曹工说mini-dubbo(1)--为了实践动态代理,我写了个简单的rpc框架
相关背景及资源:
之前本来一直在写spring源码解析这块,如下,aop部分刚好写完。以前零散看过一些文章,知道rpc调用基本就是使用动态代理,比如rmi,dubbo,feign调用等。自己也就想着试一下,于是有了mini-dubbo这个东西,暂时也不能称为一个框架,因为还不是生产级的,目前只是实现了一部分小功能,也没有监控,也没有xxx,反正就是缺的比较多。
曹工说Spring Boot源码(22)-- 你说我Spring Aop依赖AspectJ,我依赖它什么了
我就说下,里面用到的知识点吧,有兴趣的,可以克隆源码下来看看:
- 动态代理
- 服务注册和消费,使用redis作为注册中心,其中使用了redisson作为redis客户端,其中涉及到BeanFactoryPostProcessor的使用
- 因为传输层使用netty和mina,是异步的,但是上层又需要等待结果,所以用到了同步转异步
- spring的xml解析,bean definition注册,spring 扩展xml 命名空间
- 自定义的spi的相关知识
- 分层思想,从dubbo借鉴了其分层,但是mini-dubbo要少几层,因为我暂时不是很清楚dubbo的每一层的具体职责,所以我按我自己理解分的层。上层依赖下层,只通过下层的接口,查找下层接口时,直接在spring容器中查找bean即可,类似于spring mvc的设计。当下层有多个实现时,通过类似spi机制来指定具体要使用的下层实现。
- 基于第5点,所以本框架非常容易替换各层的实现,只要自己自定义一个spring bean,实现对应的接口,然后在spi文件中指定本实现的类名即可。
- netty和mina的tcp粘包拆包工作。
概要
代码我放在了如下位置:
https://gitee.com/ckl111/mini-dubbo
我介绍下代码的整体结构:
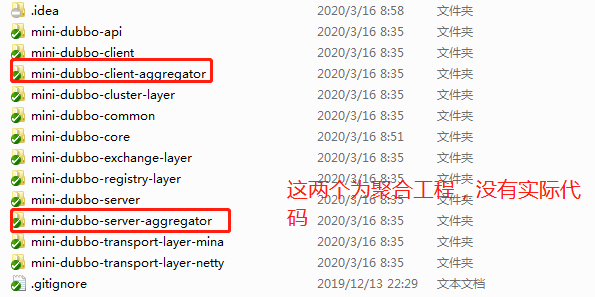
服务端聚合工程比较简单,目前也没时间去仔细弄,包含了如下module:
<modules>
<!--业务层api-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-api</module>
<!--业务层,服务端demo-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-server</module>
<!--配置层,解析xml的工作,在本层完成-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-core</module>
<module>../mini-dubbo-common</module>
</modules>
目前的大部分实现,是在客户端,包含了如下module:
<modules>
<!--业务层api-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-api</module>
<!--业务层,测试demo-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-client</module>
<!--配置层,解析xml的工作,在本层完成-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-core</module>
<module>../mini-dubbo-common</module>
<!--注册中心层-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-registry-layer</module>
<!--集群层,完成事情:负载均衡策略,集群容错策略等-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-cluster-layer</module>
<!--信息交换层,主要完成同步转异步的操作,因为下层的mina和netty为异步,本层同步等待结果-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-exchange-layer</module>
<!--传输层如使用netty实现,则需包含如下module-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-transport-layer-netty</module>
<!--传输层如使用mina实现,则需包含如下module-->
<module>../mini-dubbo-transport-layer-mina</module>
</modules>
其中,模块间的依赖关系如下:
业务模块,一般只需要依赖mini-dubbo-core模块,mini-dubbo-core主要依赖了如下模块:
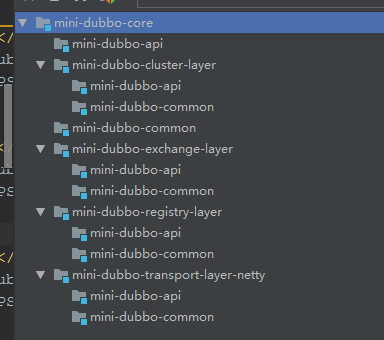
为什么这么划分,因为mini-dubbo-core模块,其实主要是完成解析业务模块(比如client)中的xml,根据其xml配置,注册对应的bean到spring 容器中,而具体的bean实现,就是放在各个模块的,比如,xml里配置netty作为传输层实现,那么mini-dubbo-core就得解析为mini-dubbo-transport-layer-netty中的一个实现类作为bean,注册到spring容器,供上层使用。
目前的分层,只是暂时的,后续可能会略有调整。
一次客户端调用的大体思路
业务module中,配置xml,示例如下:
<dubbo:registry address="redis://127.0.0.1:6379"/> <dubbo:reference id="gpsLocationUpdateService" interface="dubbo.learn.IGpsLocationUpdateService"/> <context:component-scan base-package="dubbo"></context:component-scan>
