CppUnit使用和源码解析
前言
CppUnit是一个开源的单元测试框架,支持Linux和Windows操作系统,在linux上可以直接进行源码编译,得到动态库和静态库,直接链接就可以正常使用,在Windows上可以使用VC直接进行编译,非常便于调试。CppUnit的源码框架被运用到了Java和Python等语言中,使用非常广泛,熟悉了一种语言下的CppUnit使用方法,其他语言测试框架也不在话下,本文以cppunit-1.12.1为例进行演示和说明。
一个例子
Linux下CppUnit源码编译和安装
- 解压源码文件到cppunit-1.12.1目录
- cd cppunit-1.12.1
- ./configure --prefix=安装路径(必须是绝对路径)
- make
- make install
编辑测试代码
一共三个文件main.cpp、simpleTest.h、simpleTest.c,目录下文件的组织结构如下所示:

三个文件的源码如下:
//main.cpp文件 #include "cppunit/TestResultCollector.h"
#include "cppunit/TextOutputter.h"
#include "cppunit/XmlOutputter.h"
#include "cppunit/CompilerOutputter.h"
#include "cppunit/TestResult.h"
#include "cppunit/TestRunner.h"
#include "cppunit/extensions/TestFactoryRegistry.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ostream> int main()
{
CppUnit::TestResult r;
CppUnit::TestResultCollector rc;
r.addListener(&rc); // 准备好结果收集器 CppUnit::TestRunner runner; // 定义执行实体
runner.addTest(CppUnit::TestFactoryRegistry::getRegistry("alltest").makeTest());
runner.run(r); // 运行测试 //CppUnit::TextOutputter o(&rc, std::cout);
//o.write(); // 将结果输出 //std::ofstream file;
//file.open("./UnitTest.xml");
//CppUnit::XmlOutputter xo(&rc, file);
//xo.write(); CppUnit::CompilerOutputter co(&rc, std::cout);
co.write(); return rc.wasSuccessful() ? 0 : -1;
}
//SimpleTest .h文件 #include "cppunit/extensions/HelperMacros.h" class SimpleTest : public CppUnit::TestFixture
{
CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE(SimpleTest);
CPPUNIT_TEST(test1);
CPPUNIT_TEST(test2);
CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE_END();
public:
void test1();
void test2();
};
//simpleTest.cpp文件 #include "simpleTest.h"
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include "cppunit/TestCase.h"
#include "cppunit/TestAssert.h" CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE_NAMED_REGISTRATION(SimpleTest, "alltest"); void SimpleTest::test2()
{
CPPUNIT_ASSERT(3 == 3);
} void SimpleTest::test1()
{
CPPUNIT_ASSERT(2 == 2);
}
编译命令如下:
g++ main.cpp simpleTest.cpp -o test -I /home/chusiyong/cppunit/install/include -L /home/chusiyong/cppunit/install/lib -Wl,-Bstatic -lcppunit -Wl,-Bdynamic -ldl
运行可执行文件,结果如下:
OK (2)
表示所有用例都执行成功
源码分析
1.主要类的继承关系
- Test相关类
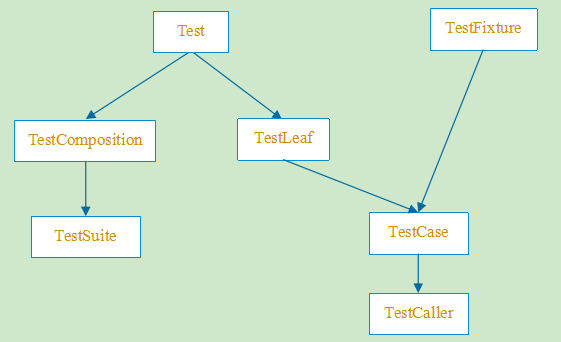
- Test类作为所有测试用例的基类,是一个抽象类,含有纯虚函数
- Test类主要的方法是run方法
- 采用Composition设计模式(类比文件和文件夹的设计方法)
- TestComposition类主要是实现类名的处理,并提供start和end的处理(配合TestListener使用)
- TestSuite类非常重要,里面可以包含多个Test类,使用Vector的方式保存
- TestFixture类主要提供setUp和tearDown方法,用于运行测试用例前和测试用例后执行
- TestLeaf类主要是实现Test类中的部分方法,在体现通用性的同时做安全措施,重写必要的virtual方法(实现Test类中模板方法中调用的函数),继承该类的子类只能是单个测试用例,不能包含子测试用例
- TestCase类是主要的测试类,每一个TestCase表示一个测试用例
- TestCaller类主要用来生成TestCase实例,将TestFixture类中的每一个测试方法,变成一个单独的TestCase实例(很重要),然后将TestCase实例加入到TestSuite中
//TestComposite.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestComposite : public Test
{
public:
TestComposite( const std::string &name = "" );
~TestComposite();
void run( TestResult *result );
std::string getName() const;
private:
const std::string m_name;
}; //TestComposite.cpp
void TestComposite::run( TestResult *result )
{
...
