09.C语言:预处理(宏定义)、字节序、地址对齐
一、预处理

预处理
gcc -E Hello.c -o hello.i
编译
gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s
汇编
gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o
链接
gcc hello.o -o hello
Makefile
# "hello.c"
# "<built-in>"
# "<command-line>"
# "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h"
# "<command-line>"
# "hello.c" # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h" # "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs-32.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stddef.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stddef.h"
typedef unsigned int size_t;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" typedef unsigned char __u_char;
typedef unsigned short int __u_short;
typedef unsigned int __u_int;
typedef unsigned long int __u_long; typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef signed short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef signed int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t; __extension__ typedef signed long long int __int64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long int __uint64_t; __extension__ typedef long long int __quad_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long int __u_quad_t;
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/typesizes.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" __extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __dev_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __uid_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __gid_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __ino_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __ino64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __mode_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __nlink_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __off_t;
__extension__ typedef __quad_t __off64_t;
__extension__ typedef int __pid_t;
__extension__ typedef struct { int __val[]; } __fsid_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __clock_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __rlim64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __id_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __time_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __useconds_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __suseconds_t; __extension__ typedef int __daddr_t;
__extension__ typedef int __key_t; __extension__ typedef int __clockid_t; __extension__ typedef void * __timer_t; __extension__ typedef long int __blksize_t; __extension__ typedef long int __blkcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __quad_t __blkcnt64_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __fsblkcnt64_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __fsfilcnt64_t; __extension__ typedef int __fsword_t; __extension__ typedef int __ssize_t; __extension__ typedef long int __syscall_slong_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned long int __syscall_ulong_t; typedef __off64_t __loff_t;
typedef __quad_t *__qaddr_t;
typedef char *__caddr_t; __extension__ typedef int __intptr_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned int __socklen_t;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
struct _IO_FILE; typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE; # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stddef.h"
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h" # "/usr/include/wchar.h"
# "/usr/include/wchar.h"
typedef struct
{
int __count;
union
{ unsigned int __wch; char __wchb[];
} __value;
} __mbstate_t;
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
typedef struct
{
__off_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos_t;
typedef struct
{
__off64_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos64_t;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stdarg.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stdarg.h"
typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
struct _IO_jump_t; struct _IO_FILE;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
typedef void _IO_lock_t; struct _IO_marker {
struct _IO_marker *_next;
struct _IO_FILE *_sbuf; int _pos;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
}; enum __codecvt_result
{
__codecvt_ok,
__codecvt_partial,
__codecvt_error,
__codecvt_noconv
};
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; char* _IO_read_ptr;
