【spring 区别】ClassXmlAplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的区别
今天写一个简单的spring使用例子,遇到这个问题:
项目结构如下:
代码如下:
package com.it.sxd; import java.nio.file.FileSystem; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; public class SayHelloTest { @Test
public void testSayHello(){
//1.读取hello。xml配置文件,实例化一个Ioc容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("hello.xml"); //2.从Ioc容器中获取ID为"hello1"的bean ,此处是“面向接口编程 而不是面向实现编程”
SayHell sayHell = context.getBean("hello1",SayHell.class);
//3.实现功能
sayHell.sayHello();
} }
代码中使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext获取一个Ioc的实例化对象,但是读取这个"hello.xml"文件,无论怎么修改路径,修改成"resources/hello.xml"或者"hello.xml",总之是没有办法识别,一直报如下的错误:
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: IOException parsing XML document from class path resource [resources/hello.xml]; nested exception is java.io.FileNotFoundException: class path resource [resources/hello.xml] cannot be opened because it does not exist
at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:344)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:304)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:181)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:217)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:188)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:252)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java:127)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java:93)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory(AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java:129)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.obtainFreshBeanFactory(AbstractApplicationContext.java:609)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:510)
at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:139)
at org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.<init>(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.java:83)
at com.it.sxd.SayHelloTest.testSayHello(SayHelloTest.java:12)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit4.runner.JUnit4TestReference.run(JUnit4TestReference.java:50)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.TestExecution.run(TestExecution.java:38)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:459)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.runTests(RemoteTestRunner.java:675)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.run(RemoteTestRunner.java:382)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.junit.runner.RemoteTestRunner.main(RemoteTestRunner.java:192)
Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException: class path resource [resources/hello.xml] cannot be opened because it does not exist
at org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource.getInputStream(ClassPathResource.java:172)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:330)
... 36 more
提示这个文件不存在,找不到。
好吧 ,我要爆炸了!!!
听说基友解读了一番,将ClassXmlAplicationContext()方法替换成FileSystemXmlApplicationContext()方法,代码如下:
package com.it.sxd; import java.nio.file.FileSystem; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; public class SayHelloTest { @Test
public void testSayHello(){
//1.读取hello。xml配置文件,实例化一个Ioc容器
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("resources/hello.xml"); //2.从Ioc容器中获取ID为"hello1"的bean ,此处是“面向接口编程 而不是面向实现编程”
SayHell sayHell = context.getBean("hello1",SayHell.class);
//3.实现功能
sayHell.sayHello();
} }
然后:

效果很好嘛~~!!!然后就好了。
下面就解读一下这两个方法的区别:
Spring容器最基本的接口就是BeanFactory. BeanFactory负责配置、创建、管理Bean,它有一个子接口ApplicationContext,也称为Spring上下文。Spring容器负责管理Bean与Bean之间的信赖关系。
BeanFactory有很多实现类,通常使用org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory类。但对于大部分J2EE应用而言,推荐使用ApplicationContext. ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,其常用实现类是org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext和org.springframework.context.support.ClassXmlAplicationContext。
Springr的配置信息通常采用XML配置文件来设置,因此,创建BeanFactory实例时,应该提供XML配置文件作为参数。、
下面详细介绍ApplicationContext的实际运用:
一:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
1.没有前缀:默认为项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app.spring.xml");
2.前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:app.spring.xml");
3.使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("file:D:/app.spring.xml");
4.可以同时加载多个文件
String[] xmlCfg = new String[] { "classpath:base.spring.xml","app.spring.xml"};
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlCfg);
5.使用通配符加载所有符合要求的文件
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("*.spring.xml");
也就是说呢,这个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext()方法,只能识别源文件夹的范围下的东西。
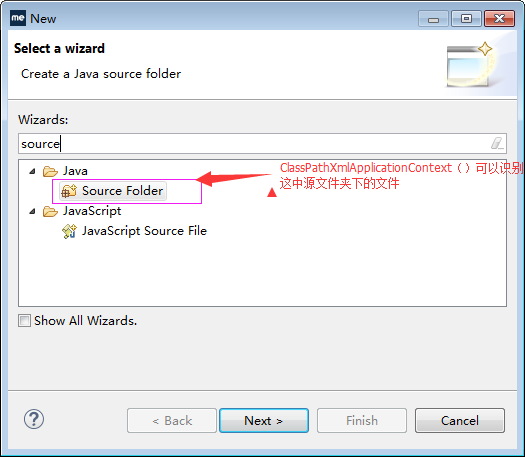
二:FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
1.默认为项目工作路径 即项目的根目录
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/resources/app.spring.xml");
2.前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:app.spring.xml");
3.使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("file:D:/app.spring.xml");
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D:/app.spring.xml");
4.可以同时加载多个文件
String[] xmlCfg = new String[] { "src/main/resources/base.spring.xml","classpath:app.spring.xml"};
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(xmlCfg);
5.使用通配符加载所有符合要求的文件
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:*.spring.xml");
代码解释:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import aoplog.LogAfterAdvice;
import aoplog.LogBeforeAdvice;
/**
* @author Michael
*
*/
public class TestApplicationContext {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
*/
// 没有前缀:默认为项目的classpath下相对路径
ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"app.spring.xml");
// 前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径
// ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
// "classpath:app.spring.xml");
// 使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径
// ApplicationContext appCt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
// "file:D:/app.spring.xml");
LogBeforeAdvice logBefore = (LogBeforeAdvice) appCt
.getBean("logBefore");
System.out.println("ClassPathXmlApplicationContext test:"
+ logBefore.getClass());
// 利用通配符文件加载
ApplicationContext appCtXx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"*.spring.xml");
// 多文件加载
String[] xmlCfg = new String[] { "classpath:base.spring.xml",
"myapp.spring.xml" };
ApplicationContext appCtMore = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
xmlCfg);
/*
* FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
*/
// 默认为项目工作路径 即项目的根目录
ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
"src/main/resources/app.spring.xml");
// 前缀classpath:表示的是项目的classpath下相对路径
// ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
// "classpath:app.spring.xml");
// 使用前缀file 表示的是文件的绝对路径
// ApplicationContext appCt2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
// "file:D:/app.spring.xml");
LogAfterAdvice logAfter = (LogAfterAdvice) appCt2.getBean("logAfter");
System.out.println("FileSystemXmlApplicationContext test:"
+ logAfter.getClass());
}
}
附录:
谈一谈什么是ClassPath以及怎么使用它:
首先:
java运行时的类路径,比如导入的类,在运行时需要将jar包放到classpath路径上。
classpath 在classpath路径上寻找指定文件,如果有多个符合的文件,以第一个为准,也就说,只要找到一个,就不在继续搜索
classpath*:会搜索所有满足条件的文件,有多少加载多少
其次:
编写的java源文件经过编译后生成class文件,需要指定目录存放这些文件。web程序默认都在web-info/classes目录下存放我们的java编译后的文件。
但是web-info目录下还有各种jar包和配置文件呢,确切说web-info根目录才是程序运行时classpath。放在根目录下的源代码,在编译之后,会将此文件copy到web-info目录。
JAVA获取classpath路径:
public URL getResource (String name);
public InputStream getResourceAsStream (String name);
这里name是资源的类路径,它是相对与“/”根路径下的位置。getResource得到的是一个URL对象来定位资源,而getResourceAsStream取得该资源输入流的引用保证程序可以从正确的位置抽取数据。
但是真正使用的不是ClassLoader的这两个方法,而是Class的 getResource和getResourceAsStream方法,因为Class对象可以从你的类得到(如YourClass.class或 YourClass.getClass()),而ClassLoader则需要再调用一次YourClass.getClassLoader()方法,不过根据JDK文档的说法,Class对象的这两个方法其实是“委托”(delegate)给装载它的ClassLoader来做的,所以只需要使用 Class对象的这两个方法就可以了。
因此,直接调用 this.getClass().getResourceAsStream(String name) ;获取流,静态化方法中则使用ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream (String name) ; 。
下面是一些得到classpath和当前类的绝对路径的一些方法。你可能需要使用其中的一些方法来得到你需要的资源的绝对路径。
1.this.getClass().getResource("")
得到的是当前类class文件的URI目录。不包括自己!
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/com/test/
2.this.getClass().getResource("/")
得到的是当前的classpath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
3.this.getClass() .getClassLoader().getResource("")
得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
4.ClassLoader.getSystemResource("")
得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
5.Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader ().getResource("")
得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。
如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/
6.ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath(“/”)
Web应用程序 中,得到Web应用程序的根目录的绝对路径。这样,我们只需要提供相对于Web应用程序根目录的路径,就可以构建出定位资源的绝对路径。
如:file:/D:/workspace/.metadata/.plugins/org.eclipse.wst.server.core/tmp0/wtpwebapps/WebProject
注意点:
1.尽量不要使用相对于System.getProperty("user.dir")当前用户目录的相对路径。这是一颗定时炸 弹,随时可能要你的命。
2.尽量使用URI形式的绝对路径资源。它可以很容易的转变为URI,URL,File对象。
3.尽量使用相对classpath的相对路径。不要使用绝对路径。使用上面ClassLoaderUtil类的public static URL getExtendResource(String relativePath)方法已经能够使用相对于classpath的相对路径定位所有位置的资源。
4.绝对不要使用硬编码的绝对路径。因为,我们完全可以使用ClassLoader类的getResource("")方法得到当前classpath的绝对路径。如果你一定要指定一个绝对路径,那么使用配置文件,也比硬编码要好得多!
