爬虫(十七):Scrapy框架(四) 对接selenium爬取京东商品数据
1. Scrapy对接Selenium
Scrapy抓取页面的方式和requests库类似,都是直接模拟HTTP请求,而Scrapy也不能抓取JavaScript动态谊染的页面。在前面的博客中抓取JavaScript渲染的页面有两种方式。一种是分析Ajax请求,找到其对应的接口抓取,Scrapy同样可以用此种方式抓取。另一种是直接用 Selenium模拟浏览器进行抓取,我们不需要关心页面后台发生的请求,也不需要分析渲染过程,只需要关心页面最终结果即可,可见即可爬。那么,如果Scrapy可以对接Selenium,那 Scrapy就可以处理任何网站的抓取了。
1.1 新建项目
首先新建项目,名为scrapyseleniumtest。
scrapy startproject scrapyseleniumtest
新建一个Spider。
scrapy genspider jd www.jd.com
修改ROBOTSTXT_OBEY为False。
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False

1.2 定义Item
这里我们就不调用Item了。
初步实现Spider的start _requests()方法。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from scrapy import Request,Spider
from urllib.parse import quote
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup class JdSpider(Spider):
name = 'jd'
allowed_domains = ['www.jd.com']
base_url = 'https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=' def start_requests(self):
for keyword in self.settings.get('KEYWORDS'):
for page in range(1, self.settings.get('MAX_PAGE') + 1):
url = self.base_url + quote(keyword)
# dont_filter = True 不去重
yield Request(url=url, callback=self.parse, meta={'page': page}, dont_filter=True)
首先定义了一个base_url,即商品列表的URL,其后拼接一个搜索关键字就是该关键字在京东搜索的结果商品列表页面。
关键字用KEYWORDS标识,定义为一个列表。最大翻页页码用MAX_PAGE表示。它们统一定义在settings.py里面。
KEYWORDS = ['iPad']
MAX_PAGE = 2
在start_requests()方法里,我们首先遍历了关键字,遍历了分页页码,构造并生成Request。由于每次搜索的URL是相同的,所以分页页码用meta参数来传递,同时设置dont_filter不去重。这样爬虫启动的时候,就会生成每个关键字对应的商品列表的每一页的请求了。
1.3 对接Selenium
接下来我们需要处理这些请求的抓取。这次我们对接Selenium进行抓取,采用Downloader Middleware来实现。在Middleware中对接selenium,输出源代码之后,构造htmlresponse对象,直接返回给spider解析页面,提取数据,并且也不在执行下载器下载页面动作。
class SeleniumMiddleware(object):
# Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined,
# scrapy acts as if the downloader middleware does not modify the
# passed objects. def __init__(self,timeout=None):
self.logger=getLogger(__name__)
self.timeout = timeout
self.browser = webdriver.Chrome()
self.browser.set_window_size(1400,700)
self.browser.set_page_load_timeout(self.timeout)
self.wait = WebDriverWait(self.browser,self.timeout) def __del__(self):
self.browser.close() @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders.