char* _IO_read_end;
char* _IO_read_base;
char* _IO_write_base;
char* _IO_write_ptr;
char* _IO_write_end;
char* _IO_buf_base;
char* _IO_buf_end; char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end; struct _IO_marker *_markers; struct _IO_FILE *_chain; int _fileno; int _flags2; __off_t _old_offset; unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[]; _IO_lock_t *_lock;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
__off64_t _offset;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
void *__pad1;
void *__pad2;
void *__pad3;
void *__pad4;
size_t __pad5; int _mode; char _unused2[ * sizeof (int) - * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)]; }; typedef struct _IO_FILE _IO_FILE; struct _IO_FILE_plus; extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdin_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdout_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stderr_;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
typedef __ssize_t __io_read_fn (void *__cookie, char *__buf, size_t __nbytes); typedef __ssize_t __io_write_fn (void *__cookie, const char *__buf,
size_t __n); typedef int __io_seek_fn (void *__cookie, __off64_t *__pos, int __w); typedef int __io_close_fn (void *__cookie);
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
extern int __underflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __uflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __overflow (_IO_FILE *, int);
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
extern int _IO_getc (_IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_putc (int __c, _IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_feof (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_ferror (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int _IO_peekc_locked (_IO_FILE *__fp); extern void _IO_flockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void _IO_funlockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_ftrylockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
extern int _IO_vfscanf (_IO_FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict,
__gnuc_va_list, int *__restrict);
extern int _IO_vfprintf (_IO_FILE *__restrict, const char *__restrict,
__gnuc_va_list);
extern __ssize_t _IO_padn (_IO_FILE *, int, __ssize_t);
extern size_t _IO_sgetn (_IO_FILE *, void *, size_t); extern __off64_t _IO_seekoff (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int, int);
extern __off64_t _IO_seekpos (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int); extern void _IO_free_backup_area (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
typedef __off_t off_t;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
typedef __ssize_t ssize_t; typedef _G_fpos_t fpos_t; # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/stdio_lim.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr; extern int remove (const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int rename (const char *__old, const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int renameat (int __oldfd, const char *__old, int __newfd,
const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern char *tempnam (const char *__dir, const char *__pfx)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ; extern int fclose (FILE *__stream); extern int fflush (FILE *__stream); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern FILE *fopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes) ; extern FILE *freopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, const char *__modes)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...); extern int printf (const char *__restrict __format, ...); extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)); extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg); extern int vprintf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg); extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)); extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, ...)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , ))); extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , ))); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int vdprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
extern int dprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , ))); extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) ; extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) ; extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf") ;
