二叉查找树(二)之 C++的实现
概要
上一章介绍了"二叉查找树的相关理论知识,并通过C语言实现了二叉查找树"。这一章给出二叉查找树的C++版本。这里不再对树的相关概念进行介绍,若遇到不明白的概念,可以在上一章查找。
目录
1. 二叉树查找树
2. 二叉查找树的C++实现3. 二叉查找树的C++实现(完整源码)
4. 二叉查找树的C++测试程序
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3576373.html
更多内容: 数据结构与算法系列 目录
(01) 二叉查找树(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
(02) 二叉查找树(二)之 C++的实现(03) 二叉查找树(三)之 Java的实现
二叉查找树简介
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),又被称为二叉搜索树。
它是特殊的二叉树:对于二叉树,假设x为二叉树中的任意一个结点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值记为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y] <= key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个结点,则key[y] >= key[x]。那么,这棵树就是二叉查找树。如下图所示:
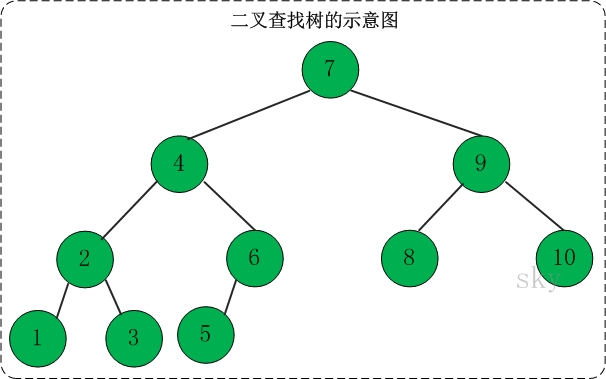
在二叉查找树中:
(01) 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(02) 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(03) 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
(04) 没有键值相等的节点(no duplicate nodes)。
二叉查找树的C++实现
1. 节点和二叉查找树的定义
1.1 二叉查找树节点
template <class T>
class BSTNode{
public:
T key; // 关键字(键值)
BSTNode *left; // 左孩子
BSTNode *right; // 右孩子
BSTNode *parent;// 父结点 BSTNode(T value, BSTNode *p, BSTNode *l, BSTNode *r):
key(value),parent(),left(l),right(r) {}
};
BSTNode是二叉查找树的节点,它包含二叉查找树的几个基本信息:
(01) key -- 它是关键字,是用来对二叉查找树的节点进行排序的。
(02) left -- 它指向当前节点的左孩子。
(03) right -- 它指向当前节点的右孩子。
(04) parent -- 它指向当前节点的父结点。
1.2 二叉树操作
template <class T>
class BSTree {
private:
BSTNode<T> *mRoot; // 根结点 public:
BSTree();
~BSTree(); // 前序遍历"二叉树"
void preOrder();
// 中序遍历"二叉树"
void inOrder();
// 后序遍历"二叉树"
void postOrder(); // (递归实现)查找"二叉树"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* search(T key);
// (非递归实现)查找"二叉树"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch(T key); // 查找最小结点:返回最小结点的键值。
T minimum();
// 查找最大结点:返回最大结点的键值。
T maximum(); // 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
BSTNode<T>* successor(BSTNode<T> *x);
// 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
BSTNode<T>* predecessor(BSTNode<T> *x); // 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到二叉树中
void insert(T key); // 删除结点(key为节点键值)
void remove(T key); // 销毁二叉树
void destroy(); // 打印二叉树
void print();
private:
// 前序遍历"二叉树"
void preOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const;
// 中序遍历"二叉树"
void inOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const;
// 后序遍历"二叉树"
void postOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const; // (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* search(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const;
// (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const; // 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。
BSTNode<T>* minimum(BSTNode<T>* tree);
// 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。
BSTNode<T>* maximum(BSTNode<T>* tree); // 将结点(z)插入到二叉树(tree)中
void insert(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z); // 删除二叉树(tree)中的结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
BSTNode<T>* remove(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z); // 销毁二叉树
void destroy(BSTNode<T>* &tree); // 打印二叉树
void print(BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction);
};
BSTree是二叉树。它包含二叉查找树的根节点和二叉查找树的操作。二叉查找树的操作中有许多重载函数,例如insert()函数,其中一个是内部接口,另一个是提供给外部的接口。
2 遍历
这里讲解前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历3种方式。
2.1 前序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(01) 访问根结点;
(02) 先序遍历左子树;
(03) 先序遍历右子树。
前序遍历代码
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::preOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
cout<< tree->key << " " ;
preOrder(tree->left);
preOrder(tree->right);
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::preOrder()
{
preOrder(mRoot);
}
2.2 中序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(01) 中序遍历左子树;
(02) 访问根结点;
(03) 中序遍历右子树。
中序遍历代码
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::inOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
inOrder(tree->left);
cout<< tree->key << " " ;
inOrder(tree->right);
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::inOrder()
{
inOrder(mRoot);
}
2.3 后序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(01) 后序遍历左子树;
