TF之BN:BN算法对多层中的每层神经网络加快学习QuadraticFunction_InputData+Histogram+BN的Error_curve
# 23 Batch Normalization import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ACTIVATION = tf.nn.tanh
N_LAYERS = 7
N_HIDDEN_UNITS = 30 def fix_seed(seed=1):
# reproducible
np.random.seed(seed)
tf.set_random_seed(seed) def plot_his(inputs, inputs_norm):
# plot histogram for the inputs of every layer for j, all_inputs in enumerate([inputs, inputs_norm]):
for i, input in enumerate(all_inputs):
plt.subplot(2, len(all_inputs), j*len(all_inputs)+(i+1))
plt.cla()
if i == 0:
the_range = (-7, 10)
else:
the_range = (-1, 1)
plt.hist(input.ravel(), bins=15, range=the_range, color='#0000FF')
plt.yticks(())
if j == 1:
plt.xticks(the_range)
else:
plt.xticks(())
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
plt.title("%s normalizing" % ("Without" if j == 0 else "With"))
plt.title('Matplotlib,BN,histogram--Jason Niu')
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.001) def built_net(xs, ys, norm):
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None, norm=False):
# weights and biases (bad initialization for this case)
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size], mean=0., stddev=1.))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1) # fully connected product
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases # normalize fully connected product
if norm:
# Batch Normalize
fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments(
Wx_plus_b,
axes=[0], )
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([out_size]))
shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_size]))
epsilon = 0.001 # apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var)
