Spring系列之JDBC对不同数据库异常如何抽象的?
前言
使用Spring-Jdbc的情况下,在有些场景中,我们需要根据数据库报的异常类型的不同,来编写我们的业务代码。比如说,我们有这样一段逻辑,如果我们新插入的记录,存在唯一约束冲突,就会返回给客户端描述:记录已存在,请勿重复操作
代码一般是这么写的:
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public String testAdd(){
try {
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO user_info (user_id, user_name, email, nick_name, status, address) VALUES (80002, '张三丰', 'xxx@126.com', '张真人', 1, '武当山');");
return "OK";
}catch (DuplicateKeyException e){
return "记录已存在,请勿重复操作";
}
}
测试一下:
如上图提示,并且无论什么更换什么数据库(Spring-Jdbc支持的),代码都不用改动
那么Spring-Jdbc是在使用不同数据库时,Spring如何帮我们实现对异常的抽象的呢?
代码实现
我们来正向看下代码:
首先入口JdbcTemplate.execute方法:
public void execute(final String sql) throws DataAccessException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Executing SQL statement [" + sql + "]");
}
...
//实际执行入口
this.execute(new ExecuteStatementCallback(), true);
}
内部方法execute
@Nullable
private <T> T execute(StatementCallback<T> action, boolean closeResources) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.obtainDataSource());
Statement stmt = null;
Object var12;
try {
stmt = con.createStatement();
this.applyStatementSettings(stmt);
T result = action.doInStatement(stmt);
this.handleWarnings(stmt);
var12 = result;
} catch (SQLException var10) {
String sql = getSql(action);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
stmt = null;
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.getDataSource());
con = null;
//SQL出现异常后,在这里进行异常转换
throw this.translateException("StatementCallback", sql, var10);
} finally {
if (closeResources) {
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt);
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.getDataSource());
}
}
return var12;
}
异常转换方法translateException
protected DataAccessException translateException(String task, @Nullable String sql, SQLException ex) {
//获取异常转换器,然后根据数据库返回码相关信息执行转换操作
//转换不成功,也有兜底异常UncategorizedSQLException
DataAccessException dae = this.getExceptionTranslator().translate(task, sql, ex);
return (DataAccessException)(dae != null ? dae : new UncategorizedSQLException(task, sql, ex));
}
获取转换器方法getExceptionTranslator
public SQLExceptionTranslator getExceptionTranslator() {
//获取转换器属性,如果为空,则生成一个
SQLExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator = this.exceptionTranslator;
if (exceptionTranslator != null) {
return exceptionTranslator;
} else {
synchronized(this) {
SQLExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator = this.exceptionTranslator;
if (exceptionTranslator == null) {
DataSource dataSource = this.getDataSource();
//shouldIgnoreXml是一个标记,就是不通过xml加载bean,默认false
if (shouldIgnoreXml) {
exceptionTranslator = new SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator();
} else if (dataSource != null) {
//如果DataSource不为空,则生成转换器SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator
exceptionTranslator = new SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(dataSource);
} else {
// 其他情况,生成SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator转换器
exceptionTranslator = new SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator();
}
this.exceptionTranslator = (SQLExceptionTranslator)exceptionTranslator;
}
return (SQLExceptionTranslator)exceptionTranslator;
}
}
}
转换方法:
因为默认的转换器是SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator,所以这里调用SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator的doTranslate方法
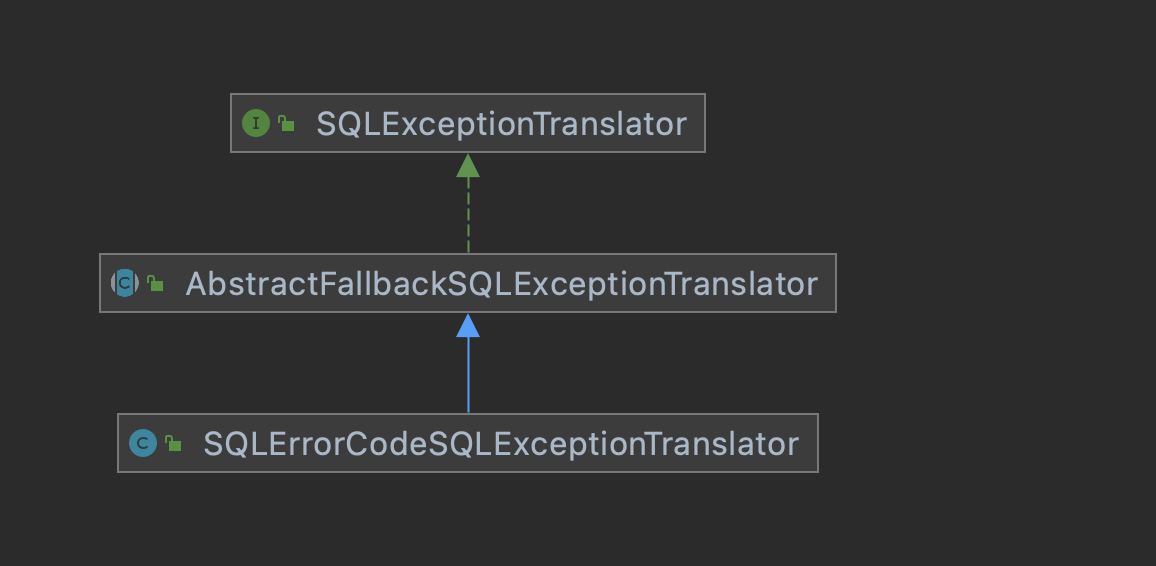
类图调用关系如上,实际先调用的是AbstractFallbackSQLExceptionTranslator.translate的方法
@Nullable
public DataAccessException translate(String task, @Nullable String sql, SQLException ex) {
