Tensorflow Probability Distributions 简介
摘要:Tensorflow Distributions提供了两类抽象:distributions和bijectors。distributions提供了一系列具备快速、数值稳定的采样、对数概率计算以及其他统计特征计算方法的概率分布。bijectors提供了一系列针对distribution的可组合的确定性变换。
1、Distributions
1.1 methods
一个distribution至少实现以下方法:sample、log_prob、batch_shape_tensor、event_shape_tensor;同时也实现了一些其他方法,例如:cdf、survival_function、quantile、mean、variance、entropy等;Distribution基类实现了给定log_prob计算prob、给定log_cdf计算log_survival_fn的方法。
1.2 shape semantics
将一个tensor的形状分为三个部分:sample shape、batch shape、event shape。
sample shape:描述从给定概率分布上独立同分布的采样形状;
batch shape:描述从概率分布上独立、非同分布的采样形状,也即,我们可以指定一组参数不同的相同分布,batch shape通常用来为机器学习中一个batch的样本每个样本指定一个分布;
event shape:描述从概率分布上单次采样的形状;
1.3 sampling
reparameterization:distributions拥有一个reparameterization属性,这个属性表明了自动化微分和采样之间的关系。目前包括两种:“fully reparameterized” 和 “not reparameterized”。
fully reparameterized:例如,对于分布dist = Normal(loc, scale),采样y = dist.sample()的内部过程为x = tf.random_normal([]); y = scale * x + loc. 样本y是reparameterized的,因为它是参数loc、scale及无参数样本x的光滑函数。
not reparameterized:例如,gamma分布使用接收-拒绝的方式进行采样,是参数的非光滑函数。
end to end automatic differentiation:通过与tensorflow结合,一个fully reparameterized的分布可以进行端到端的自动微分。例如,要最小化分布Y的期望损失E [φ(Y)],可以使用蒙特卡洛近似的方法最小化
 这使得我们可以使用SN作为期望损失的估计,还可以使用ΔλSN作为梯度ΔλE [φ(Y)]的估计,其中λ是分布Y的参数。
这使得我们可以使用SN作为期望损失的估计,还可以使用ΔλSN作为梯度ΔλE [φ(Y)]的估计,其中λ是分布Y的参数。
1.4 high order distributions
TransformedDistribution:对一个基分布执行一个可逆可微分转换即可得到一个TransformedDistribution。例如,可以从一个Exponential分布得到一个标准Gumbel分布:
standard_gumbel = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Exponential(rate=1.),
bijector=tfb.Chain([
tfb.Affine(
scale_identity_multiplier=-1.,
event_ndims=0),
tfb.Invert(tfb.Exp()),
]))
standard_gumbel.batch_shape # ==> []
standard_gumbel.event_shape # ==> []
基于gumbel分布,可以构建一个Gumbel-Softmax(Concrete)分布:
alpha = tf.stack([
tf.fill([28 * 28], 2.),
tf.ones(28 * 28)]) concrete_pixel = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=standard_gumbel,
bijector=tfb.Chain([
tfb.Sigmoid(),
tfb.Affine(shift=tf.log(alpha)),
]),
batch_shape=[2, 28 * 28])
concrete_pixel.batch_shape # ==> [2, 784]
concrete_pixel.event_shape # ==> []
Independent:对batch shape和event shape进行转换。例如:
image_dist = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Independent(concrete_pixel),
bijector=tfb.Reshape(
event_shape_out=[28, 28, 1],
event_shape_in=[28 * 28]))
image_dist.batch_shape # ==> [2]
image_dist.event_shape # ==> [28, 28, 1]
Mixture:定义了由若干分布组合成的新的分布,例如:
image_mixture = tfd.MixtureSameFamily(
mixture_distribution=tfd.Categorical(
probs=[0.2, 0.8]),
components_distribution=image_dist)
image_mixture.batch_shape # ==> []
image_mixture.event_shape # ==> [28, 28, 1]
1.5 distribution functionals
functional以一个分布作为输入,输出一个标量,例如:entropy、cross entropy、mutual information、kl距离等。
p = tfd.Normal(loc=0., scale=1.)
q = tfd.Normal(loc=-1., scale=2.)
