Java系列--第三篇 基于Maven的Android开发CAIO
学习要打好基础,这里用一个项目来学习一下Android的组件,参考网址为这个但不限于这个。有些东西的学习,理解三遍理论还不如一遍操作,所谓理论来自实践,实践是检验真理的唯一标准。所以,虽然看懂了那篇文章,还是自己做一遍来加深理解。
1,cmd下面生成项目
mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeArtifactId=android-quickstart -DarchetypeGroupId=de.akquinet.android.archetypes -DarchetypeVersion=1.0.11 -DgroupId=com.vanceinfo.android -DartifactId=CAIO
2, 导入项目至Kepler,新建一个类,然后Alt+Shift+S,选择Override/Implement Method, override onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState),方法内容先不管它,去到项目的AndroidManifest.xml文件中,将<activity android:name=".HelloAndroidActivity" >改为<activity android:name=".SpinnerActivity" >,等下启动时就来到这个组件来显示,接着来到layout的文件夹中,新建一个叫spinner.xml文件,使用Graphic layout,先拖入linearLayout,然后拖一个label,一个spinner,还有一个button共四个组件进来,由eclipse自动为我们生成的xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/label"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="下拉框1:"
/> <Spinner
android:id="@+id/spinner1"
android:layout_width="150dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false"
/> <TextView
android:id="@+id/label"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="下拉框2:"
/> <Spinner
android:id="@+id/spinner2"
android:layout_width="150dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false"
/> <Button
android:id="@+id/ok"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/ok"
/> </LinearLayout>
layout_linear
保存之后,重新回到刚刚的onCreate方法里,base下一行输入setContentView(R.layout.spinner);告诉程序我们要显示的是spinner这个组件。整个的程序源码应该是这样子:
package com.vanceinfo.android; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Spinner; public class SpinnerActivity extends Activity { private Spinner spinner1;
private Spinner spinner2;
private Button ok;
private ArrayAdapter countiesAdapter;
private String[] mCounties={"beijing","guangdong","guangxi","hunan"};
private List<String> allCounties=new ArrayList<String>();
private String result="你选择的是:"; @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.spinner); spinner1=(Spinner)findViewById(R.id.spinner1);
spinner2=(Spinner)findViewById(R.id.spinner2);
ok=(Button)findViewById(R.id.ok); for(int i=0;i<mCounties.length;i++){
allCounties.add(mCounties[i]);
} countiesAdapter=new ArrayAdapter<String>(SpinnerActivity.this,android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item,allCounties);
countiesAdapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item);
spinner1.setAdapter(countiesAdapter); ArrayAdapter adapter=ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(SpinnerActivity.this,R.array.counties,android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item);
adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item);
spinner2.setAdapter(adapter); //单击第一个下拉按钮时,显示选择的值。
spinner1.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() { /* (non-Javadoc)
* @see android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener#onItemSelected(android.widget.AdapterView, android.view.View, int, long)
*/
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> adapter, View view,
int position, long id) {
String str=(String)spinner1.getAdapter().getItem((int)id);
setTitle(result+str); } /* (non-Javadoc)
* @see android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener#onNothingSelected(android.widget.AdapterView)
*/
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0) { } }); //单击第二个下拉按钮时,显示选择的值。
spinner2.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() { /* (non-Javadoc)
* @see android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener#onItemSelected(android.widget.AdapterView, android.view.View, int, long)
*/
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> adapter, View view,
int position, long id) {
String str=(String)spinner2.getAdapter().getItem(position);
setTitle(result+str);
} /* (non-Javadoc)
* @see android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener#onNothingSelected(android.widget.AdapterView)
*/
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub }
}); //单击确定按钮,提取选择的值.