Assert.notNull(ex, "Cannot translate a null SQLException");
//这里才真正调用SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator.doTranslate方法
DataAccessException dae = this.doTranslate(task, sql, ex);
if (dae != null) {
return dae;
} else {
//如果没有找到响应的异常,则调用其他转换器,输入递归调用,这里后面说
SQLExceptionTranslator fallback = this.getFallbackTranslator();
return fallback != null ? fallback.translate(task, sql, ex) : null;
}
}
实际转换类SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator的方法:
//这里省略了一些无关代码,只保留了核心代码
//先获取SQLErrorCodes集合,在根据返回的SQLException中获取的ErrorCode进行匹配,根据匹配结果进行返回响应的异常
protected DataAccessException doTranslate(String task, @Nullable String sql, SQLException ex) {
....
SQLErrorCodes sqlErrorCodes = this.getSqlErrorCodes();
String errorCode = Integer.toString(ex.getErrorCode());
...
if (Arrays.binarySearch(sqlErrorCodes.getDuplicateKeyCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) {
this.logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false);
return new DuplicateKeyException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx);
}
...
return null;
}
上面的SQLErrorCodes是一个错误码集合,但是不是全部数据库的所有错误码集合,而是只取了相应数据库的错误码集合,怎么保证获取的是当前使用的数据库的错误码,而不是其他数据库的错误码呢?当然Spring为我们实现了,在SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator中:
public class SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator extends AbstractFallbackSQLExceptionTranslator {
private SingletonSupplier<SQLErrorCodes> sqlErrorCodes;
//默认构造方法,设置了如果转换失败,下一个转换器是SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator
public SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator() {
this.setFallbackTranslator(new SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator());
}
//前面生成转换器的时候,exceptionTranslator = new SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(dataSource);
//使用的是本构造方法,传入了DataSource,其中有数据库厂商信息,本文中是MYSQL
public SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(DataSource dataSource) {
this();
this.setDataSource(dataSource);
}
//从错误码工厂SQLErrorCodesFactory里,获取和数据源对应的厂商的所有错误码
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.sqlErrorCodes = SingletonSupplier.of(() -> {
return SQLErrorCodesFactory.getInstance().resolveErrorCodes(dataSource);
});
this.sqlErrorCodes.get();
}
}
错误码工厂SQLErrorCodesFactory的resolveErrorCodes方法:
//既然是工厂,里面肯定有各种数据库的错误码,本文中使用的是MYSQL,我们看一下实现逻辑
@Nullable
public SQLErrorCodes resolveErrorCodes(DataSource dataSource) {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "DataSource must not be null");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up default SQLErrorCodes for DataSource [" + this.identify(dataSource) + "]");
}
//从缓存中拿MYSQL对应的SQLErrorCodes
SQLErrorCodes sec = (SQLErrorCodes)this.dataSourceCache.get(dataSource);
if (sec == null) {
synchronized(this.dataSourceCache) {
sec = (SQLErrorCodes)this.dataSourceCache.get(dataSource);
if (sec == null) {
try {
String name = (String)JdbcUtils.extractDatabaseMetaData(dataSource, DatabaseMetaData::getDatabaseProductName);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(name)) {
SQLErrorCodes var10000 = this.registerDatabase(dataSource, name);
return var10000;
}
} catch (MetaDataAccessException var6) {
logger.warn("Error while extracting database name", var6);
}
return null;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SQLErrorCodes found in cache for DataSource [" + this.identify(dataSource) + "]");
}
return sec;
}
**缓存dataSourceCache如何生成的? **
public SQLErrorCodes registerDatabase(DataSource dataSource, String databaseName) {
//根据数据库类型名称(这里是MySQL),获取错误码列表