return cls(timeout=crawler.settings.get('SELENIUM_TIMEOUT')) def process_request(self, request, spider):
'''
在下载器中间件中对接使用selenium,输出源代码之后,构造htmlresponse对象,直接返回
给spider解析页面,提取数据
并且也不在执行下载器下载页面动作
htmlresponse对象的文档:
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
''' print('PhantomJS is Starting')
page = request.meta.get('page', 1)
self.wait = WebDriverWait(self.browser, self.timeout)
# self.browser.set_page_load_timeout(30)
# self.browser.set_script_timeout(30)
try:
self.browser.get(request.url)
if page > 1:
input = self.wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-skip > input')))
input.clear()
input.send_keys(page)
time.sleep(5) # 将网页中输入跳转页的输入框赋值给input变量 EC.presence_of_element_located,判断输入框已经被加载出来
input = self.wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-skip > input')))
# 将网页中调准页面的确定按钮赋值给submit变量,EC.element_to_be_clickable 判断此按钮是可点击的
submit = self.wait.until(EC.element_to_be_clickable((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-skip > a')))
input.clear()
input.send_keys(page)
submit.click() # 点击按钮
time.sleep(5) # 判断当前页码出现在了输入的页面中,EC.text_to_be_present_in_element 判断元素在指定字符串中出现
self.wait.until(EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-num > a.curr'),str(page)))
# 等待 #J_goodsList 加载出来,为页面数据,加载出来之后,在返回网页源代码
self.wait.until(EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-num > a.curr'),str(page)))
return HtmlResponse(url=request.url, body=self.browser.page_source, request=request, encoding='utf-8',status=200)
except TimeoutException:
return HtmlResponse(url=request.url, status=500, request=request)
首先我在__init__()里对一些对象进行初始化,包括WebDriverWait等对象,同时设置页面大小和页面加载超时时间。在process_request()方法中,我们通过Request的meta属性获取当前需要爬取的页码,将页码赋值给input变量,再将翻页的点击按钮框赋值给submit变量,然后在数据框中输入页码,等待页面加载,直接返回htmlresponse给spider解析,这里我们没有经过下载器下载,直接构造response的子类htmlresponse返回。(当下载器中间件返回response对象时,更低优先级的process_request将不在执行,转而执行其他的process_response()方法,本例中没有其他的process_response(),所以直接将结果返回给spider解析。)
1.4 解析页面
Response对象就会回传给Spider内的回调函数进行解析。所以下一步我们就实现其回调函数,对网页来进行解析。
def parse(self, response):
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
lis = soup.find_all(name='li', class_="gl-item")
for li in lis:
proc_dict = {}
dp = li.find(name='span', class_="J_im_icon")
if dp:
proc_dict['dp'] = dp.get_text().strip()
else:
continue
id = li.attrs['data-sku']
title = li.find(name='div', class_="p-name p-name-type-2")
proc_dict['title'] = title.get_text().strip()
price = li.find(name='strong', class_="J_" + id)
proc_dict['price'] = price.get_text()
comment = li.find(name='a', id="J_comment_" + id)
proc_dict['comment'] = comment.get_text() + '条评论'
url = 'https://item.jd.com/' + id + '.html'
proc_dict['url'] = url
proc_dict['type'] = 'JINGDONG'
yield proc_dict
这里我们采用BeautifulSoup进行解析,匹配所有商品,随后对结果进行遍历,依次选取商品的各种信息。
1.5 储存结果
提取完页面数据之后,数据会发送到item pipeline处进行数据处理,清洗,入库等操作,所以我们此时当然需要定义项目管道了,在此我们将数据存储在mongodb数据库中。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
import pymongo class MongoPipeline(object): def __init__(self,mongo_url,mongo_db,collection):
self.mongo_url = mongo_url
self.mongo_db = mongo_db
self.collection = collection @classmethod
#from_crawler是一个类方法,由 @classmethod标识,是一种依赖注入的方式,它的参数就是crawler
