java 多线程和并行程序设计
多线程使得程序中的多个任务可以同时执行
在一个程序中允许同时运行多个任务。在许多程序设计语言中,多线程都是通过调用依赖系统的过程或函数来实现的




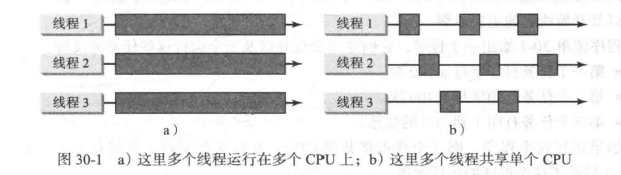
为什么需要多线程?多个线程如何在单处理器系统中同时运行?
多线程可以使您的程序更具响应性和交互性,并提高性能。在许多情况下需要多线程,例如动画和客户端/服务器计算。因为大多数时候CPU处于空闲状态 - 例如,CPU在用户输入数据时什么都不做 - 多个线程在单处理器系统中共享CPU时间是切实可行的。
1、创建任务和线程
一个任务类必须实现Runnable接口。任务必须从线程运行。

一旦定义了一个TaskClass,就可以用它的构造方法创建一个任务。
例子:
TaskClass task = new TaskClass();
任务必须在线程中执行。使用下面的语句创建任务的线程
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
然后调用start()方法告诉Java虚拟机该线程准备运行
thread.start()
例子:

public class TaskThreadDemo {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Runnable printA = new PrintChar('a', 100);
Runnable printB = new PrintChar('b', 100);
Runnable printNum = new PrintNum(100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(printA);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(printB);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(printNum);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
class PrintChar implements Runnable{
private char charToPrint;
private int times;
public PrintChar(char c,int t) {
charToPrint = c;
times = t;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<times; i++) {
System.out.print(charToPrint);
}
}
}
class PrintNum implements Runnable{
private int lastNumber;
public PrintNum(int n) {
lastNumber = n;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1; i<=lastNumber; i++) {
System.out.print(" " + i);
}
}
}
2、Thread类









3、线程池
之前运用实现Runnable接口来定义一个任务类,以及如何创建一个线程来运行一个任务

该方法对大量的任务而言是不够高效的,为每个任务开始一个新线程可能会限制吞吐量并且造成性能降低。
线程池是管理并发执行任务个数的理想方法。
Java提供Executor接口来执行线程池中的任务,提供ExecutorService接口来管理和控制任务。
Executorservice是Executor的子接口

为了创建一个Executor对象,可以使用Executor类中的静态方法


例子:
public class TaskThreadDemo {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executor.execute(new PrintChar('a', 100));
executor.execute(new PrintChar('b', 100));
executor.execute(new PrintNum(100));
executor.shutdown();
}
}
4、线程同步
例子:
public class AccountWithoutSync {
private static Account account = new Account();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executorService.execute(new AddAPennyTask());
}
executorService.shutdown();
//等待 全部任务 完成
while(!executorService.isTerminated()) {
}
System.out.println(account.getBalance());
}
private static class AddAPennyTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
account.deposit(1);
}
}
public static class Account {
private int balance = 0;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void deposit(int amount) {
int newBalance = balance + amount;
try {
Thread.sleep(5);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
balance = balance + newBalance;
}
}
}

这个例子中出错了
原因是:

因为线程不安全,所以数据遭到破坏
synchronized关键字
为避免竞争状态,应该防止多个线程同时进入程序的某一特定部分,程序中的这部分称为临界区。
使用关键字synchronized来同步方法,以便一次只有一个线程可以访问这个方法
例子:


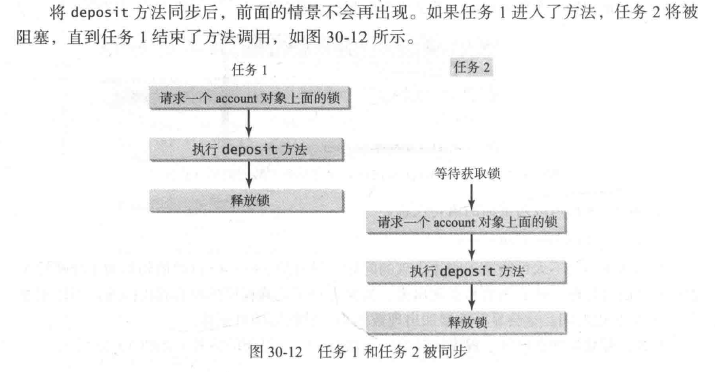
调用一个对象上的同步实例方法,需要给该对象加锁。而调用一个类上的同步静态方法,需要给该类加锁。
同步语句
当执行方法中某一个代码块时,同步语句不仅可用与this对象加锁,而且可用于对任何对象加锁。这个代码块称为同步块。同步语句的一般形式如下:

利用加锁同步
之前的用的同步实例方法

实际上 在执行之前都隐式地需要一个加在实例上的锁



例子:
部分代码:
public static class Account {
private int balance = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //创建一个锁
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void deposit(int amount) {
lock.lock();//获取该锁
try {
int newBalance = balance + amount;
Thread.sleep(5);
balance = newBalance;
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}finally {
lock.unlock();//释放该锁
}
}
}
线程间协作

例子:

public class ThreadCooperation {
private static Account account = new Account();
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executorService.execute(new DepositTask());
executorService.execute(new withdrawTask());
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("Thread 1 \t Thread 2 \t Balance");
System.out.println();
}
public static class DepositTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
account.deposit((int)(Math.random() * 10) + 1);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class withdrawTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
account.withdraw((int)(Math.random() * 10) + 1);
}
}
}
public static class Account {
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition newDeposit = lock.newCondition(); //线程间的协作
private int balance = 0;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void withdraw(int accountNumber) {
lock.lock();
try {
while(balance < accountNumber) {
System.out.println("\t\tWait for a deposit, wait to withdraw :" + accountNumber);
newDeposit.await();
}
balance -= accountNumber;
System.out.println("\t\tWithdraw: " + accountNumber + "\t\t" + "balance: " + getBalance());
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void deposit(int accountNumber) {
lock.lock();
try {
balance += accountNumber;
System.out.println("Deposit " + accountNumber + "\t\t\t\t balance: " + getBalance());
newDeposit.signalAll();
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
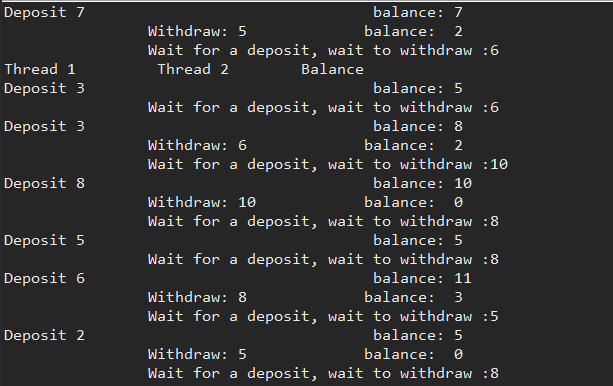


消费者/生产者

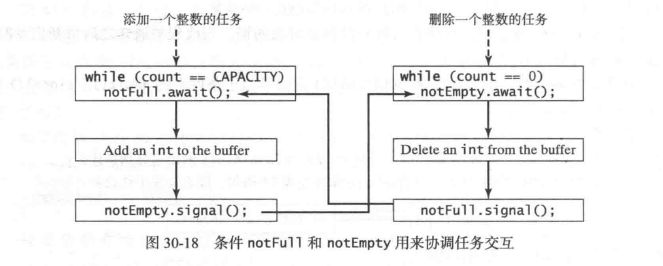
public class ComsumerProducer {
private static Buffer buffer = new Buffer();
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService excurtor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
excurtor.execute(new ProducerTask());
excurtor.execute(new ConsumerTask());
excurtor.shutdown();
}
private static class ProducerTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
int i = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println("Producer writes " + i);
buffer.write(i++);
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private static class ConsumerTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
while(true) {
System.out.println("\t\tConsumer reads " + buffer.read());
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private static class Buffer{
private static final int CAPACITY = 3;
private LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
private static Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
public void write(int value) {
lock.lock();
try{
while(queue.size() == CAPACITY) {
System.out.println("Wait for notNull condition");
notFull.await();
}
queue.offer(value);
notEmpty.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int read() {
lock.lock();
int value = 0;
try {
while(queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("\t\tWait for notEmpty condition");
notEmpty.await();
}
value = queue.pop();
notFull.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
return value;
}
}
}
}