doRunChildTests( result );
...
} void TestComposite::doRunChildTests( TestResult *controller)
//关键方法,调用每一个子用例的run方法
{
int childCount = getChildTestCount();
for ( int index =0; index < childCount; ++index )
{
if ( controller->shouldStop() )
break; getChildTestAt( index )->run( controller );
}
} std::string TestComposite::getName() const //获取测试用例名称
{
return m_name;
}
//TestSuite.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestSuite : public TestComposite
{
public:
TestSuite( std::string name = "" );
~TestSuite();
void addTest( Test *test ); //添加测试用例
virtual void deleteContents(); //删除测试用例
int getChildTestCount() const; //根据vector获取子用例个数
Test *doGetChildTestAt( int index ) const;//根据index获取子用例对象
private:
CppUnitVector<Test *> m_tests; //保存子用例
}; //TestSuite.cpp
void TestSuite::deleteContents() //删除所有测试用例
{
int childCount = getChildTestCount();
for ( int index =0; index < childCount; ++index )
delete getChildTestAt( index ); m_tests.clear();
} void TestSuite::addTest( Test *test ) //添加测试用例
{
m_tests.push_back( test );
} int TestSuite::getChildTestCount() const //获取子测试用例的个数
{
return m_tests.size();
} Test *TestSuite::doGetChildTestAt( int index ) const//根据index获取子用例对象
{
return m_tests[index];
}
//TestLeaf.h 没有实现run方法,不能生成实例对象
class CPPUNIT_API TestLeaf: public Test
{
public:
int countTestCases() const; //Test类中的checkIsValidIndex方法调用
int getChildTestCount() const;//Test类中的checkIsValidIndex方法调用
Test *doGetChildTestAt( int index ) const;//Test类中的getChildTestAt方法调用
}; //TestLeaf.cpp
int TestLeaf::countTestCases() const
{
return 1;
} int TestLeaf::getChildTestCount() const
{
return 0;
} Test *TestLeaf::doGetChildTestAt( int index ) const
{
checkIsValidIndex( index );
return NULL; // never called, checkIsValidIndex() always throw.
}
//TestFixture.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestFixture //接口
{
public:
virtual ~TestFixture() {};
virtual void setUp() {};//运行用例前调用
virtual void tearDown() {};//运行用例后调用
};
//TestCase.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestCase : public TestLeaf, public TestFixture
{
public:
TestCase( const std::string &name );
TestCase();
~TestCase();
virtual void run(TestResult *result); //实现纯虚方法
std::string getName() const; //获取用例名称
virtual void runTest(); //子类实现 private:
TestCase( const TestCase &other );
TestCase &operator=( const TestCase &other ); private:
const std::string m_name;
}; //TestCase.cpp
//说明:运行测试用例的时候,是采用的保护性运行方式,保证一个用例执行失败后续的用例可以继续执行
//采用try{...}catch{...}的模式,失败就抛异常,然后记录,继续执行
void TestCase::run( TestResult *result )
{
result->startTest(this);
if ( result->protect( TestCaseMethodFunctor( this, &TestCase::setUp ), this, "setUp() failed" ))
{
result->protect( TestCaseMethodFunctor( this, &TestCase::runTest ), this);
} result->protect( TestCaseMethodFunctor( this, &TestCase::tearDown ), this, "tearDown() failed");
result->endTest( this );
}
- TestCaseMethodFunctor类:函数对象,作用就是封装方法,便于使用
class TestCaseMethodFunctor : public Functor
{
public:
typedef void (TestCase::*Method)(); TestCaseMethodFunctor( TestCase *target,
Method method )
: m_target( target )
, m_method( method )
{
} bool operator()() const //重载()操作符
{
(m_target->*m_method)(); //直接调用测试用例的地方
return true;
} private:
TestCase *m_target;
Method m_method;
};
template <class Fixture>
