spring源码解析之前置知识点
本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.
最近在看spring源码,但是spring的体系太庞大了,在这里记录一下阅读源码中遇到知识点
@PostConstruct
被注解的方法,在对象加载完依赖注入后执行
看个demo
package com.day01.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.day01")
public class SpringConfig { }
IndexDao
package com.day01.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class IndexDao { public IndexDao(){
System.out.println("IndexDao 构造方法");
}
}
IndexService
@Service
public class IndexService {
@Autowired
private IndexDao indexDao; public IndexService(){
System.out.println("IndexService 构造方法");
} @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("IndexService init方法");
} public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} }
Testday01
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
看结果
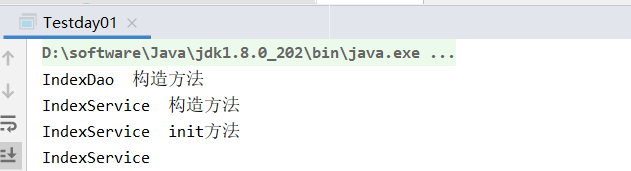
可以看出在spring项目中,在一个bean的初始化过程中,方法执行先后顺序为Constructor > @Autowired > @PostConstruct
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是Spring框架的提供的一个扩展点,通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口,程序员就可插手bean实例化的过程
看demo
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization");
}
//这里也可以产生代理对象 Proxy.newProxyInstance(),也是aop实现的原理
return bean;
} /**
* 初始化之后
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization");
}
return bean;
} }
运行上文的Testday01,看下结果
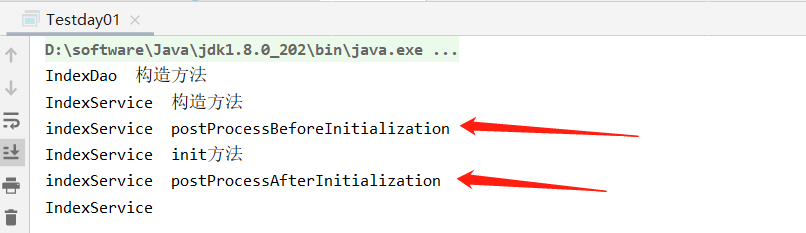
可以看出
===Spring IOC容器实例化Bean===
===调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法===
===调用bean实例的初始化方法===
===调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法===
值得说明的是这个接口可以设置多个,会形成一个列表,那么如何确定他们的执行顺序呢?
Ordered和PriorityOrdered
Spring提供了Ordered和PriorityOrdered接口,来处理相同接口实现类的优先级问题
看个demo
TestBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor , PriorityOrdered { /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization");
}
//这里也可以产生代理对象 Proxy.newProxyInstance(),也是aop实现的原理
return bean;
} /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization");
}
return bean;
} @Override
public int getOrder() {
return 100;//注意这里
}
}
TestBeanPostProcessor2
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor2 implements BeanPostProcessor , PriorityOrdered { /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization2");
}
//这里也可以产生代理对象 Proxy.newProxyInstance(),也是aop实现的原理
return bean;
} /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization2");
}
return bean;
} @Override
public int getOrder() {
return 99;
}
}
运行test类,看结果
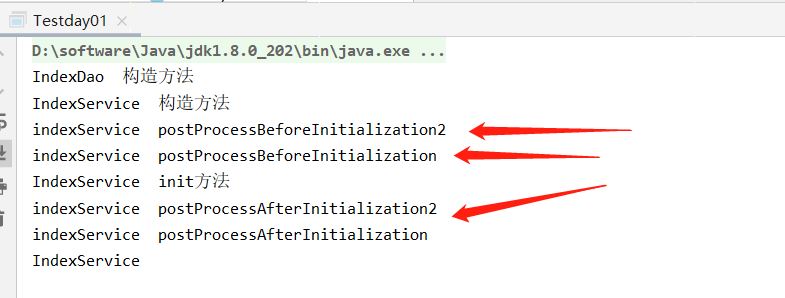
这段代码的逻辑:
1. 若对象o1是Ordered接口类型,o2是PriorityOrdered接口类型,那么o2的优先级高于o1
2. 若对象o1是PriorityOrdered接口类型,o2是Ordered接口类型,那么o1的优先级高于o2
3. 其他情况,若两者都是Ordered接口类型或两者都是PriorityOrdered接口类型,调用Ordered接口的getOrder方法得到order值,order值越大,优先级越小
若2个对象中有一个对象实现了PriorityOrdered接口,那么这个对象的优先级更高。
若2个对象都是PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的实现类,那么比较Ordered接口的getOrder方法得到order值,值越低,优先级越高
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
spring的扩展点之一:实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前修改beandefinitions属性。
例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。
可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置'order'属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序
看个demo
@Component
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===============TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor============"); }
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
IndexService indexService2 = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
System.out.println(indexService);
System.out.println(indexService2);
}
运行一下,看结果

可以看到,spring管理的bean默认是单例的,我们把indexService改成prototype试一下
@Component
