ansible的剧本
ansible的playbook的介绍-yaml
ansible的playbook是使用yaml语言写的
YAML标记语言介绍
YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式。YAML参考了其他多种语言包括XML、C语言、Python、Perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等。Clark Evans在2001年在首次发表了这种语言另外Ingy dtNet与Oren Ben-Kiki也是这语言的共同设计者。
YAML Ain't Markup Language即YAML不是XML。不过在开发的这种语言时YAML的意思其实是"Yet Another Markup Language"仍是一种标记语言。其特性
YAML的可读性好
YAML和脚本语言的交互性好
YAML使用实现语言的数据类型
YAML有一个一致的信息模型
YAML易于实现
YAML可以基于流来处理
YAML表达能力强扩展性好
它的基本语法规则如下。
• 大小写敏感
• 使用缩进表示层级关系
• 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。
• 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
# 表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略。
yaml支持的数据类型
对象:
对象的一组键值对,使用冒号结构表示。
my_key: my_value
数组:
数据结构的子成员是一个数组,则可以在该项下面缩进一个空格
languages:
- python
- perl
- ruby
纯量
纯量是最基本的、不可再分的值
字符串
var: abc
布尔值
var: true
整数
var: 123
浮点数
var: 12.30
Null
var: ~
时间
time: 2001-12-14
日期
date 20:10:20
当需要执行的任务有多个时,需要一条一条编辑ansible命令,然后执行,而且当需要重复执行时,又要重新编辑执行,这样效率不高,因此ansible就可以利用playbook来完成将任务写到一个YAML格式的文件中,然后利用ansible-playbook进行调用该文件,从而实现了多条语句,可重复执行的效果,类似shell脚本的效果,ansible的playbook要借助YAML文件来实现,YAML文件扩展名通常为.yaml或.yml
使用playbook的基本命令格式
Usage: ansible-playbook [options] playbook.yml [playbook2 ...]
-C, --check 干跑一次 不会真正落地
-f FORKS 做高并发
--list-hosts 列出匹配的主机
--syntax-check 检查语法
playbook的基础组件
hosts:运行指定任务的目标主机,多个主机用:冒号分隔
remote_user:在远程主机上执行任务的用户;可以全局指定,也可以单个任务指定,如果是root用户执行可以不用写,默认是root
sudo_user:表示以sudo方式运行任务时,切换为哪个用户身份运行
tasks: 任务列表
使用palybook来管理被控机
1 创建剧本
编写ansible的剧本,创建yaml语言的文件,文件的位置可以任意,为了规范,好记,最好有一个单独的目录存放剧本
我创建了mkdir /palybook这个目录来存在剧本
:后缀名是.yaml 或 yml
[root@master ~]# vim p1.yml
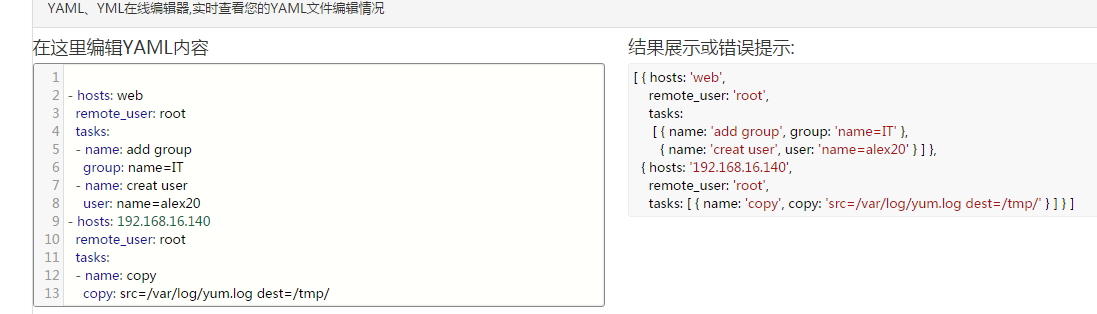
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group
group: name=IT
- name: creat user
user: name=alex20
- hosts: 192.168.16.140
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy
copy: src=/var/log/yum.log dest=/tmp/
文件翻译成python的语言的格式
文件的解释:
- hosts: web # 应用的主机 web是主机组
remote_user: root # 使用root来执行这个playbook
tasks: # 要执行的任务
- name: add group # 任务的名字,可以随意写
group: name=IT # group 是执行的模块名 后面是模块的参数
- name: creat user # 任务的名字
user: name=alex20 # 使用user模块创建用户 alex20
- hosts: 192.168.16.140 # 140这台主机执行下面的命令
remote_user: root # root用户执行
tasks: # 执行任务
- name: copy # 任务的名字
copy: src=/var/log/yum.log dest=/tmp/ # 使用copy模块来复制文件
p1.yml
执行playbook
1 测试p1.yml的语法是否正确
[root@master ~]#ansible-playbook --syntax-check p1.yml
2 测试执行
[root@master ~]# ansible-playbook --check p1.yml
3 运行
[root@master ~]# ansible-playbook p1.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group
group: name=IT
- name: creat user
user: name=alex20
- hosts: 192.168.16.140
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy
copy: src=/var/log/yum.log dest=/tmp/
[root@bogon palybook]# ansible-playbook p1.yml PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.138]
ok: [192.168.16.139] TASK [add group] ***************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.139]
ok: [192.168.16.138] TASK [creat user] **************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.139]
ok: [192.168.16.138] PLAY [192.168.16.140] ********************************************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.140] TASK [copy] ********************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.140] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.140 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
剧本局用幂等性 : 幂等性 不管执行多少次,等到的结果都是一样的
2 剧本的传参- 5种方式
编写playbook
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p2.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create{{user}}
user: name={{user}}
cat p2.yml
2.1 在命令行中使用-e 传参:
ansible-playbook -e user=alex21 p2.yml
PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.138]
ok: [192.168.16.139] TASK [createalex21] ************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.139]
changed: [192.168.16.138] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
ansible-playbook -e user=alex21 p2.yml
在web主机组上查看用户alex1创建成功
2.2 在hosts文件中实现传参
编写vim /etc/ansible/hosts文件
[web]
192.168.16.138 user=alex23
192.168.16.139 user=alex24
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
ansible-playbook p2.yml
PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.139]
ok: [192.168.16.138] TASK [createalex23] ************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.139]
changed: [192.168.16.138] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
ansible-playbook p2.yml
在被控节点发现在138上创建alex23
在被控节点发现在138上创建alex24
2.3 编写vim /etc/ansible/hosts文件
[web]
192.168.16.138
192.168.16.139
[web:vars]
user=alex25
ansible-playbook p2.yml
PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.138]
ok: [192.168.16.139] TASK [createalex25] ************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.138]
changed: [192.168.16.139] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
ansible-playbook p2.yml
在被控节点上创建alex25的用户
2.4 在palybook中传参
编写playbook