其中的dubbo:reference就代表了一个远端的服务,业务代码中可以自动注入该接口,当调用该接口时,实际就会发起rpc调用。
熟悉的同学已经知道了,这块肯定是生成了一个动态代理。
继续之前,我们看看dubbo的十层架构:

可以看到,我们这边是比dubbo少了几层,首先proxy,目前直接用了jdk动态代理,没有其他技术,所以就没有抽出一层;然后monitor层,现在肯定是没有的,这部分其实才是一个框架的重头戏,但是我也不会前端,所以这块估计暂时没有;接下来是protocol层,我暂时不太清楚dubbo的设计,所以就没弄这层。
知道了分层结构后,我们可以回到第一点,即动态代理那里,我们的动态代理,只依赖下层的接口。目前,各层之间的接口,放在mini-dubbo-common模块中,定义如下:
注册中心层,负责接收上层传来的调用参数等上下文,并返回结果
/**
* 注册中心层的rpc调用者
* 1:接收上层传下来的业务参数,并返回结果
*
* 本层:会根据不同实现,去相应的注册中心,获取匹配的服务提供者列表,传输给下一层
*/
public interface RegistryLayerRpcInvoker { Object invoke(RpcContext rpcContext);
}
集群层,接收上层注册中心层传来的服务提供者列表和rpc调用上下文,并返回最终结果
public interface ClusterLayerRpcInvoker { /**
* 由注册中心层提供对应service的服务提供者列表,本方法可以根据负载均衡策略,进行筛选
* @param providerList
* @param rpcContext
* @return
*/
Object invoke(List<ProviderHostAndPort> providerList, RpcContext rpcContext);
}
exchange层,上层集群层,会替我们选好某一台具体的服务提供者,然后让我们去调用,本层完成同步转异步
public interface ExchangeLayerRpcInvoker { /**
*
* @param providerHostAndPort 要调用的服务提供者的地址
* @param rpcContext rpc上下文,包含了要调用的参数等
* @return rpc调用的结果
*/
Object invoke(ProviderHostAndPort providerHostAndPort, RpcContext rpcContext);
}
传输层,本层目前有两个简单实现,netty和mina。
/**
*
* 本层为传输层,上层为exchange层。
* 上层exchange,目前有一个默认实现,主要是完成同步转异步的操作。
* 上层将具体的传输工作交给底层的传输层,比如netty和mina,然后在一个future上等待传输层完成工作
*
* 本层会完成实际的发送工作和接收返回响应的工作
*/
public interface TransportLayerRpcInvoker { /**
*
* @param providerHostAndPort 要调用的服务提供者的地址
* @param rpcContext rpc上下文,包含了要调用的参数等
* @return rpc调用的结果
*/
Object invoke(ProviderHostAndPort providerHostAndPort, RpcContext rpcContext);
}
其中,我们的最上边的动态代理层,只依赖于下层,其中,示例代码如下:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
// 1.从spring容器中,获取下层的实现bean;如果有多个,则根据spi文件中指定的为准
RegistryLayerRpcInvoker registryLayerRpcInvoker =
SpiServiceLoader.loadService(RegistryLayerRpcInvoker.class); RpcContext rpcContext = new RpcContext();
rpcContext.setProxy(proxy);
rpcContext.setMethod(method);
rpcContext.setArgs(args);
rpcContext.setServiceName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
// 2.调用下层
Object o = registryLayerRpcInvoker.invoke(rpcContext);
return o;
}
这里1处,可以看到,我们通过SpiServiceLoader.loadService(RegistryLayerRpcInvoker.class)去获取具体的下层实现,这是我们自定义的一个工具类,其内部实现一会再说。
2处调用下层实现,获取结果。
registry,注册中心层的实现
@Service
public class RedisRegistryRpcInvoker implements RegistryLayerRpcInvoker { @Autowired
private RedisRegistry redisRegistry; @Override
public Object invoke(RpcContext rpcContext) {
//1.获取集群层实现
ClusterLayerRpcInvoker clusterLayerRpcInvoker = SpiServiceLoader.loadService(ClusterLayerRpcInvoker.class);
//2.从redis中,根据服务名,获取服务提供者列表
List<ProviderHostAndPort> list = redisRegistry.getServiceProviderList(rpcContext.getServiceName());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
