Mininet系列实验(四):基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率
1 实验目的
熟悉Mininet自定义拓扑脚本的编写与损耗率的设定;
熟悉编写POX脚本,测量路径损耗速率
2 实验原理
在SDN环境中,控制器可以通过对交换机下发流表操作来控制交换机的转发行为,此外,还可以利用控制器测量路径的损耗率。在本实验中,基于Mininet脚本,设置特定的交换机间的路径损耗速率,然后编写POX脚本,实现对路径的损耗率的测量
3 实验内容
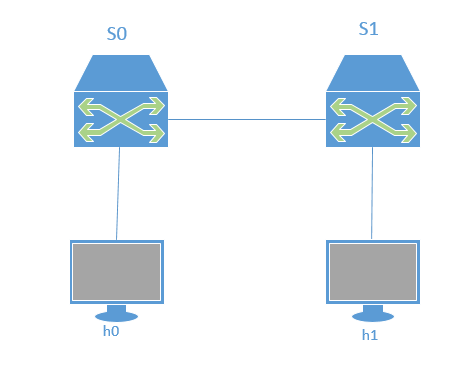
这是本实验的拓扑图,在该环境下,h0向h1发送数据包,由于在mininet脚本中设置了连接损耗率,在传输过程中会丢失一些包,本次实验的目的是展示如何通过控制器计算路径损耗速率(h0-s0-s1-h1)。这里假设控制器预先知道网络拓扑,所以没有显示发现网络的代码以及其他相关代码。控制器将向s0和s1发送flow_stats_request,当控制器接收到来自s0的response时,将特定流的数据包数保存在input_pkts中,当控制器接收到来自s1的response时,将接收到特定流的数据包数保存在output_pkts中,差值就是丢失的数据包数量。
搭建环境:本实验需要安装POX和支持OpenFlow1.3协议的Mininet。POX的安装教程如下:
Https://blog.csdn.net/shallynever/article/details/48522941
关于python中的logging以及相关函数的使用说明:
https://www.jb51.net/article/126681.htm
1.1 在装有mininet的虚拟机上创建脚本mymininet.py
cd mininet gedit mymininet.py
1.2 编辑脚本(稍微解释了一下)
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
# 调用关于mininet和time的一些模块
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.node import Node
from mininet.link import TCLink
from mininet.log import setLogLevel, info
from threading import Timer
from mininet.util import quietRun
from time import sleep
#定义mynet函数
def myNet(cname='controller', cargs='-v ptcp:'):
#通过使用OVS抓取来创建网络
#诊断信息然后开始创建节点,其中有控制器C0和交换机s0,s1,还有主机h0,h1
info( "*** Creating nodes\n" )
controller = Node( 'c0', inNamespace=False )
switch = Node( 's0', inNamespace=False )
switch1 = Node( 's1', inNamespace=False )
h0 = Node( 'h0' )
h1 = Node( 'h1' )
#诊断以后开始创建链路(这一块不是很懂)
info( "*** Creating links\n" )
#这是链路选项设置,丢包以及延迟还有带宽等等
linkopts0=dict(bw=100, delay='1ms', loss=0)
linkopts1=dict(bw=100, delay='1ms', loss=10)
#链路0,1,2分别表示h0和s0,s0和s1,h1和s1的链路并调用以上两行的参数
link0=TCLink( h0, switch, **linkopts0)
link1 = TCLink( switch, switch1, **linkopts1)
link2 = TCLink( h1, switch1, **linkopts0)
#MAC地址设置:按照拓扑图来设置的,这一块有些不理解,个人理解为,链路0,2只需要设置一个能连上
#s0/s1的端口就行,而1需要左边的s0端口和右边的s1端口
link0.intf2.setMAC("0:0:0:0:0:1")
link1.intf1.setMAC("0:0:0:0:0:2")
link1.intf2.setMAC("0:1:0:0:0:1")
link2.intf2.setMAC("0:1:0:0:0:2")
#诊断后设置主机ip
info( "*** Configuring hosts\n" )
h0.setIP( '192.168.123.1/24' )
h1.setIP( '192.168.123.2/24' )
#通过使用OVS开始网络连接,然后单引号里的意思是搭建和删除桥梁
info( "*** Starting network using Open vSwitch\n" )
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp0' )
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-br dp0' )
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp1' )
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-br dp1' )
#控制器的设置不是很懂
controller.cmd( cname + ' ' + cargs + '&' )
#打印出每个交换机的链路信息
for intf in switch.intfs.values():
print intf
print switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-port dp0 %s' % intf )
for intf in switch1.intfs.values():
print intf
print switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl add-port dp1 %s' % intf )
# 控制器和交换机同属根命名空间所以我们可以通过环回接口连接,对了,10.0.0.13是别的up主的主机
# ip,需要用自己的,因为控制器是你自己的
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl set-controller dp0 tcp:10.0.0.13:6633' )
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl set-controller dp1 tcp:10.0.0.13:6633' )
