【LeetCode题解】225_用队列实现栈(Implement-Stack-using-Queues)
更多 LeetCode 题解笔记可以访问我的 github。
@
描述
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是
push to back,peek/pop from front,size, 和is empty这些操作是合法的。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
解法一:双队列,入快出慢
思路
为了实现栈这种数据结构后入先出(last in first out, LIFO)的效果,解法一借助于两个队列。其中,一个队列保存栈的所有元素(设为队列1 q1),另一个队列用于辅助实现入栈、出栈的效果(设为队列2 q2)。相关操作的底层实现细节见下面对应的小节。
入栈(push)
入栈时,直接将新的元素 x 压入队列1 q1 的队尾(rear),并且用变量 top 保存栈顶元素,方便后面的查看栈顶元素(peek)操作,具体的实现步骤见图1。
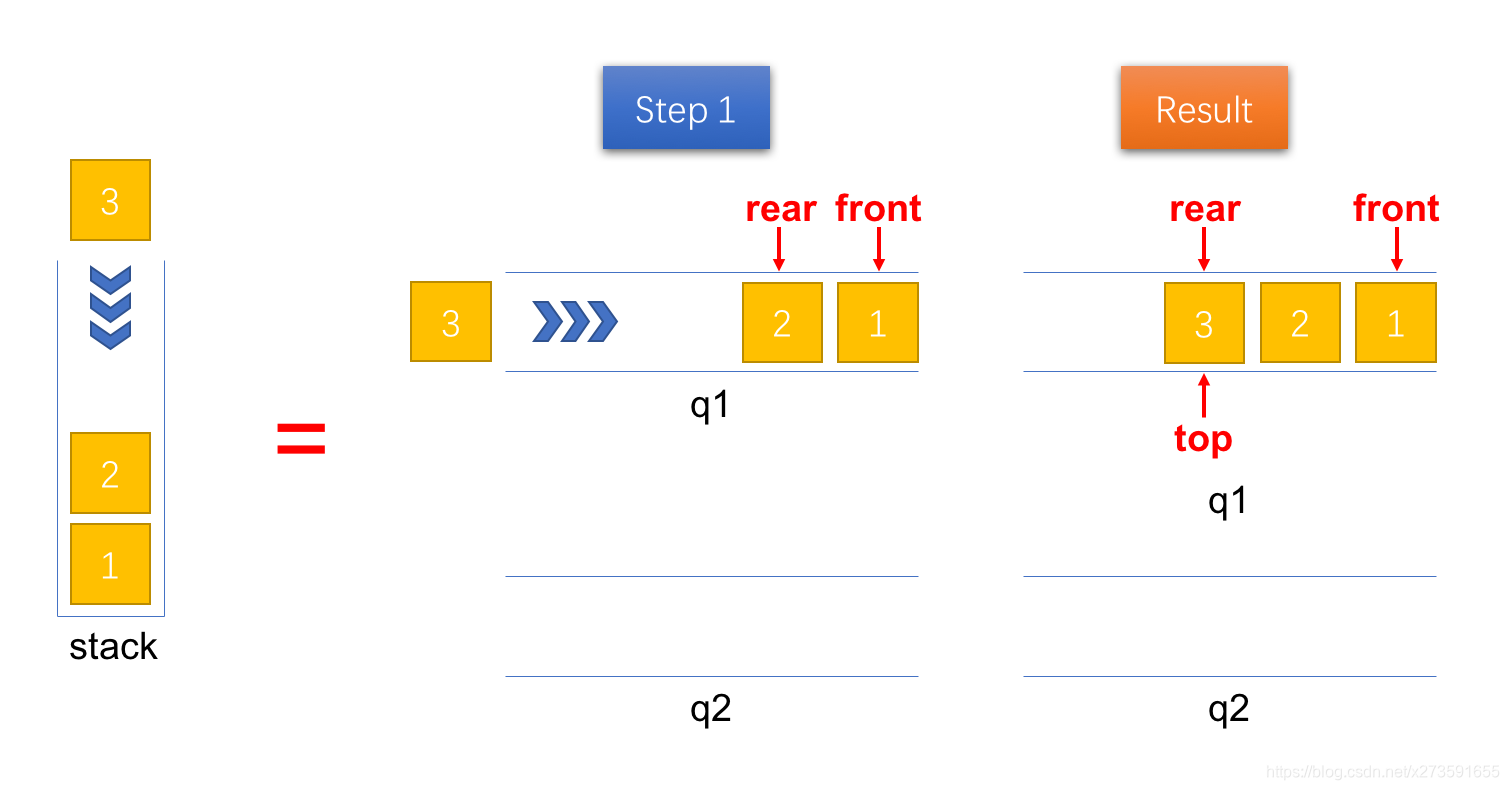
图1:将一个元素压入栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
top = x;
q1.add(x);
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
出栈(pop)
由于入栈时直接将元素入队到队列1 q1 中,因此,栈顶的元素位于队列1 q1 的尾部。为了能将栈顶元素(队列1 q1 尾部的元素)弹出,必须先将队列1 q1 队尾之前的元素出队。这里,我们借助另一个队列(辅助队列 q2)实现这一过程——将队列1 q1 队尾之前的元素出队并入队到队列2 q2 中。 之后,将队列1 q1 中唯一个元素(栈顶元素)出队。最后,再将两个队列的引用进行交换即可完成出栈操作。具体的实现步骤如图2所示。
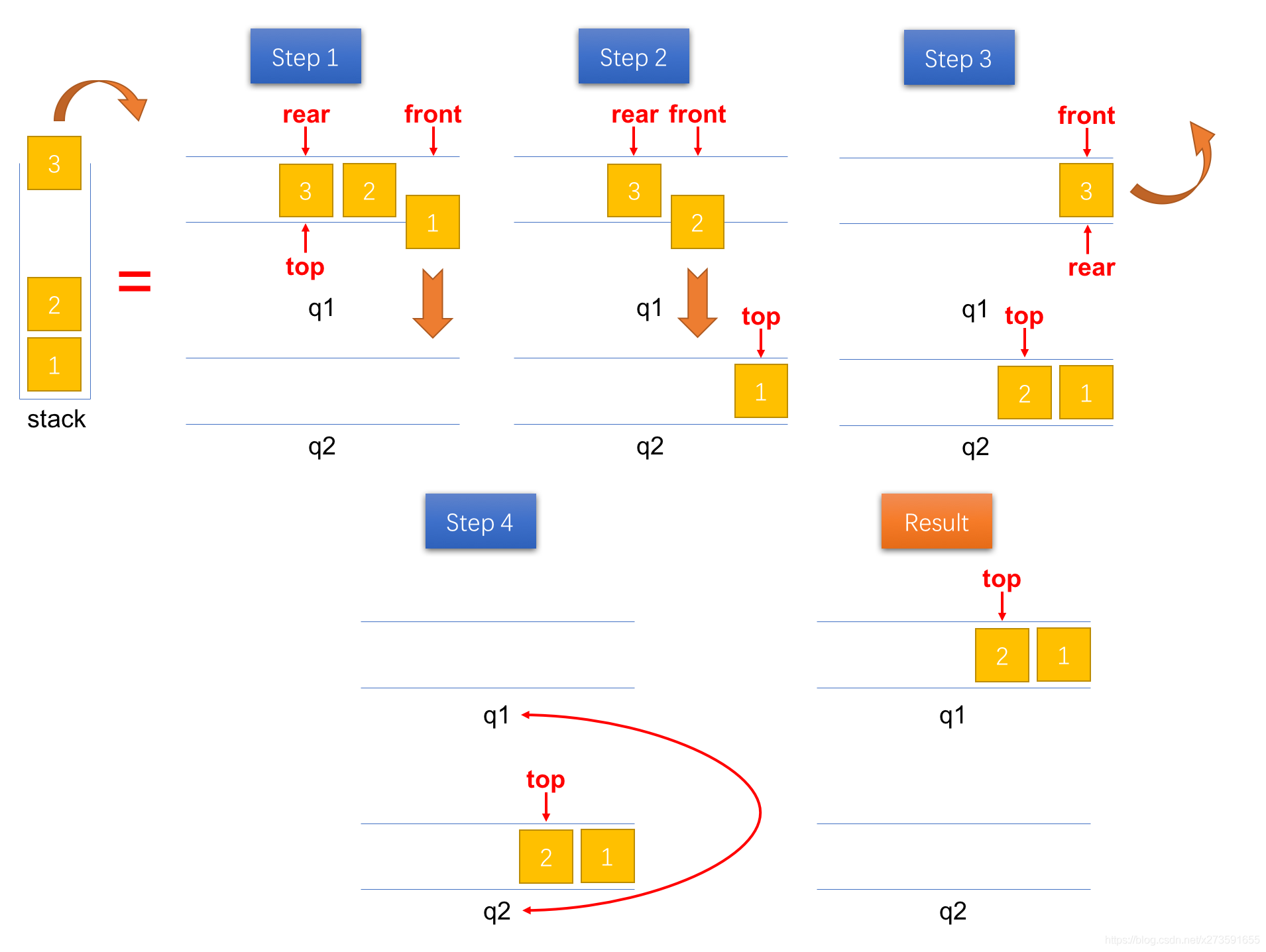
图2:将一个元素出栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (q1.size() == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The queue is empty!");
}
while (q1.size() > 1) {
top = q1.remove();
q2.add(top);
}
int res = q1.remove();