class TestCaller : public TestCase
{
public:
TestCaller( std::string name, TestMethod test ) :
TestCase( name ),
m_ownFixture( true ),
m_fixture( new Fixture() ),
m_test( test )
{
} TestCaller(std::string name, TestMethod test, Fixture& fixture) :
TestCase( name ),
m_ownFixture( false ),
m_fixture( &fixture ),
m_test( test )
{
} TestCaller(std::string name, TestMethod test, Fixture* fixture) :
TestCase( name ),
m_ownFixture( true ),
m_fixture( fixture ),
m_test( test )
{
} ~TestCaller()
{
if (m_ownFixture)
delete m_fixture;
} void runTest()
{
(m_fixture->*m_test)(); //运行测试用例的地方
} void setUp()
{
m_fixture->setUp ();
} void tearDown()
{
m_fixture->tearDown ();
} std::string toString() const
{
return "TestCaller " + getName();
} private:
TestCaller( const TestCaller &other );
TestCaller &operator =( const TestCaller &other ); private:
bool m_ownFixture;
Fixture *m_fixture; //new出来的测试对象,即TestCase
typedef void (Fixture::*TestMethod)();
TestMethod m_test;//Testcase中的一个测试方法
};
- TestListener相关类

- TestListener类和TestResult类之间是采用观察者模式,TestResult类将测试用例的执行结果通知给TestListener类
- TestListener类将保持的结果,通过OutPutter类显示出来
- TestSuccessListener类主要作用是实现多线程安全
class CPPUNIT_API TestListener
{
public:
virtual ~TestListener() {}
virtual void addFailure( const TestFailure & /*failure*/ ) {}
//主要的函数,当测试用例执行失败时,调用该接口将结果保持到观察者实例中
};
//TestSuccessListener.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestSuccessListener : public TestListener,
public SynchronizedObject
{
public:
TestSuccessListener( SynchronizationObject *syncObject = 0 );
virtual ~TestSuccessListener();
virtual void reset();
void addFailure( const TestFailure &failure ); //添加失败信息
virtual bool wasSuccessful() const; //判断执行结果 private:
bool m_success;
}; //TestSuccessListener.cpp
void TestSuccessListener::addFailure( const TestFailure &failure )
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject ); //多线程时的锁
m_success = false;
} bool TestSuccessListener::wasSuccessful() const
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
return m_success;
} void TestSuccessListener::reset()
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
m_success = true;
}
//TestResultCollector.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestResultCollector : public TestSuccessListener
{
public:
TestResultCollector( SynchronizationObject *syncObject = 0 );
virtual ~TestResultCollector(); void addFailure( const TestFailure &failure ); virtual void reset(); virtual int testErrors() const;
virtual int testFailures() const;
virtual int testFailuresTotal() const; virtual const TestFailures& failures() const; protected:
void freeFailures(); typedef CppUnitDeque<Test *> Tests;
Tests m_tests; typedef CppUnitDeque<TestFailure *> TestFailures;
TestFailures m_failures; int m_testErrors;
}; //TestResultCollector.cpp
void TestResultCollector::freeFailures() //释放所有错误信息
{
TestFailures::iterator itFailure = m_failures.begin();
while ( itFailure != m_failures.end() )
delete *itFailure++;
m_failures.clear();
} void TestResultCollector::reset() //将Listener的状态变成初始状态
{
TestSuccessListener::reset(); ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
freeFailures();
m_testErrors = 0;
m_tests.clear();
} void TestResultCollector::addFailure( const TestFailure &failure )//添加错误信息
{