#诊断并等待交换机连接上控制器,在连接完成前会一秒一个点
info( '*** Waiting for switch to connect to controller' )
while 'is_connected' not in quietRun( 'ovs-vsctl show' ):
sleep( 1 )
info( '.' )
info( '\n' )
#运行测试20次h0和h1的传输情况
#info( "*** Running test\n" )
h0.cmdPrint( 'ping -Q 0x64 -c 20 ' + h1.IP() )
#休息一秒后关闭网络:删除“桥梁”
sleep( 1 )
info( "*** Stopping network\n" )
controller.cmd( 'kill %' + cname )
switch.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp0' )
switch.deleteIntfs()
switch1.cmd( 'ovs-vsctl del-br dp1' )
switch1.deleteIntfs()
info( '\n' )
#主函数,看不懂,意思应当是如果是个主函数就设定info的等级然后开始获取网络demo然后运行
#mynet()函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
setLogLevel( 'info' )
info( '*** Scratch network demo (kernel datapath)\n' )
Mininet.init()
myNet()
2.1 我们在pox文件里面创建脚本
cd pox gedit flow_stats.py
2.2 编辑脚本 (中文部分是对程序的解释,未翻译部分是对具体代码的代码解释)
#!/usr/bin/python
# Copyright 2012 William Yu
# wyu@ateneo.edu
#
# This file is part of POX.
#
# POX is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# POX is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with POX. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
#
"""
This is a demonstration file created to show how to obtain flow
and port statistics from OpenFlow 1.0-enabled switches. The flow
statistics handler contains a summary of web-only traffic.
"""
# standard includes
from pox.core import core
from pox.lib.util import dpidToStr
import pox.openflow.libopenflow_01 as of
from pox.lib.addresses import IPAddr, EthAddr
# include as part of the betta branch
from pox.openflow.of_json import *
from pox.lib.recoco import Timer
import time
log = core.getLogger()
#初始化网络的参数0
src_dpid = 0
dst_dpid = 0
input_pkts = 0
output_pkts = 0
def getTheTime():
#设定当地时间的函数
flock = time.localtime()
then = "[%s-%s-%s" %(str(flock.tm_year),str(flock.tm_mon),str(flock.tm_mday))
if int(flock.tm_hour)<10:
hrs = "0%s" % (str(flock.tm_hour))
else:
hrs = str(flock.tm_hour)
if int(flock.tm_min)<10:
mins = "0%s" % (str(flock.tm_min))
else:
mins = str(flock.tm_min)
if int(flock.tm_sec)<10:
secs = "0%s" % (str(flock.tm_sec))
else:
secs = str(flock.tm_sec)
then +="]%s.%s.%s" % (hrs,mins,secs)
return then
# 用于将请求发送到连接到控制器的所有交换机的定时器功能的处理程序
def _timer_func ():
for connection in core.openflow._connections.values():
connection.send(of.ofp_stats_request(body=of.ofp_flow_stats_request()))
connection.send(of.ofp_stats_request(body=of.ofp_port_stats_request()))
log.debug("Sent %i flow/port stats request(s)", len(core.openflow._connections))
# 显示在事件的JSON格式结构中接收到的流统计信息的处理程序由ofp_flow_stats()定义
def _handle_flowstats_received (event):
#stats = flow_stats_to_list(event.stats)
#log.debug("FlowStatsReceived from %s: %s", dpidToStr(event.connection.dpid), stats)
global src_dpid, dst_dpid, input_pkts, output_pkts
#print "src_dpid=", dpidToStr(src_dpid), "dst_dpid=", dpidToStr(dst_dpid)
for f in event.stats:
if f.match.dl_type==0x0800 and f.match.nw_dst==IPAddr("192.168.123.2") and f.match.nw_tos==0x64 and event.connection.dpid==src_dpid:
#print "input: ", f.byte_count, f.packet_count
input_pkts = f.packet_count
