//construct function
//complex() :re(0), im(0) {}//不可以,ambiguous
complex& operator +=(const complex&);//two choices,member func or non-member func,
//here is member func,do not need to change the value,so is const
double real()const { return re; }
double imag()const { return im; }
int func(const complex& param)
{
return param.re + param.im;
}
private:
double re, im;
friend complex& __doapl(complex*, const complex&);//return value :pass by reference }; inline complex&
__doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re += r.re;//第一参数将会被改动
ths->im += r.im;//第二参数不会被改动
return *ths; }
inline complex&
complex::operator+=(const complex& r)//the right is not change,so is const,the left
{//has already existed,so return by reference
return __doapl(this, r);
}
inline double
real(const complex& x)
{
return x.real();
}
inline double
imag(const complex& x)
{
return x.imag();
}
//"+"has more than one cases,so set it as the non-member func
inline complex
operator +(const complex& x, const complex& y)
{//the sum result will be put in a local variable,so return by value
return complex(real(x) + real(y), imag(x) + imag(y));
} inline complex
operator +(const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex(real(x) + y, imag(y));
} inline complex
operator +(double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex(x + real(y), imag(y));
}
inline complex
operator +(const complex& x)
{
return x;
} inline complex
operator -(const complex& x)
{
return complex(-real(x), -imag(x));
} inline bool
operator ==(const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return real(x) == real(y) && imag(x) == imag(y);
}
inline bool
operator ==(const complex& x, double y)
{
return real(x) == y && imag(x) == ;
} inline bool
operator ==(double x, complex& y)
{
return x == real(y) && iamg(y) == ;
} inline bool
operator !=(const complex& x, complex& y)
{
return real(x) != real(y) || imag(x) != imag(y);
} inline bool
operator !=(const complex& x, double y)
{
return real(x) != y || imag(x) != ;
} inline bool
operator !=(double x, complex& y)
{
return x != real(y) || imag(y) != ;
} inline complex
conj(const complex& x)
{
return complex(real(x), -imag(x));
} #endif
测试代码有时间再补
C++ class without pointer members的更多相关文章
- C++类设计2(Class with pointer members)
二 Class with pointer members(Class String) 1. 测试代码(使用效果) int main() { String s1(), String s2("h ...
- C++类设计1(Class without pointer members)
class complex{ public: complex (double r = 0, double i = 0):re(r), im(i){} //inline complex& ope ...
- C++Primer 5th 练习 12.19
这阵子真是太忙了, 连续做了四个课设. 当然这并不能作为好久没写博客的借口, 没写博客的主要原因只有一个: 懒. 最近又开始回顾C++的语法与特性(据说C++就是一门需要反复回顾的语言),以及学习C+ ...
- Google C++ Style Guide
Background C++ is one of the main development languages used by many of Google's open-source project ...
- 4、Type fundamentals
1.All Types Are Derived from System.Object The CLR requires all objects to be created using the new ...
- C and C++ : Partial initialization of automatic structure
Refer to: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10828294/c-and-c-partial-initialization-of-automatic-st ...
- [转] 关于c++的头文件依赖
http://www.cnblogs.com/yvesliao/p/3938730.html PS: 使用单向依赖 正在看google c++编程规范,里面对头文件依赖是这么说的: 1 2 3 4 5 ...
- Google C++ 代码规范
Google C++ Style Guide Table of Contents Header Files Self-contained Headers The #define Guard For ...
- What is The Rule of Three?
Question: What does copying an object mean? What are the copy constructor and the copy assignment op ...
随机推荐
- C++ explicit的作用
explicit作用: 在C++中,explicit关键字用来修饰类的构造函数,被修饰的构造函数的类,不能发生相应的隐式类型转换,只能以显示的方式进行类型转换. explicit使用注意事项: * e ...
- 20180923-WebService
什么是webservice? 什么是远程调用技术?答:系统和系统之间的调用,从远程系统当中获取业务数据. Webservice是web服务,他是用http传输SOAP协议数据的一种远程调用 ...
- eclipse配置class注释模板
/** * Copyright (c) ${year}, All Rights Reserved. * */ ${filecomment} ${package_declaration} ${typec ...
- Codeforces Round #620 (Div. 2) E
LCA的倍增 模板: ], depth[maxn]; int dist[maxn],head[maxn]; void add(int u,int v,int dist0){ a[tot].next=h ...
- 组件向外暴露v-model绑定的参数
<template> <div class="search-box"> <i class="icon-search">< ...
- 《JavaScript高级程序设计》读书笔记(三)基本概念第三小节 String、Object类型
内容---语法 上一小节---数据类型 本小节 String类型---流程控制语句---理解函数 String类型--零个或者多个16位Unicode字符组成字符序列,即字符串--可以由双引号&quo ...
- python numpy的var std cov研究
var:表示方差, 即各项-均值的平方求和后再除以N , std:表示标准差,是var的平方根. cov:协方差 ,与var类似,但是除以(N-1) import numpy as np # 构建测试 ...
- [LeetCode] 735. Asteroid Collision
行星碰撞. 题意是给一个数组 asteroids,表示在同一行的行星.对于数组中的每一个元素,其绝对值表示行星的大小,正负表示行星的移动方向(正表示向右移动,负表示向左移动).每一颗行星以相同的速度移 ...
- juypter
juypter 1. jupyter 1.1. 它是什么? Jupyter Notebooks 是一款开源的网络应用,我们可以将其用于创建和共享代码与文档. 以前叫ipython no ...
- C语言函数不能返回数组,但可以返回结构体
为什么C语言函数可以返回结构体,却不可以返回数组?有这样的问题并不奇怪,因为C语言数组和结构体本质上都是管理一块内存,那为何编译器要区别对待二者呢? C语言函数为什么不能返回数组? 在C语言程序开发中 ...