//2.调用集群层实现,获取结果
Object o = clusterLayerRpcInvoker.invoke(list, rpcContext);
return o;
}
}
集群层实现,本层我也不算懂,模仿dubbo实现了一下。
主要实现了以下两种:
- Failover,出现失败,立即重试其他服务器。可以设置重试次数。
- Failfast,请求失败以后,返回异常结果,不进行重试。
以failover为例:
@Slf4j
@Service
public class FailoverClusterLayerRpcInvoker implements ClusterLayerRpcInvoker { @Autowired
private LoadBalancePolicy loadBalancePolicy; @Override
public Object invoke(List<ProviderHostAndPort> providerList, RpcContext rpcContext) {
ExchangeLayerRpcInvoker exchangeLayerRpcInvoker =
SpiServiceLoader.loadService(ExchangeLayerRpcInvoker.class); int retryTimes = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < retryTimes; i++) {
// 1.根据负载均衡策略,选择1台服务提供者
ProviderHostAndPort providerHostAndPort = loadBalancePolicy.selectOne(providerList);
try {
// 调用下层,获取结果
Object o = exchangeLayerRpcInvoker.invoke(providerHostAndPort, rpcContext);
return o;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("fail to invoke {},exception:{},will try another",
providerHostAndPort,e);
// 2.如果调用失败,进入下一次循环
continue;
}
} throw new RuntimeException("fail times extend");
}
}
其中,一共会尝试3次,每次的逻辑:根据负载均衡策略,选择1台去调用;如果有问题,则换一台。
调用下层时,获取了下层的接口:ExchangeLayerRpcInvoker
exchange层,这层完成同步转异步的操作,目前只有一个实现:
@Service
public class Sync2AsyncExchangeImpl implements ExchangeLayerRpcInvoker { public static ConcurrentHashMap<String, CompletableFuture<Object>> requestId2futureMap =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); @Override
public Object invoke(ProviderHostAndPort providerHostAndPort, RpcContext rpcContext) {
String requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
rpcContext.setRequestId(requestId);
rpcContext.setRequestId2futureMap(requestId2futureMap); CompletableFuture<Object> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
requestId2futureMap.put(requestId, completableFuture); /**
* 交给具体的底层去解决
*/
TransportLayerRpcInvoker transportLayerRpcInvoker =
SpiServiceLoader.loadService(TransportLayerRpcInvoker .class); transportLayerRpcInvoker.invoke(providerHostAndPort, rpcContext); Object s = null;
try {
s = completableFuture.get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return s;
}
}
这层大家可以简单理解为:主线程调用传输层之前,生成一个id和一个completablefuture,放到一个全局map,然后将id传给下层,然后在completablefuture上阻塞;下层拿到id后,在消息里传输;服务端再将id传输回来,然后客户端拿着id找到completablefuture,并唤醒主线程。
信息传输层,以netty为例,具体的netty相关的知识,大家就得自己先学习一下:
简单步骤如下:
//1.初始化客户端连接
public void initChannel() {
Bootstrap b = configBootStrap();
ChannelFuture future = null;
try {
future = b.connect(providerHostAndPort.getHost(), providerHostAndPort.getPort()).sync();
if (future.isSuccess()) {
channel = future.channel();
return;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
...