if f.match.dl_type==0x0800 and f.match.nw_dst==IPAddr("192.168.123.2") and f.match.nw_tos==0x64 and event.connection.dpid==dst_dpid:
#print "output: ", f.byte_count, f.packet_count
output_pkts = f.packet_count
if input_pkts !=0:
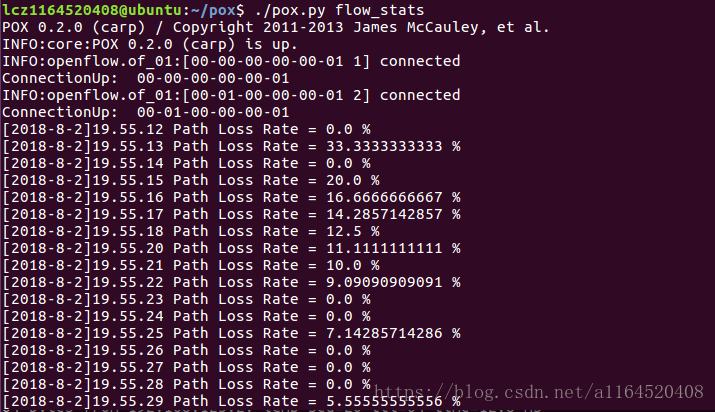
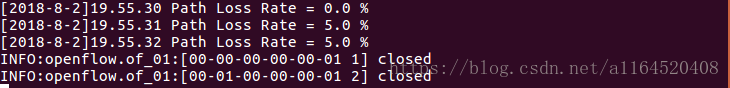
print getTheTime(), "Path Loss Rate =", (input_pkts-output_pkts)*1.0/input_pkts*100, "%"
# 处理程序以显示JSON格式接收的端口统计信息
def _handle_portstats_received (event):
#print "\n<<<STATS-REPLY: Return PORT stats for Switch", event.connection.dpid,"at ",getTheTime()
#for f in event.stats:
#if int(f.port_no)<65534:
#print " PortNo:", f.port_no, " Fwd's Pkts:", f.tx_packets, " Fwd's Bytes:", f.tx_bytes, " Rc'd Pkts:", f.rx_packets, " Rc's Bytes:", f.rx_bytes
#print " PortNo:", f.port_no, " TxDrop:", f.tx_dropped, " RxDrop:", f.rx_dropped, " TxErr:", f.tx_errors, " RxErr:", f.rx_errors, " CRC:", f.rx_crc_err, " Coll:", f.collisions
stats = flow_stats_to_list(event.stats)
log.debug("PortStatsReceived from %s: %s", dpidToStr(event.connection.dpid), stats)
def _handle_ConnectionUp (event):
global src_dpid, dst_dpid
print "ConnectionUp: ", dpidToStr(event.connection.dpid)
for m in event.connection.features.ports:
if m.name == "s0-eth0":
src_dpid = event.connection.dpid
elif m.name == "s1-eth0":
dst_dpid = event.connection.dpid
#设置网络的参数(优先级,时间,端口号)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =1
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.match.in_port =1
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = of.OFPP_ALL))
event.connection.send(msg)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =1
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.match.in_port =2
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = of.OFPP_ALL))
event.connection.send(msg)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =10
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.hard_timeout = 0
msg.match.dl_type = 0x0800
msg.match.nw_tos = 0x64
msg.match.in_port=1
msg.match.nw_dst = "192.168.123.2"
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = 2))
event.connection.send(msg)
msg = of.ofp_flow_mod()
msg.priority =10
msg.idle_timeout = 0
msg.hard_timeout = 0
msg.match.dl_type = 0x0800
msg.match.nw_tos = 0x64
msg.match.nw_dst = "192.168.123.1"
msg.actions.append(of.ofp_action_output(port = 1))
event.connection.send(msg)
# 启动模块的主函数
def launch ():
# attach handsers to listners
core.openflow.addListenerByName("FlowStatsReceived",
_handle_flowstats_received)
core.openflow.addListenerByName("PortStatsReceived",
_handle_portstats_received)
core.openflow.addListenerByName("ConnectionUp", _handle_ConnectionUp)
# 定时器每5秒执行一次
Timer(1, _timer_func, recurring=True)
3 执行两个脚本
此处为mymininet的脚本
此处为flow_stats脚本
总结:
1.能看懂2/3的脚本内容,以及脚本的程序意义
2.明白了pox的安装
3.对网络的了解还是不够深刻
Mininet系列实验(四):基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率的更多相关文章
- Mininet实验 基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率
实验原理 在SDN环境中,控制器可以通过对交换机下发流表操作来控制交换机的转发行为,此外,还可以利用控制器测量路径的损耗率.在本实验中,基于Mininet脚本,设置特定的交换机间的路径损耗速率,然后编 ...
