茅坑杀手与Alias Method离散采样
说起Alias,你可能第一个联想到的是Linux中的Alias命令,就像中世纪那些躲在茅坑下面(是真的,起码日本有粪坑忍者,没有马桶的年代就是社会的噩梦)进行刺杀的杀手一样,让人防不胜防,对于那些被这个命令坑过的人来说,电脑必须时刻出现在视野内,因为你不知道你身边的杀手朋友什么时候会模仿中世纪茅坑杀手在你的终端执行这样一条命令。
alias cd=rm -rf

(如果不懂这个梗,给一个小提示,alias命令是给某个命令重命名,这里把cd命令改成了rm -rf命令,你每次进入目录其实是删除了目录)
说回正题,前段时间看同事写的代码有一个应用到权重的地方,对于系统中用到的两个数据源,我们希望有一定比例走新数据源,一定比例走老数据源(感觉用的花里胡哨,直接配置中心搞一个开关不就好了),看到他们写的代码中使用了Alias Method来实现权重,所以就专门学习了一下(虽然感觉在新老数据源这个场景中使用有点鸡肋,但是掌握一门权重算法的实现还是很有帮助的)。
先贴出一篇国外写的很好的博客:
https://www.keithschwarz.com/darts-dice-coins/
飞镖,骰子,硬币:离散采样方法
一. 原理
权重算法的本质是指定时间发生的几率,比如用户的每一次请求我有30%的几率打到服务器A,有20%的几率到服务器B,还有50%的几率到服务器C。那么给出未来十次的用户请求序列,要求给出它们会分别打到哪个服务器。
最简单的实现当然是产生一个位于0.0~1.0之间的随机数。
- 当随机数位于
0~0.3时,请求服务器A - 当随机数位于
0.3~0.5时,请求服务器B - 当随机数位于
0.5~1时,请求服务器C
这种方式实现简单,生成一个随机数,然后在对应时间上if-else判断即可,但是存在精度问题。
另一种实现方式是离散算法,通过概率分布构造几个点,[30, 50, 100],代表三个区间,再生成1~100的整数,看它位于哪个区间,比如45位于[30~50]区间,就说明本次请求打到服务器B。
现在进入正题Alias Method算法,Alias Method的最终结果是要构造拼装出一个每一列合都为1的矩形,若每一列最后都要为1,那么要将所有元素都乘以概率类型的数量(此处为3)。
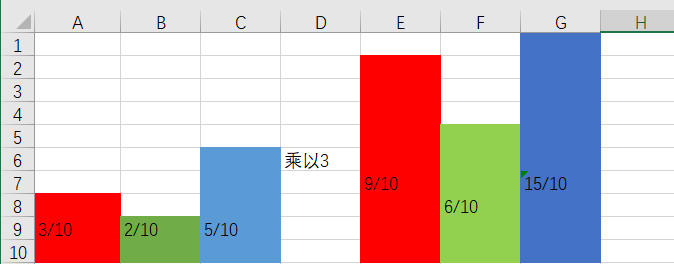
此时右边乘以3之后的模型概率大于一或者小于一,需要用大于一去补足小于一的,而且必须满足每列必须至多只有两种组合。
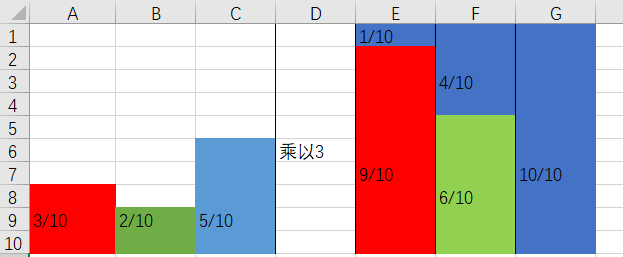
根据填充后的上图我们可以得到两个数组,分别是位于下方的[9/10, 6/10, 10/10]组成的Prod数组[0.9, 0.6, 1]以及上方用来填充的颜色的序号[3, 3, NULL],第一个3代表红色列被第三列蓝色填充,第二个3代表绿色列被第三列蓝色填充,第三列概率大于1,不需要填充,为NULL。
| T | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | |
| Prob | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1 |
| Alias | 3 | 3 | NULL |
得到这两个数组之后,随机取其中的一列(代表事件),比如是第二列,让Prob[2]的值与一个随机小数f比较,如果f小于Prob[2],那么结果就是2,否则就是Alias[2],即3,若为第三列,Prob[3]必定大于小数f,结果就是3。
可以来简单验证一下,比如随机到第三列的概率是1/3,第三列全部为红色,则第三列事件3发生概率就是1/3乘1,蓝色再其他列上部分还有覆盖,分别是1/3乘2/5和1/3乘1/10,最终的结果还是为0.5,符合原来的pdf概率。这种算法初始化较复杂,但生成随机结果的时间复杂度为O(1),是一种性能非常好的算法。
二. 代码实现
下面是一个较为完整的代码实现,该实例在使用中只需要在AliasMethod中初始化好我们之前所说的Alias和Prob数组即可。
import java.util.*;
/**
* @description 权重算法
*/
public final class AliasMethod {
/**
* The random number generator used to sample from the distribution.