- hosts: web
vars:
- user: alex26
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create{{user}}
user: name={{user}}
ansible-playbook p2.yml
PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.139]
ok: [192.168.16.138] TASK [createalex26] ************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.139]
changed: [192.168.16.138] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
ansible-playbook p2.yml
在被控节点上创建 alex26
2.5 利用 register传参
使用registe之前先看一个例子
编写playbook. p3.yml
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p3.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: yum
yum: name=bc
- name: sum
shell: echo "4+2"| bc
register: he
- name: echo
shell: echo {{he}} > /tmp/sum.txt
cat p3.yml
在被控机上可以看到,是字典形式的,前面都有u 这是代表unicode
cat sum.txt
{stderr_lines: [], uchanged: True, uend: u2019-- ::59.209104, failed: False, ustdout: u6, ucmd:uecho "4+2"| bc, urc: , ustart: u2019-- ::59.204147, ustderr: u, udelta: u0::00.004957, stdout_lines: [u6]}
正确的写法:
编写playbook. p3.yml
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p3.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: yum
yum: name=bc
- name: sum
shell: echo "4+2"| bc
register: he
- name: echo
shell: echo {{he.stdout}} > /tmp/sum.txt
被控机:
[root@bogon tmp]# cat sum.txt
使用register创建用户alex27
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p4.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: yum
yum: name=bc
- name: sum
shell: echo "25+2"| bc
register: user
- name: add user{{user.stdout}}
user: name=alex{{user.stdout}}
cat p4.yml
ansible-playbook p4.yml
总结: 传参的优先级
-e > playbook > hosts 文件
3 使用tag
tag使用标记执行的模块的,可以选择单独执行某一个模块
现有 p5.yml 的文件,已知在被控节点上,已经安装好了,redis软件,如果我们执行copy模块来把主控节点的# ceshi
文件拷贝到被控节点上/etc/redis.conf上,
我们可以使用tag是执行copy 模块
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p5.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install redis
yum: name=redis
- name: copy
copy: src=/etc/redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf
- name: service redis start
service: name=redis state=started
具体的写法
1 我在节点的//etc/redis.conf 文件的最后添加了 # ceshi 来检验,copy模块是否成功
如果多个模块有tags标签,.想运行多个模块,可以用逗号将tags名字分开
ansible-playbook -t copyfile p5.yml
PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.139]
ok: [192.168.16.138] TASK [copy] ********************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.139]
changed: [192.168.16.138] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
ansible-playbook -t copyfile p5.yml
从运行的结果中可以看出只运行了 copy模块
在被控节点上:看到,说明copy成功
[root@bogon tmp]# tail -1 /etc/redis.conf
# ceshi
4 补充模块:setup
用来收集被控端主机的信息:
ansible 192.168.16.169 -m setup
192.168.16.138 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.16.138"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [],
"ansible_apparmor": {
"status": "disabled"
},
"ansible_architecture": "x86_64",
"ansible_bios_date": "07/31/2013",
"ansible_bios_version": "6.00",
"ansible_cmdline": {
"BOOT_IMAGE": "/vmlinuz-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64",
"LANG": "en_US.UTF-8",
"crashkernel": "auto",
"quiet": true,
"rd.lvm.lv": "centos/swap",
"rhgb": true,
"ro": true,
"root": "/dev/mapper/centos-root"
},
"ansible_date_time": {
"date": "2019-07-17",
"day": "",
"epoch": "",
"hour": "",
"iso8601": "2019-07-17T07:36:32Z",
"iso8601_basic": "20190717T153632604168",
"iso8601_basic_short": "20190717T153632",
"iso8601_micro": "2019-07-17T07:36:32.604252Z",
"minute": "",
"month": "",
"second": "",
"time": "15:36:32",
"tz": "CST",
"tz_offset": "+0800",
"weekday": "Wednesday",
"weekday_number": "",
"weeknumber": "",
"year": ""
},
"ansible_default_ipv4": {
"address": "192.168.16.138",
"alias": "eno16777736",
"broadcast": "192.168.16.255",
"gateway": "192.168.16.2",
"interface": "eno16777736",
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:ba:8f:d2",
"mtu": ,
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "192.168.16.0",
"type": "ether"
},
"ansible_default_ipv6": {},
"ansible_device_links": {
"ids": {
"dm-0": [
"dm-name-centos-root",
"dm-uuid-LVM-122vaa2zigMi2y4jShiO0EFiCfRG0imyrXbbOGLi9aszGNyoVKnK0m4fBF3NclZH"
],
"dm-1": [
"dm-name-centos-swap",
"dm-uuid-LVM-122vaa2zigMi2y4jShiO0EFiCfRG0imyiUq0NKSuO7SQHoEQMcGOaZ6JPI4yhzgR"
],
"sda2": [
"lvm-pv-uuid-vraMCf-JSqM-a2Uo-onaI-cVS5-3YJX-x5R6F2"
],
"sr0": [
"ata-VMware_Virtual_IDE_CDROM_Drive_10000000000000000001"
]
},
"labels": {
"sr0": [
"CentOS\\x207\\x20x86_64"
]
},
"masters": {
"sda2": [
"dm-0",
"dm-1"
]
},
"uuids": {
"dm-0": [
"47577089-a032-4e19-9648-878f5330e70d"
],
"dm-1": [
"a6a9dfb6-b70c-43bc-81c3-4281b8a8df46"
],
"sda1": [
"ae1ee2e5-f71c-4bb7-822e-01e5f145592e"
],
"sr0": [
"2015-12-09-23-14-10-00"
]
}
},
"ansible_devices": {
"dm-0": {
"holders": [],
"host": "",
"links": {
"ids": [
"dm-name-centos-root",
"dm-uuid-LVM-122vaa2zigMi2y4jShiO0EFiCfRG0imyrXbbOGLi9aszGNyoVKnK0m4fBF3NclZH"
],
"labels": [],
"masters": [],
"uuids": [
"47577089-a032-4e19-9648-878f5330e70d"
]
},
"model": null,