【spring 区别】ClassXmlAplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的区别的更多相关文章
- Spring中ClassPathXmlApplication与FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的区别
Spring中ClassPathXmlApplication与FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的区别 一.概述 在项目中遇到加载不到Spring配置文件,简单分析后,写此 ...
- Spring中ClassPathXmlApplication与FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的区别以及ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的具体路径
一.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的具体路径 String s[] = System.getProperty("java.class.path"). ...
- Spring 注释 @Autowired 和@Resource 的区别
Spring 注释 @Autowired 和@Resource 的区别 一. @Autowired和@Resource都可以用来装配bean,都可以写在字段上,或者方法上. 二. @Autowired ...
- Spring和SpringBoot比较,解惑区别
1.概述: 对于Spring和SpringBoot到底有什么区别,我听到了很多答案,刚开始迈入学习SpringBoot的我当时也是一头雾水,随着经验的积累.我慢慢理解了这两个框架到底有什么区别,我相信 ...
- Spring中BeanFactory与FactoryBean的区别
在Spring中有BeanFactory和FactoryBean这2个接口,从名字来看很相似,比较容易搞混. 一.BeanFactory BeanFactory是一个接口,它是Spring中工厂的顶层 ...
- Spring Boot @EnableAutoConfiguration和 @Configuration的区别
Spring Boot @EnableAutoConfiguration和 @Configuration的区别 在Spring Boot中,我们会使用@SpringBootApplication来开启 ...
- 【Java面试】Spring中 BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别
一个工作了六年多的粉丝,胸有成竹的去京东面试. 然后被Spring里面的一个问题卡住,唉,我和他说,6年啦,Spring都没搞明白? 那怎么去让面试官给你通过呢? 这个问题是: Spring中Bean ...
- jQuery方法区别:click() bind() live() delegate()区别
今天看到一篇jquery 事件的文章,自己写了个小例子,虽然2种方式都可以实现,但是不太明白,找了点资料 $("#box1").delegate("p",&qu ...
- JAVA基础之——三大特征、接口和抽象类区别、重载和重写区别、==和equals区别、JAVA自动装箱和拆箱
1 java三大特征 1)封装:即class,把一类实体定义成类,该类有变量和方法. 2)继承:从已有的父类中派生出子类,子类实现父类的抽象方法. 3)多态:通过父类对象可以引用不同的子类,从而实现不 ...
随机推荐
- 关于笔记本安装双系统windows and linux
ps1.安装完成后,补充下如何设在win7为默认启动系统, 大家也都知道,在linux 运行当软件都是以配置文件来设置参数当,当然grub菜单也不例外, 修改菜单可以进入grub.conf [root ...
- hdu1114 Piggy-Bank (DP基础 完全背包)
链接:Piggy-Bank 大意:已知一只猪存钱罐空的时候的重量.现在的重量,已知若干种钱的重量和价值,猪里面装着若干钱若干份,求猪中的钱的价值最小值. 题解: DP,完全背包. g[j]表示组成重量 ...
- NOIP2011 聪明的质监员
描述 小T 是一名质量监督员,最近负责检验一批矿产的质量.这批矿产共有 n 个矿石,从 1到n 逐一编号,每个矿石都有自己的重量 wi 以及价值vi .检验矿产的流程是: 1 .给定m 个区间[Li ...
- hibernate中的session缓存
1.什么是session缓存? 在 Session 接口的实现中包含一系列的 Java 集合, 这些 Java 集合构成了 Session 缓存. 只要 Session 实例没有结束生命周期, 且没有 ...
- uc_client是如何与UCenter进行通信的
以用户登录为例介绍,其它注销,改密码,消息,头像,好友均类同. 从用户xxx在某一应用程序的login.php,输入用户名,密码讲起.先用uc_user_login函数到uc_server验证此用户和 ...
- Nginx图片剪裁模块探究 http_image_filter_module
官方地址:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_image_filter_module.html 煮酒品茶:前半部安装和官方说明,后半部分实践 #yum ins ...
- Git 怎样保证fork出来的project和原project(上游项目)同步更新
1. 在 Fork 的代码库中添加上游代码库的 remote 源,该操作只需操作一次即可. 如: 其中# upstream 表示上游代码库名, 可以任意. git remote add upstre ...
- 64. 海明距离(Hamming Distance)
[本文链接] http://www.cnblogs.com/hellogiser/p/hamming-distance.html [介绍] 在信息领域,两个长度相等的字符串的海明距离是在相同位置上不同 ...
- c++标准库中几个常见的数据结构的区别和应用规则
转载自http://www.lifecrunch.biz/archives/202 vector和built-in数组类似,它拥有一段连续的内存空间,并且起始地址不变,因此它能非常好的支持随即存取,即 ...
- cocos2d-x的Android工程开启c++0x特性
首先一定要确定你所安装NDK支持c++0x(我安装的android-ndk-r8) 文本打开 项目目录/proj.android/jni/Application.mk 在APP_CPPFLAGS那一行 ...