SQLErrorCodes sec = this.getErrorCodes(databaseName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Caching SQL error codes for DataSource [" + this.identify(dataSource) + "]: database product name is '" + databaseName + "'");
}
this.dataSourceCache.put(dataSource, sec);
return sec;
}
public SQLErrorCodes getErrorCodes(String databaseName) {
Assert.notNull(databaseName, "Database product name must not be null");
//从errorCodesMap根据key=MYSQL获取SQLErrorCodes
SQLErrorCodes sec = (SQLErrorCodes)this.errorCodesMap.get(databaseName);
if (sec == null) {
Iterator var3 = this.errorCodesMap.values().iterator();
while(var3.hasNext()) {
SQLErrorCodes candidate = (SQLErrorCodes)var3.next();
if (PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(candidate.getDatabaseProductNames(), databaseName)) {
sec = candidate;
break;
}
}
}
if (sec != null) {
this.checkCustomTranslatorRegistry(databaseName, sec);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SQL error codes for '" + databaseName + "' found");
}
return sec;
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("SQL error codes for '" + databaseName + "' not found");
}
return new SQLErrorCodes();
}
}
//SQLErrorCodesFactory构造方法中,生成的errorCodesMap,map的内容来自org/springframework/jdbc/support/sql-error-codes.xml文件
protected SQLErrorCodesFactory() {
Map errorCodes;
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory lbf = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
lbf.setBeanClassLoader(this.getClass().getClassLoader());
XmlBeanDefinitionReader bdr = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(lbf);
Resource resource = this.loadResource("org/springframework/jdbc/support/sql-error-codes.xml");
if (resource != null && resource.exists()) {
bdr.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
} else {
logger.info("Default sql-error-codes.xml not found (should be included in spring-jdbc jar)");
}
resource = this.loadResource("sql-error-codes.xml");
if (resource != null && resource.exists()) {
bdr.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
logger.debug("Found custom sql-error-codes.xml file at the root of the classpath");
}
errorCodes = lbf.getBeansOfType(SQLErrorCodes.class, true, false);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("SQLErrorCodes loaded: " + errorCodes.keySet());
}
} catch (BeansException var5) {
logger.warn("Error loading SQL error codes from config file", var5);
errorCodes = Collections.emptyMap();
}
this.errorCodesMap = errorCodes;
}
sql-error-codes.xml文件中配置了各个数据库的主要的错误码
这里列举了MYSQL部分,当然还有其他部分,我们可以看到唯一性约束错误码是1062,就可以翻译成DuplicateKeyException异常了
<bean id="MySQL" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes">
<property name="databaseProductNames">
<list>
<value>MySQL</value>
<value>MariaDB</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="badSqlGrammarCodes">
<value>1054,1064,1146</value>
</property>
<property name="duplicateKeyCodes">
<value>1062</value>
</property>
<property name="dataIntegrityViolationCodes">
<value>630,839,840,893,1169,1215,1216,1217,1364,1451,1452,1557</value>
</property>
<property name="dataAccessResourceFailureCodes">
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property name="cannotAcquireLockCodes">
<value>1205,3572</value>
</property>
<property name="deadlockLoserCodes">
<value>1213</value>
</property>
</bean>
你已经看到,比如上面的错误码值列举了一部分,如果出现了一个不在其中的错误码肯定是匹配不到,Spring当然能想到这种情况了
/**
*@公-众-号:程序员阿牛
*在AbstractFallbackSQLExceptionTranslator中,看到如果查找失败会获取下一个后续转换器
*/
@Nullable
public DataAccessException translate(String task, @Nullable String sql, SQLException ex) {
Assert.notNull(ex, "Cannot translate a null SQLException");
DataAccessException dae = this.doTranslate(task, sql, ex);