xent = p.cross_entropy(q)
kl = p.kl_divergence(q)
# ==> xent - p.entropy()
2、Bijectors
2.1 definition
Bijector API提供了针对distribution的可微分双向映射(differentialble, bijective map, diffeomorphism)转换接口。给定随机变量X和一个diffeomorphism F,可以定义一个新的随机变量Y,Y的密度可由下式计算:
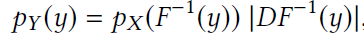
其中DF-1是F的Jacobian的逆。(参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100287713)
每个bijector子类都对应一个F,TransformedDistribution自动计算Y=F(X)的密度。bijector使得我们可以利用已有的分布构建许多其他分布。
bijector主要包含以下三个函数:
forward:实现x → F (x),TransformedDistribution.sample函数使用该函数将一个tensor转换为另一个tensor;
inverse:forward的逆变换,实现y → F-1(y),TransformedDistribution.log_prob使用该函数计算对数概率(上式);
inverse_log_det_jacobian:计算log |DF−1(y)|,TransformedDistribution.log_prob使用该函数计算对数概率(上式);
通过使用bijectors,TransformedDistribution可以自动高效地实现sample、log_prob、prob,对于具有恒定Jacobian的bijector,TransformedDistribution自动实现一些基础统计量,如mean、variance、entropy等。
以下实现了对Laplace的放射变换:
vector_laplace = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Laplace(loc=0., scale=1.),
bijector=tfb.Affine(
shift=tf.Variable(tf.zeros(d)),
scale_tril=tfd.fill_triangular(
tf.Variable(tf.ones(d * (d + 1) / 2)))),
event_shape=[d])
由于tf.Variables,该分布是可学习的。
2.2 composability
bijectors可以构成高阶bijectors,例如Chain、Invert。
chain bijector可以构建一系列丰富的分布,例如创建一个多变量logit-Normal分布:
matrix_logit_mvn =
tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Normal(0., 1.),
bijector=tfb.Chain([
tfb.Reshape([d, d]),
tfb.SoftmaxCentered(),
tfb.Affine(scale_diag=diag),
]),
event_shape=[d * d])
Invert可以通过交换inverse和forward函数,高效地将bijectors数量翻倍,例如:
softminus_gamma = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Gamma(
concentration=alpha,
rate=beta),
bijector=tfb.Invert(tfb.Softplus()))
2.3 caching
bijector自动缓存操作的输入输出对,包括log det jacobian。caching的意义时,当inverse计算很慢或数值不稳定或难以实现时,可以高效的执行inverse操作。当计算采样结果的概率是,缓存被触发。如果q(x)是x=f(ε)的密度,且ε~r,那么caching可以降低计算q(xi)的计算成本:
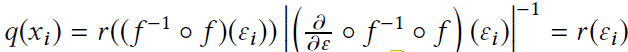
caching机制也可用来进行高效地重要性采样(importance sampling):

3、 应用
3.1 核密度估计(KDE)
例如,可以通过以下代码构建一个由n个mvn_diag分布作为kernel的混合高斯模型,其中每个kernel的权重为1/n。注意,此时Independent会对分布的shape进行重定义(reinterpret),tfd.Normal(loc=x, scale=1.)创建了一个batch_shape = n*d, event_shape = []的分布,对其Independent之后,变为batch_shape = n, event_shape = d的分布。
Independent文档:https://www.tensorflow.org/probability/api_docs/python/tfp/distributions/Independent?hl=zh-cn
f = lambda x: tfd.Independent(tfd.Normal(
loc=x, scale=1.))
n = x.shape[0].value
kde = tfd.MixtureSameFamily(
mixture_distribution=tfd.Categorical(
probs=[1 / n] * n),
components_distribution=f(x))
3.2 变分自编码器(VAE)
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1312.6114.pdf
博客:https://spaces.ac.cn/archives/5253
def make_encoder(x, z_size=8):
net = make_nn(x, z_size * 2) return tfd.MultivariateNormalDiag(
loc=net[..., :z_size],
scale=tf.nn.softplus(net[..., z_size:]))) def make_decoder(z, x_shape=(28, 28, 1)):
net = make_nn(z, tf.reduce_prod(x_shape)) logits = tf.reshape(
net, tf.concat([[-1], x_shape], axis=0))
return tfd.Independent(tfd.Bernoulli(logits)) def make_prior(z_size=8, dtype=tf.float32):
return tfd.MultivariateNormalDiag(
loc=tf.zeros(z_size, dtype))) def make_nn(x, out_size, hidden_size=(128, 64)):
net = tf.flatten(x) for h in hidden_size:
net = tf.layers.dense(
net, h, activation=tf.nn.relu)
return tf.layers.dense(net, out_size)
3.3 Edward概率编程
tfd是Edward的后端。以下代码实现一个随机循环神经网络(stochastic rnn),其隐藏状态是随机的。
stochastic rnn论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.7610.pdf
from edward.models import Normal z = x = []
z[0] = Normal(loc=tf.zeros(K), scale=tf.ones(K))
h = tf.layers.dense(
z[0], 512, activation=tf.nn.relu)
loc = tf.layers.dense(h, D, activation=None)
x[0] = Normal(loc=loc, scale=0.5)
for t in range(1, T):
inputs = tf.concat([z[t - 1], x[t - 1]], 0)
loc = tf.layers.dense(
inputs, K, activation=tf.tanh)
z[t] = Normal(loc=loc, scale=0.1)
h = tf.layers.dense(
z[t], 512, activation=tf.nn.relu)
loc = tf.layers.dense(h, D, activation=None)
x[t] = Normal(loc=loc, scale=0.5)