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf")
;
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ; extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ; extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , )));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf") __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf") __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , )));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream); extern int getchar (void); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar_unlocked (void);
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream); extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream); extern int putchar (int __c); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream); extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c); extern int getw (FILE *__stream); extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream); extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern char *gets (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__deprecated__)); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ; extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ; extern int fputs (const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream); extern int puts (const char *__s); extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream); extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ; extern size_t fwrite (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream); extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence); extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ; extern void rewind (FILE *__stream); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence); extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos); extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, const fpos_t *__pos);
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void perror (const char *__s); # "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h"
extern int sys_nerr;
extern const char *const sys_errlist[];
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern FILE *popen (const char *__command, const char *__modes) ; extern int pclose (FILE *__stream); extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "hello.c" int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("Hello , world !\n"); return ;
}
hello.i
.file "hello.c"
.section .rodata
.LC0:
.string "Hello , world !"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB0:
.cfi_startproc
pushl %ebp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset
.cfi_offset , -
movl %esp, %ebp
.cfi_def_cfa_register
andl $-, %esp
subl $, %esp
movl $.LC0, (%esp)
call puts
movl $, %eax
leave
.cfi_restore
.cfi_def_cfa ,
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE0:
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 4.8.4-2ubuntu1~14.04.3) 4.8.4"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
hello.s
gcc编译过程:http://lib.csdn.net/article/c/66184
1.去掉程序中的注释;
2.文件包含:当对C源程序进行预处理时,文件包含指的是将.c文件包含的头文件内容复制到当前.c文件中。
1》、第一种:#include <stdio.h> 直接去系统头文件目录下寻找所包含的头文件。
2》、第二种:#include "head.h" 先在当前目录下寻找所包含的头文件,如果找不到,则再去系统头文件目录下寻找所包含的头文件。
3.宏替换
当对C源程序进行预处理时,如果程序中有事先定义好的宏,则会将所有的宏后面的字符串替换,例如:
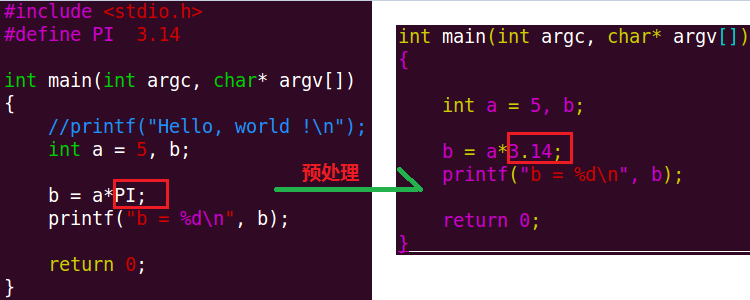
1》预定义宏:
__FILE__ //正在编译的文件名(字符串常量)
__LINE__ //文件当前的行号(整型常量)
__FUNCTION__ //当前所在的函数名(字符串常量)
__DATE__ //预编译文件的日期(字符串常量)
__TIME__ //预编译文件的时间(字符串常量)
__STDC__ //判断编译器是否遵循ANSI C,是则为1(整型常量)
Predefine Macros

2》不带参数的宏:#define 宏名 字符串
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: noParamMacros.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 01:00:07 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #define PI 3.14*2
#define M 60
#define S "HelloWorld" int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%f\n", PI);
printf("%d\n", M);
printf("%s\n", S); return ;
}
noParamMacros.c
3》带参数的宏:可以像函数一样被调用。
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: paramMacros.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 01:40:15 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #define FUN(a, b) a+b*a #define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1 int fun(int a, int b){
return a+b*a;
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int a = , b =;
int c; c = fun(a, b); //函数调用
printf("c = %d\n", c); c = FUN(a, b); //宏调用 float f; #if (DataType == FALSE)