"partitions": {},
"removable": "",
"rotational": "",
"sas_address": null,
"sas_device_handle": null,
"scheduler_mode": "",
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": "",
"size": "17.47 GB",
"support_discard": "",
"vendor": null,
"virtual":
},
"dm-1": {
"holders": [],
"host": "",
"links": {
"ids": [
"dm-name-centos-swap",
"dm-uuid-LVM-122vaa2zigMi2y4jShiO0EFiCfRG0imyiUq0NKSuO7SQHoEQMcGOaZ6JPI4yhzgR"
],
"labels": [],
"masters": [],
"uuids": [
"a6a9dfb6-b70c-43bc-81c3-4281b8a8df46"
]
},
"model": null,
"partitions": {},
"removable": "",
"rotational": "",
"sas_address": null,
"sas_device_handle": null,
"scheduler_mode": "",
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": "",
"size": "2.00 GB",
"support_discard": "",
"vendor": null,
"virtual":
},
"fd0": {
"holders": [],
"host": "",
"links": {
"ids": [],
"labels": [],
"masters": [],
"uuids": []
},
"model": null,
"partitions": {},
"removable": "",
"rotational": "",
"sas_address": null,
"sas_device_handle": null,
"scheduler_mode": "deadline",
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": "",
"size": "4.00 KB",
"support_discard": "",
"vendor": null,
"virtual":
},
"sda": {
"holders": [],
"host": "",
"links": {
"ids": [],
"labels": [],
"masters": [],
"uuids": []
},
"model": "VMware Virtual S",
"partitions": {
"sda1": {
"holders": [],
"links": {
"ids": [],
"labels": [],
"masters": [],
"uuids": [
"ae1ee2e5-f71c-4bb7-822e-01e5f145592e"
]
},
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": ,
"size": "500.00 MB",
"start": "",
"uuid": "ae1ee2e5-f71c-4bb7-822e-01e5f145592e"
},
"sda2": {
"holders": [
"centos-root",
"centos-swap"
],
"links": {
"ids": [
"lvm-pv-uuid-vraMCf-JSqM-a2Uo-onaI-cVS5-3YJX-x5R6F2"
],
"labels": [],
"masters": [
"dm-0",
"dm-1"
],
"uuids": []
},
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": ,
"size": "19.51 GB",
"start": "",
"uuid": null
}
},
"removable": "",
"rotational": "",
"sas_address": null,
"sas_device_handle": null,
"scheduler_mode": "deadline",
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": "",
"size": "20.00 GB",
"support_discard": "",
"vendor": "VMware,",
"virtual":
},
"sr0": {
"holders": [],
"host": "",
"links": {
"ids": [
"ata-VMware_Virtual_IDE_CDROM_Drive_10000000000000000001"
],
"labels": [
"CentOS\\x207\\x20x86_64"
],
"masters": [],
"uuids": [
"2015-12-09-23-14-10-00"
]
},
"model": "VMware IDE CDR10",
"partitions": {},
"removable": "",
"rotational": "",
"sas_address": null,
"sas_device_handle": null,
"scheduler_mode": "cfq",
"sectors": "",
"sectorsize": "",
"size": "4.03 GB",
"support_discard": "",
"vendor": "NECVMWar",
"virtual":
}
},
"ansible_distribution": "CentOS",
"ansible_distribution_file_parsed": true,
"ansible_distribution_file_path": "/etc/redhat-release",
"ansible_distribution_file_variety": "RedHat",
"ansible_distribution_major_version": "",
"ansible_distribution_release": "Core",
"ansible_distribution_version": "",
"ansible_dns": {
"nameservers": [
"192.168.16.2"
]
},
"ansible_domain": "",
"ansible_effective_group_id": ,
"ansible_effective_user_id": ,
"ansible_eno16777736": {
"active": true,
"device": "eno16777736",
"features": {
"busy_poll": "off [fixed]",
"fcoe_mtu": "off [fixed]",
"generic_receive_offload": "on",
"generic_segmentation_offload": "on",
"highdma": "off [fixed]",
"large_receive_offload": "off [fixed]",
"loopback": "off [fixed]",
"netns_local": "off [fixed]",
"ntuple_filters": "off [fixed]",
"receive_hashing": "off [fixed]",
"rx_all": "off",
"rx_checksumming": "off",
"rx_fcs": "off",
"rx_vlan_filter": "on [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_offload": "on",
"rx_vlan_stag_filter": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_stag_hw_parse": "off [fixed]",
"scatter_gather": "on",
"tcp_segmentation_offload": "on",
"tx_checksum_fcoe_crc": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ip_generic": "on",
"tx_checksum_ipv4": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ipv6": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_sctp": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksumming": "on",
"tx_fcoe_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gre_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gso_robust": "off [fixed]",
"tx_ipip_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_lockless": "off [fixed]",
"tx_mpls_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_nocache_copy": "off",
"tx_scatter_gather": "on",
"tx_scatter_gather_fraglist": "off [fixed]",
"tx_sit_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp6_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp_ecn_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp_segmentation": "on",
"tx_udp_tnl_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_offload": "on [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_stag_hw_insert": "off [fixed]",
"udp_fragmentation_offload": "off [fixed]",
"vlan_challenged": "off [fixed]"
},