if (dae != null) {
return dae;
} else {
SQLExceptionTranslator fallback = this.getFallbackTranslator();
return fallback != null ? fallback.translate(task, sql, ex) : null;
}
}
SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator的后置转换器是什么?
//构造方法中已经指定,SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator
public SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator() {
this.setFallbackTranslator(new SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator());
}
SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator的转换方法逻辑如下:
/**
*@公-众-号:程序员阿牛
*可以看出实际按照子类类型来判断,返回相应的错误类,如果匹配不到,则找到下一个处理器,这里的处理其我们可以根据构造方法青松找到*SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator
*/
@Nullable
protected DataAccessException doTranslate(String task, @Nullable String sql, SQLException ex) {
if (ex instanceof SQLTransientException) {
if (ex instanceof SQLTransientConnectionException) {
return new TransientDataAccessResourceException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLTransactionRollbackException) {
return new ConcurrencyFailureException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLTimeoutException) {
return new QueryTimeoutException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
} else if (ex instanceof SQLNonTransientException) {
if (ex instanceof SQLNonTransientConnectionException) {
return new DataAccessResourceFailureException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLDataException) {
return new DataIntegrityViolationException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException) {
return new DataIntegrityViolationException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLInvalidAuthorizationSpecException) {
return new PermissionDeniedDataAccessException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLSyntaxErrorException) {
return new BadSqlGrammarException(task, sql != null ? sql : "", ex);
}
if (ex instanceof SQLFeatureNotSupportedException) {
return new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
} else if (ex instanceof SQLRecoverableException) {
return new RecoverableDataAccessException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
return null;
}
SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator的转换方法:
/**
*@公-众-号:程序员阿牛
*可以看出根据SQLState的前两位来判断异常,根据匹配结果返回相应的异常信息
*/
@Nullable
protected DataAccessException doTranslate(String task, @Nullable String sql, SQLException ex) {
String sqlState = this.getSqlState(ex);
if (sqlState != null && sqlState.length() >= 2) {
String classCode = sqlState.substring(0, 2);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Extracted SQL state class '" + classCode + "' from value '" + sqlState + "'");
}
if (BAD_SQL_GRAMMAR_CODES.contains(classCode)) {
return new BadSqlGrammarException(task, sql != null ? sql : "", ex);
}
if (DATA_INTEGRITY_VIOLATION_CODES.contains(classCode)) {
return new DataIntegrityViolationException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (DATA_ACCESS_RESOURCE_FAILURE_CODES.contains(classCode)) {
return new DataAccessResourceFailureException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (TRANSIENT_DATA_ACCESS_RESOURCE_CODES.contains(classCode)) {
return new TransientDataAccessResourceException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
if (CONCURRENCY_FAILURE_CODES.contains(classCode)) {
return new ConcurrencyFailureException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex);
}
}
return ex.getClass().getName().contains("Timeout") ? new QueryTimeoutException(this.buildMessage(task, sql, ex), ex) : null;
}
为什么SQLState可以得出错误类型?