TestSuccessListener::addFailure( failure ); ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
if ( failure.isError() )
++m_testErrors;
m_failures.push_back( failure.clone() );
} int TestResultCollector::testFailuresTotal() const //返回错误信息的个数(包括error)
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
return m_failures.size();
} int TestResultCollector::testFailures() const //返回失败用例的个数(不包括error)
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
return m_failures.size() - m_testErrors;
} //返回错误信息
const TestResultCollector::TestFailures & TestResultCollector::failures() const
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
return m_failures;
} //返回error的个数
int TestResultCollector::testErrors() const
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
return m_testErrors;
}
- TestFailure类:用于表示测试用例的执行结果,一个测试用例执行失败就会生成一个TestFailure类的实例
- TestFailure可以表示用例执行失败,也可以表示error,二者的区别是:测试用例执行失败时抛出的异常是已知的,如果执行用例时抛出未知异常,就是error
//TestFailure.cpp.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestFailure
{
public:
TestFailure( Test *failedTest, Exception *thrownException, bool isError );
virtual ~TestFailure ();
virtual Test *failedTest() const; //返回失败用例对象
virtual Exception *thrownException() const; //返回抛出的对象
virtual SourceLine sourceLine() const; //获取抛出异常的代码行号
virtual bool isError() const; //判断是用例失败还是error
virtual std::string failedTestName() const;//获取失败测试用例的名称
virtual TestFailure *clone() const;//克隆 protected:
Test *m_failedTest;
Exception *m_thrownException;
bool m_isError; private:
TestFailure( const TestFailure &other );
TestFailure &operator =( const TestFailure& other );
}; //TestFailure.cpp
TestFailure::TestFailure( Test *failedTest,
Exception *thrownException,
bool isError ) :
m_failedTest( failedTest ), //失败的用例
m_thrownException( thrownException ), //抛出的异常
m_isError( isError )//是用例失败还是未知异常
{
}
- 多线程安全同步机制
SynchronizedObject类起到一个域名的包装作用,防止名称空间被污染
SynchronizationObject类似一个基类,提供lock和unlock的接口,可以依据不同的平台进行继承实现互斥锁
ExclusiveZone类的作用是封装SynchronizationObject类,方便使用互斥锁,关键就是在构造函数中调用lock函数,析构函数中调用unlock函数,无需手动调用lock和unlock函数
class CPPUNIT_API SynchronizedObject
{
public: class SynchronizationObject //实现互斥锁的基类
{
public:
SynchronizationObject() {}
virtual ~SynchronizationObject() {} virtual void lock() {}
virtual void unlock() {}
}; SynchronizedObject( SynchronizationObject *syncObject =0 );
virtual ~SynchronizedObject(); protected: class ExclusiveZone //封装SynchronizationObject类的使用方式
{
SynchronizationObject *m_syncObject; public:
ExclusiveZone( SynchronizationObject *syncObject )
: m_syncObject( syncObject )
{
m_syncObject->lock(); //构造函数中调用lock函数
} ~ExclusiveZone()
{
m_syncObject->unlock();//析构函数中调用unlock函数
}
}; virtual void setSynchronizationObject( SynchronizationObject *syncObject ); protected:
SynchronizationObject *m_syncObject; private:
SynchronizedObject( const SynchronizedObject © );
void operator =( const SynchronizedObject © );
};
- TestResult类,与TestListener类组成观察者模式,其中TestResult类是被观察者,TestListener类是观察者
TestResult类的runTest方法是运行测试用例的源头,里面会执行测试用例,并将测试用例的执行结果通知给所有的观察者
TestResult类的runTest方法会调用每一个测试用例的run方法
TestResult类的关键代码如下:
//TestResult.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestResult : protected SynchronizedObject
{
public: TestResult( SynchronizationObject *syncObject = 0 );