"hw_timestamp_filters": [],
"ipv4": {
"address": "192.168.16.138",
"broadcast": "192.168.16.255",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "192.168.16.0"
},
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:ba:8f:d2",
"module": "e1000",
"mtu": ,
"pciid": "0000:02:01.0",
"promisc": false,
"speed": ,
"timestamping": [
"tx_software",
"rx_software",
"software"
],
"type": "ether"
},
"ansible_env": {
"HOME": "/root",
"LANG": "en_US.UTF-8",
"LESSOPEN": "||/usr/bin/lesspipe.sh %s",
"LOGNAME": "root",
"MAIL": "/var/mail/root",
"PATH": "/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin",
"PWD": "/root",
"SHELL": "/bin/bash",
"SHLVL": "",
"SSH_CLIENT": "192.168.16.137 60835 22",
"SSH_CONNECTION": "192.168.16.137 60835 192.168.16.138 22",
"SSH_TTY": "/dev/pts/2",
"TERM": "xterm",
"USER": "root",
"XDG_RUNTIME_DIR": "/run/user/0",
"XDG_SESSION_ID": "",
"_": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"ansible_fibre_channel_wwn": [],
"ansible_fips": false,
"ansible_form_factor": "Other",
"ansible_fqdn": "bogon",
"ansible_hostname": "bogon",
"ansible_hostnqn": "",
"ansible_interfaces": [
"lo",
"eno16777736"
],
"ansible_is_chroot": false,
"ansible_iscsi_iqn": "",
"ansible_kernel": "3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64",
"ansible_lo": {
"active": true,
"device": "lo",
"features": {
"busy_poll": "off [fixed]",
"fcoe_mtu": "off [fixed]",
"generic_receive_offload": "on",
"generic_segmentation_offload": "on",
"highdma": "on [fixed]",
"large_receive_offload": "off [fixed]",
"loopback": "on [fixed]",
"netns_local": "on [fixed]",
"ntuple_filters": "off [fixed]",
"receive_hashing": "off [fixed]",
"rx_all": "off [fixed]",
"rx_checksumming": "on [fixed]",
"rx_fcs": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_filter": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_offload": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_stag_filter": "off [fixed]",
"rx_vlan_stag_hw_parse": "off [fixed]",
"scatter_gather": "on",
"tcp_segmentation_offload": "on",
"tx_checksum_fcoe_crc": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ip_generic": "on [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ipv4": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_ipv6": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksum_sctp": "off [fixed]",
"tx_checksumming": "on",
"tx_fcoe_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gre_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_gso_robust": "off [fixed]",
"tx_ipip_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_lockless": "on [fixed]",
"tx_mpls_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_nocache_copy": "off [fixed]",
"tx_scatter_gather": "on [fixed]",
"tx_scatter_gather_fraglist": "on [fixed]",
"tx_sit_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_tcp6_segmentation": "on",
"tx_tcp_ecn_segmentation": "on",
"tx_tcp_segmentation": "on",
"tx_udp_tnl_segmentation": "off [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_offload": "off [fixed]",
"tx_vlan_stag_hw_insert": "off [fixed]",
"udp_fragmentation_offload": "on",
"vlan_challenged": "on [fixed]"
},
"hw_timestamp_filters": [],
"ipv4": {
"address": "127.0.0.1",
"broadcast": "host",
"netmask": "255.0.0.0",
"network": "127.0.0.0"
},
"ipv6": [
{
"address": "::1",
"prefix": "",
"scope": "host"
}
],
"mtu": ,
"promisc": false,
"timestamping": [
"rx_software",
"software"
],
"type": "loopback"
},
"ansible_local": {},
"ansible_lsb": {},
"ansible_lvm": {
"lvs": {
"root": {
"size_g": "17.47",
"vg": "centos"
},
"swap": {
"size_g": "2.00",
"vg": "centos"
}
},
"pvs": {
"/dev/sda2": {
"free_g": "0.04",
"size_g": "19.51",
"vg": "centos"
}
},
"vgs": {
"centos": {
"free_g": "0.04",
"num_lvs": "",
"num_pvs": "",
"size_g": "19.51"
}
}
},
"ansible_machine": "x86_64",
"ansible_machine_id": "081f932dd7fb4b96a333f27e0f3928de",
"ansible_memfree_mb": ,
"ansible_memory_mb": {
"nocache": {
"free": ,
"used":
},
"real": {
"free": ,
"total": ,
"used":
},
"swap": {
"cached": ,
"free": ,
"total": ,
"used":
}
},
"ansible_memtotal_mb": ,
"ansible_mounts": [
{
"block_available": ,
"block_size": ,
"block_total": ,
"block_used": ,
"device": "/dev/sda1",
"fstype": "xfs",
"inode_available": ,
"inode_total": ,
"inode_used": ,
"mount": "/boot",
"options": "rw,relatime,attr2,inode64,noquota",
"size_available": ,
"size_total": ,
"uuid": "ae1ee2e5-f71c-4bb7-822e-01e5f145592e"
},
{
"block_available": ,
"block_size": ,
"block_total": ,
"block_used": ,
"device": "/dev/mapper/centos-root",
"fstype": "xfs",
"inode_available": ,
"inode_total": ,
"inode_used": ,
"mount": "/",
"options": "rw,relatime,attr2,inode64,noquota",
"size_available": ,
"size_total": ,
"uuid": "47577089-a032-4e19-9648-878f5330e70d"
}
],
"ansible_nodename": "bogon",
"ansible_os_family": "RedHat",
"ansible_pkg_mgr": "yum",
"ansible_proc_cmdline": {
"BOOT_IMAGE": "/vmlinuz-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64",