Tensorflow Probability Distributions 简介的更多相关文章
- PRML读书笔记——2 Probability Distributions
2.1. Binary Variables 1. Bernoulli distribution, p(x = 1|µ) = µ 2.Binomial distribution + 3.beta dis ...
- PRML读书会第二章 Probability Distributions(贝塔-二项式、狄利克雷-多项式共轭、高斯分布、指数族等)
主讲人 网络上的尼采 (新浪微博: @Nietzsche_复杂网络机器学习) 网络上的尼采(813394698) 9:11:56 开始吧,先不要发言了,先讲PRML第二章Probability Dis ...
- PRML Chapter 2. Probability Distributions
PRML Chapter 2. Probability Distributions P68 conjugate priors In Bayesian probability theory, if th ...
- Common Probability Distributions
Common Probability Distributions Probability Distribution A probability distribution describes the p ...
- Study note for Continuous Probability Distributions
Basics of Probability Probability density function (pdf). Let X be a continuous random variable. The ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 8: Normal Distribution
PDF version PDF & CDF The probability density function is $$f(x; \mu, \sigma) = {1\over\sqrt{2\p ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 7: Uniform Distribution
PDF version PDF & CDF The probability density function of the uniform distribution is $$f(x; \al ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 6: Exponential Distribution
PDF version PDF & CDF The exponential probability density function (PDF) is $$f(x; \lambda) = \b ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 5: Hypergemometric Distribution
PDF version PMF Suppose that a sample of size $n$ is to be chosen randomly (without replacement) fro ...
随机推荐
- 【Django必备01】——什么是Django框架?有什么优势?模块组成介绍。
01.什么是Django框架? Django是一个开放源代码的Web应用框架,由Python写成.采用了MTV的框架模式.使用这种架构,程序员可以方便.快捷地创建高品质.易维护.数据库驱动的应用程序. ...
- python基础学习之集合set
.集合:set 特点:无序,不可重复(自动去重),可更改,可以与元组.列表互相转换 格式:s = {'x','y','z'} 转换:(转回用set) s = {'x','y','z'} ...
- sqli-labs系列——第五关
less5 更改id后无果,不能用union联合查询 此处用报错注入 报错注入的概念:(1). 通过floor报错 and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat ...
- 【Azure 应用服务】App Service 在使用GIt本地部署,上传代码的路径为/home/site/repository,而不是站点的根目录/home/site/wwwroot。 这个是因为什么?
问题描述 App Service 在使用GIt本地部署,上传代码的路径为/home/site/repository,而不是站点的根目录/home/site/wwwroot. 这个是因为什么? 并且通过 ...
- C# - 实现类型的比较
IComparable<T> .NET 里,IComparable<T>是用来作比较的最常用接口. 如果某个类型的实例需要与该类型的其它实例进行比较或者排序的话,那么该类型就可 ...
- Redis实战篇(三)基于HyperLogLog实现UV统计功能
如果现在要开发一个功能: 统计APP或网页的一个页面,每天有多少用户点击进入的次数.同一个用户的反复点击进入记为 1 次,也就是统计 UV 数据. 让你来开发这个统计模块,你会如何实现? 如果统计 P ...
- spring5源码编译过程中必经的坑
spring源码编译流程:Spring5 源码下载 第 一 步 : https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/archive/v5.0.2 ...
- Python基础(十五):Python的3种字符串格式化,做个超全对比!
有时候,为了更方便.灵活的运用字符串.在Python中,正好有3种方式,支持格式化字符串的输出 . 3种字符串格式化工具的简单介绍 python2.5版本之前,我们使用的是老式字符串格式化输出%s. ...
- Vulkan移植GpuImage(三)从A到C的滤镜
前面移植了几个比较复杂的效果后,算是确认了复杂滤镜不会对框架造成比较大的改动,开始从头移植,现已把A到C的所有滤镜用vulkan的ComputeShader实现了,讲一些其中实现的过程. Averag ...
- spieces-in-pieces动画编辑器
前言: 制作灵感来源于 http://species-in-pieces.com/ 这个网站,此网站作者是来自阿姆斯特丹的设计师 Bryan James,其借用纯CSS技术表现出30种濒危动物的碎片拼 ...