virtual ~TestResult(); virtual void addListener( TestListener *listener );//添加测试用例
virtual void removeListener( TestListener *listener );//移除测试用例 virtual void addFailure( Test *test, Exception *e );//添加失败信息 virtual void runTest( Test *test );//入口方法 protected:
void addFailure( const TestFailure &failure ); //将失败的消息通知给所有的观察者 protected:
typedef CppUnitDeque<TestListener *> TestListeners;
TestListeners m_listeners;//保存所有的监听者
}; //TestResult.cpp
void TestResult::addListener( TestListener *listener )//添加测试用例
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
m_listeners.push_back( listener );
} void TestResult::removeListener ( TestListener *listener )//移除测试用例
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
removeFromSequence( m_listeners, listener );
} void TestResult::runTest( Test *test )//入口方法
{
startTestRun( test );
test->run( this );
endTestRun( test );
} void TestResult::addFailure( Test *test, Exception *e )//用例失败时被调用
{
TestFailure failure( test, e, false );
addFailure( failure );
} void TestResult::addFailure( const TestFailure &failure )//将失败的消息通知给所有的观察者
{
ExclusiveZone zone( m_syncObject );
for ( TestListeners::iterator it = m_listeners.begin();
it != m_listeners.end();
++it )
(*it)->addFailure( failure );
}
- OutPutter相关类
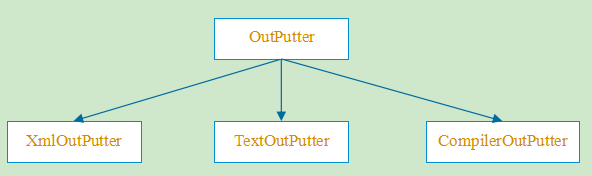
- OutPutter是公共的基类,提供统一的接口
class CPPUNIT_API Outputter
{
public:
virtual ~Outputter() {} virtual void write() =0; //关键方法
};
TextOutputter类:将执行结果按照文本模式打印出来,一般是输出到屏幕(一般在调试中使用)
XmlOutPutter类:将执行结果按照xml模式打印出来,一般是保存到xml文件中(一般在自动化中使用)
CompilerOutPutter类:将执行的结果以编译器兼容的模式打印出来,便于调试,一般不怎么使用
总结:就是将TestResult类中的Failure信息以不同的格式输出
2. 创建测试用例的相关类
- 创建测试用例的相关类主要使用了工厂模式
- 创建的具体过程使用了宏进行简化
- 相关类如下
- ConcretTestFixtureFactory类:用于创建测试用例对象
class TestFixtureFactory
{
public:
virtual TestFixture *makeFixture() =0; //用于创建具体测试用例的公共方法 virtual ~TestFixtureFactory() {}
}; //使用工厂方法模式
template<class TestFixtureType>
class ConcretTestFixtureFactory : public CPPUNIT_NS::TestFixtureFactory
{
TestFixture *makeFixture()
{
return new TestFixtureType(); //根据具象的类型创建实例
}
};
- TestSuiteBuilderContextBase类:用于将测试用例对象添加到suite中
//TestSuiteBuilderContextBase.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestSuiteBuilderContextBase
{
public:
TestSuiteBuilderContextBase( TestSuite &suite,
const TestNamer &namer,
TestFixtureFactory &factory ); virtual ~TestSuiteBuilderContextBase(); void addTest( Test *test ); protected:
TestFixture *makeTestFixture() const; //创建测试用例 TestSuite &m_suite; //用于保存测试用例的suite
const TestNamer &m_namer; //保存suite的名称
TestFixtureFactory &m_factory; //创建测试用例的工厂
}; //TestSuiteBuilderContextBase.cpp
TestSuiteBuilderContextBase::TestSuiteBuilderContextBase(
TestSuite &suite,
const TestNamer &namer,
TestFixtureFactory &factory )
: m_suite( suite )
, m_namer( namer )
, m_factory( factory )
{//构造函数
} TestFixture *TestSuiteBuilderContextBase::makeTestFixture() const
{
return m_factory.makeFixture();
} void TestSuiteBuilderContextBase::addTest( Test *test ) //添加用例到suite
{
m_suite.addTest( test );
}
- TestFactory类
class CPPUNIT_API TestFactory
{
public:
virtual ~TestFactory() {}
virtual Test* makeTest() = 0;
};
- TestSuiteFactory类:此处调用的TestCaseType::suite()返回的suite就是包含测试用例的suite
template<class TestCaseType>
class TestSuiteFactory : public TestFactory
{
public:
virtual Test *makeTest()
{