*/
private final Random random;
/**
* The probability and alias tables.
*/
private final int[] alias;
private final double[] probability;
/**
* Constructs a new AliasMethod to sample from a discrete distribution and
* hand back outcomes based on the probability distribution.
* <p>
* Given as input a list of probabilities corresponding to outcomes 0, 1,
* ..., n - 1, this constructor creates the probability and alias tables
* needed to efficiently sample from this distribution.
*
* @param probabilities The list of probabilities.
*/
public AliasMethod(List<Double> probabilities) {
this(probabilities, new Random());
}
/**
* Constructs a new AliasMethod to sample from a discrete distribution and
* hand back outcomes based on the probability distribution.
* <p>
* Given as input a list of probabilities corresponding to outcomes 0, 1,
* ..., n - 1, along with the random number generator that should be used
* as the underlying generator, this constructor creates the probability
* and alias tables needed to efficiently sample from this distribution.
*
* @param probabilities The list of probabilities.
* @param random The random number generator
*/
public AliasMethod(List<Double> probabilities, Random random) {
/* Begin by doing basic structural checks on the inputs. */
if (probabilities == null || random == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (probabilities.size() == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Probability vector must be nonempty.");
}
/* Allocate space for the probability and alias tables. */
probability = new double[probabilities.size()];
alias = new int[probabilities.size()];
/* Store the underlying generator. */
this.random = random;
/* Compute the average probability and cache it for later use. */
final double average = 1.0 / probabilities.size();
/* Make a copy of the probabilities list, since we will be making
* changes to it.
*/
probabilities = new ArrayList<>(probabilities);
/* Create two stacks to act as worklists as we populate the tables. */
Deque<Integer> small = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<Integer> large = new ArrayDeque<>();
/* Populate the stacks with the input probabilities. */
for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.size(); ++i) {
/* If the probability is below the average probability, then we add
* it to the small list; otherwise we add it to the large list.
*/
if (probabilities.get(i) >= average) {
large.add(i);
} else {
small.add(i);
}
}
/* As a note: in the mathematical specification of the algorithm, we
* will always exhaust the small list before the big list. However,
* due to floating point inaccuracies, this is not necessarily true.
* Consequently, this inner loop (which tries to pair small and large
* elements) will have to check that both lists aren't empty.
*/
while (!small.isEmpty() && !large.isEmpty()) {
/* Get the index of the small and the large probabilities. */
int less = small.removeLast();
int more = large.removeLast();
/* These probabilities have not yet been scaled up to be such that
* 1/n is given weight 1.0. We do this here instead.
*/
probability[less] = probabilities.get(less) * probabilities.size();
alias[less] = more;
/* Decrease the probability of the larger one by the appropriate
* amount.
*/
probabilities.set(more,
(probabilities.get(more) + probabilities.get(less)) - average);
/* If the new probability is less than the average, add it into the
* small list; otherwise add it to the large list.
*/
if (probabilities.get(more) >= 1.0 / probabilities.size()) {
large.add(more);
} else {
small.add(more);
}
}
/* At this point, everything is in one list, which means that the
* remaining probabilities should all be 1/n. Based on this, set them
* appropriately. Due to numerical issues, we can't be sure which
* stack will hold the entries, so we empty both.
