ceph-csi源码分析(8)-cephfs driver分析
更多 ceph-csi 其他源码分析,请查看下面这篇博文:kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航
ceph-csi源码分析(8)-cephfs driver分析
当ceph-csi组件启动时指定的driver type为cephfs时,会启动cephfs driver相关的服务。然后再根据controllerserver、nodeserver的参数配置,决定启动ControllerServer与IdentityServer,或NodeServer与IdentityServer。
基于tag v3.0.0
https://github.com/ceph/ceph-csi/releases/tag/v3.0.0
cephfs driver,与rbd driver类似,同样包括了controllerserver、nodeserver与IdentityServer,且大部分方法逻辑一致,只是最后调用的cli命令稍有不同,所以大部分方法的分析可以参考rbd driver部分。
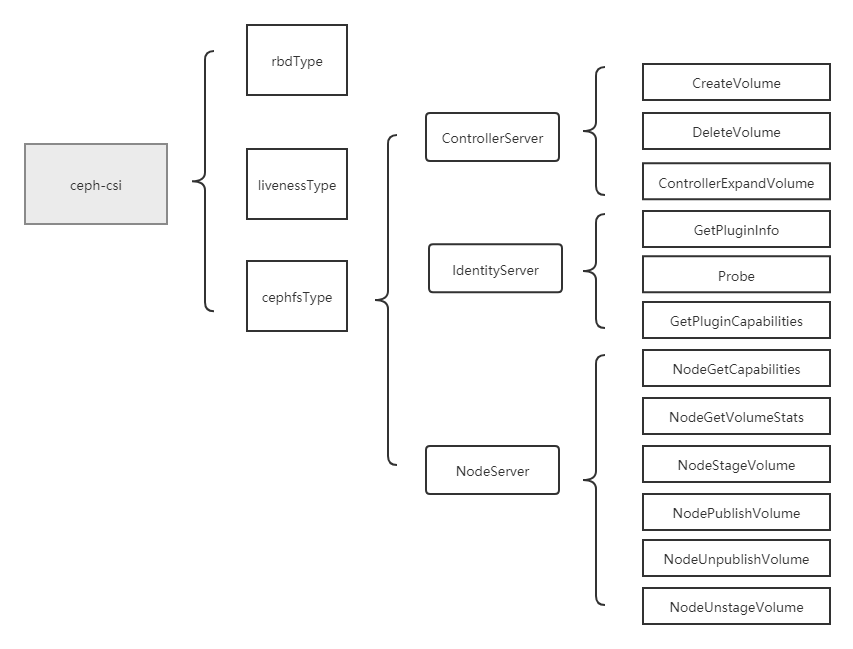
其中,controllerserver主要包括了CreateVolume(创建存储)、DeleteVolume(删除存储)、ControllerExpandVolume(存储扩容):
CreateVolume:调用ceph存储后端,创建存储(与rbd逻辑类似,不过cephfs这里创建的是目录,而不是rbd image)。
DeleteVolume:调用ceph存储后端,删除存储(与rbd逻辑类似,不过cephfs这里删除的是目录,而不是rbd image)。
ControllerExpandVolume:调用ceph存储后端,扩容存储(重新设置cephfs目录的quota)。
nodeserver主要包括了NodeGetCapabilities(获取driver能力)、NodeGetVolumeStats(存储探测及metrics获取)、NodeStageVolume(mount stagingPath)、NodePublishVolume(mount targetPath)、NodeUnpublishVolume(umount targetPath)、NodeUnstageVolume(umount stagingPath):
NodeGetCapabilities:获取ceph-csi driver的能力。
NodeGetVolumeStats:探测挂载存储的状态,并返回该存储的相关metrics给kubelet。
NodeStageVolume:将cephfs的远端目录挂载到node上的staging path。
NodePublishVolume:将NodeStageVolume方法中的staging path,mount到target path。
NodeUnpublishVolume:解除掉stagingPath到targetPath的挂载。
NodeUnstageVolume:将cephfs的远端目录到node上的staging path的挂载解除掉。
IdentityServer主要包括了GetPluginInfo(获取driver信息)、Probe(探测接口)、GetPluginCapabilities(获取driver能力)三个方法:
GetPluginInfo:用于获取该ceph-csi driver的信息,如driver名称、版本等。
Probe:一个探测接口,用于探测该driver是否启动。
GetPluginCapabilities:用于获取driver的能力。
cephfs挂载知识讲解
cephfs挂载分为fuse挂载和内核挂载。
一个cephfs存储挂载给pod,一共分为2个步骤,分别如下:
1.kubelet组件调用cephfsType-nodeserver-ceph-csi的NodeStageVolume方法,将cephfs的远端目录挂载到node上的staging path;
2.kubelet组件调用cephfsType-nodeserver-ceph-csi的NodePublishVolume方法,将上一步骤中的staging path mount到target path。
可以看出,与rbd image挂载给pod相比,在NodeStageVolume方法中少了一个map rbd/nbd device的操作,同样的,在NodeUnstageVolume方法中也会少一个unmap rbd/nbd device的操作。
cephfs解除挂载知识讲解
一个cephfs存储从pod中解除挂载,一共分为2个步骤,分别如下:
1.kubelet组件调用cephfsType-nodeserver-ceph-csi的NodeUnpublishVolume方法,解除掉stagingPath与targetPath的挂载关系。