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
return res;
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(n) $,其中 \(n\) 表示未出栈前元素的数目。出栈操作需要从队列1
q1出队 \(n\) 个元素,同时入队 \(n-1\) 个元素到队列2q2,因此需要 \(2n - 1\) 次操作。因此LinkedList的添加和删除操作的时间复杂度是 \(O(1)\) 的,因此,总的时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\) - 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
查看栈顶元素(peek)
因为我们用变量 top 保存了栈顶的元素,因此只需要返回该变量即可,代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return top;
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
是否为空(empty)
队列1 q1 中保存了栈中的所有元素,因此,如果想要知道栈是否为空,只需要判断队列1 q1 中是否还有元素,代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
Java 实现
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class MyStack {
/**
* The main queue using to store all the elements in the stack
*/
private Queue<Integer> q1;
/**
* The auxiliary queue using to implement `pop` operation
*/
private Queue<Integer> q2;
/**
* The top element in the stack
*/
private int top;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
top = x;
q1.add(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (q1.size() == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
while (q1.size() > 1) {
top = q1.remove();
q2.add(top);
}
int res = q1.remove();
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
return res;
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return top;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
}
Python 实现
from collections import deque
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self._q1, self._q2, self._top = deque(), deque(), None
def push(self, x):
"""
Push element x onto stack.
:type x: int
:rtype: void
"""
self._top = x
self._q1.append(x)
def pop(self):
"""
Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
:rtype: int
"""
if not self._q1:
raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!")
while len(self._q1) > 1:
self._top = self._q1.popleft()
self._q2.append(self._top)
res = self._q1.popleft()
self._q1, self._q2 = self._q2, self._q1
return res
def top(self):
"""
Get the top element.
:rtype: int
"""
return self._top
def empty(self):
"""
Returns whether the stack is empty.
:rtype: bool
"""
return not self._q1
解法二:双队列,入慢出快
思路
与解法一相同的是,解法二也借助于两个队列。不同之处在于解法二在入栈时,已经在队列中将元素排列成出栈的顺序。因此,解法二实现的栈的入栈操作是 \(O(n)\) 的时间复杂度,而出栈操作则只需要 \(O(1)\) 的时间复杂度。相关操作的底层实现细节见下面对应的小节。
入栈(push)