return TestCaseType::suite(); //关键方法,该方法的实现是宏定义
}
};
- TestFactoryRegistry类:用于从TestFactoryRegistryList类中获取指定名称的TestFactoryRegistry实例
- TestFactoryRegistryList类:单例类,根据名称保存所有的TestFactoryRegistry实例
- AutoRegisterSuite类:封装TestSuiteFactory的注册方式
3.框架入口类
- TestRunner类是整个CppUnit的入口类,将TestSuite类、TestResult类以及TestListener类联合在一起,然后提供统一的入口方法,便于使用
- TestListener实例包含在TestResult实例里面
- 部分代码如下:
//TestRunner.h
class CPPUNIT_API TestRunner
{
public:
TestRunner( );
virtual ~TestRunner();
//将需要运行的测试用例添加进来
virtual void addTest( Test *test );
//运行指定的测试用例
virtual void run( TestResult &controller, const std::string &testPath = "" ); protected:
//内部类,对suite进行了包装
class CPPUNIT_API WrappingSuite : public TestSuite
{
public:
WrappingSuite( const std::string &name = "All Tests" ); int getChildTestCount() const; std::string getName() const; void run( TestResult *result ); protected:
Test *doGetChildTestAt( int index ) const; bool hasOnlyOneTest() const; Test *getUniqueChildTest() const;
}; protected:
WrappingSuite *m_suite; private:
TestRunner( const TestRunner © );
void operator =( const TestRunner © );
private:
}; //TestRunner.cpp
void TestRunner::addTest( Test *test )
{
m_suite->addTest( test );
} void TestRunner::run( TestResult &controller,
const std::string &testPath )
{
TestPath path = m_suite->resolveTestPath( testPath );
Test *testToRun = path.getChildTest(); controller.runTest( testToRun );
}
4.重要宏的解析
- CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE_NAMED_REGISTRATION
CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE_NAMED_REGISTRATION(SimpleTest, "alltest");
//展开后如下
static CPPUNIT_NS::AutoRegisterSuite<SimpleTest> autoRegisterRegistry__12("alltest");
- CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE、CPPUNIT_TEST以及CPPUNIT_TEST_SUITE_END宏,这三个红必须配合使用,不能单独使用,用于声明需要运行的测试用例
private:
//根据typeid(SimpleTest)为名称生成TestNamer类的实例,就是对名称的封装
static const CPPUNIT_NS::TestNamer &getTestNamer__()
{
static CPPUNIT_NS::TestNamer testNamer(typeid(SimpleTest));
return testNamer;
} public: //将测试用例添加到suite中
static void addTestsToSuite( CPPUNIT_NS::TestSuiteBuilderContextBase &baseContext )
{
CPPUNIT_NS::TestSuiteBuilderContext<SimpleTest> context(baseContext)
context.addTest(( new CPPUNIT_NS::TestCaller<SimpleTest>(context.getTestNameFor( #testMethod), &SimpleTest::testMethod, context.makeFixture())))
} //对外接口,被TestSuiteFactory中的makeTest方法调用,返回一个完整的suite,等待被运行
static CPPUNIT_NS::TestSuite *suite()
{
const CPPUNIT_NS::TestNamer &namer = getTestNamer__();
std::auto_ptr<CPPUNIT_NS::TestSuite> suite(new CPPUNIT_NS::TestSuite(namer.getFixtureName()));
CPPUNIT_NS::ConcretTestFixtureFactory<SimpleTest> factory;
CPPUNIT_NS::TestSuiteBuilderContextBase context(*suite.get(), namer, factory );
SimpleTest::addTestsToSuite( context );
return suite.release();
}
CppUnit使用和源码解析的更多相关文章
- Go语言备忘录:net/http包的使用模式和源码解析
本文是晚辈对net/http包的一点浅显的理解,文中如有错误的地方请前辈们指出,以免误导! 转摘本文也请注明出处:Go语言备忘录:net/http包的使用模式和源码解析,多谢! 目录: 一.http ...
- Dubbo原理和源码解析之服务引用
一.框架设计 在官方<Dubbo 开发指南>框架设计部分,给出了引用服务时序图: 另外,在官方<Dubbo 用户指南>集群容错部分,给出了服务引用的各功能组件关系图: 本文将根 ...
- Dubbo原理和源码解析之标签解析
一.Dubbo 配置方式 Dubbo 支持多种配置方式: XML 配置:基于 Spring 的 Schema 和 XML 扩展机制实现 属性配置:加载 classpath 根目录下的 dubbo.pr ...
- Dubbo原理和源码解析之“微内核+插件”机制
github新增仓库 "dubbo-read"(点此查看),集合所有<Dubbo原理和源码解析>系列文章,后续将继续补充该系列,同时将针对Dubbo所做的功能扩展也进行 ...