2.kubelet组件调用cephfsType-nodeserver-ceph-csi的NodeUnstageVolume方法,先解除掉targetPath到远端cephfs存储(目录)的挂载关系。
cephfs存储挂载给pod后,node上会出现2个mount关系,示例如下:
# mount | grep ceph-fuse
ceph-fuse on /home/cld/kubernetes/lib/kubelet/plugins/kubernetes.io/csi/pv/pvc-fa752c51-79d4-42f2-a3ff-9d7afe8767b5/globalmount type fuse.ceph-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=0,group_id=0,allow_other)
ceph-fuse on /home/cld/kubernetes/lib/kubelet/pods/87f7e220-8b2d-4cd3-8395-12794940fa2e/volumes/kubernetes.io~csi/pvc-fa752c51-79d4-42f2-a3ff-9d7afe8767b5/mount type fuse.ceph-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=0,group_id=0,allow_other,_netdev)
其中/home/cld/kubernetes/lib/kubelet/plugins/kubernetes.io/csi/pv/pvc-fa752c51-79d4-42f2-a3ff-9d7afe8767b5/globalmount为staging path;而/home/cld/kubernetes/lib/kubelet/pods/87f7e220-8b2d-4cd3-8395-12794940fa2e/volumes/kubernetes.io~csi/pvc-fa752c51-79d4-42f2-a3ff-9d7afe8767b5/mount为target path。
cephfs driver分析
下面将对cephfs driver中与rbd driver不一致的展开分析。
(1)cephfs扩容逻辑
cephfs driver没有NodeExpandVolume(node端存储扩容),与rbd存储扩容分为两大步骤不一样,cephfs存储扩容只需一步,就是csi的ControllerExpandVolume,主要负责将cephfs存储扩容(即重新设置cephfs目录的quota)。
cephfs driver的NodeGetCapabilities方法中,相比于rbd driver,也少了node端存储扩容的能力。
// internal/cephfs/nodeserver.go
// NodeGetCapabilities returns the supported capabilities of the node server.
func (ns *NodeServer) NodeGetCapabilities(ctx context.Context, req *csi.NodeGetCapabilitiesRequest) (*csi.NodeGetCapabilitiesResponse, error) {
return &csi.NodeGetCapabilitiesResponse{
Capabilities: []*csi.NodeServiceCapability{
{
Type: &csi.NodeServiceCapability_Rpc{
Rpc: &csi.NodeServiceCapability_RPC{
Type: csi.NodeServiceCapability_RPC_STAGE_UNSTAGE_VOLUME,
},
},
},
{
Type: &csi.NodeServiceCapability_Rpc{
Rpc: &csi.NodeServiceCapability_RPC{
Type: csi.NodeServiceCapability_RPC_GET_VOLUME_STATS,
},
},
},
},
}, nil
}
(2)NodeStageVolume
将cephfs的远端目录挂载到node上的staging path。
NodeStageVolume
主要逻辑:
(1)校验请求参数;
(2)构建volOptions;
(3)检查stagingPath是否是挂载点;
(4)调用ns.mount进行挂载操作。
// internal/cephfs/nodeserver.go
// NodeStageVolume mounts the volume to a staging path on the node.