为了使得队列1 q1 中的出队顺序和出栈顺序是一致的,需要借助另一个队列(辅助队列 q2)。每次有新的元素压入栈时,将该元素入队到队列2 q2 中。接着,将队列1 q1 中的所有元素出队并入队到队列2 q2 中。最后,再将两个队列的引用进行交换,则队列1 q1 中出队的顺序即为实际的出栈顺序。具体的操作步骤如图3所示。
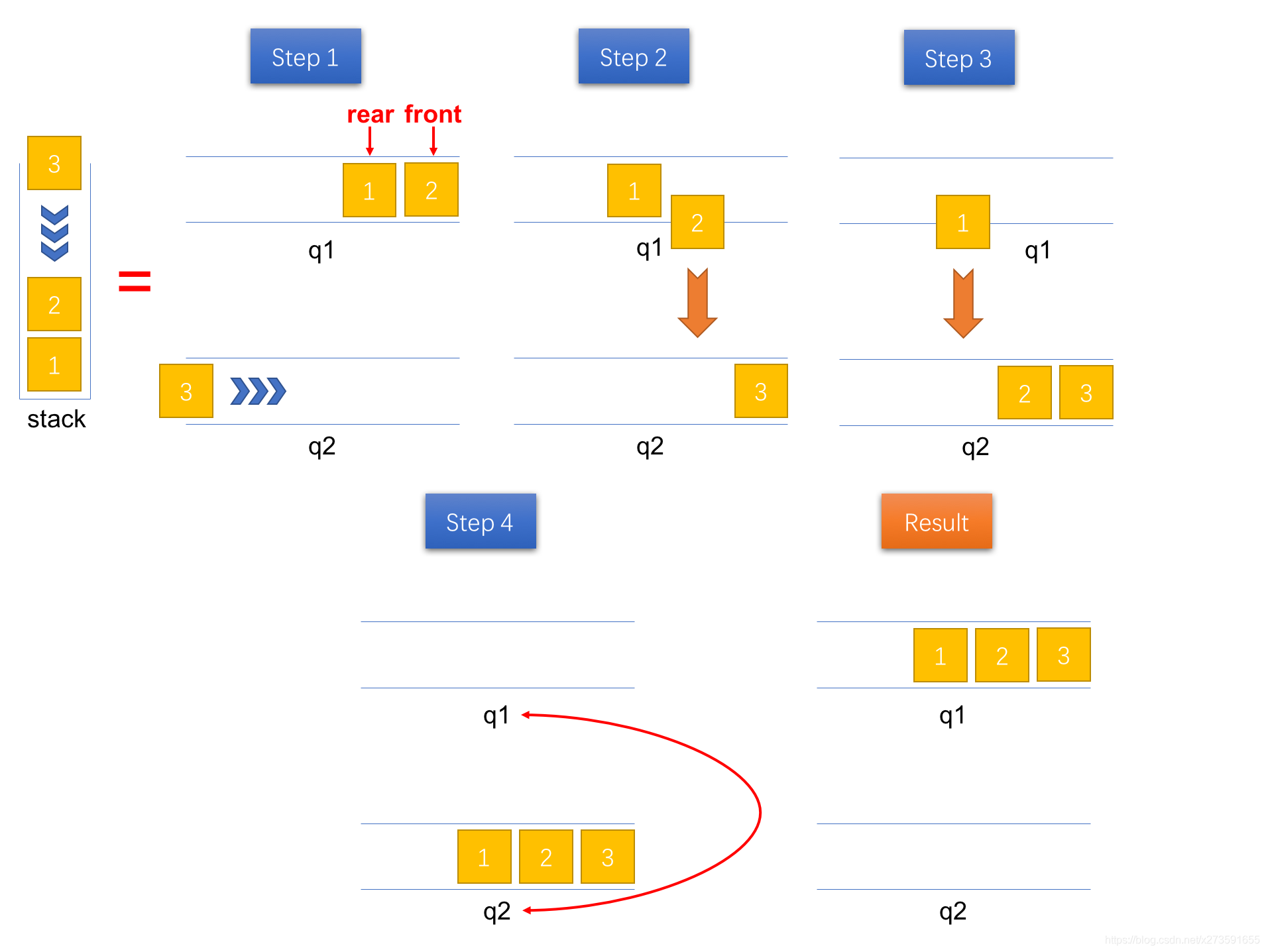
图3:将一个元素压入栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
q2.add(x);
while (!q1.isEmpty()) {
q2.add(q1.remove());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:\(O(n)\),其中 \(n\) 表示入栈前元素的数目。入栈操作需要 \(n+1\) 个入队操作,同时还需要 \(n\) 个出队操作,因此,总共需要 \(2n + 1\) 个操作。由于
LinkedList的添加和删除操作的时间复杂度是 \(O(1)\) 的,因此,总的时间复杂度是 \(O(n)\) 的 - 空间复杂度:\(O(1)\)
出栈(pop)
由于在入栈时已经将队列中的元素排列成出栈的顺序,因此,只需要出队队列1 q1 中队首的元素即可。
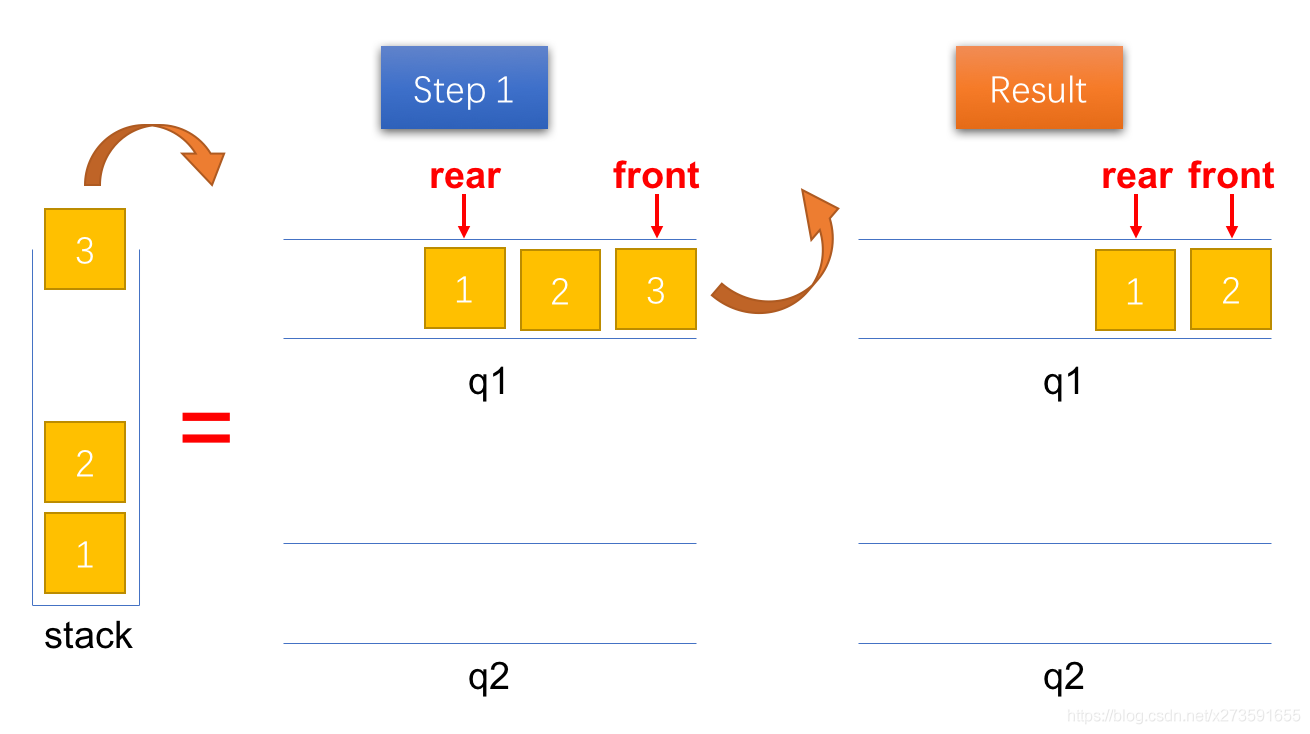
图4:将一个元素出栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (q1.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return q1.remove();
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
查看栈顶元素(peek)
同理,只需要返回队列1 q1 队首元素即可。
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
if (q1.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return q1.peek();
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
是否为空(empty)
这个操作和解法一的没什么不同,故不再赘言。
Java 实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Queue;
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> q1;
private Queue<Integer> q2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
q2.add(x);
while (!q1.isEmpty()) {
q2.add(q1.remove());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (q1.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return q1.remove();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
if (q1.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return q1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
}
Python 实现
from collections import deque
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self._q1, self._q2 = deque(), deque()
def push(self, x):
"""
Push element x onto stack.
:type x: int
:rtype: void
"""
self._q2.append(x)
while self._q1:
self._q2.append(self._q1.popleft())
self._q1, self._q2 = self._q2, self._q1
def pop(self):
"""
Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
:rtype: int
"""
if not self._q1:
raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!")
return self._q1.popleft()
def top(self):
"""
Get the top element.
:rtype: int
"""
if not self._q1:
raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!")
return self._q1[0]
def empty(self):
"""
Returns whether the stack is empty.