阻塞队列

阻塞队列在试图向一个满队列添加元素或者从空队列中删除元素时会导致线程阻塞。BlockingQueue接口继承了Queue,并且提供同步的put和take方法向队列尾部添加元素,以及从队列头部删除元素

java支持三个具体的阻塞队列ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue




例子:
用阻塞队列做的消费者/生产者
public class ConsumerProducerUsingBlockingQueue {
private static ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> buffer = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(2);
public static void main(String [] args) {
ExecutorService excutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
excutor.execute(new ProducerTask());
excutor.execute(new ConsumerTask());
excutor.shutdown();
}
private static class ProducerTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
int i = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println("Producer writes " + i);
buffer.put(i++);
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private static class ConsumerTask implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
while(true) {
System.out.println("\t\tConsumer reads " + buffer.take());
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}

信号量
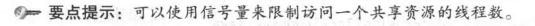
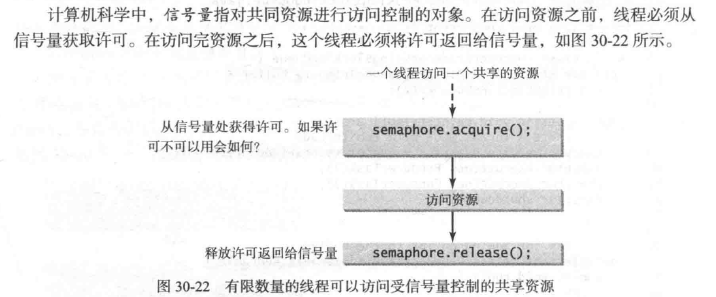

例子:



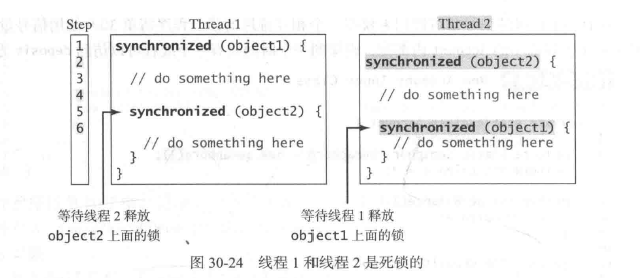
同步合集


并行编程
java 多线程和并行程序设计的更多相关文章
- [Java多线程]-并发,并行,synchonrized同步的用法
一.多线程的并发与并行: 并发:多个线程同时都处在运行中的状态.线程之间相互干扰,存在竞争,(CPU,缓冲区),每个线程轮流使用CPU,当一个线程占有CPU时,其他线程处于挂起状态,各线程断续推进. ...
- JAVA多线程---高并发程序设计
先行发生原则 程序顺序原则:一个线程内保证语义的串行性 volatile:volatile变量的写,先发生于读,这保证了volatile变量的可见性 锁规则:解锁必然发生在随后的加锁前 传递性:A优先 ...
- Java多线程程序设计详细解析
一.理解多线程 多线程是这样一种机制,它允许在程序中并发执行多个指令流,每个指令流都称为一个线程,彼此间互相独立. 线程又称为轻量级进程,它和进程一样拥有独立的执行控制,由操作系统负责调度,区别在于线 ...
- Java多线程--并行模式与算法
Java多线程--并行模式与算法 单例模式 虽然单例模式和并行没有直接关系,但是我们经常会在多线程中使用到单例.单例的好处有: 对于频繁使用的对象可以省去new操作花费的时间: new操作的减少,随之 ...
- 已看1.熟练的使用Java语言进行面向对象程序设计,有良好的编程习惯,熟悉常用的Java API,包括集合框架、多线程(并发编程)、I/O(NIO)、Socket、JDBC、XML、反射等。[泛型]\
1.熟练的使用Java语言进行面向对象程序设计,有良好的编程习惯,熟悉常用的Java API,包括集合框架.多线程(并发编程).I/O(NIO).Socket.JDBC.XML.反射等.[泛型]\1* ...
- Java多线程原理+基础知识(超级超级详细)+(并发与并行)+(进程与线程)1
Java多线程 我们先来了解两个概念!!!! 1.什么是并发与并行 2.什么是进程与线程 1.什么是并发与并行 1.1并行:两个事情在同一时刻发生 1.2并发:两个事情在同一时间段内发生 并发与并行的 ...
- Java多线程专题1: 并发与并行的基础概念
合集目录 Java多线程专题1: 并发与并行的基础概念 什么是多线程并发和并行? 并发: Concurrency 特指单核可以处理多任务, 这种机制主要实现于操作系统层面, 用于充分利用单CPU的性能 ...
- 从JAVA多线程理解到集群分布式和网络设计的浅析
对于JAVA多线程的应用非常广泛,现在的系统没有多线程几乎什么也做不了,很多时候我们在何种场合如何应用多线程成为一种首先需要选择的问题,另外关于java多线程的知识也是非常的多,本文中先介绍和说明一些 ...
- 学习笔记之JAVA多线程
Java程序设计实用教程 by 朱战立 & 沈伟 孙鑫Java无难事 Java 多线程与并发编程专题(http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-c ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ4943 NOI2017蚯蚓排队(哈希+链表)
能看懂题就能想到正解.维护所有长度不超过k的数字串的哈希值即可,用链表维护一下蚯蚓间连接情况.由于这样的数字串至多只有nk个,计算哈希值的总复杂度为O(nk),而分裂的复杂度为O(ck^2),询问复杂 ...
- MT【36】反函数有关的一道题
解答:$\frac{7}{2}$ 做适当的变换,再令$x-1=t$容易划归到我们熟悉的题型,$2^t=\frac{3}{2}-t,log_2t=\frac{3}{2}-t$作图或者利用函数单调性可得$ ...
- android第二课:运行你的应用
如果你按照前面课程创建了 Android 项目,它包含了可以立即运行的 "Hello World"源代码文件. 由两该条件来决定如何运行你的应用:你是否拥有运行着 Android ...
- 在Android中afinal框架下實現sqlite數據庫版本升級的辦法
public abstract void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db,int oldVersion,int new Version) 這個方法在實現時需要重寫. pub ...
- Windows下修改Tomcat黑窗口标题
在Tomcat的bin目录下,新建文件setenv.bat. 在文件内输入: set TITLE=MYTomcat-%date% %time%[%cd%] 可以把MYTomcat修改为自己定义的名字. ...
- spring aop 获取request、response对象
在网上看到有不少人说如下方式获取: 1.在web.xml中添加监听 <listener> <listener-class> org. ...
- eclipse启动速度优化
1. 在eclipse.ini文件中添加如下参数(红色部分) -startup plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher_1.3.0.v20140415-2008.ja ...
- A1022. Digital Library
A Digital Library contains millions of books, stored according to their titles, authors, key words o ...
- 【java】详解native方法的使用
目录结构: contents structure [+] 关于native关键字 使用native关键字 使用步骤 案例 编写.java文件 编译.java文件 获得.h文件 编写hello.cpp文 ...
- cookies 不同端口 是可以共享的
cookies 不同端口,是跨域吗? 我部署了两套系统在同一个ip上!8080,和8090! 这样.cookies,算跨域吗? 两套系统都记录了都有一个 historyItem的key的cookies ...