因为数据库是根据 X/Open 和 SQL Access Group SQL CAE 规范 (1992) 所进行的定义,SQLERROR 返回 SQLSTATE 值。SQLSTATE 值是包含五个字符的字符串 。五个字符包含数值或者大写字母, 代表各种错误或者警告条件的代码。SQLSTATE 有个层次化的模式:头两个字符标识条件的通常表示错误条件的类别, 后三个字符表示在该通用类中的子类。成功的状态是由 00000 标识的。SQLSTATE 代码在大多数地方都是定义在 SQL 标准里
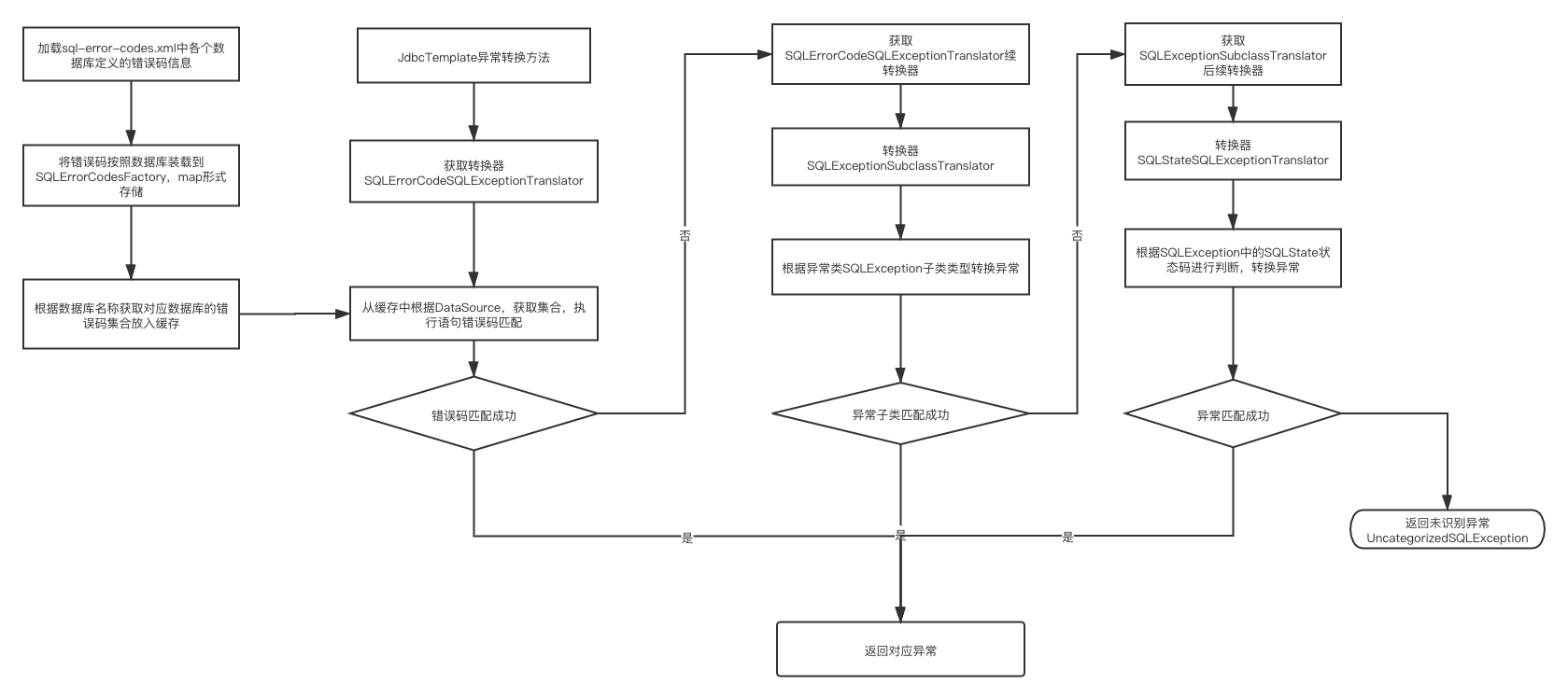
处理流程图
用到了哪些设计模式?