func (ns *NodeServer) NodeStageVolume(ctx context.Context, req *csi.NodeStageVolumeRequest) (*csi.NodeStageVolumeResponse, error) {
var (
volOptions *volumeOptions
)
if err := util.ValidateNodeStageVolumeRequest(req); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Configuration
stagingTargetPath := req.GetStagingTargetPath()
volID := volumeID(req.GetVolumeId())
if acquired := ns.VolumeLocks.TryAcquire(req.GetVolumeId()); !acquired {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, util.VolumeOperationAlreadyExistsFmt), volID)
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Aborted, util.VolumeOperationAlreadyExistsFmt, req.GetVolumeId())
}
defer ns.VolumeLocks.Release(req.GetVolumeId())
volOptions, _, err := newVolumeOptionsFromVolID(ctx, string(volID), req.GetVolumeContext(), req.GetSecrets())
if err != nil {
if !errors.Is(err, ErrInvalidVolID) {
return nil, status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
// gets mon IPs from the supplied cluster info
volOptions, _, err = newVolumeOptionsFromStaticVolume(string(volID), req.GetVolumeContext())
if err != nil {
if !errors.Is(err, ErrNonStaticVolume) {
return nil, status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
// get mon IPs from the volume context
volOptions, _, err = newVolumeOptionsFromMonitorList(string(volID), req.GetVolumeContext(),
req.GetSecrets())
if err != nil {
return nil, status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
}
}
// Check if the volume is already mounted
isMnt, err := util.IsMountPoint(stagingTargetPath)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, "stat failed: %v"), err)
return nil, status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
if isMnt {
util.DebugLog(ctx, "cephfs: volume %s is already mounted to %s, skipping", volID, stagingTargetPath)
return &csi.NodeStageVolumeResponse{}, nil
}
// It's not, mount now
if err = ns.mount(ctx, volOptions, req); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
util.DebugLog(ctx, "cephfs: successfully mounted volume %s to %s", volID, stagingTargetPath)
return &csi.NodeStageVolumeResponse{}, nil
}
ns.mount
这里的挂载分为fuse挂载和内核挂载,不同的挂载调用不同的本地command来进行。
// internal/cephfs/nodeserver.go
func (*NodeServer) mount(ctx context.Context, volOptions *volumeOptions, req *csi.NodeStageVolumeRequest) error {
stagingTargetPath := req.GetStagingTargetPath()
volID := volumeID(req.GetVolumeId())
cr, err := getCredentialsForVolume(volOptions, req)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, "failed to get ceph credentials for volume %s: %v"), volID, err)
return status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
defer cr.DeleteCredentials()
m, err := newMounter(volOptions)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, "failed to create mounter for volume %s: %v"), volID, err)
return status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
util.DebugLog(ctx, "cephfs: mounting volume %s with %s", volID, m.name())
readOnly := "ro"
fuseMountOptions := strings.Split(volOptions.FuseMountOptions, ",")
kernelMountOptions := strings.Split(volOptions.KernelMountOptions, ",")
if req.VolumeCapability.AccessMode.Mode == csi.VolumeCapability_AccessMode_MULTI_NODE_READER_ONLY ||
req.VolumeCapability.AccessMode.Mode == csi.VolumeCapability_AccessMode_SINGLE_NODE_READER_ONLY {
switch m.(type) {
case *fuseMounter:
if !csicommon.MountOptionContains(strings.Split(volOptions.FuseMountOptions, ","), readOnly) {
volOptions.FuseMountOptions = util.MountOptionsAdd(volOptions.FuseMountOptions, readOnly)
fuseMountOptions = append(fuseMountOptions, readOnly)
}
case *kernelMounter:
if !csicommon.MountOptionContains(strings.Split(volOptions.KernelMountOptions, ","), readOnly) {
volOptions.KernelMountOptions = util.MountOptionsAdd(volOptions.KernelMountOptions, readOnly)
kernelMountOptions = append(kernelMountOptions, readOnly)
}
}
}
if err = m.mount(ctx, stagingTargetPath, cr, volOptions); err != nil {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx,
"failed to mount volume %s: %v Check dmesg logs if required."),
volID,
err)
return status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
if !csicommon.MountOptionContains(kernelMountOptions, readOnly) && !csicommon.MountOptionContains(fuseMountOptions, readOnly) {
// #nosec - allow anyone to write inside the stagingtarget path
err = os.Chmod(stagingTargetPath, 0777)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, "failed to change stagingtarget path %s permission for volume %s: %v"), stagingTargetPath, volID, err)
uErr := unmountVolume(ctx, stagingTargetPath)
if uErr != nil {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, "failed to umount stagingtarget path %s for volume %s: %v"), stagingTargetPath, volID, uErr)
}
return status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
}
return nil
}
fuse挂载
// internal/cephfs/volumemounter.go
func (m *fuseMounter) mount(ctx context.Context, mountPoint string, cr *util.Credentials, volOptions *volumeOptions) error {
if err := util.CreateMountPoint(mountPoint); err != nil {
return err
}
return mountFuse(ctx, mountPoint, cr, volOptions)
}
func mountFuse(ctx context.Context, mountPoint string, cr *util.Credentials, volOptions *volumeOptions) error {
args := []string{
mountPoint,
"-m", volOptions.Monitors,
"-c", util.CephConfigPath,
"-n", cephEntityClientPrefix + cr.ID, "--keyfile=" + cr.KeyFile,