} throw new RuntimeException();
} private Bootstrap configBootStrap() {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast("lengthFieldPrepender", new LengthFieldPrepender(2));
p.addLast("lengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder",
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
65536, 0,
2, 0, 2));
p.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
p.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new ClientHandler()); }//拦截器设置
});
return b;
}
使用连接的channle,发送数据:
public void sendMessage(String messageContent) {
synchronized (lockObj) {
if (channel == null) {
initChannel();
}
}
ChannelFuture channelFuture = channel.writeAndFlush(messageContent);
channelFuture.addListener(new GenericFutureListener<Future<? super Void>>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<? super Void> future) throws Exception {
System.out.println("发送请求消息成功");
}
});
}
netty接收到服务端相应后,根据requestId来获取future,唤醒上层线程
@Slf4j
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext cx) {
log.info("channelActive,local address:{},remote address:{}",
cx.channel().localAddress(),cx.channel().remoteAddress());
} /**
* 读取信息
*
* @param ctx 渠道连接对象
* @param msg 信息
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ResponseVO responseVO = JSONObject.parseObject((String) msg, ResponseVO.class);
String requestId = responseVO.getRequestId(); //1.获取future
CompletableFuture<Object> completableFuture = Netty4ClientRpcInvoker.requestId2futureMap
.get(requestId);
//2.将结果塞进future,在此future上阻塞的线程被唤醒
completableFuture.complete(responseVO.getContent());
log.info("client channelRead,thread:{}", Thread.currentThread());
log.info("客户端端读写远程地址是-----------"
+ ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "信息是:" + msg.toString()); }
}
如何根据spi进行切换
之前我们提到了可以根据spi,随意切换实现,比如我们想使用mina来传输的话:
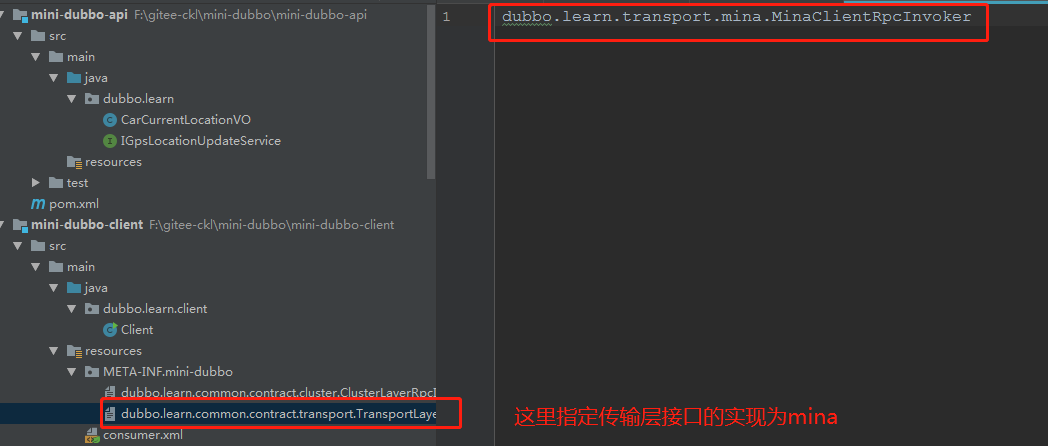
这里的spi的原理也很简单:
dubbo.learn.common.spi.SpiServiceLoader#loadService
public static <T> T loadService(Class<T> clazz) {
//先查找缓存
Object cached = spiName2ServiceMap.get(clazz.getName());
if (cached != null) {
return (T) cached;
}
//2.从spring容器获取该class的全部实现bean
Map<String, T> map = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(clazz);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(map)) {
return null;
}
if (map.size() == 1) {
Object o = map.values().iterator().next();
return clazz.cast(o);
}
//读取spi文件,获取用户指定的实现
String s = SpiParser.getSpiForSpecifiedService(clazz);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(s)) {
log.error("发现多个服务实现bean:{},且在spi中未指定要使用的bean",map);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
// 根据用户spi中的实现,来返回相应的bean
Object specifiedServiceInSpiFile = map.values().stream().filter(v -> Objects.equals(v.getClass().getName(), s))
.findFirst().orElse(null);
if (specifiedServiceInSpiFile == null) {
log.error("spi中指定的服务在bean集合中未找到。" +
"发现多个服务实现bean:{},在spi中指定的服务为:{}",map,s);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
spiName2ServiceMap.put(clazz.getName(),specifiedServiceInSpiFile);
return (T) specifiedServiceInSpiFile;
}
总结
里面细节比较多,最近工作比较忙,所以,大家可以先把代码弄下来,直接自己运行下,依赖的就只有一个redis而已。
后续我会接着优化该框架,欢迎大家加进来,一起开发;如果觉得还不错,就star一下吧。
源码路径:
https://gitee.com/ckl111/mini-dubbo
曹工说mini-dubbo(1)--为了实践动态代理,我写了个简单的rpc框架的更多相关文章
- Dubbo服务调用的动态代理和负载均衡
Dubbo服务调用的动态代理及负载均衡源码解析请参见:http://manzhizhen.iteye.com/blog/2314514
- 将dubbo中使用的动态代理作为工具类
ReflectUtils package per.qiao.util.javassistUtil; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java. ...