组合模式
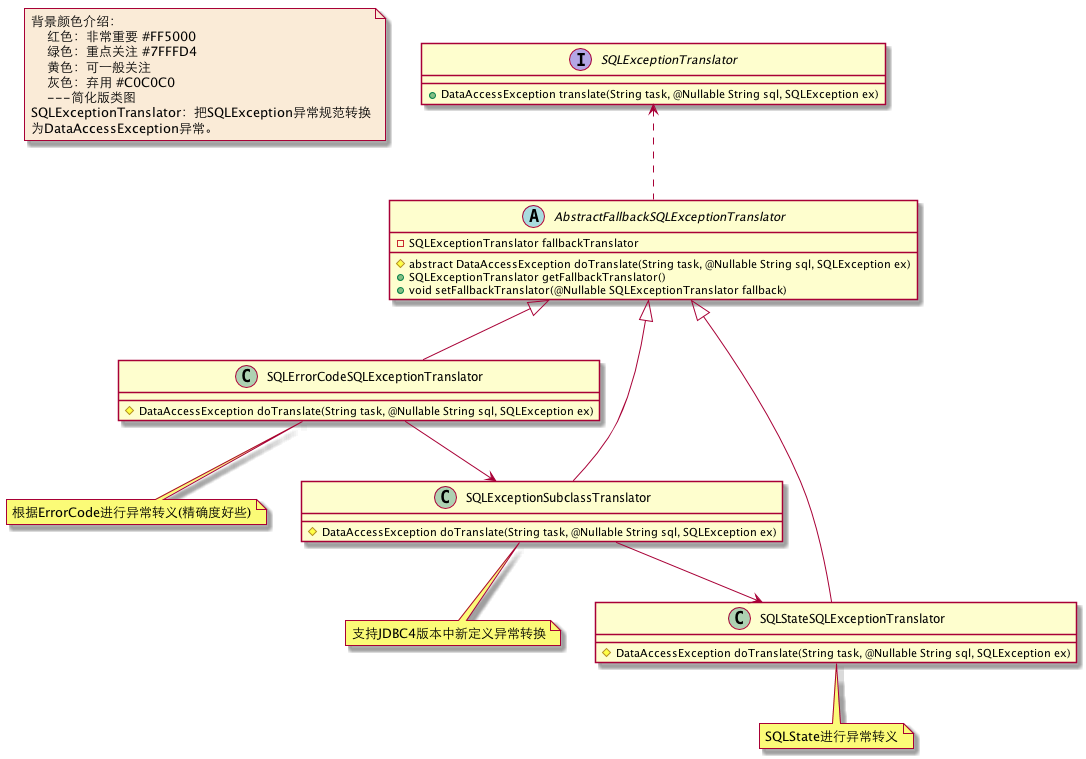
通过上图大家有没有发现三个实现类之间的关系—组合关系,组合关系在父类AbstractFallbackSQLExceptionTranslator中变成了递归调用,这里充满了智慧(Composite设计模式)。
单例模式
在SQLErrorCodesFactory(单例模式)
策略模式
根据数据库的不同,获取不同的errorcodes集合
---------------------END---------------------
关注:程序员阿牛,Spring系列更多文章,为你呈现
Spring系列之JDBC对不同数据库异常如何抽象的?的更多相关文章
- Spring系列之不同数据库异常如何抽象的?
前言 使用Spring-Jdbc的情况下,在有些场景中,我们需要根据数据库报的异常类型的不同,来编写我们的业务代码.比如说,我们有这样一段逻辑,如果我们新插入的记录,存在唯一约束冲突,就会返回给客户端 ...
- Spring系列 之数据源的配置 数据库 数据源 连接池的区别
Spring系列之数据源的配置 数据源,连接池,数据库三者的区别 连接池:这个应该都学习过,比如c3p0,druid等等,连接池的作用是为了提高程序的效率,因为频繁的去创建,关闭数据库连接,会对性能有 ...