*/
while (!small.isEmpty()) {
probability[small.removeLast()] = 1.0;
}
while (!large.isEmpty()) {
probability[large.removeLast()] = 1.0;
}
}
/**
* Samples a value from the underlying distribution.
*
* @return A random value sampled from the underlying distribution.
*/
public int next() {
/* Generate a fair die roll to determine which column to inspect. */
int column = random.nextInt(probability.length);
/* Generate a biased coin toss to determine which option to pick. */
boolean coinToss = random.nextDouble() < probability[column];
/* Based on the outcome, return either the column or its alias. */
return coinToss ? column : alias[column];
}
}
另外,stackoverflow上有一个回答,关于程序中掷骰子这个事件的模型改用什么数据结构,无疑可以使用Alias Method,感兴趣的老铁可以自己画画它的概率模型。
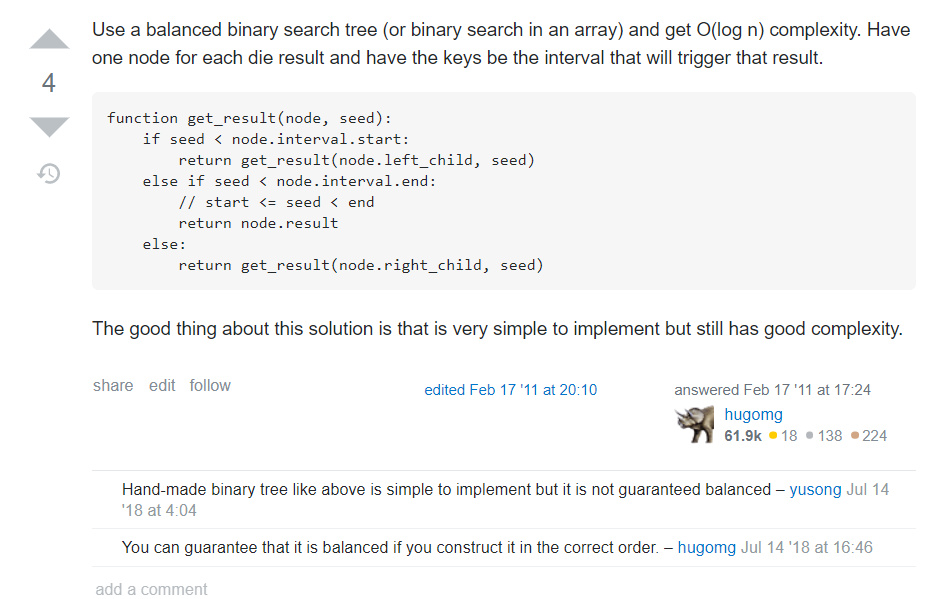
另外回答中还有各种千奇百怪的,比如说下面这个,使用平衡二叉搜索树,骰子的每一个面设置一个节点。
三. 最后
没有最后,点个关注点个在看,你懂我意思吗? 我向你敬礼!salute。(该不会就只看懂个茅坑杀手吧)
茅坑杀手与Alias Method离散采样的更多相关文章
- Alias Method解决随机类型概率问题
举个例子,游戏中玩家推倒了一个boss,会按如下概率掉落物品:10%掉武器 20%掉饰品 30%掉戒指 40%掉披风.现在要给出下一个掉落的物品类型,或者说一个掉落的随机序列,要求符合上述概率. 一般 ...
- Alias Method for Sampling 采样方法
[Alias Method for Sampling]原理 对于处理离散分布的随机变量的取样问题,Alias Method for Sampling 是一种很高效的方式. 在初始好之后,每次取样的复杂 ...
- 算法名称 Alias Method
public class AliasMethod { /* The probability and alias tables. */ private int[] _alias; private dou ...
- Alias sample(别名采样)
应用场景:加权采样,即按照随机事件出现的概率抽样 具体算法: 举例如上,随机事件出现的概率依次是1/2,1/3,1/12,1/12;记随机事件的个数为N,则所有事件概率乘以N后概率为2,4/3,1/3 ...