"LANG": "en_US.UTF-8",
"crashkernel": "auto",
"quiet": true,
"rd.lvm.lv": [
"centos/root",
"centos/swap"
],
"rhgb": true,
"ro": true,
"root": "/dev/mapper/centos-root"
},
"ansible_processor": [
"",
"GenuineIntel",
"Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4200M CPU @ 2.50GHz"
],
"ansible_processor_cores": ,
"ansible_processor_count": ,
"ansible_processor_threads_per_core": ,
"ansible_processor_vcpus": ,
"ansible_product_name": "VMware Virtual Platform",
"ansible_product_serial": "VMware-56 4d 95 3c 07 3c 26 00-1c 3c 27 56 a2 ba 8f d2",
"ansible_product_uuid": "564D953C-073C-2600-1C3C-2756A2BA8FD2",
"ansible_product_version": "None",
"ansible_python": {
"executable": "/usr/bin/python",
"has_sslcontext": true,
"type": "CPython",
"version": {
"major": ,
"micro": ,
"minor": ,
"releaselevel": "final",
"serial":
},
"version_info": [
,
,
,
"final",
]
},
"ansible_python_version": "2.7.5",
"ansible_real_group_id": ,
"ansible_real_user_id": ,
"ansible_selinux": {
"status": "disabled"
},
"ansible_selinux_python_present": true,
"ansible_service_mgr": "systemd",
"ansible_ssh_host_key_ecdsa_public": "AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBAIq8nwF4vJxd4021uQqf5zq97+bHlmOyMgre4fRvbfTqN0c04W8jI0Nekxw+l3cJh8nhefcAzAJjhbKebK7Ndc=",
"ansible_ssh_host_key_ed25519_public": "AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIBQ4Ae+rq830BkdOrn/FcZ3ZLhntv7nYPniwU4K7qmnH",
"ansible_ssh_host_key_rsa_public": "AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDoT4LU9LSj0whFKHRtdXL/Y9hgHCqafBn0LqPJy/Am+rXjHkGWmvC/JrhgYNk931vYiOT77KbreSpFEvumFAnr+MnyTVNnJuCLO7tgA9IvINF+Y/JwWoVobQj8vYIz0PBzDsiLSF8iGZyNcPQJFYjyh4cZqWSyo3PZxhghVIVjfcaZM9bVHvy2W7Vbh5GqCQRkkjEl5DkR+wlX+6t1MBRohTPms8VGbhpO4jI9YJtOcKGacjHoQN869Hk7X44sgPYgC41WTcJLmhba6Vkcx6z61wA0tKifvKODfMqm3VLiEOtL4Sb0oIu5Iw+VUYDEddQ8vJWRca4LjI8odsE92tDB",
"ansible_swapfree_mb": ,
"ansible_swaptotal_mb": ,
"ansible_system": "Linux",
"ansible_system_capabilities": [
"cap_chown",
"cap_dac_override",
"cap_dac_read_search",
"cap_fowner",
"cap_fsetid",
"cap_kill",
"cap_setgid",
"cap_setuid",
"cap_setpcap",
"cap_linux_immutable",
"cap_net_bind_service",
"cap_net_broadcast",
"cap_net_admin",
"cap_net_raw",
"cap_ipc_lock",
"cap_ipc_owner",
"cap_sys_module",
"cap_sys_rawio",
"cap_sys_chroot",
"cap_sys_ptrace",
"cap_sys_pacct",
"cap_sys_admin",
"cap_sys_boot",
"cap_sys_nice",
"cap_sys_resource",
"cap_sys_time",
"cap_sys_tty_config",
"cap_mknod",
"cap_lease",
"cap_audit_write",
"cap_audit_control",
"cap_setfcap",
"cap_mac_override",
"cap_mac_admin",
"cap_syslog",
"",
"36+ep"
],
"ansible_system_capabilities_enforced": "True",
"ansible_system_vendor": "VMware, Inc.",
"ansible_uptime_seconds": ,
"ansible_user_dir": "/root",
"ansible_user_gecos": "root",
"ansible_user_gid": ,
"ansible_user_id": "root",
"ansible_user_shell": "/bin/bash",
"ansible_user_uid": ,
"ansible_userspace_architecture": "x86_64",
"ansible_userspace_bits": "",
"ansible_virtualization_role": "guest",
"ansible_virtualization_type": "VMware",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python",
"gather_subset": [
"all"
],
"module_setup": true
},
"changed": false
}
ansible 192.168.16.138 -m setup
参数说明:
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses #ipv4的所有地址
ansible_all_ipv6_addresses #ipv6的所有地址
ansible_architecture #系统的架构
ansible_bios_date #bios的出厂时间
ansible_bios_version #bios的版本
ansible_date_time #系统时间
ansible_default_ipv4 #系统的默认ipv4地址
ansible_default_ipv6 #系统默认的ipv6地址
ansible_distribution #系统的名称
ansible_distribution_major_version #系统的主版本号
ansible_dns #系统dns
ansible_env #系统环境
ansible_kernel #系统内核版本
ansible_machine #系统架构
ansible_memtotal_mb #系统的内存大小
ansible_os_family #系统的家族
ansible_pkg_mgr #系统包的管理工具
ansible_nodename #系统主机名
ansible_processor_cores #每颗cpu上的核心数
ansible_processor_count #cpu的颗数
ansible_processor_vcpus #cpu的总数= 颗数*核数
ansible_python #python版本
ansible_system #系统
5 template模块补充
template 和copy的模块的功能一样 ,都是向远程主机上传送文件的,可以copy是送的是原封不动的文件,template 可以将文件中的变量渲染出来
现有如下的文件,我们想把/etc/redis.conf 文件 传到远程的主机上,但/etc/redis.conf 问bind 的ip 是远程主机的ip,这时需要使用 template
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p5.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy
copy: src=/etc/redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf
- name: service redis start
service: name=redis state=started
看主机的ip
ansible 192.168.16.139 -m setup -a "filter=*ipv4*"
192.168.16.139 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.16.139"
],
"ansible_default_ipv4": {
"address": "192.168.16.139",
"alias": "eno16777736",
"broadcast": "192.168.16.255",
"gateway": "192.168.16.2",
"interface": "eno16777736",
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:aa:b6:83",
"mtu": ,
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "192.168.16.0",
"type": "ether"
},
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
来编写主节点的/etc/redis.conf文件:
bind {{ansible_default_ipv4.address}}
主节点的剧本