- Spring MVC系列之JDBC Demo(SpringBoot)(七)
前言 前面我们了解了Spring MVC的基本使用,其实和.NET或.NET Core MVC无异,只是语法不同而已罢了,本节我们将和和数据库打交道,从最基础的JDBC讲解起,文中若有错误之处,还望指 ...
- Spring Boot系列(三) Spring Boot 之 JDBC
数据源 类型 javax.sql.DataSource javax.sql.XADataSource org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.embedded,Enbe ...
- Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介 -7个部分
Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介 Spring AOP 和 IOC 容器入门 在这由三部分组成的介绍 Spring 框架的系列文章的第一期中,将开始学习如何用 Spring 技术构建轻量级 ...
- Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介(转载)
Spring 系列: Spring 框架简介 http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/wa-spring1/ Spring AOP 和 IOC 容器入门 在 ...
- Spring系列
Spring系列之访问数据库 阅读目录 一.概述 二.JDBC API的最佳实践 三.Spring对ORM的集成 回到顶部 一.概述 Spring的数据访问层是以统一的数据访问异常层体系为核心,结 ...
- Spring系列(零) Spring Framework 文档中文翻译
Spring 框架文档(核心篇1和2) Version 5.1.3.RELEASE 最新的, 更新的笔记, 支持的版本和其他主题,独立的发布版本等, 是在Github Wiki 项目维护的. 总览 历 ...
- Spring系列之AOP的原理及手动实现
目录 Spring系列之IOC的原理及手动实现 Spring系列之DI的原理及手动实现 引入 到目前为止,我们已经完成了简易的IOC和DI的功能,虽然相比如Spring来说肯定是非常简陋的,但是毕竟我 ...
随机推荐
- WEB安全新玩法 [10] 防范竞争条件支付漏洞
服务器端业务逻辑,特别是涉及数据库读写时,存在着关键步骤的时序问题,如果设计或代码编写不当就可能存在竞争条件漏洞.攻击者可以利用多线程并发技术,在数据库的余额字段更新之前,同时发起多次兑换积分或购买商 ...
- CentOS7下OpenLDAP部署
OpenLDAP作为开源的LDAP服务,可用于搭建统一认证平台,在很多企业内部应用比较广泛,本文将介绍在CentOS7下OpenLDAP的部署. 环境: CentOS 7.4 OpenLDAP 2.4 ...
- 🔥 LeetCode 热题 HOT 100(21-30)
46. 全排列 思路:典型回溯法 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { Linke ...
- 浅谈MySQL与mongodb的区别
讨论MySQL与mongodb使用上的区别以及可能适用的应用场景,不深入到数据库的实现细节方面.鉴于个人水平有限,文章可能存在错误之处,希望各位指正. 代码编写 mongodb支持reactor,可以 ...
- Java8 Lambda表达式(二)
目录 一.Java8 内置的四大核心函数式接口 1. 消费型接口 Consumer 2. 供给型接口 Supplier 3. 函数型接口 Function 4.断言型接口 Predicate 二.方法 ...
- JUC学习笔记(四)
JUC学习笔记(一)https://www.cnblogs.com/lm66/p/15118407.html JUC学习笔记(二)https://www.cnblogs.com/lm66/p/1511 ...
- vulnhub-DC:8靶机渗透记录
准备工作 在vulnhub官网下载DC:8靶机DC: 8 ~ VulnHub 导入到vmware,设置成NAT模式 打开kali准备进行渗透(ip:192.168.200.6) 信息收集 利用nmap ...
- Haskell Interactive Development in Emacs
Installation Following haskell-mode. Use MELPA repository: add the following into ~/.emacs (require ...
- MySQL-19-分布式架构MyCat
MyCAT基础架构图(实验环境) MyCAT实验环境准备 1 环境准备 两台虚拟机: db01(10.0.0.51) db02(10.0.0.52) 每台创建四个mysql实例:3307 3308 3 ...
- javaWeb之Maven
为什么要学这个技术? 在JavaWeb开发中,需要使用大量的jar包 如何能够让一个工具自动帮我们导入和配置这个jar包 一.Maven项目架构管理工具 核心思想:约定大于配置 有约束,不要去违反 M ...