f = fun(3.1, 4.5); //Data type is error
printf("f = %f\n", f);
#else
f = FUN(3.1, 4.5); //Data type is correct
printf("f = %f\n", f);
#endif return ;
}
paramMacros.c
在上述例子中,由于传参时,可能会传一个表达式,这是调用带参宏就会导致结果不正确,所以一般在定义带参宏时,都会如下去定义: #define FUN(a, b) (a)+(b)*(a)
4.条件编译:在编译程序之前,按照某个条件来选择需要编译哪一段代码。
1》第一种方式:
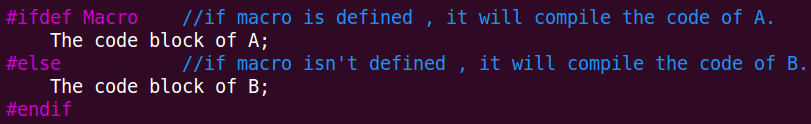
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: ifdef.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 02:51:43 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #define DEBUG //有如下两个函数,如果要测试这两个函数是否正确,则必须写主函数测试
void fun1(void){
printf("hello world\n");
} void fun2(void){
printf("This is a good idea !\n");
} //下面为测试代码
#ifdef DEBUG
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
fun1();
fun2(); return ;
}
#endif
ifdef.c
2》第二种方式:
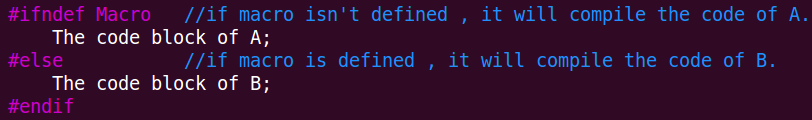
#ifdef __HEAD_H_
#define __HEAD_H_ #include <stdio.h> int x = ; #endif //该条件编译的作用是,防止头文件被多次(重复)包含。
ifndef
3》第三种方式:
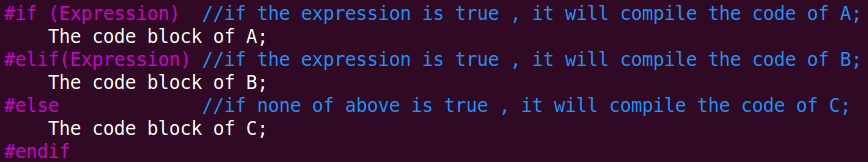
//用于注释一段代码
#if (0)
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#endif
if.c
二、字节序
1.计算机在存储多字节数据时,数据内部各个字节的存储顺序称为字节序;
4字节:unsigned int word = 0x12345678;
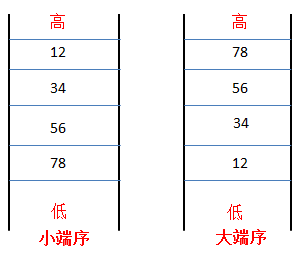
2.端序
1》小端序(little-endian):最高有效位所在的字节放在最高字节位置,其他字节依次放在低字节位置,则该字节序称为高位优先。
2》大端序(big-endian):最低有效位所在的字节放在最高字节位置,其他字节依次放在低字节位置,则该字节序称为低位优先。
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: endian.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 04:34:11 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h> #define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1 bool is_little_endian(void){
bool ret;
unsigned int word = 0x12345678; unsigned char byte0 = *((unsigned char *)&word + );
unsigned char byte1 = *((unsigned char *)&word + );
unsigned char byte2 = *((unsigned char *)&word + );
unsigned char byte3 = *((unsigned char *)&word + ); printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte0, byte0);
printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte1, byte1);
printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte2, byte2);
printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte3, byte3); if(byte0 == 0x78){
printf("the machine is little endian !\n");
ret = TRUE;
}else if(byte0 == 0x12){
printf("the machine is big endian !\n");
ret = FALSE;
} return ret;
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(is_little_endian() == TRUE){
printf("Little endian is true !\n");
} return ;
}
执行结果: 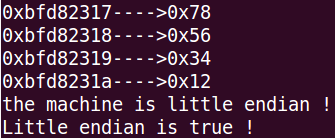
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: endian1.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 05:02:58 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> union A{
unsigned int word;
unsigned char byte;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
union A un; un.word = 0x12345678;
if(un.byte == 0x78){
printf("the machine is little endian !\n");
}else if(un.byte == 0x12){
printf("the machine is big endian !\n");
} return ;
}
使用结构体判断大小端序
三、地址对齐
为了提高CPU从内存中存取数据的效率,在给数据分配内存空间时,会有意的将数据放在某些地址位置,这种分配空间的方式称为地址对齐。
1》自然对齐:在给数据分配空间是时,如果数据的起始地址能够被数据的长度整除,则该分配空间的方式为自然对齐。
2》数据的M值:
对于每一个数据都有M值,M值如下:
1)对于基本数据类型:
如果该数据的长度小于机器字字长,则它的M值为自身的长度;
如果该数据的长度大于或者等于机器字长,则它的M值为机器字长;
2)对于数组:
M值为元素的M值;
3)对于结构体,共用体:
M值为成员中最大的M值;
3》适当对齐:在给数据分配空间时,如果数据的起始地址能够被数据的M值整除,则该分配空间的方式为适当对齐。
4》结构体的存储:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: align.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 05:15:23 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> struct param{
char a;
short b;
int c;
}; struct param1{
char a;
int b;
short c;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct param p1;
printf("sizeof(struct param) = %d\tsizeof p1 = %d\n", sizeof(struct param), sizeof p1); struct param1 p2;
printf("sizeof(struct param1) = %d\tsizeof p2 = %d\n", sizeof(struct param1), sizeof p2); return ;
}
structAlign.c
执行结果:
09.C语言:预处理(宏定义)、字节序、地址对齐的更多相关文章
- C语言中宏定义(#define)时do{}while(0)的价值(转)
C语言中宏定义(#define)时do{}while(0)的价值 最近在新公司的代码中发现到处用到do{...}while(0),google了一下,发现Stack Overflow上早有很多讨论,总 ...
- c 语言中宏定义和定义全局变量的区别
宏定义和定义全局变量的区别: 1 作用时间不同. 宏定义在编译期间即会使用并替换,而全局变量要到运行时才可以. 2 本质类型不同. 宏定义的只是一段字符,在编译的时候被替换到引用的位置.在运行中是没有 ...
- C基础:关于预处理宏定义命令
为了程序的通用性,可以使用#define预处理宏定义命令,它的具体作用,就是方便程序段的定义和修改. 1.关于预定义替代 #define Conn(x,y) x##y#define ToChar(x) ...
- 【编程基础】C语言常见宏定义
我们在使用C语言编写程序的时候,常常会使用到宏定义以及宏编译指令,有的可能比较常用,有的可能并不是很常用,是不是所有的C语言宏定义以及宏指令你都清楚呢? 指令 用途详细介绍 # 空指令,无任何效果 # ...