#通过crawler我们可以拿到全局配置的每个配置信息,在全局配置settings.py中的配置项都可以取到。
#所以这个方法的定义主要是用来获取settings.py中的配置信息
def from_crawler(cls,crawler):
return cls(
mongo_url=crawler.settings.get('MONGO_URL'),
mongo_db = crawler.settings.get('MONGO_DB'),
collection = crawler.settings.get('COLLECTION')
) def open_spider(self,spider):
self.client = pymongo.MongoClient(self.mongo_url)
self.db = self.client[self.mongo_db] def process_item(self,item, spider):
# name = item.__class__.collection
name = self.collection
self.db[name].insert(dict(item))
return item def close_spider(self,spider):
self.client.close()
1.6 配置settings文件
配置settings文件,将项目中使用到的配置项在settings文件中配置,本项目中使用到了KEYWORDS,MAX_PAGE,SELENIUM_TIMEOUT(页面加载超时时间),MONGOURL,MONGODB,COLLECTION。
KEYWORDS=['iPad']
MAX_PAGE=2 MONGO_URL = 'localhost'
MONGO_DB = 'test'
COLLECTION = 'ProductItem' SELENIUM_TIMEOUT = 30
以及修改配置项,激活下载器中间件和item pipeline。
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'scrapyseleniumtest.middlewares.SeleniumMiddleware': 543,
}
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'scrapyseleniumtest.pipelines.MongoPipeline': 300,
}
1.7 执行结果
项目中所有需要开发的代码和配置项开发完成,运行项目。
scrapy crawl jd

运行项目之后,在mongodb中查看数据,已经执行成功。
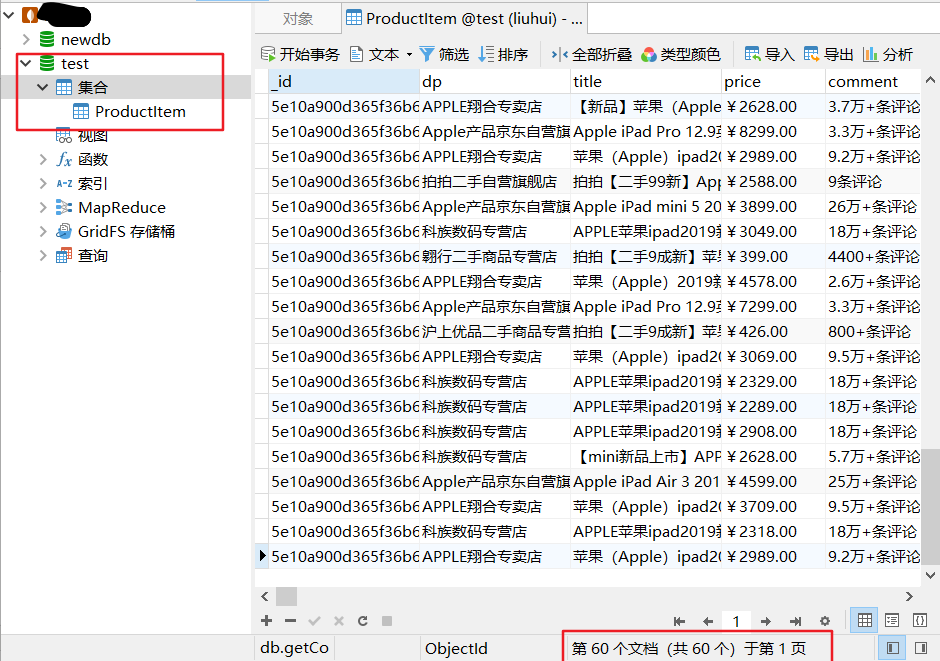
1.8 完整代码
items.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
from scrapy import Item,Field class ProductItem(Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
# dp = Field()
# title = Field()
# price = Field()
# comment = Field()
# url = Field()
# type = Field()
pass
jd.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from scrapy import Request,Spider
from urllib.parse import quote
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup class JdSpider(Spider):
name = 'jd'
allowed_domains = ['www.jd.com']
base_url = 'https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=' def start_requests(self):
for keyword in self.settings.get('KEYWORDS'):
for page in range(1, self.settings.get('MAX_PAGE') + 1):
url = self.base_url + quote(keyword)
# dont_filter = True 不去重
yield Request(url=url, callback=self.parse, meta={'page': page}, dont_filter=True) def parse(self, response):
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'lxml')
lis = soup.find_all(name='li', class_="gl-item")
for li in lis:
proc_dict = {}
dp = li.find(name='span', class_="J_im_icon")
if dp:
proc_dict['dp'] = dp.get_text().strip()
else:
continue
id = li.attrs['data-sku']
title = li.find(name='div', class_="p-name p-name-type-2")
proc_dict['title'] = title.get_text().strip()
price = li.find(name='strong', class_="J_" + id)
proc_dict['price'] = price.get_text()
comment = li.find(name='a', id="J_comment_" + id)
proc_dict['comment'] = comment.get_text() + '条评论'
url = 'https://item.jd.com/' + id + '.html'
proc_dict['url'] = url
proc_dict['type'] = 'JINGDONG'
yield proc_dict
middlewares.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your spider middleware
#
# See documentation in:
# https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html from scrapy import signals
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse
from logging import getLogger
from selenium.common.exceptions import TimeoutException
import time class ScrapyseleniumtestSpiderMiddleware(object):
# Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined,
# scrapy acts as if the spider middleware does not modify the
# passed objects. @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders.
s = cls()
crawler.signals.connect(s.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened)
return s def process_spider_input(self, response, spider):
# Called for each response that goes through the spider
# middleware and into the spider. # Should return None or raise an exception.
return None def process_spider_output(self, response, result, spider):
# Called with the results returned from the Spider, after
# it has processed the response. # Must return an iterable of Request, dict or Item objects.
for i in result:
yield i def process_spider_exception(self, response, exception, spider):
# Called when a spider or process_spider_input() method
# (from other spider middleware) raises an exception. # Should return either None or an iterable of Response, dict
# or Item objects.
pass def process_start_requests(self, start_requests, spider):
# Called with the start requests of the spider, and works
# similarly to the process_spider_output() method, except
# that it doesn’t have a response associated. # Must return only requests (not items).
for r in start_requests:
yield r def spider_opened(self, spider):
spider.logger.info('Spider opened: %s' % spider.name) class SeleniumMiddleware(object):
# Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined,
# scrapy acts as if the downloader middleware does not modify the
# passed objects. def __init__(self,timeout=None):
self.logger=getLogger(__name__)
self.timeout = timeout
self.browser = webdriver.Chrome()
self.browser.set_window_size(1400,700)
self.browser.set_page_load_timeout(self.timeout)
self.wait = WebDriverWait(self.browser,self.timeout) def __del__(self):
self.browser.close() @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders.
return cls(timeout=crawler.settings.get('SELENIUM_TIMEOUT')) def process_request(self, request, spider):
'''
在下载器中间件中对接使用selenium,输出源代码之后,构造htmlresponse对象,直接返回
给spider解析页面,提取数据
并且也不在执行下载器下载页面动作
htmlresponse对象的文档:
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
''' print('PhantomJS is Starting')
page = request.meta.get('page', 1)
self.wait = WebDriverWait(self.browser, self.timeout)
# self.browser.set_page_load_timeout(30)
# self.browser.set_script_timeout(30)
try:
self.browser.get(request.url)
if page > 1:
input = self.wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-skip > input')))
input.clear()
input.send_keys(page)
time.sleep(5) # 将网页中输入跳转页的输入框赋值给input变量 EC.presence_of_element_located,判断输入框已经被加载出来
input = self.wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-skip > input')))
# 将网页中调准页面的确定按钮赋值给submit变量,EC.element_to_be_clickable 判断此按钮是可点击的
submit = self.wait.until(EC.element_to_be_clickable((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-skip > a')))
input.clear()
input.send_keys(page)
submit.click() # 点击按钮
time.sleep(5) # 判断当前页码出现在了输入的页面中,EC.text_to_be_present_in_element 判断元素在指定字符串中出现
self.wait.until(EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-num > a.curr'),str(page)))
# 等待 #J_goodsList 加载出来,为页面数据,加载出来之后,在返回网页源代码
self.wait.until(EC.text_to_be_present_in_element((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '#J_bottomPage > span.p-num > a.curr'),str(page)))
return HtmlResponse(url=request.url, body=self.browser.page_source, request=request, encoding='utf-8',status=200)
except TimeoutException:
return HtmlResponse(url=request.url, status=500, request=request) def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
# Called with the response returned from the downloader. # Must either;
# - return a Response object
# - return a Request object
# - or raise IgnoreRequest
return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider):
# Called when a download handler or a process_request()
# (from other downloader middleware) raises an exception. # Must either:
# - return None: continue processing this exception
# - return a Response object: stops process_exception() chain
# - return a Request object: stops process_exception() chain
pass def spider_opened(self, spider):
spider.logger.info('Spider opened: %s' % spider.name)
pipelines.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
import pymongo class MongoPipeline(object): def __init__(self,mongo_url,mongo_db,collection):
self.mongo_url = mongo_url
self.mongo_db = mongo_db