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===============TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor============");
BeanDefinition indexService = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("indexService");
String scope = indexService.getScope();
System.out.println(scope);//singleton
//indexService.setScope("singleton");
indexService.setScope("prototype");//设置为原型
System.out.println(scope);//singleton
}
}
看下结果

BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,并可以注册bean到spring容器中,一共要实现以下两个方法:
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException:
该方法的实现中,主要用来对bean定义做一些改变。 void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException:
该方法用来注册更多的bean到spring容器中,详细观察入参BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,看看这个参数能带给我们什么能力。
看个demo
public class IndexService2 {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public IndexService2(){
System.out.println("IndexService2 构造方法");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("IndexService2 init方法");
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService2 hello");
}
}
注意:IndexService2并没有@Component注解,说明这个类并没有交给spring管理,继续
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
GenericBeanDefinition genericBeanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
genericBeanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
genericBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(IndexService2.class);//将IndexService2交给spring管理
registry.registerBeanDefinition("indexService2",genericBeanDefinition);
} @Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("===============MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor============");
}
}
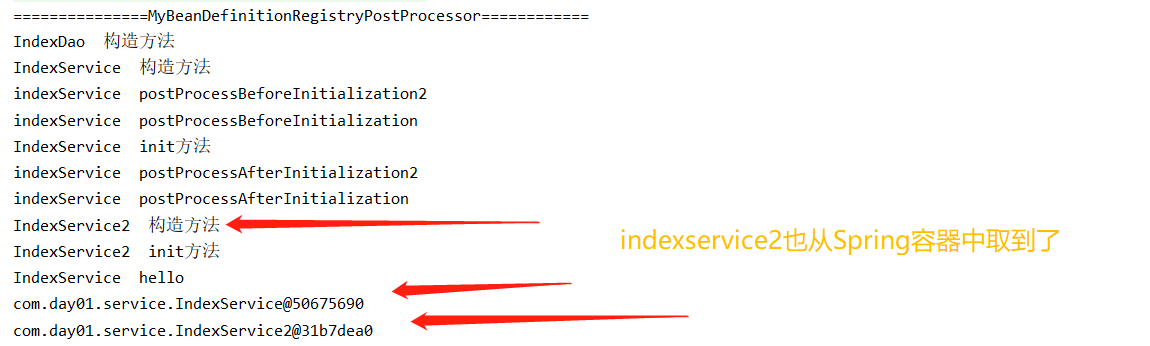
注意上述代码中通过BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 将IndexService2手动注册交给spring管理
运行test类
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
IndexService2 indexService2 = (IndexService2) applicationContext.getBean("indexService2");
System.out.println(indexService);
System.out.println(indexService2);
}
看结果
ApplicationContextAware
我们可以通过注解@Autowired 很简单方便获取bean,虽然这种方法很简单方便,但是有些特殊场景用不了,比如静态方法中不能使用
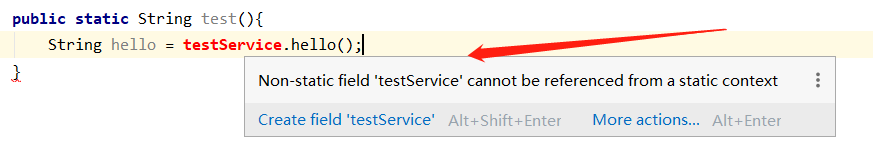
此时可以借助ApplicationContextAware获取bean
看个demo
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl { public String hello(){
return "hello world";
} }
这里无法注入TestServiceImpl 无法使用,看demo
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
@Autowired
private TestServiceImpl testService; /**
* 实现ApplicationContextAware接口, 注入Context到静态变量中.
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
ApplicationContextUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext;
} /**
* 获取静态变量中的ApplicationContext.
*/
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
} /**
* 从静态变量applicationContext中得到Bean, 自动转型为所赋值对象的类型.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(name);
} /**
* 从静态变量applicationContext中得到Bean, 自动转型为所赋值对象的类型.
*/
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) {
return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType);
} /*public static String test(){
String hello = testService.hello();
}*/
}
看测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
System.out.println(indexService);
/*IndexService2 indexService2 = (IndexService2) applicationContext.getBean("indexService2");
System.out.println(indexService2);*/
String testServiceImpl = ((TestServiceImpl) ApplicationContextUtil.getBean("testServiceImpl")).hello();
System.out.println(testServiceImpl);
}
看结果
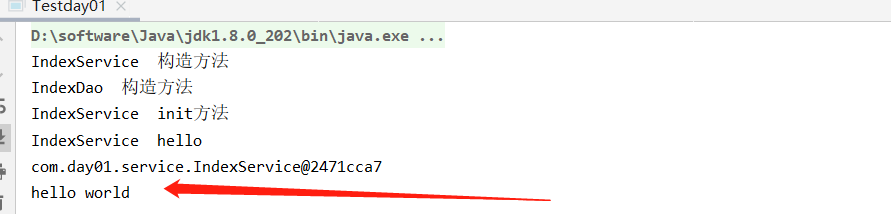
ok,今天就先到这里,以后有新的内容随时补充吧
spring源码解析之前置知识点的更多相关文章
- spring 源码解析
1. [文件] spring源码.txt ~ 15B 下载(167) ? 1 springн┤┬вио╬Ш: 2. [文件] spring源码分析之AOP.txt ~ 15KB 下载( ...