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p5.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy
template: src=/etc/redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf
- name: service redis start
service: name=redis state=started
ansible-playbook p5.yml
在被控节点上会看到grep bind /etc/redis.conf bind变成自己的主机ip了
bind 192.168.16.138
注意
在传输文件的时候src可以写相对路径和绝对路径
在写相对路径的时候,需要跟playbook文件同级创建templates目录
playbook的文件里写
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: yum
yum: name=redis
- name: copyfile
template: src=redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf
tags: copyfile
- name: start
service: name=redis state=started
跟playbook文件同级创建templates目录
6 Handlers: 在发生改变时执行的操作(类似puppet通知机制)
在Handlers:默认是不执行的,当遇到notify 才执行,当notify 里面的内容改变了,才会触发handlers执行
[root@bogon palybook]# cat p5.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy
template: src=/etc/redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf
notify: restart
- name: service redis start
service: name=redis state=started
handlers:
- name: restart
service: name=redis state=restarted
ansible-playbook p5.yml
PLAY [web] ********************************************************************************************* TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.138]
ok: [192.168.16.139] TASK [copy] ********************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.139]
changed: [192.168.16.138] TASK [service redis start] *****************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.16.138]
ok: [192.168.16.139] RUNNING HANDLER [restart] ******************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.16.139]
changed: [192.168.16.138] PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.16.138 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
192.168.16.139 : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
7 when
条件判断
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: context
copy: content="大弦嘈嘈如急雨" dest=/tmp/shi.txt
when: ansible_distribution_major_version==""
- name: context
copy: content="小弦切切如私语" dest=/tmp/shi.txt
when: ansible_distribution_major_version=="" - hosts: web
tasks:
- name: context
copy: content="大弦嘈嘈如急雨" dest=/tmp/shi.txt
when: user==""
- name: context
copy: content="小弦切切如私语" dest=/tmp/shi.txt
when: user==""
ansible-playbook -e user= p13.yml
8 循环
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: createuser
user: name={{item}}
with_items:
- alex40
- alex41
- alex42
- alex43
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: createuser
user: name={{item}}
with_items:
- alex50
- alex51
- alex52
- alex53
- name: creategroup
group: name={{item}}
with_items:
- wusir50
- wusir51
- wusir52
创建alex60 61 62 63 用户,组分别是 wusir60 61 62 63
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: creategroup
group: name={{item}}
with_items:
- wusir60
- wusir61
- wusir62
- wusir63
- name: createuser
user: name={{item.name}} group={{item.group}}
with_items:
- {"name":"alex60","group":"wusir60"}
- {"name":"alex61","group":"wusir61"}
- {"name":"alex62","group":"wusir62"}
- {"name":"alex63","group":"wusir63"}
==================================================
php.ini
时区
on66
部署rpm包的lamp环境
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: install mysql-server
yum: name=mysql-server state=present
- name: install php
yum: name=php state=present
- name: httpd conf
copy: src=/home/ansible/file/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf mode=644
- name: mysql conf
copy: src=/home/ansible/file/my.cnf dest=/etc/my.cnf mode=644
- name: php conf
copy: src=/home/ansible/file/php.ini dest=/etc/php.ini mode=644
notify:
- start mysql
- start httpd
- name: service status
shell: netstat -anplt | grep -E '(mysqld|httpd)' > /tmp/lamp.status
- name: get lamp.status
fetch: src=/tmp/lamp.status dest=/tmp/
- name: test page
copy: src=/home/ansible/file/test.html dest=/var/www/html/test.html
handlers:
- name: start mysql
service: name=mysqld state=started
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
=============================================
变量使用
常用的变量一般就两种
一种为用户自己定义的变量
一种为facts获取的变量(即ansible webserver -m setup查到的变量)
#ansible webserver -m setup //获取webserver信息
一自定义变量
1.用户在.yml文件自定义变量
示例:
[root@master ansible]# vim /home/ansible/1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
vars:
- var1: "abc"
- var2: 123
tasks:
- name: test vars
shell: echo "{{ var1 }} {{ var2 }}" >> /tmp/var.txt
[root@master ansible]# vim /home/ansible/1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
vars:
- packname: "nmap"
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ packname }} state=present
2.通过-e参数传递的变量
[root@master ansible]# ansible-playbook 1.yml -e packname=nmap
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ packname }} state=present
3.通过主机或者主机组配置文件传递的变量
主机:
[root@master ansible]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
192.168.10.201 packname=nmap
192.168.10.202 packname=nmap