- SpringCloud Alibaba (四):Dubbo RPC框架
Dubbo简介 Apache Dubbo |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能.轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现.致 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(23)-- ASM又立功了,Spring原来是这么递归获取注解的元注解的
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(24)-- Spring注解扫描的瑞士军刀,asm技术实战(上)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(27)-- Spring的component-scan,光是include-filter属性的各种配置方式,就够玩半天了.md
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(28)-- Spring的component-scan机制,让你自己来进行简单实现,怎么办
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 20155334 曹翔 Exp3 免杀原理与实践
20155334 曹翔 Exp3 免杀原理与实践 小记:这次实验,困难重重,失败练练,搞得我们是心急如焚,焦头烂额,哭爹喊娘 一.基础问题回答 杀软是如何检测出恶意代码的? 每个杀软都有自己的检测库, ...
- 曹工说Tomcat1:从XML解析说起
一.前言 第一次被人喊曹工,我相当诧异,那是有点久的事情了,楼主13年校招进华为,14年在东莞出差,给东莞移动的通信设备进行版本更新.他们那边的一个小伙子来接我的时候,这么叫我的,刚听到的时候,心里一 ...
随机推荐
- Fourier级数
目录 Fourier级数 函数的Fourier级数的展开 Fourier级数习题: Fourier级数 函数的Fourier级数的展开 Euler--Fourier公式 我们探讨这样一个问题: 假设\ ...
- cs231n spring 2017 lecture3 Loss Functions and Optimization
1. Loss function是用来量化评估当前预测的好坏,loss function越小表明预测越好. 几种典型的loss function: 1)Multiclass SVM loss:一般的S ...
- mysql 事务处理 (转)
事务处理在各种管理系统中都有着广泛的应用,比如人员管理系统,很多同步数据库操作大都需要用到事务处理.比如说,在人员管理系统中,你删除一个人员,你即需要删除人员的基本资料,也要删除和该人员相关的信息,如 ...
- 【一定要记得填坑】LG_3822_[NOI2017]整数
挺好的一道题,由于快noip了,所以打算noip之后再添题解的坑.
- JStorm:任务调度
前一篇文章 JStorm:概念与编程模型 介绍了JStorm的基本概念以及编程模型方面的知识,本篇主要介绍自己对JStorm的任务调度方面的认识,主要从三个方面介绍: 调度角色 调度方法 自定义调度 ...
- 接口测试-chap6-获取页面动态token
1.在发起某些请求时,可能会要求必须是从某个页面进行请求,此时会验证页面的token 2.这个token是动态生成的,每次请求时值都是不同的, 不可以通过fiddler抓取的值作为固定值传入,通过fi ...
- Linux上的软件ClamAV
ClamAV是使用广泛且基于GPL License的开源代码的典型杀毒软件,它支持各种平台,如:windows.linux.Unix等操作系统,并被广泛应用于其他应用程序,如:邮件客户端服务器.HTT ...
- caffe之mac下环境搭建
参考 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-09/135026.html 1. 安装brew,也叫homebrew,mac下类似于ubuntu的apt-get功能 cu ...
- [洛谷P4549] [模板] 裴蜀定理
18.10.03模拟赛T1. 出题人xcj(Mr.Handsome)十分良心,给了一道送分题...... 互测题好久没有出现送分题了.xcj真棒. 题目传送门 幸亏之前看过,否则真的是送分题都拿不到. ...
- linux系统下rpm包的安装、删除、效验、查询
详细课程 使用 RPM RPM 有五个基本的操作 模式(不包括包的编译): 安装,卸载,升级,查询,校验.本节将对它们一一介绍.要了解完整的细节和选项,可以使用 rpm --help, 或转到 the ...