:rtype: bool
"""
return not self._q1
解法三:单队列
思路
上面两种解法都借助于两个队列,实际上,只借助于一个队列也可以实现栈的先入先出效果。
入栈(push)
入栈时,新添加的元素位于队列的队尾,但是对于栈而言,它其实是栈顶元素。为了使得新添加的元素位于队首,可以将其之前的所有元素出队并重新入队。最终,队列中元素的顺序和出栈的顺序是一致的。具体的操作步骤如下图所示。
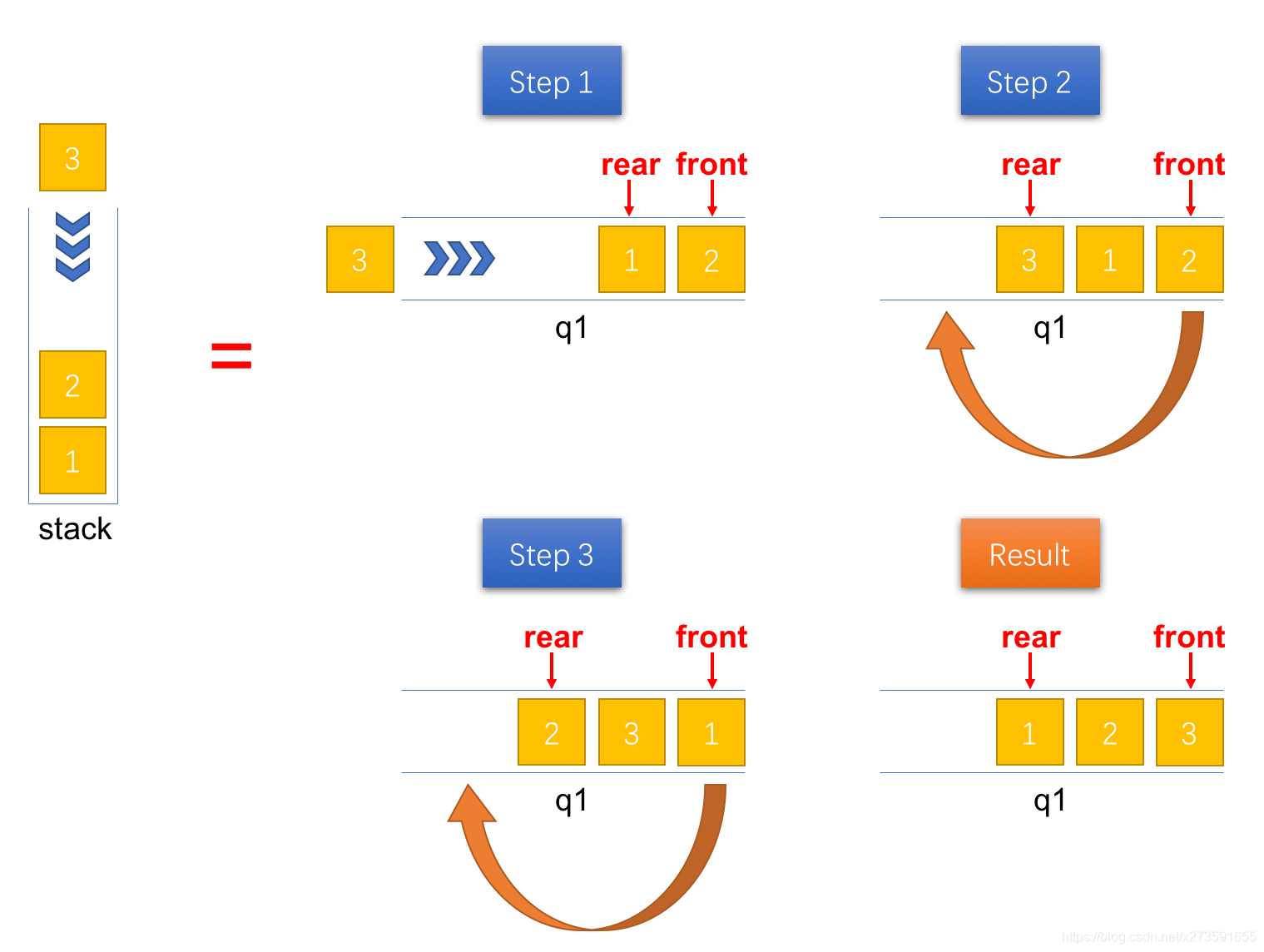
图5:将一个元素压入栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue.add(x);
for (int i = 0; i < queue.size() - 1; ++i) {
queue.add(queue.remove());
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:\(O(n)\),其中 \(n\) 表示入栈前栈内元素的数目。入栈操作需要 \(n\) 次的出队操作,同时也需要 \(n + 1\)次的入队操作,因此,需要总的操作次数为 \(2n + 1\) 次。由于
LinkedList的添加和删除操作的时间复杂度是 \(O(1)\) 的,因此,总的时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\) - 空间复杂度:\(O(1)\)
出栈(pop)
由于在入栈时已经将队列中的元素排列成出栈的顺序,因此,只需要出队队列 q1 中队首的元素即可。
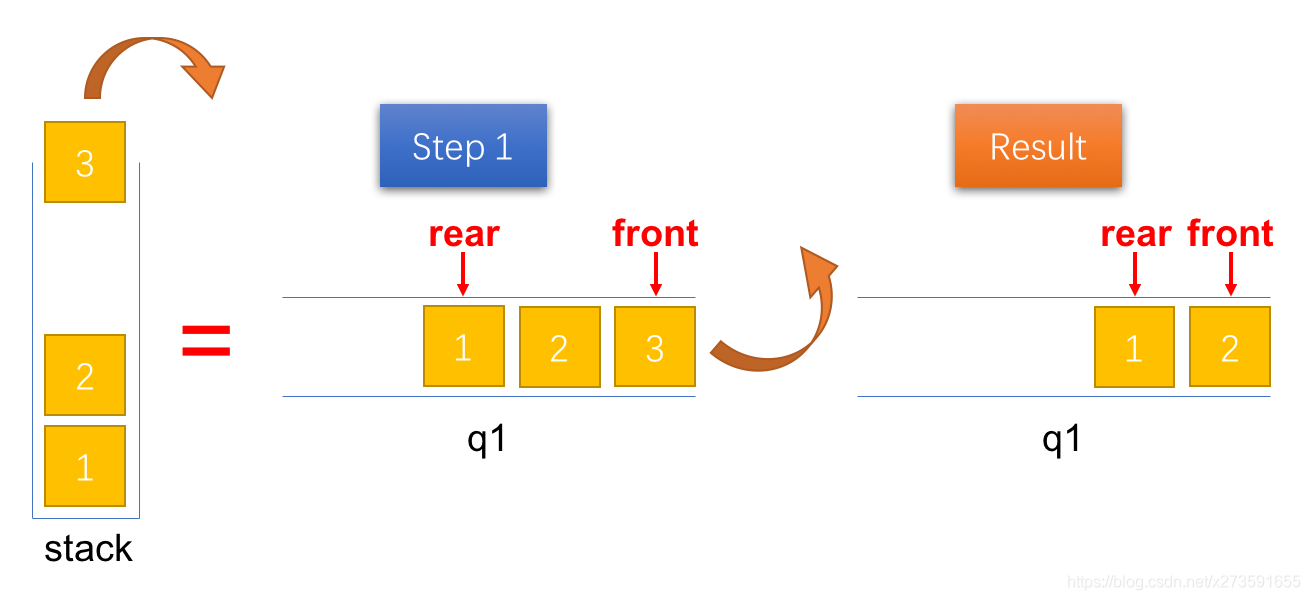
图6:将一个元素出栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return queue.remove();
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
查看栈顶元素(peek)
同理,只需要返回队列 q1 的队首元素即可。
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return queue.peek();
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
是否为空(empty)
队列 q1 中保存了栈中的所有元素,因此,如果想要知道栈是否为空,只需要判断队列 q1 中是否还有元素,代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
复杂度分析如下:
- 时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
- 空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
Java 实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.Queue;
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue.add(x);
for (int i = 0; i < queue.size() - 1; ++i) {
queue.add(queue.remove());
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return queue.remove();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!");
}
return queue.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
Python 实现
from collections import deque
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self._q = deque()
def push(self, x):
"""
Push element x onto stack.
:type x: int
:rtype: void
"""
self._q.append(x)
for _ in range(len(self._q) - 1):
self._q.append(self._q.popleft())
def pop(self):
"""
Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
:rtype: int
"""
if not self._q:
raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!")
return self._q.popleft()
def top(self):
"""
Get the top element.
:rtype: int
"""
if not self._q:
raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!")
return self._q[0]
def empty(self):
"""
Returns whether the stack is empty.