[root@master ansible]# ansible-playbook 1.yml
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ packname }} state=present
主机组
[root@master ansible]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
192.168.10.201
192.168.10.202
[webserver:vars]
packname=nmap
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ packname }} state=present
二.通过facts获取的系统的变量
即ansible webserver -m setup查到的变量
1.获取系统变量
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: hostname ipaddrss
shell: echo "{{ ansible_nodename}} {{ ansible_all_ipv4_addresses }}" > /tmp/facts.txt
- name: fetch file /tmp/facts
fetch: src=/tmp/facts.txt dest=/tmp
[root@master ansible]# cat /tmp/192.168.10.202/tmp/facts.txt
agent202.puppet.com [u'192.168.10.202']
2.本地facts(facts.d)自定义系统变量
客户端定义
在管控端创建如下目录:
[root@agent202 ~]# mkdir -p /etc/ansible/facts.d
创建文件:
[root@agent202 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/facts.d/test.fact
[general]
test_test1=123
test_test2=abc
[root@master ansible]# ansible webserver -m setup |grep ansible_local -A 5 //-C 5 上下5行
"ansible_local": {
"test": {
"general": {
"test_test1": "123",
"test_test2": "abc"
}
}
}
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test
shell: echo "{{ ansible_local.test.general.test_test1 }} {{ ansible_local.test.general.test_test2 }}" > /tmp/facts.txt
- name: fetch file /tmp/facts
fetch: src=/tmp/facts.txt dest=/tmp
[root@master ansible]# cat /tmp/192.168.10.202/tmp/facts.txt
123 abc
变量注册:
经常在playbook中,存储某个命令的结果在变量中,以备日后访问是很有用的. 这样使用命令模块可以在许多方面除去写站(site)特异事件,据哥例子 你可以检测某一个特定程序是否存在
这个 ‘register’ 关键词决定了把结果存储在哪个变量中
经常在playbook中,存储某个命令的结果在变量中,以备日后访问是很有用的. 这样使用命令模块可以在许多方面除去写站(site)特异事件,据哥例子 你可以检测某一个特定程序是否存在
这个 ‘register’ 关键词决定了把结果存储在哪个变量中
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: user root
shell: grep ^root /etc/passwd
register: pass_contents
- name: call pass_contents
shell: echo {{ pass_contents.stdout }} > /tmp/call.txt
如想查看那些值可以引用
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: user root
shell: grep ^root /etc/passwd
register: pass_contents
- name: call pass_contents
shell: echo {{ pass_contents }} > /tmp/call.txt
[root@agent202 ~]# cat /tmp/call.txt
{uchanged: True, uend: u2016-11-03 22:31:09.754515, ustdout: uroot:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash, ucmd: ugrep ^root /etc/passwd, ustart: u2016-11-03 22:31:09.750428, udelta: u0:00:00.004087, ustderr: u, urc: 0, stdout_lines: [uroot:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash], uwarnings: []}
剧本中的条件判断
ansible和puppet软件相同 是可以支持条件判断,使用when语句
如:
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package nmap
yum: name=nmap state=present
when: ansible_nodename == "agent202.puppet.com"
- name: install package httpd
yum: name=nmap state=present
when: ansible_nodename == "agent201.puppet.com"
使用注册变量
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: package is install
shell: rpm -q httpd|awk -F'-' '{print $1}'
register: httpd_install
- name: test httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
when: httpd_install.stdout == 'httpd'
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: mysql user
shell: grep ^mysql /etc/passwd | awk -F':' '{print $1}'
register: mysql_install
- name: test mysqld service
service: name=mysqld state=restarted
when: mysql_install.rc == 0
剧本中的循环
如:添加 abc1-abc3用户
[root@master ansible]# cat 1.yml
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add new users
user: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- abc1
- abc2
- abc3
剧本中的roles
你现在已经学过 tasks 和 handlers,那怎样组织 playbook 才是最好的方式呢?简单的回答就是:使用 roles ! Roles 基于一个已知的文件结构,去自动的加载某些 vars_files,tasks 以及 handlers。基于 roles 对内容进行分组,使得我们可以容易地与其他用户分享 roles 。
存放角色的位置:/etc/ansible/roles
如
roles/
common/ # this hierarchy represents a "role" 这里的结构代表了一个 "role"
tasks/ #
main.yml # <-- tasks file can include smaller files if warranted
handlers/ #
main.yml # <-- handlers file
templates/ # <-- files for use with the template resource
ntp.conf.j2 # <------- templates end in .j2
files/ #
bar.txt # <-- files for use with the copy resource
foo.sh # <-- script files for use with the script resource
vars/ #
main.yml # <-- variables associated with this role
defaults/ #
main.yml # <-- default lower priority variables for this role
meta/ #
main.yml # <-- role dependencies
apache/
common/
files/ 存放模块调用的文件(如:copy 和 script)
templates/ 存放模板文件
tasks/ 任务存放的目录,至少包含一个main.yml的文件,该目录下也可以有其他.yml文件,但是需要在main.yml文件中用include指令将其他.yml文件包含进来(类似 puppet)
handlers/ 存放相关触发执行器的目录,至少应该包含一个main.yml的文件,文件中定义了触发器的任务清单,该目录下也可以有其他.yml文件,但是需要在main.yml文件中用include指令将其他.yml文件包含进来
vars/ 变量存放的目录,至少应该包含一个main.yml的文件,文件中定义了相关的变量及其值,该目录下也可以有其他.yml文件,但是需要在main.yml文件中用include指令将其他.yml文件包含进来
defaults/ 默认变量存放的目录,至少应该包含一个main.yml的文件,文件中定义了此角色使用的默认变量,该目录下也可以有其他.yml文件,但是需要在main.yml文件中用include指令将其他.yml文件包含进来
meta/ 用于存放此角色元数据,至少应该包含一个main.yml的文件,文件中定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系, 该目录下也可以有其他.yml文件,但是需要在main.yml文件中用include指令将其他.yml文件包含进来
如何调用定义的角色?