"-r", volOptions.RootPath,
"-o", "nonempty",
}
if volOptions.FuseMountOptions != "" {
args = append(args, ","+volOptions.FuseMountOptions)
}
if volOptions.FsName != "" {
args = append(args, "--client_mds_namespace="+volOptions.FsName)
}
_, stderr, err := util.ExecCommand(ctx, "ceph-fuse", args[:]...)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Parse the output:
// We need "starting fuse" meaning the mount is ok
// and PID of the ceph-fuse daemon for unmount
match := fusePidRx.FindSubmatch([]byte(stderr))
// validMatchLength is set to 2 as match is expected
// to have 2 items, starting fuse and PID of the fuse daemon
const validMatchLength = 2
if len(match) != validMatchLength {
return fmt.Errorf("ceph-fuse failed: %s", stderr)
}
pid, err := strconv.Atoi(string(match[1]))
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to parse FUSE daemon PID: %w", err)
}
fusePidMapMtx.Lock()
fusePidMap[mountPoint] = pid
fusePidMapMtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
内核挂载
// internal/cephfs/volumemounter.go
func (m *kernelMounter) mount(ctx context.Context, mountPoint string, cr *util.Credentials, volOptions *volumeOptions) error {
if err := util.CreateMountPoint(mountPoint); err != nil {
return err
}
return mountKernel(ctx, mountPoint, cr, volOptions)
}
func mountKernel(ctx context.Context, mountPoint string, cr *util.Credentials, volOptions *volumeOptions) error {
if err := execCommandErr(ctx, "modprobe", "ceph"); err != nil {
return err
}
args := []string{
"-t", "ceph",
fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", volOptions.Monitors, volOptions.RootPath),
mountPoint,
}
optionsStr := fmt.Sprintf("name=%s,secretfile=%s", cr.ID, cr.KeyFile)
mdsNamespace := ""
if volOptions.FsName != "" {
mdsNamespace = fmt.Sprintf("mds_namespace=%s", volOptions.FsName)
}
optionsStr = util.MountOptionsAdd(optionsStr, mdsNamespace, volOptions.KernelMountOptions, netDev)
args = append(args, "-o", optionsStr)
return execCommandErr(ctx, "mount", args[:]...)
}
(3)NodeUnstageVolume
将cephfs的远端目录到node上的staging path的挂载解除掉。
NodeUnstageVolume
主要逻辑:
(1)校验请求参数;
(2)调用unmountVolume解除cephfs的远端目录到node上的staging path的挂载。
// internal/cephfs/nodeserver.go
// NodeUnstageVolume unstages the volume from the staging path.
func (ns *NodeServer) NodeUnstageVolume(ctx context.Context, req *csi.NodeUnstageVolumeRequest) (*csi.NodeUnstageVolumeResponse, error) {
var err error
if err = util.ValidateNodeUnstageVolumeRequest(req); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
volID := req.GetVolumeId()
if acquired := ns.VolumeLocks.TryAcquire(volID); !acquired {
klog.Errorf(util.Log(ctx, util.VolumeOperationAlreadyExistsFmt), volID)
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Aborted, util.VolumeOperationAlreadyExistsFmt, volID)
}
defer ns.VolumeLocks.Release(volID)
stagingTargetPath := req.GetStagingTargetPath()
// Unmount the volume
if err = unmountVolume(ctx, stagingTargetPath); err != nil {
return nil, status.Error(codes.Internal, err.Error())
}
util.DebugLog(ctx, "cephfs: successfully unmounted volume %s from %s", req.GetVolumeId(), stagingTargetPath)
return &csi.NodeUnstageVolumeResponse{}, nil
}
unmountVolume
// internal/cephfs/volumemounter.go
func unmountVolume(ctx context.Context, mountPoint string) error {
if err := execCommandErr(ctx, "umount", mountPoint); err != nil {
if strings.Contains(err.Error(), fmt.Sprintf("exit status 32: umount: %s: not mounted", mountPoint)) ||
strings.Contains(err.Error(), "No such file or directory") {
return nil
}
return err
}
fusePidMapMtx.Lock()
pid, ok := fusePidMap[mountPoint]
if ok {
delete(fusePidMap, mountPoint)
}
fusePidMapMtx.Unlock()
if ok {
p, err := os.FindProcess(pid)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf(util.Log(ctx, "failed to find process %d: %v"), pid, err)
} else {
if _, err = p.Wait(); err != nil {
klog.Warningf(util.Log(ctx, "%d is not a child process: %v"), pid, err)
}
}
}
return nil
}
ceph-csi源码分析(8)-cephfs driver分析的更多相关文章
- 老李推荐:第6章8节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-小结
老李推荐:第6章8节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-小结 本章我们重点围绕处理网络过来的命令的MonkeySourceNetwork这个事 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章7节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-注入按键事件实例
老李推荐:第6章7节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-注入按键事件实例 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员能胜 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章6节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令队列
老李推荐:第6章6节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令队列 事件源在获得字串命令并把它翻译成对应的MonkeyEvent事件后,会把这些 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章4节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-翻译命令字串
老李推荐:第6章4节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-翻译命令字串 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员能胜任自 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章5节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-事件
老李推荐:第6章5节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-事件 从网络过来的命令字串需要解析翻译出来,有些命令会在翻译好后直接执行然后返回,但有 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章3节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令翻译类
老李推荐:第6章3节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-命令翻译类 每个来自网络的字串命令都需要进行解析执行,只是有些是在解析的过程中直接执行 ...