- C语言在宏定义中使用语句表达式和预处理器运算符
语句表达式的亮点在于定义复杂功能的宏.使用语句表达式来定义宏,不仅可以实现复杂的功能,而且还能避免宏定义带来的歧义和漏洞.下面以一个简单的最小值的宏为例子一步步说明. 1.灰常简单的么,使用条件运算符 ...
- C语言中宏定义与C++中的内联函数
一,宏定义:在预处理的时候把宏定义的内容替换到代码中,正常编译. 1,无参数宏定义和有参数宏定义 (1)宏定义不能加分号,比如:#define PI 3.24;错的,#define PI 3.24 ...
- 零基础逆向工程16_C语言10_宏定义_头文件_内存分配_文件读写
#define 无参数的宏定义的一般形式为:#define 标识符 字符序列 如:#define TRUE 1 注意事项: 1.之作字符序列的替换工作,不作任何语法的检查 2.如果宏定义不当,错误要到 ...
- C语言中宏定义(#define)时do{}while(0)的价值
最近在新公司的代码中发现到处用到do{...}while(0),google了一下,发现Stack Overflow上早有很多讨论,总结了一下讨论,加上自己的理解,do{...}while(0)的价值 ...
- c语言中宏定义和常量定义的区别
他们有共同的好处就是"一改全改,避免输入错误"哪两者有不同之处吗?有的. 主要区别就在于,宏定义是在编译之前进行的,而const是在编译阶段处理的 宏定义不占用内存单元而const ...
- C语言中宏定义(#define)时do{}while(0)
参考链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/fengc5/p/5083134.html 1.用于宏定义, 在该函数可以调用其它的宏,做其它内容的处理
随机推荐
- POJ2208 Pyramids 四面体体积
POJ2208给定四面体六条棱(有序)的长度 求体积 显然用高中立体几何的方法就可以解决. 给出代码 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> # ...
- 【高德地图API】地理编码与逆地理编码
一.地理编码 该功能实现地理编码服务,即地址匹配,从已知的地址描述到对应的经纬度坐标的转换,即根据地址信息,查询该地址所对应的点坐标等,地址(address) 为必选项,城市(city)为可选项. & ...
- Thinkphp模板标签if和eq的区别和比较
在TP模板语言中.if和eq都可以用于变量的比较.总结以下几点: 1.两个变量的比较: <if condition=”$item.group_id eq $one.group_id”> & ...
- bzoj 1029: [JSOI2007]建筑抢修【贪心+堆】
第一想法是按照结束时间贪心,但是这样有反例 所以先按照t贪心,能选则选,把选的楼的持续时间放进大根堆里,当当前的楼不能选的时候如果当前的持续时间比大根堆里最大的要小,就用这个替换最大,这样总数不变但是 ...
- bzoj 1574: [Usaco2009 Jan]地震损坏Damage【dfs】
和March的那道不一样,只是非常单纯的带着贪心的dfs 首先一个点被隔断,与它相邻的所有点也会被隔断,打上删除标记,从1dfs即可 #include<iostream> #include ...
- 2017杭电多校第六场03Inversion
传送门 Inversion Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) To ...
- ActiveMQ应用
一. 概述与介绍 ActiveMQ 是Apache出品,最流行的.功能强大的即时通讯和集成模式的开源服务器.ActiveMQ 是一个完全支持JMS1.1和J2EE 1.4规范的 JMS Provide ...
- 每天学点Linux命令: 管道| 与 xargs的区别
先看一个例子: find ./ -print | xargs grep a 输出: grep: ./: 是一个目录 ./less:abc ./afile:abcde ./afile:AaAbBcB . ...
- 【日常总结】scrollTop、scrollHeight与clientHeight的重要关系
前言 在做一个需求的时候涉及懒加载,百度了一下,发现scrollTop.scrollHeight与clientHeight这三个元素起到了重要作用,以前做过类似demo但是时间过太久忘记了,现在已经完 ...
- [转]iOS WebKit browsers and auto-zooming form controls
问题描述:https://github.com/jquery/jquery-mobile/issues/2581 本文转自:http://www.456bereastreet.com/archive/ ...