- hosts: webserver
remote_user: root
roles:
- apache
创建一个测试roles
1.创建角色的目录结构
mkdir -pv /etc/ansible/roles/apache/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,default,meta}
2.定义任务:
[root@master ansible]# vim /etc/ansible/roles/apache/tasks/main.yml
[root@master tasks]# cat /etc/ansible/roles/apache/tasks/main.yml
- name: install apache
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: get main configure file
template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- name: get sub configure file
template: src=robin.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/robin.conf
- name: create robin dir
file: path=/srv/robin state=directory
- name: get web page
template: src=index.html.j2 dest=/var/www/html/index.html
notify:
- restart apache
3.触发器任务:
[root@master tasks]# cat /etc/ansible/roles/apache/handlers/main.yml
- name: start apache
service: name=httpd state=present
4.准备需要的文件
[root@master files]# ls /etc/ansible/roles/apache/templates
httpd.conf.j2 index.html.j2 robin.conf.j2
ansible的剧本的更多相关文章
- Ansible yaml 剧本(傻瓜式)
优化ansible安装MySQL: Ansible部署MySQL编译安装 - xiao智 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) Ansible yaml 剧本(傻瓜式): --- - hosts: ...
- 2.Ansible Playbook剧本
1.playbook?playbook翻译过来就是"剧本",那playbook组成如下 play: 定义的是主机的角色 task: 定义的是具体执行的任务 playbook: 由一 ...
- ansible的剧本play(四)
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAA68AAAETCAYAAADZDzDOAAAAAXNSR0IArs4c6QAAAARnQU1BAACxjw
- ansible批量管理软件部署及剧本
服务器版本信息: Centos6.9 [root@db02 ~]# uname -a Linux db02 -.el6.x86_64 # SMP Tue Mar :: UTC x86_64 x86_6 ...
- ansible服务及剧本编写
第1章 ansible软件概念说明 python语言是运维人员必会的语言,而ansible是一个基于Python开发的自动化运维工具 (saltstack).其功能实现基于SSH远程连接服务:ansi ...
- ansible 剧本
ansible的管理与剧本 首先我们安装一个ansible. 在7版本,直接用yum安装就可以 yum -y install ansible 然后清空ansible的配置文件,在里面写入自己需要管 ...
- ansible的管理与剧本
首先我们安装一个ansible. 在7版本,直接用yum安装就可以 yum -y install ansible 然后清空ansible的配置文件,在里面写入自己需要管理的服务器的ip和相应的登陆密码 ...
- Linux中ansible批量管理软件部署及剧本编写
服务器版本信息: Centos6.9 [root@db02 ~]# uname -a Linux db02 2.6.32-696.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue Mar 21 19:29: ...
- 剧本--ansible
剧本不喜欢, 1.1 编写剧本规范:(PYyaml语法格式文件) 剧本中有层级划分 每个层级都要用两个空格进行区分 第一级标题 第二级标题 第三级标题 强调注意:一定使用ansible软件配置剧本时, ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot 中aop整合方法执行日志
今天事情不多, 处理完手中的事边想着捣鼓一下AOP, 着手开始写才发现, 多久不用, 自己已经忘得差不多了, 捣鼓半天之后, 慢慢整出这个小demo,以便于以后查阅回顾 1 .先创建一个注解, 用来作 ...
- JS实现旋转的魔方
js <script> window.onload = function () { let cube = document.querySelector('.cube') let timer ...
- VScode 配置为 LaTeX 编辑器(IDE)
VScode 配置为 LaTeX IDE 在Windows中,配置VScode作为LaTeX的编辑器(IDE),并使用SumatraPDF预览PDF文件.主要是LaTeX Workshop扩展的设置, ...
- etcd安装和简单使用
etcd作为一个高可用强一致性的服务发现存储仓库,在Kubernetes等开源项目中用的很多,这里简单记录下安装和常用命令以及api 安装 安装包可以从 https://github.com/etcd ...
- 10_Redis_多数据库
一:概念: 一个Redis实例可以包括多个数据库,客户端可以指定连接某个redis实例的哪个数据库,就好比一个mysql中创建多个数据库,客户端连接时指定连接哪个数据库. 一个Redis实例最多可提供 ...
- String特性之 “字符串驻留池”
1. 字符串驻留池,就是一块与堆区并行的存放字符串对象的内存区,JVM的驻留池机制规定: 在池中创建一个String对象,第二行会先在池中寻找是否有值与"abc"相同的String ...
- 一图一知-TS之symbol
- Android基础相关面试问题-activity面试问题(生命周期,任务栈,启动模式,跳转协议,启动流程)
关于Android的一些面试题在15年就已经开了这个专栏了,但是一直木有坚持收集,而每次面对想要跳槽时大脑一片空白,也有些恐惧,因为毕境面试都是纯技术的沟通,要想让公司对你的技术能有所认可会全方位的进 ...
- UESTC 2016 Summer Training #1 J - Objects Panel (A) 按条件遍历树
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> using namespace std; typed ...
- FirstWriting
在很久很久以前,你拥有我我拥有你 <外面的世界> 在很久很久以前我就有搞一个类似博客的东西的想法,不过一直都没有尝试着搞-- 某天(10号左右吧)刷知乎看到github和hexo可以搭建博 ...