- Dubbo原理和源码解析之服务暴露
github新增仓库 "dubbo-read"(点此查看),集合所有<Dubbo原理和源码解析>系列文章,后续将继续补充该系列,同时将针对Dubbo所做的功能扩展也进行 ...
- Go语言备忘录(3):net/http包的使用模式和源码解析
本文是晚辈对net/http包的一点浅显的理解,文中如有错误的地方请前辈们指出,以免误导! 转摘本文也请注明出处:Go语言备忘录(3):net/http包的使用模式和源码解析,多谢! 目录: 一.h ...
- Spring源码解析02:Spring IOC容器之XmlBeanFactory启动流程分析和源码解析
一. 前言 Spring容器主要分为两类BeanFactory和ApplicationContext,后者是基于前者的功能扩展,也就是一个基础容器和一个高级容器的区别.本篇就以BeanFactory基 ...
- Spring源码解析 | 第二篇:Spring IOC容器之XmlBeanFactory启动流程分析和源码解析
一. 前言 Spring容器主要分为两类BeanFactory和ApplicationContext,后者是基于前者的功能扩展,也就是一个基础容器和一个高级容器的区别.本篇就以BeanFactory基 ...
- rest-framework之视图和源码解析
视图和源码解析 通过使用mixin类编写视图: from rest_framework import mixins from rest_framework import generics class ...
随机推荐
- 上海开发票/v电13543443967
关于事项:Iㄋ5一★4З44一★ㄋ9.б7开发票的准备资料必须要公司名称个人的话就用个人名字和身份证去税务柜台申请办理!公司的话要提供公司全称就是营业执照上的名称,纳税人税号,如果是开普通增值税发票的 ...
- 入门大数据---Python基础
前言 由于AI的发展,包括Python集成了很多计算库,所以淡入了人们的视野,成为一个极力追捧的语言. 首先概括下Python中文含义是蟒蛇,它是一个胶水语言和一个脚本语言,胶水的意思是能和多种语言集 ...
- html+css快速入门教程(3)
练习: 1.画盒子 2.相框 5 基础选择器 5.1 id选择器 ID选择器与类选择器的定义与引用方式类似,只是定义的符号不一样.ID通常表示唯一值,因此,ID选择器在CSS 中通常只出现一次.如果出 ...
- Vue 封装axios(四种请求)及相关介绍(十三)
Vue 封装axios(四种请求)及相关介绍 首先axios是基于promise的http库 promise是什么? 1.主要用于异步计算 2.可以将异步操作队列化,按照期望的顺序执行,返回符合预期的 ...
- 浅谈bfs
广搜(bfs) 定义 广度优先算法,简称BFS.是一种图形搜索演算法,简单的说,BFS是从根节点开始,沿着树的宽度遍历树的节点,如果发现目标,终止. 与dfs的相似之处与不同 结合深搜理解 相同点:都 ...
- python运行时报错can't find '__main__' module in 'xxx' 的解决办法
刚开始学习python,想要使用pycharm来编辑和运行程序,所以就安装了下pycharm ,写了个简单的代码决定运行下,结果出现如下错误: 度娘找了一番,解决了问题,发现错误主要因为在这里 没有运 ...
- 打包发布 Qt Quick/Widgets 程序
使用的QT自带的部署工具(windeployqt.exe,路径QT安装路径),版本替换debug/release Qt Quick "C:\Qt\Qt5.8.0\5.8\mingw53_32 ...
- 图片文件分布式存储方案设计模式(c#--sqlserver)
1.为了降低web服务器的压力,申请了2台文件服务器,用来存放图片文件.但是两台文件服务器如何让程序自己选择呢? 于是我用了一个算法,思路如下: 从状态表筛选出可用的图片服务器集合记作C,并获取集合的 ...
- web网页多语言的实现方案_前端实现多语言切换
实现的效果 需要在web中实现多语言的切换,当用户语言切换完成后下次重新打开网页,也是上次设置的语言进行显示. 资源网站搜索大全https://55wd.com 实现步骤 1.在用户点击切换语言后,把 ...
- 巧用transform: scale()
巧用transform: scale() 移动端font-size小于12px时line-height问题 由于出现的场景是字体小于12px的时候,所以可以将原来包括 font-size 在内的属性放 ...