- SDN实验 3: Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
验 3:Mininet 实验--测量路径的损耗率 一.实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设定:初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX ...
- 实验 3:Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设 定:初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX 控制器脚本编写,测试路径损耗率. 实验任务 h0 向 ...
- 基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率
基于Mininet测量路径的损耗率 控制器采用POX,基于OVS仿真 Mininet脚本 创建Node mininet.node Node 创建链路连接 mininet.link TCLink 设置i ...
- 实验 3:Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
一.实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设定;初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX 控制器脚本编写,测试路径损耗率. 二.实验任务 h ...
- 软件定义网络实验记录③--Mininet 实验——测量路径的损耗率
一.实验目的 在实验 2 的基础上进一步熟悉 Mininet 自定义拓扑脚本,以及与损耗率相关的设定: 初步了解 Mininet 安装时自带的 POX 控制器脚本编写,测试路径损耗率. 二.实验任务 ...
- Mininet 系列实验(四)
实验内容 本次实验拓扑图: 在该环境下,h0 向 h1 发送数据包,由于在 mininet 脚本中设置了连接损耗率,在传输过程中会丢失一些包,本次实验的目的是展示如何通过控制器计算路径损耗速率(h0- ...
- Mininet 系列实验(七)
实验内容 本实验在基于 Mininet 脚本的不同拓扑环境下使用 OpenDaylight 控制交换机行为.任务一:一台交换机两台主机,从1端口进入的数据流转发到 2 端口,从 2 端口进入的数据流转 ...
- Mininet 系列实验(六)
写在前面 这次实验遇到了非常多问题,非常非常多,花了很多时间去解决,还是有一些小问题没有解决,但是基本上能完成实验.建议先看完全文再开始做实验. 实验内容 先看一下本次实验的拓扑图: 在该环境下,假设 ...
随机推荐
- linux查看日志报错
查看运行时错误: tail -f catalina.out | grep -C 10 'Exception' 10是行数: 单引号里面的是要查找的关键字:
- stm32 ADXL345传感器
加速度灵敏度轴 沿敏感轴加速时相应输出电压增加 寄存器映射 寄存器定义 0x31-DATA_FORMAT SELF_TEST位:设置为1,自测力应用至传感器,造成输出数据转换.值为0时,禁用自测力 S ...
- 云端的ABAP Restful服务开发
愉快的暑假结束了,今天是小朋友新学期开学后的第一个周日,不知道各位家长是否和小朋友们一起,已经适应了新学期的生活了么? Jerry从少的可怜的属于自己的周末时光挤了一小部分时间出来,写了这篇文章. J ...
- 从客户发送http请求到服务器返回http之间发生了什么
由于我知识有限,可能会有模糊或者错误的地方,欢迎讨论与指正. 1.浏览器发出http请求 当用户访问一个url时,浏览器便会开始生成一个http请求. 首先获取http请求中所需要的参数,如url,c ...
- java,单文件和多文件上传代码范例
上传一个单文件,用request.getFile得到文件(下面的功能是上传到阿里云) @RequestMapping(value = {"/content"}, method = ...
- L ==> E · L · K
三剑客:Elastic Stack 在学习ELK前,先对 Lucene作基本了解. 今天才知道关系型数据库的索引是 B-Tree,罪过... 减少磁盘寻道次数 ---> 提高查询性能 Lucen ...
- GitLab初识以及代码迁移
目录 一.理论概述 1.什么是gitlib 2.GitLab服务构成 3.Git对比SVN 二.部署 1.简单操作GitLab 三.项目实践:SVN代码迁移至GitLab 环境 1.Linux下部署S ...
- artDialog提示框
API网址 http://aui.github.io/artDialog/doc/index.html 相关资料下载 https://code.google.com/archive/p/artdial ...
- 剑指Offer(三十):连续子数组的最大和
.# 剑指Offer(三十):连续子数组的最大和 搜索微信公众号:'AI-ming3526'或者'计算机视觉这件小事' 获取更多算法.机器学习干货 csdn:https://blog.csdn.net ...
- 请求类型 GET 和 POST 的区别
一.GET 一个简单的 GET 请求: xmlhttp.open("GET","demo_get.asp",true); xmlhttp.send(); 在上面 ...