(02) 后序遍历右子树;
(03) 访问根结点。
后序遍历代码
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::postOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
postOrder(tree->left);
postOrder(tree->right);
cout<< tree->key << " " ;
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::postOrder()
{
postOrder(mRoot);
}
看看下面这颗树的各种遍历方式:

对于上面的二叉树而言,
(01) 前序遍历结果: 3 1 2 5 4 6
(02) 中序遍历结果: 1 2 3 4 5 6
(03) 后序遍历结果: 2 1 4 6 5 3
3. 查找
递归版本的代码
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const
{
if (x==NULL || x->key==key)
return x; if (key < x->key)
return search(x->left, key);
else
return search(x->right, key);
} template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search(T key)
{
search(mRoot, key);
}
非递归版本的代码
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const
{
while ((x!=NULL) && (x->key!=key))
{
if (key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else
x = x->right;
} return x;
} template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch(T key)
{
iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}
4. 最大值和最小值
查找最大值的代码
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::maximum(BSTNode<T>* tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL; while(tree->right != NULL)
tree = tree->right;
return tree;
} template <class T>
T BSTree<T>::maximum()
{
BSTNode<T> *p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != NULL)
return p->key; return (T)NULL;
}
查找最小值的代码
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::minimum(BSTNode<T>* tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL; while(tree->left != NULL)
tree = tree->left;
return tree;
} template <class T>
T BSTree<T>::minimum()
{
BSTNode<T> *p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != NULL)
return p->key; return (T)NULL;
}
5. 前驱和后继
节点的前驱:是该节点的左子树中的最大节点。
节点的后继:是该节点的右子树中的最小节点。
查找前驱节点的代码
/*
* 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::predecessor(BSTNode<T> *x)
{
// 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。
if (x->left != NULL)
return maximum(x->left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。
BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent;
while ((y!=NULL) && (x==y->left))
{
x = y;
y = y->parent;
} return y;
}
查找后继节点的代码
/*
* 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::successor(BSTNode<T> *x)
{
// 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。
if (x->right != NULL)
return minimum(x->right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。
BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent;
while ((y!=NULL) && (x==y->right))
{
x = y;
y = y->parent;
} return y;
}
6. 插入
插入节点的代码
/*
* 将结点插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 插入的结点
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::insert(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z)
{
BSTNode<T> *y = NULL;
BSTNode<T> *x = tree; // 查找z的插入位置
while (x != NULL)
{
y = x;
if (z->key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else
x = x->right;
} z->parent = y;
if (y==NULL)
tree = z;
else if (z->key < y->key)
y->left = z;
else
y->right = z;
} /*
* 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::insert(T key)
{
BSTNode<T> *z=NULL; // 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if ((z=new BSTNode<T>(key,NULL,NULL,NULL)) == NULL)
return ; insert(mRoot, z);
}
注:本文实现的二叉查找树是允许插入相同键值的节点的。若想禁止二叉查找树中插入相同键值的节点,可以参考"二叉查找树(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现"中的插入函数进行修改。
7. 删除
删除节点的代码
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::remove(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z)
{
BSTNode<T> *x=NULL;
BSTNode<T> *y=NULL; if ((z->left == NULL) || (z->right == NULL) )
y = z;
else
y = successor(z); if (y->left != NULL)
x = y->left;
else
x = y->right; if (x != NULL)
x->parent = y->parent; if (y->parent == NULL)
tree = x;
else if (y == y->parent->left)
y->parent->left = x;
else
y->parent->right = x; if (y != z)
z->key = y->key; return y;
} /*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::remove(T key)
{
BSTNode<T> *z, *node; if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != NULL)
if ( (node = remove(mRoot, z)) != NULL)
delete node;
}
8. 打印
打印二叉查找树的代码
/*
* 打印"二叉查找树"
*