self.collection = collection @classmethod
#from_crawler是一个类方法,由 @classmethod标识,是一种依赖注入的方式,它的参数就是crawler
#通过crawler我们可以拿到全局配置的每个配置信息,在全局配置settings.py中的配置项都可以取到。
#所以这个方法的定义主要是用来获取settings.py中的配置信息
def from_crawler(cls,crawler):
return cls(
mongo_url=crawler.settings.get('MONGO_URL'),
mongo_db = crawler.settings.get('MONGO_DB'),
collection = crawler.settings.get('COLLECTION')
) def open_spider(self,spider):
self.client = pymongo.MongoClient(self.mongo_url)
self.db = self.client[self.mongo_db] def process_item(self,item, spider):
# name = item.__class__.collection
name = self.collection
self.db[name].insert(dict(item))
return item def close_spider(self,spider):
self.client.close()
settings.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for scrapyseleniumtest project
#
# For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or
# commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation:
#
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html BOT_NAME = 'scrapyseleniumtest' SPIDER_MODULES = ['scrapyseleniumtest.spiders']
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'scrapyseleniumtest.spiders' # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = 'scrapyseleniumtest (+http://www.yourdomain.com)' # Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16)
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay
# See also autothrottle settings and docs
#DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3
# The download delay setting will honor only one of:
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16 # Disable cookies (enabled by default)
#COOKIES_ENABLED = False # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default)
#TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False # Override the default request headers:
#DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
# 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
# 'Accept-Language': 'en',
#} # Enable or disable spider middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
#SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'scrapyseleniumtest.middlewares.ScrapyseleniumtestSpiderMiddleware': 543,
#} # Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
#DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'scrapyseleniumtest.middlewares.ScrapyseleniumtestDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
#}
DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'scrapyseleniumtest.middlewares.SeleniumMiddleware': 543,
}
# Enable or disable extensions
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html
#EXTENSIONS = {
# 'scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole': None,
#} # Configure item pipelines
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
#ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# 'scrapyseleniumtest.pipelines.ScrapyseleniumtestPipeline': 300,
#}
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'scrapyseleniumtest.pipelines.MongoPipeline': 300,
}
# Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html
#AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True
# The initial download delay
#AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5
# The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies
#AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60
# The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to
# each remote server
#AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0
# Enable showing throttling stats for every response received:
#AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings
#HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True
#HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0
#HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache'
#HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = []
#HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage'
KEYWORDS=['iPad']
MAX_PAGE=2 MONGO_URL = 'localhost'
MONGO_DB = 'test'
COLLECTION = 'ProductItem' SELENIUM_TIMEOUT = 30
爬虫(十七):Scrapy框架(四) 对接selenium爬取京东商品数据的更多相关文章
- Scrapy实战篇(八)之Scrapy对接selenium爬取京东商城商品数据
本篇目标:我们以爬取京东商城商品数据为例,展示Scrapy框架对接selenium爬取京东商城商品数据. 背景: 京东商城页面为js动态加载页面,直接使用request请求,无法得到我们想要的商品数据 ...
- selenium模块使用详解、打码平台使用、xpath使用、使用selenium爬取京东商品信息、scrapy框架介绍与安装
今日内容概要 selenium的使用 打码平台使用 xpath使用 爬取京东商品信息 scrapy 介绍和安装 内容详细 1.selenium模块的使用 # 之前咱们学requests,可以发送htt ...
- 爬虫系列(十三) 用selenium爬取京东商品
这篇文章,我们将通过 selenium 模拟用户使用浏览器的行为,爬取京东商品信息,还是先放上最终的效果图: 1.网页分析 (1)初步分析 原本博主打算写一个能够爬取所有商品信息的爬虫,可是在分析过程 ...