ok.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
setTitle(result+spinner1.getSelectedItem()+" - >> "+spinner2.getSelectedItem());
}
}); } }
SpinnerActivity
因为我们演示的第二个下拉框的值是在外部定义的,所以,在values文件夹下加入arrays.xml,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string-array name="counties">
<item>AAA</item>
<item>BBB</item>
<item>CCC</item>
<item>DDD</item>
<item>EEE</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
string-array_of_arrays
在string.xml中加入一条
<string name="ok">确定</string>
最后编译,即可将apk放入模拟器运行了。不过很让我伤心纠结的是Run as Android Application是运行不起来的,Debug as Android Application也是运行不起来,从logCat看到错误是Maven将我的apk名字变了,变成了好象groupId -1....apk. 整了一个下午都没有找到解决方法。实在无奈,先暂时用模拟器运行着吧。
09-14 11:17:17.993: E/AndroidRuntime(436): java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to instantiate activity ComponentInfo{com.vanceinfo.android/com.vanceinfo.android.SpinnerActivity}: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.vanceinfo.android.SpinnerActivity in loader dalvik.system.PathClassLoader[/data/app/com.vanceinfo.android-1.apk]
apk被改名了
不过,作为开发人员,不能调试,终究是件不太能放心的事情,好吧,我就用DDMS来调吧,方法是启动模拟器,来到Kepler中打上断点,切换至DDMS,选择要调试的进程,然后你在模拟器中的操作,就会绿条到代码的断点处了。我还是截个图示吧
上图的绿虫说明就是我将要调试的进程了。
以上说了这么多,就是为了将这个下拉框展示出来 ,其实我个人的理解是如果对Java的Swing很了解的话,对于Android组件开发就很简单了。单单就这个下拉框 来说注意android.widget.ArrayAdapter的实例化就是关键,我们这里使用的一个是常见的直接new,另一个就是使用其静态方法createFromResource,另外android.R.layout.下面还有一些自动生成的属性,要根据情况善于利用,需要注意的是一定要打全android.R.layout,如果你为省事而少打前面那个android,估计你就等着郁闷为什么会没有吧。
3,创建4种类型的对话框,新建一个AlertDialogActivity,并去到AndroidMainifest.xml中更改启动的组件为这个,而不是2中的spinner. 接着新建一个alertdialog.xml和alertdialog_text_entry.xml。最后去到string.xml里添加
<string name="alert_button1">有两个button的对话框1</string>
<string name="alert_button2">有三个button的对话框2</string>
<string name="alert_button3">能进行输入的对话框3</string>
<string name="alert_button4">进度框</string>
displayItem_on_string
如果使用Eclipse创建xml的话是有好处的,有很多可视化的操作,单击那个带+号的a按钮即可
写对话框的API,主要是android.app.AlertDialog.Builder,他有setPositiveButton针对于确定,setNeutralButton可针对于详情,还有setNegativeButton针对于当用户按取消时对应的按钮。注册他们的单击事件即可完成功能。
还有android.app.ProgressDialog也可用于对话框,主要用在当一些需长时间运行,给用户一个提示:正在处理中,请稍后。。。
全部源码:
package com.vanceinfo.android; import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.AlertDialog.Builder;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast; public class AlertDialogActivity extends Activity { private Button button1;
private Button button2;
private Button button3;
private Button button4; /* (non-Javadoc)
* @see android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle)
*/
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.alertdialog);
setTitle("4种对话框"); button1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
button2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
button3=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button3);
button4=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button4); button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View v) {
Builder builder= new AlertDialog.Builder(AlertDialogActivity.this);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
builder.setTitle("哇哈哈!");
builder.setMessage("去不去?");
builder.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "你选择了确定按钮!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "你选择了取消按钮!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
builder.show();
}
}); button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
new AlertDialog.Builder(AlertDialogActivity.this)
.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setTitle("温馨提示")
.setMessage("提示内容:三个按钮")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "你选择了确定按钮!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setNeutralButton("详情", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "你选择了详情按钮!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "你选择了取消按钮!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.show();
}
}); button3.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
LayoutInflater inflater=LayoutInflater.from(AlertDialogActivity.this);
final View textEntryView=inflater.inflate(R.layout.alertdialog_text_entry, null); final EditText usernameET=(EditText)textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.username_value);
final EditText passwordET=(EditText)textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.password_value);
//final String username=usernameET.getText().toString(); new AlertDialog.Builder(AlertDialogActivity.this)