- 【MATLAB】对离散采样信号添加高斯白噪声(已知Eb/N0)
(1)首先计算已知信号序列(采样之后得到的信号)的平均功率.该序列在第n个点处的功率为: 如果已知的信号序列中的总共的点数为N个,则该序列的平均功率为: 在MATLAB中求平均功率的方法是: Pav= ...
- alias sample method——运行时间复杂度为O(1)的抽样算法
根据离散离散概率分布抽样是一个常见的问题.这篇文章将介绍运行时间复杂度为O(1)的 alias method 抽样算法思想. 下面举例说明: 比如 a,b,c,d 的概率分别为 0.1,0.2,0.3 ...
- JAVA基于权重的抽奖
https://blog.csdn.net/huyuyang6688/article/details/50480687 如有4个元素A.B.C.D,权重分别为1.2.3.4,随机结果中A:B:C:D的 ...
- Node2vec 代码分析
Node2vec 代码从Github上clone到本地,主要是main.py和node2vec.py两个文件. 下面把我的读代码注释放到上面来, import numpy as np import n ...
- matlab的fda工具使用方法
MATLAB中用FDATool设计滤波器及使用 该文章讲述了MATLAB中用FDATool设计滤波器及使用. 1. 在Matlab中键入fdatool运行Filter Design and Analy ...
随机推荐
- [SWPU2019]Web1 空格过滤用/**/ 注释过滤闭合单引号 imformation_schema.columns/tables过滤 用5.7新特性 或无名注入(此处database()不能用)
0x00 知识点 二次注入流程分析 二次注入漏洞在CTF中常见于留言板和注册登录功能,简单来说可以分为两个步骤: 插入恶意数据(发布帖子,注册账号),用mysql_escape_string()函数对 ...
- [BJDCTF 2nd]xss之光
[BJDCTF 2nd]xss之光 进入网址之后发现存在.git泄露,将源码下载下来,只有index.php文件 <?php $a = $_GET['yds_is_so_beautiful']; ...
- 从零开始的sql注入学习(挖坑不填)
首先,本人是小白,这篇文章也只是总结了一下大佬们的sql注入方法,要是有错,请各位大佬指出,以便学习. 虽然我是菜鸡,但是太过基础的sql注入问题也就不再重复的解释了.直接从常用的说起. 实战中常用的 ...
- Scrum 冲刺第四天
一.每日站立式会议 1.会议内容 1)进行每日工作汇报 张博愉: 昨天已完成的工作:搜寻测试相关的资料 今日工作计划:编写测试计划 工作中遇到的困难:对测试接触得较少,有点头疼 张润柏: 昨天已完成的 ...
- Unity发布WebGL改变鼠标样式
记录:前段时间遇到一个需求,就是打包出来要在某种情况下鼠标的样子要改变成想要的样式. 详细代码如下 public Texture2D[] hand;//小指图标 /// <summary> ...
- 八、git学习之——忽略特殊文件、配置别名、搭建git服务器
原文来自 一.忽略特殊文件 有些时候,你必须把某些文件放到Git工作目录中,但又不能提交它们,比如保存了数据库密码的配置文件啦,等等,每次git status都会显示Untracked files . ...
- 搭建本地yum镜像源
Blog:博客园 个人 目录 概述 语法说明 参数说明 部署 配置阿里云源 同步源 建仓 Nginx配置 配置定时计划 yum配置 概述 由于内网有大量机器不能访问公网,安装软件比较费劲,那么,如何让 ...
- 带宽、延时、吞吐率、PPS 这些都是啥?
Linux 网络协议栈是根据 TCP/IP 模型来实现的,TCP/IP 模型由应用层.传输层.网络层和网络接口层,共四层组成,每一层都有各自的职责. 应用程序要发送数据包时,通常是通过 socket ...
- 简洁404页面源码 | 自适应404页面HTML好看的404源码下载
description:源码 源码下载 源码网 源码自适应 源码图片 页面源码 页面源码下载 错误页源码 php源码 html源码 动漫 源码 演示图如下: HTML代码片段: 1 <!DOCT ...
- Docker修改默认的网段
一,问题 docker安装后默认的网段是172.17网段的,和真实环境网段冲突导致本机电脑无法连接docker机器. 二,解决办法 修改docker默认网段 1,先把docker停止 systemct ...