- 老李推荐:第6章2节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-获取命令字串
老李推荐:第6章2节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-事件源-事件源概览-获取命令字串 从上一节的描述可以知道,MonkeyRunner发送给Monkey的命令 ...
- 老李推荐:第5章7节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-启动运行: 循环获取并执行事件 - runMonkeyCycles
老李推荐:第5章7节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-启动运行: 循环获取并执行事件 - runMonkeyCycles poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开 ...
- 老李推荐:第5章6节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》Monkey原理分析-启动运行: 初始化事件源
老李推荐:第5章6节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析>Monkey原理分析-启动运行: 初始化事件源 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员能胜任自动化测试 ...
随机推荐
- 痞子衡嵌入式:串行NOR Flash的Continuous read模式下软复位后i.MXRT无法启动问题解决方案之RESET#
大家好,我是痞子衡,是正经搞技术的痞子.今天痞子衡给大家介绍的是i.MXRT上使能NOR Flash的Continuous read模式在软复位后无法正常启动问题的解决经验. 前一篇文章 <在i ...
- 用户添加到sudoer列表## Allow root to run any commands anywhere root ALL=(ALL) ALL Iron ALL=(ALL) ALL
将用户添加到sudoer列表 李序锴关注 2017.12.20 15:03:25字数 605阅读 4,067 默认情况下,linux没有将当前用户列入到sudoer列表中(在redhat系列的linu ...
- Java中日志组件详解
avalon-logkit Java中日志组件详解 lanhy 发布于 2020-9-1 11:35 224浏览 0收藏 作为开发人员,我相信您对日志记录工具并不陌生. Java还具有功能强大且功能强 ...
- Docker------Linux安装Docker
1.添加yum源 yum install epel-release –y yum clean all yum list 2.安装并运行Docker yum install docker-io –y s ...
- 如何用WINPE备份电脑系统;电脑备份 听语音
如何用WINPE备份电脑系统:电脑备份 听语音 原创 | 浏览:1046 | 更新:2017-09-30 15:09 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 分步阅读 备份系统已经成为一种常态,我们在安装完成系统 ...
- 所有的 Unix Like 系统都会内建 vi 文书编辑器。vim 是vi的升级版本,它不仅兼容vi的所有指令 ,而且还有一些新的特性在里面。
所有的 Unix Like 系统都会内建 vi 文书编辑器.vim 是vi的升级版本,它不仅兼容vi的所有指令 ,而且还有一些新的特性在里面. https://blog.csdn.net/carolz ...
- IPMI中sol的使用
IPMI中sol的使用 转载韦远科 最后发布于2013-05-09 15:19:18 阅读数 7920 收藏 http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-1838361-id-3 ...
- Linux进阶之TCP三次握手四次挥手
TCP(Transfer control protocol)传输控制协议 一.两种传输模式: TCP面向有连接 可靠 常用于点对点 微信 UDP面向无连接 高速 常用于点对面 直播 二.数据方向: 在 ...
- 10.1 ifconfig:配置或显示网络接口信息
ifconfig命令 用于配置网卡IP地址等网络参数或显示当前网络的接口状态,其类似于Windows下的ipconfig命令,这两个命令很容易混淆,读者需要区分一下.此外,ifconfig命令在配置网 ...
- 微信小程序使用同声传译实现语音识别功能
我使用同声传译语音识别功能是为了实现微信小程序首页的语音搜索功能,如果你也是那么恭喜你,你可以ctrl+c.ctrl+v再改一改,如果你不是那么你也不要着急的走可以看完我的文章会对你有所帮助! 首先是 ...