- 利用selenium爬取京东商品信息存放到mongodb
利用selenium爬取京东商城的商品信息思路: 1.首先进入京东的搜索页面,分析搜索页面信息可以得到路由结构 2.根据页面信息可以看到京东在搜索页面使用了懒加载,所以为了解决这个问题,使用递归.等待 ...
- python爬虫——用selenium爬取京东商品信息
1.先附上效果图(我偷懒只爬了4页) 2.京东的网址https://www.jd.com/ 3.我这里是不加载图片,加快爬取速度,也可以用Headless无弹窗模式 options = webdri ...
- 爬虫之selenium爬取京东商品信息
import json import time from selenium import webdriver """ 发送请求 1.1生成driver对象 2.1窗口最大 ...
- 一起学爬虫——使用selenium和pyquery爬取京东商品列表
layout: article title: 一起学爬虫--使用selenium和pyquery爬取京东商品列表 mathjax: true --- 今天一起学起使用selenium和pyquery爬 ...
- 爬虫—Selenium爬取JD商品信息
一,抓取分析 本次目标是爬取京东商品信息,包括商品的图片,名称,价格,评价人数,店铺名称.抓取入口就是京东的搜索页面,这个链接可以通过直接构造参数访问https://search.jd.com/Sea ...
- Scrapy 通过登录的方式爬取豆瓣影评数据
Scrapy 通过登录的方式爬取豆瓣影评数据 爬虫 Scrapy 豆瓣 Fly 由于需要爬取影评数据在来做分析,就选择了豆瓣影评来抓取数据,工具使用的是Scrapy工具来实现.scrapy工具使用起来 ...
随机推荐
- leetcode菜鸡斗智斗勇系列(5)--- 寻找拥有偶数数位的数字
1.原题: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-numbers-with-even-number-of-digits/ Given an array nums of ...
- [Linux] day07——查看及过滤文本
查看及过滤文本 =====================================cat concatenate -n 添加行号------------------- ...
- Python 数组
使用之前要先导入函数库 import numpy as np 数组名=np.zeros(数组大小,数据类型) 初始化为0值,这里的数据类型只能是数值类型,字符类型不能用 一.一维数组 impo ...
- 利用SSH在本机和远程服务器之间传输文件或文件夹
1.从远程服务器上下载文件到本机 scp <服务器用户名>@<服务器地址>:<服务器中要下载的文件路径> <下载到本机的绝对路径> 2.从本机上传本地文 ...
- 富文本编辑器summernote的基本使用
summernote比较突出的优点就是能保持复制过来的东西的原有样式,并且比较流畅. 官方文档地址:https://summernote.org/getting-started 我是用到cdn引入 & ...
- gerrit关闭管理员权限后解决办法
问题描述:gerrit以管理员的身份登录后,create new list和 create new group不显示,导致无法创建新的项目和权限组 出现问题:gerrit可视化页面误删all_proj ...
- LUOGU P6034 Ryoku与最初之人笔记 简要题解
比赛的时候有个地方忘记取模怒砍80,调了一下午Orz(虽然我总共貌似就打这个比赛半个多小时 我们一眼看到涉及到公约数/同余 和 xor,所以我们想到了一些关于xor的性质 a+b >= a xo ...
- 「NOIP2015」运输计划
传送门 Luogu 解题思路 首先这题可以直接二分答案,然后我们每次都把属于长度大于二分值的路径上的边标记一次,表示选这条边可以优化几条路径. 然后我们显然是要选一条覆盖次数等于需要覆盖的路径数并且长 ...
- Centos7 网卡Device does not seem to be present解决办法
1.ifconfig -a 查看当前所有网卡 2.修改网络配置文件 3.在原来文件的基础上,修改网卡名称 DEVICE=ens32 NAME=ens32 并且把UUID以及mac地址删掉 mv ifc ...
- ajax请求QQ音乐
搜索歌曲 function go() { var val = document.getElementById("name").value; ...