.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setTitle("温馨提醒")
.setView(textEntryView)
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "用户名="+usernameET.getText().toString()+"\n密码="+passwordET.getText().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
})
.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(AlertDialogActivity.this, "你选择了确定取消!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.show();
}
}); button4.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
ProgressDialog dialog=new ProgressDialog(AlertDialogActivity.this);
dialog.setTitle("处理中。。。");
dialog.setMessage("请稍后。。。");
dialog.show();
}
});
} }
AlertDialogActivity
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".AlertDialogActivity" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/alert_button1" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/alert_button2" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/alert_button3" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/alert_button4" /> </LinearLayout>
alertdialog.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
> <TextView
android:id="@+id/username_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
android:layout_marginRight="20dip"
android:text="输 入 用 户 名"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"/> <EditText
android:id="@+id/username_value"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text=""
android:capitalize="none"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
android:layout_marginRight="20dip"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"/> <TextView
android:id="@+id/password_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="输 入 你 密 码"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
android:layout_marginRight="20dip"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"/> <EditText
android:id="@+id/password_value"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text=""
android:password="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
android:layout_marginRight="20dip"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"/> </LinearLayout>
alertdialog_text_entry.xml
4,看到了吧,我每新加一个activity就要去更改一下androidmainifest.xml。为什么不创建一个主界面了,然后由主界面去到各个小界面?所以,我们就创建一个叫MainActivity的组,该组件就两个button按钮,两个Activity之间的通讯靠的就是android.content.Intent,所以,当单击的时候,我们新建这个Intent,举个例子
spinner.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SpinnerActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
click_Intent
新建main.xml至res/layout下面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <ScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="17.10"
android:orientation="vertical" > <Button
android:id="@+id/spinner"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/spinner" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/alertDialog"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/alertDialog" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView> </LinearLayout>
main.xml
由于在main.xml中使用了两个变量,所以在string.xml又加上两个变量:
<string name="spinner">Spinner下拉框</string>
<string name="alertDialog">4种AlertDialog</string>
variable
最后就是更改AndroidManifest.xml,将首次更改为.MainActivity,并且还将原来的那两个加上去
<activity android:name=".SpinnerActivity"/>
<activity android:name=".AlertDialogActivity"></activity>
如此一来,再附上完整的MainActivity源码,就可以运行了。
package com.vanceinfo.android; import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button spinner;
private Button alertDialog;
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle)
*/
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
spinner=(Button)findViewById(R.id.spinner);
alertDialog=(Button)findViewById(R.id.alertDialog); spinner.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SpinnerActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}); alertDialog.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, AlertDialogActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
MainActivity
最终运行图应该像下面这样子
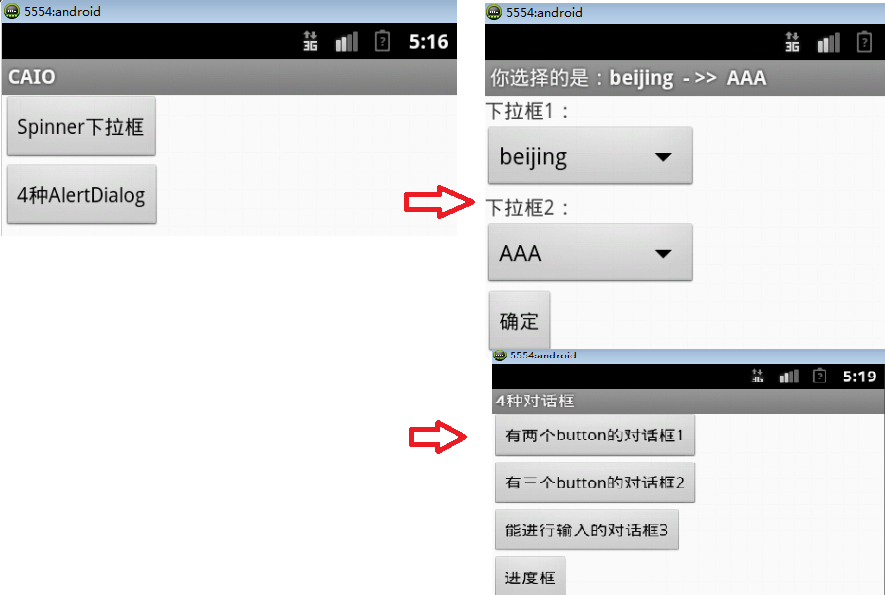
5,以上,关于如何实现这个项目,大部分就是按照这个套路来完成的。再写也是一些复制粘贴源码,还不如直接上传我的源码在这里。由于源码里面注释都很多,推荐下载这份源码以学习Android组件开发。
Java系列--第三篇 基于Maven的Android开发CAIO的更多相关文章
- Java系列--第七篇 基于Maven的Android开发实战项目
本篇是基于<Android应用案例开发大全,吴亚峰等著>的项目开发实例源码,其中有些图片,我做了一些修改,用于个人学习,请勿用于商业. 1, 日程管理专家 mvn archetype:ge ...
- Java系列--第二篇 基于Maven的Android开发HelloAndroidWorld
曾经写过一篇Android环境配置的随笔,个人感觉特繁琐,既然有Maven,何不尝试用用Maven呢,经网上搜索这篇文章但不限于这些,而做了一个基于Maven的Android版的Hello Andro ...