mean, var = mean_var_with_update() Wx_plus_b = tf.nn.batch_normalization(Wx_plus_b, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon) # Wx_plus_b = (Wx_plus_b - fc_mean) / tf.sqrt(fc_var + 0.001) #进行BN一下
# Wx_plus_b = Wx_plus_b * scale + shift # activation
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs #输出激活结果 fix_seed(1) if norm:
# BN for the first input
fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments(
xs,
axes=[0],
)
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1]))
shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
epsilon = 0.001
# apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var)
mean, var = mean_var_with_update()
xs = tf.nn.batch_normalization(xs, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon) # record inputs for every layer
layers_inputs = [xs] # build hidden layers
for l_n in range(N_LAYERS):
layer_input = layers_inputs[l_n]
in_size = layers_inputs[l_n].get_shape()[1].value output = add_layer(
layer_input, # input
in_size, # input size
N_HIDDEN_UNITS, # output size
ACTIVATION, # activation function
norm, # normalize before activation
)
layers_inputs.append(output) # build output layer
prediction = add_layer(layers_inputs[-1], 30, 1, activation_function=None) cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
return [train_op, cost, layers_inputs] fix_seed(1)
x_data = np.linspace(-7, 10, 2500)[:, np.newaxis] #水平轴-7~10
np.random.shuffle(x_data)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 8, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 5 + noise xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) # [num_samples, num_features]
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) #建立两个神经网络作对比