:rtype: bool
"""
return not self._q
【LeetCode题解】225_用队列实现栈(Implement-Stack-using-Queues)的更多相关文章
- LeetCode 225:用队列实现栈 Implement Stack using Queues
题目: 使用队列实现栈的下列操作: push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈 pop() -- 移除栈顶元素 top() -- 获取栈顶元素 empty() -- 返回栈是否为空 Implement th ...
- [Swift]LeetCode225. 用队列实现栈 | Implement Stack using Queues
Implement the following operations of a stack using queues. push(x) -- Push element x onto stack. po ...
- leetcode:Implement Stack using Queues 与 Implement Queue using Stacks
一.Implement Stack using Queues Implement the following operations of a stack using queues. push(x) - ...
- leetcode 155. Min Stack 、232. Implement Queue using Stacks 、225. Implement Stack using Queues
155. Min Stack class MinStack { public: /** initialize your data structure here. */ MinStack() { } v ...
- 【LeetCode】232 & 225 - Implement Queue using Stacks & Implement Stack using Queues
232 - Implement Queue using Stacks Implement the following operations of a queue using stacks. push( ...
- 232. Implement Queue using Stacks,225. Implement Stack using Queues
232. Implement Queue using Stacks Total Accepted: 27024 Total Submissions: 79793 Difficulty: Easy Im ...
- Implement Queue by Two Stacks & Implement Stack using Queues
Implement Queue by Two Stacks Implement the following operations of a queue using stacks. push(x) -- ...
- [LeetCode] Implement Stack using Queues 用队列来实现栈
Implement the following operations of a stack using queues. push(x) -- Push element x onto stack. po ...
- LeetCode 225 Implement Stack using Queues(用队列来实现栈)(*)
翻译 用队列来实现栈的例如以下操作. push(x) -- 将元素x加入进栈 pop() -- 从栈顶移除元素 top() -- 返回栈顶元素 empty() -- 返回栈是否为空 注意: 你必须使用 ...
随机推荐
- 如何处理由Dll缺失造成的程序直接崩溃的问题。
问题描述:在开发一个上位机程序时(C#.winform),使用到了Kvaser的SDK,而这个SDK是基于对应的Kvaser驱动开发的.当前PC如果没有装Kvaser驱动, 程序启动时,会直接奔溃.调 ...
- Android-Could not find method implementation() for arguments
当AndroidStudio加载工程的时候:报以下错误: 详细错误: Could not find method implementation() for arguments [file collec ...
- [leetcode 8] String to Integer
1 题目: Implement atoi to convert a string to an integer. Hint: Carefully consider all possible input ...
- 个人作业四--Alpha阶段个人总结
一.个人总结 在alpha 结束之后, 每位同学写一篇个人博客, 总结自己的alpha 过程: 请用自我评价表:http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/p/3852177.html 有 ...
- C/C++掌握技能(一)
1.在编译器中输入代码并将其保存为.cpp文件(C语言的文件扩展名.c,但为了使用C++中的一些好用的特性,请把文件扩展名改为C++的.cpp)2.等价头文件:#include<stdio.h& ...
- Linux例行工作与系统管理(13)
Linux 系统的任务是由cron(crond)这个系统服务来控制的,Linux系统上面原本就有非常多的计划性工作,因此这个系统服务是默认启动的.另外,由于使用者自己也可以设置计划任务,所以Linux ...
- OSX10.12搭建IPv6本地环境测试APP
前记 最近刚换了工作,生活终于又安定下来了,又可以更博了 正文 最近公司在上线APP(整体全是用JS去写的,就用了我原生的一个控制器),然后APP就去上线,就被苹果巴巴给拒了.通过阅读苹果回复的邮件, ...
- Linux - DNF包管理
简介 link DNF(Dandified Yum)是新一代的RPM软件包管理器. DNF包管理器克服了YUM包管理器的一些瓶颈,提升了包括用户体验,内存占用,依赖分析,运行速度等多方面的内容. DN ...
- vue项目警告There are multiple modules with names that only differ in casing
执行npm run dev后出现了警告提示: warning in ./src/components/Public/yearSelectCell.vue There are multiple modu ...
- [原创]K8 Struts2 Exp 20170310 S2-045(Struts2综合漏洞利用工具)
工具: K8 Struts2 Exploit组织: K8搞基大队[K8team]作者: K8拉登哥哥博客: http://qqhack8.blog.163.com发布: 2014/7/31 10:24 ...