- Spring源码解析之八finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法即初始化单例bean
Spring源码解析之八finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法即初始化单例bean 七千字长文深刻解读,Spirng中是如何初始化单例bean的,和面试中最常问的Sprin ...
- Spring源码解析 - AbstractBeanFactory 实现接口与父类分析
我们先来看类图吧: 除了BeanFactory这一支的接口,AbstractBeanFactory主要实现了AliasRegistry和SingletonBeanRegistry接口. 这边主要提供了 ...
- Spring源码解析——循环依赖的解决方案
一.前言 承接<Spring源码解析--创建bean>.<Spring源码解析--创建bean的实例>,我们今天接着聊聊,循环依赖的解决方案,即创建bean的ObjectFac ...
- Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计
Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计 1 IoC容器系列的设计:BeanFactory和ApplicatioContext 在Spring容器中,主要分为两个主要的容器系列,一个是实现BeanFac ...
- Spring源码解析系列汇总
相信我,你会收藏这篇文章的 本篇文章是这段时间撸出来的Spring源码解析系列文章的汇总,总共包含以下专题.喜欢的同学可以收藏起来以备不时之需 SpringIOC源码解析(上) 本篇文章搭建了IOC源 ...
- Spring源码解析之PropertyPlaceholderHelper(占位符解析器)
Spring源码解析之PropertyPlaceholderHelper(占位符解析器) https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39471249/article/details/7 ...
- Spring源码解析之BeanFactoryPostProcessor(三)
在上一章中笔者介绍了refresh()的<1>处是如何获取beanFactory对象,下面我们要来学习refresh()方法的<2>处是如何调用invokeBeanFactor ...
- Spring源码解析之ConfigurationClassPostProcessor(二)
上一个章节,笔者向大家介绍了spring是如何来过滤配置类的,下面我们来看看在过滤出配置类后,spring是如何来解析配置类的.首先过滤出来的配置类会存放在configCandidates列表, 在代 ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript之预编译
javascript是一种解释性弱类型语言,在浏览器中执行时,浏览器会先预览某段代码进行语法分析,检查语法的正确与否,然后再进行预编译,到最后才会从上往下一句一句开始执行这段代码,简单得来说可以表示为 ...
- MySQL之唯一索引、外键的变种、SQL语句数据行操作补充
0.唯一索引 unique对num进行唯一限制,表示num是独一无二的,uql是唯一索引名称 上面为联合索引:num和xx不能完全一样 1.外键的变种 a. 用户表和部门表 用户: 1 alex 1 ...
- Matplotlib 误差线的绘制和子图的创建方式
一.绘制误差线 使用errorbar方法可以绘制误差线. x = np.linspace(0,10,50) dy=0.8 y = np.cos(x) + dy*np.random.randn(50) ...
- linux 批量删除文件
来源;https://www.cnblogs.com/sinpo/p/7106998.html linux下批量删除文件 1. 在linux批量删除多级目录下同一格式的文件,可采用find + e ...
- Python 输出 log 到文件的方法
import loggingfrom logging.handlers import RotatingFileHandler module_name = "test_module" ...
- cocos2dx初体验
我们创建工程后总会自带一个HelloWorld类,短短的几行代码就出来了一个游戏的雏形,请问我们真的理解它了吗?如果我们能早一点弄明白这几行代码,我们或许会比现在走得更远. 理解HelloWorld类 ...
- [Qt] 打开文件夹 Windows
bool ok = QDesktopServices::openUrl(QUrl("c:/users/administrator/desktop/dir"));
- Zabbix数据库表分区
zabbix的监控主机数量将近300,且运行了一年时间了,最近zabbix server服务监控历史数据等服务不断自身告警.查询性能也变得很低 关于历史数据的两个参数,在zabbix server的配 ...
- 模块sys,os
Python的强大之处在于他有非常丰富和强大的标准库和第三方库,几乎你想实现的任何功能都有相应的Python库支持,以后的课程中会深入讲解常用到的各种库,现在,我们先来象征性的学2个简单的. 在Pyt ...
- 你的GitHub,怎么和我用的不太一样?
说起代码托管,相信绝大多数人脑海中浮现出的第一个词都是"GitHub".经过多年的发展,GitHub俨然已经成为了代码托管领域的标签- 随着国内互联网环境的优化,互联网产业链的不断 ...