train_op, cost, layers_inputs = built_net(xs, ys, norm=False)
train_op_norm, cost_norm, layers_inputs_norm = built_net(xs, ys, norm=True) sess = tf.Session()
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init) # record cost
cost_his = []
cost_his_norm = []
record_step = 5 plt.ion()
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 3))
for i in range(250):
if i % 50 == 0:
# plot histogram
all_inputs, all_inputs_norm = sess.run([layers_inputs, layers_inputs_norm], feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
plot_his(all_inputs, all_inputs_norm) # train on batch每一步都run一下
sess.run([train_op, train_op_norm], feed_dict={xs: x_data[i*10:i*10+10], ys: y_data[i*10:i*10+10]}) if i % record_step == 0:
# record cost
cost_his.append(sess.run(cost, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
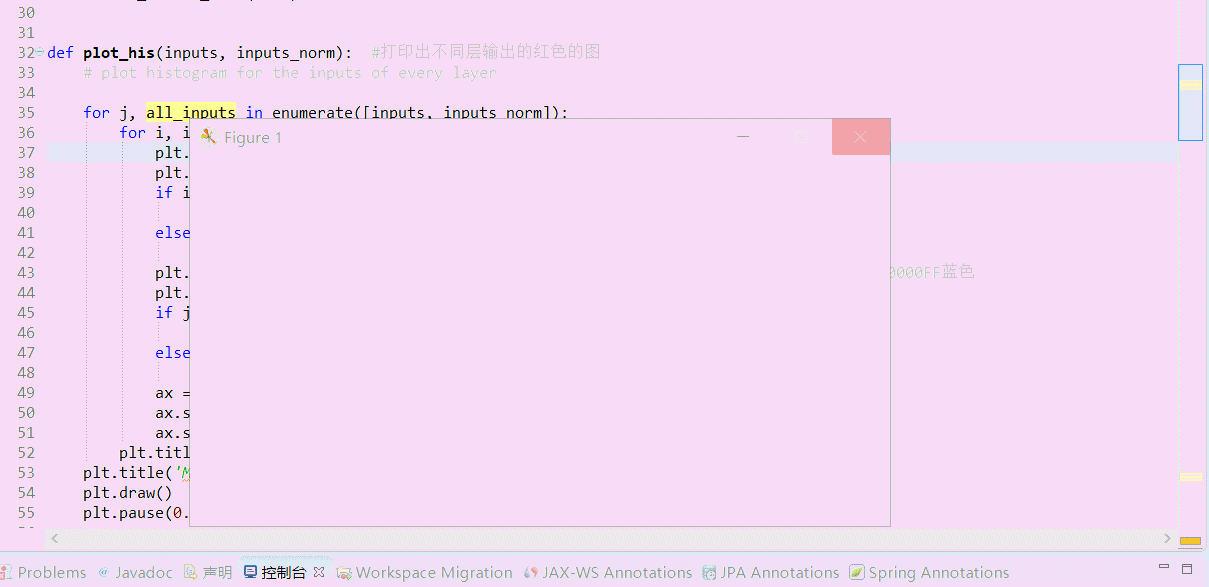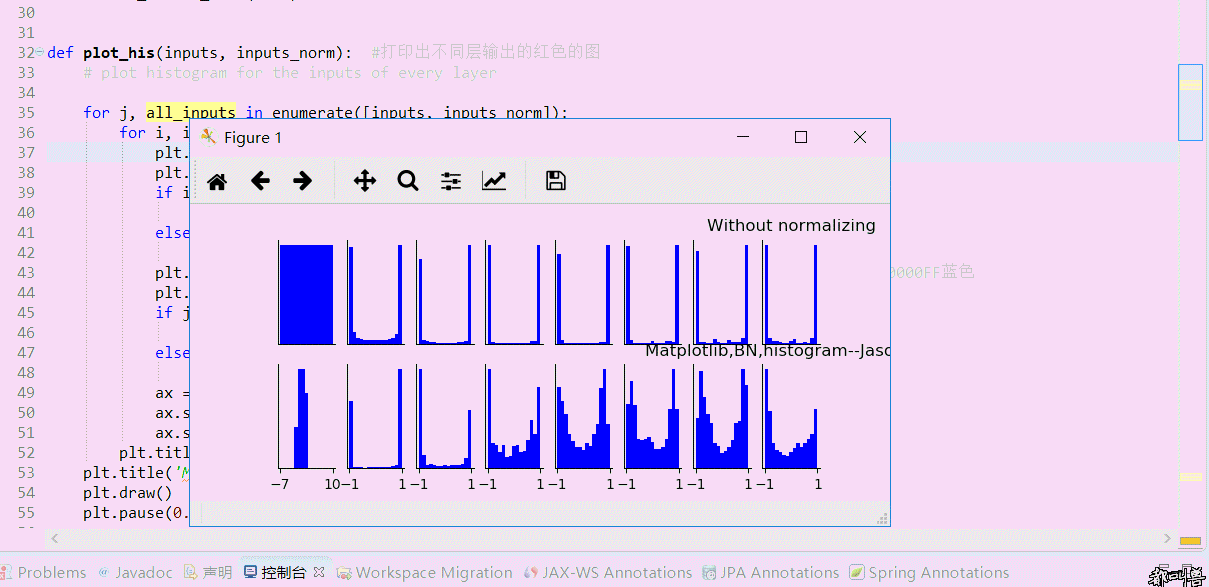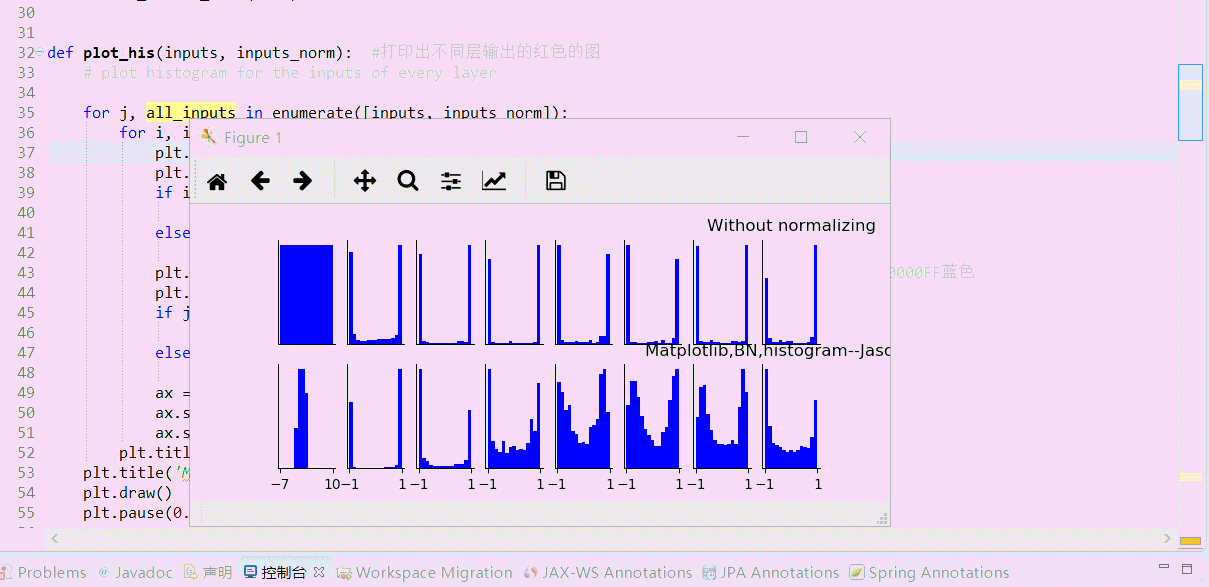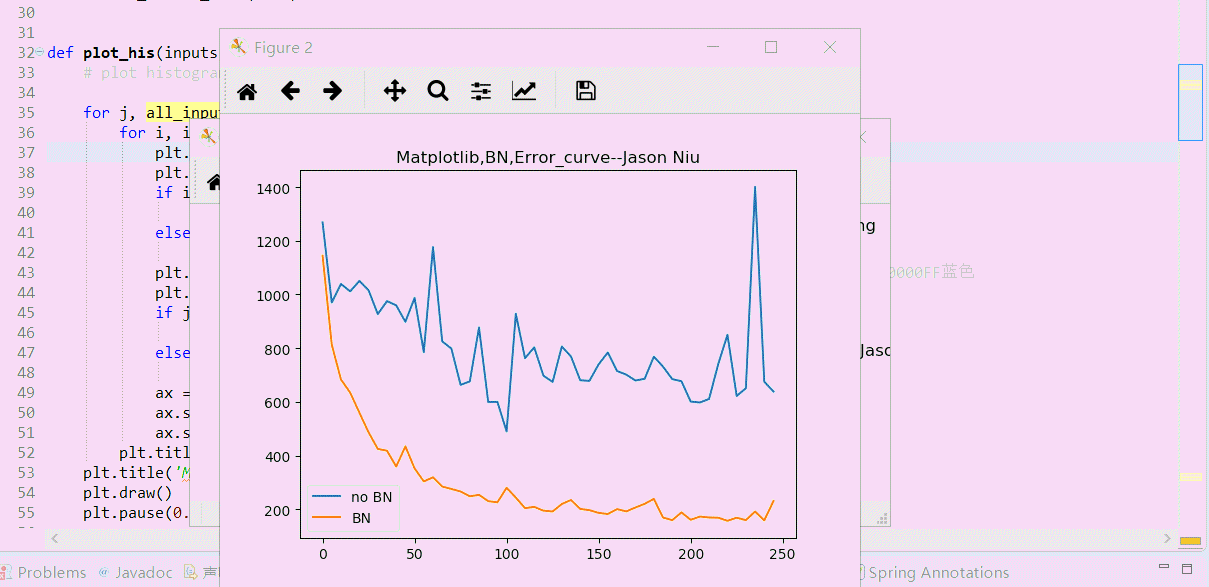
cost_his_norm.append(sess.run(cost_norm, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})) #以下是绘制误差值Cost误差曲线的方法
plt.ioff()
plt.figure()
plt.title('Matplotlib,BN,Error_curve--Jason Niu')
plt.plot(np.arange(len(cost_his))*record_step, np.array(cost_his), label='no BN') # no norm
plt.plot(np.arange(len(cost_his))*record_step, np.array(cost_his_norm), label='BN') # norm
plt.legend()
plt.show()
TF之BN:BN算法对多层中的每层神经网络加快学习QuadraticFunction_InputData+Histogram+BN的Error_curve的更多相关文章
- Batch Normalization的算法本质是在网络每一层的输入前增加一层BN层(也即归一化层),对数据进行归一化处理,然后再进入网络下一层,但是BN并不是简单的对数据进行求归一化,而是引入了两个参数λ和β去进行数据重构
Batch Normalization Batch Normalization是深度学习领域在2015年非常热门的一个算法,许多网络应用该方法进行训练,并且取得了非常好的效果. 众所周知,深度学习是应 ...