- Java系列--第八篇 基于Maven的SSME之定时邮件发送
关于ssme这个我的小示例项目,想做到麻雀虽小,五脏俱全,看到很多一些web都有定时发送邮件的功能,想我ssme也加入一下这种功能,经查询相关文档,发现spring本身自带了一个调度器quartz,下 ...
- Java系列--第五篇 基于Maven的SSME之Token及Parameterized单元测试
本来在第四篇要说完的,但是写着写着,我觉得内容有点多起来了,所以就另开这篇,在这里专门讲述Token的定义,JSP自定义标签以及如何用Parameterized的来做单元测试. 1,新建包com.va ...
- Java系列--第四篇 基于Maven的SSME之发送邮件
在系列第一篇中,使用的是mybatis得到了一个小小的项目,而该项目的用户对象是有邮件地址的,如果按照邮件地址给对方去一封邮件会不会更能体现针对性呢,所以,我在这篇准备加入发送邮件的功能,利用的就是s ...
- Java系列--第六篇 基于Maven的SSME之多国语言实现
如果你的网站足够强大,以致冲出了国门,走向了国际的话,你就需要考虑做多国语言了,不过,未雨绸缪,向来是我辈程序人员的优秀品质,谁知道那天,我们的网站被国外大公司看中收购,从而飞上枝头变凤凰.不扯这么多 ...
- javascript面向对象系列第三篇——实现继承的3种形式
× 目录 [1]原型继承 [2]伪类继承 [3]组合继承 前面的话 学习如何创建对象是理解面向对象编程的第一步,第二步是理解继承.本文是javascript面向对象系列第三篇——实现继承的3种形式 [ ...
- .net基础学java系列(三)徘徊反思
.net基础学java系列(三)徘徊反思 上一篇文章:.net基础学java系列(二)IDE 之 插件 这两天晚上看完了IDEA的教学视频:https://edu.51cto.com/course/1 ...
- Socket-IO 系列(三)基于 NIO 的同步非阻塞式编程
Socket-IO 系列(三)基于 NIO 的同步非阻塞式编程 缓冲区(Buffer) 用于存储数据 通道(Channel) 用于传输数据 多路复用器(Selector) 用于轮询 Channel 状 ...
随机推荐
- 深拷贝与浅拷贝(mutableCopy与Copy)详解 iOS
深拷贝与浅拷贝(mutableCopy与Copy)详解 iOS ios中并不是所有的对象都支持copy,mutableCopy,遵守NSCopying 协议的类可以发送copy消息,遵守NSMutab ...
- iOS推送 再备
这是一篇编译的文章,内容均出自Parse.com的iOS开发教程,同时作者还提供了视频讲解.本文将带领开发者一步一步向着iOS推送通知的深处探寻,掌握如何配置iOS推送通知的奥义. 介绍一点点背景资料 ...
- 『C # 开发』VS 2008 修改默认生成代码模版
作为Coder,或许会因为每次写代码前要把版权信息Ctrl+C/V上去而蛋疼 ╮(╯▽╰)╭ 可作为Code Copyer,又何尝不蛋疼呢,怎么会容忍作业上署上别人的姓名,学号,XXX 还是要先S ...
- PHP 中的数组
PHP中的数组是指一个键/值对的集合.PHP中的数组是使用哈系表构建的,这意味着访问每一个值都会有一个平均的O(1)复杂度. $arr=array([key=>]value,....); 在这里 ...
- android R.id.转化为view
LayoutInflater inflater=(LayoutInflater)getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE); View view ...
- log4jdbc
log4jdbc http://www.blogjava.net/badqiu/archive/2010/08/20/329464.html http://blog.csdn.net/sfdev/ar ...
- 百度贴吧的网络爬虫(v0.4)源码及解析
更新:感谢评论中朋友的提醒,百度贴吧现在已经改成utf-8编码了吧,需要把代码中的decode('gbk')改成decode('utf-8'). 百度贴吧的爬虫制作和糗百的爬虫制作原理基本相同,都 ...
- 嵌入式linux内核制作
今天来总结一下mini2440的内核制作过程. 一. 将内核文件拷贝至目标目录,解压. 二.清除中间文件 命令:make distclean 三.配置内核文件 将开发板厂商制作好的内核文件拷贝至内核文 ...
- 移动web app开发框架
文章地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/soulaz/p/5586787.html jQuery Mobile jQuery Mobile框架能够帮助你快速开发出支持多种移动设备的Mo ...
- log.sh
#!/bin/echo Warnning, this library must only be sourced! # vim: set expandtab smarttab shiftwidth=4 ...