- 信息检索中的TF/IDF概念与算法的解释
https://blog.csdn.net/class_brick/article/details/79135909 概念 TF-IDF(term frequency–inverse document ...
- 深度学习归一化:BN、GN与FRN
在深度学习中,使用归一化层成为了很多网络的标配.最近,研究了不同的归一化层,如BN,GN和FRN.接下来,介绍一下这三种归一化算法. BN层 BN层是由谷歌提出的,其相关论文为<Batch No ...
- 任意半径局部直方图类算法在PC中快速实现的框架。
在图像处理中,局部算法一般来说,在很大程度上会获得比全局算法更为好的效果,因为他考虑到了图像领域像素的信息,而很多局部算法可以借助于直方图获得加速.同时,一些常规的算法,比如中值滤波.最大值滤波.最小 ...
- 06 - 从Algorithm 算法派生类中删除ExecuteInformation() 和ExecuteData() VTK 6.0 迁移
在先前的vtk中,如vtkPointSetAlgorithm 等算法派生类中定义了虚方法:ExecuteInformation() 和 ExecuteData().这些方法的定义是为了平稳的从VTK4 ...
- 1145: 零起点学算法52——数组中删数II
1145: 零起点学算法52--数组中删数II Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MB 64bit IO Format: %lldSubmitted: 293 ...
- KMP算法 --- 在文本中寻找目标字符串
KMP算法 --- 在文本中寻找目标字符串 很多时候,为了在大文本中寻找到自己需要的内容,往往需要搜索关键字.这其中就牵涉到字符串匹配的算法,通过接受文本和关键词参数来返回关键词在文本出现的位置.一般 ...
- 剑指Offer——算法复杂度中的O(logN)底数是多少
剑指Offer--算法复杂度中的O(logN)底数是多少 前言 无论是计算机算法概论.还是数据结构书中,关于算法的时间复杂度很多都用包含O(logN)这样的描述,但是却没有明确说logN的底数究竟是多 ...
- 机器学习算法中如何选取超参数:学习速率、正则项系数、minibatch size
机器学习算法中如何选取超参数:学习速率.正则项系数.minibatch size 本文是<Neural networks and deep learning>概览 中第三章的一部分,讲机器 ...
随机推荐
- Windows下Oracle 11g创建数据库
以前开发的时候用得比较多的是mysql和sql server,oracle用的比较少,用起来比较生疏,mysql和sql server用起来比较类似,就oracle的使用方式和他们不同,oracle在 ...
- Java的动手动脑(四)
日期:2018.10.18 星期四 博客期:019 Part1:回答为啥会报错 答案:当然会报错啦!因为平常的编程过程中,系统会对我们写的类自动生成一个默认无参形式的构造方法,类似于C++中的体制!这 ...
- 第八单元 正文处理命令及tar命令
使用cat命令进行文件的纵向合并 两种文件的纵向合并方法 归档文件和归档技术 归档的目的 什么是归档 tar命令的功能 tar命令的常用选项 使用tar命令创建.查看及抽取归档文件 使用tar命令 ...
- Java并发编程基础-线程安全问题及JMM(volatile)
什么情况下应该使用多线程 : 线程出现的目的是什么?解决进程中多任务的实时性问题?其实简单来说,也就是解决“阻塞”的问题,阻塞的意思就是程序运行到某个函数或过程后等待某些事件发生而暂时停止 CPU 占 ...
- Django知识点汇总
Python的WEB框架有Django.Tornado.Flask 等多种,Django相较与其他WEB框架其优势为:大而全,框架本身集成了ORM.模型绑定.模板引擎.缓存.Session等诸多功能. ...
- sass编写高质量的css---(基础语法结构)
一:基础1.Sass:最早也是最成熟的CSS预处理语言2.Less:兼容CSS的最流行的css预处理语言3.Stylus:主要用于node.js社区 二:scss写法1)混入@mixin alert( ...
- K8s-Pod控制器
在K8s-Pod文档中我们创建的Pod是非托管的Pod,因为Pod被设计为用后就弃的对象,如果Pod正常关闭,K8s会将该Pod清除,它没有自愈的能力.Pod控制器是用来保持Pod状态的一种对象资 ...
- Spring Cloud与Spring Boot版本匹配关系
Spring Cloud是什么? “Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common pat ...
- std::string 是什么
#include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <string> using std::cout; usi ...
- (原创)C# 压缩解压那些事儿
吐槽: 搜狗推广API的报告服务太坑爹了!!! 搜狗推广API的报告服务太坑爹了!!! 搜狗推广API的报告服务太坑爹了!!! 搜狗的太垃圾了,获取下来的压缩包使用正常方式无法解压!!没有专门的API ...