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::print(BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction)
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
if(direction==) // tree是根节点
cout << setw() << tree->key << " is root" << endl;
else // tree是分支节点
cout << setw() << tree->key << " is " << setw() << key << "'s " << setw() << (direction==?"right child" : "left child") << endl; print(tree->left, tree->key, -);
print(tree->right,tree->key, );
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::print()
{
if (mRoot != NULL)
print(mRoot, mRoot->key, );
}
9. 销毁
销毁二叉查找树的代码
/*
* 销毁二叉树
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::destroy(BSTNode<T>* &tree)
{
if (tree==NULL)
return ; if (tree->left != NULL)
return destroy(tree->left);
if (tree->right != NULL)
return destroy(tree->right); delete tree;
tree=NULL;
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::destroy()
{
destroy(mRoot);
}
二叉查找树的C++实现(完整源码)
二叉查找树的C++实现文件(BSTree.h)
/**
* C++ 语言: 二叉查找树
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2013/11/07
*/ #ifndef _BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_HPP_
#define _BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_HPP_ #include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; template <class T>
class BSTNode{
public:
T key; // 关键字(键值)
BSTNode *left; // 左孩子
BSTNode *right; // 右孩子
BSTNode *parent;// 父结点 BSTNode(T value, BSTNode *p, BSTNode *l, BSTNode *r):
key(value),parent(),left(l),right(r) {}
}; template <class T>
class BSTree {
private:
BSTNode<T> *mRoot; // 根结点 public:
BSTree();
~BSTree(); // 前序遍历"二叉树"
void preOrder();
// 中序遍历"二叉树"
void inOrder();
// 后序遍历"二叉树"
void postOrder(); // (递归实现)查找"二叉树"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* search(T key);
// (非递归实现)查找"二叉树"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch(T key); // 查找最小结点:返回最小结点的键值。
T minimum();
// 查找最大结点:返回最大结点的键值。
T maximum(); // 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
BSTNode<T>* successor(BSTNode<T> *x);
// 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
BSTNode<T>* predecessor(BSTNode<T> *x); // 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到二叉树中
void insert(T key); // 删除结点(key为节点键值)
void remove(T key); // 销毁二叉树
void destroy(); // 打印二叉树
void print();
private:
// 前序遍历"二叉树"
void preOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const;
// 中序遍历"二叉树"
void inOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const;
// 后序遍历"二叉树"
void postOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const; // (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* search(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const;
// (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const; // 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。
BSTNode<T>* minimum(BSTNode<T>* tree);
// 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。
BSTNode<T>* maximum(BSTNode<T>* tree); // 将结点(z)插入到二叉树(tree)中
void insert(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z); // 删除二叉树(tree)中的结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
BSTNode<T>* remove(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z); // 销毁二叉树
void destroy(BSTNode<T>* &tree); // 打印二叉树
void print(BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction);
}; /*
* 构造函数
*/
template <class T>
BSTree<T>::BSTree():mRoot(NULL)
{
} /*
* 析构函数
*/
template <class T>
BSTree<T>::~BSTree()
{
destroy();
} /*
* 前序遍历"二叉树"
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::preOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
cout<< tree->key << " " ;
preOrder(tree->left);
preOrder(tree->right);
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::preOrder()
{
preOrder(mRoot);
} /*
* 中序遍历"二叉树"
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::inOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
inOrder(tree->left);
cout<< tree->key << " " ;
inOrder(tree->right);
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::inOrder()
{
inOrder(mRoot);
} /*
* 后序遍历"二叉树"
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::postOrder(BSTNode<T>* tree) const
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
postOrder(tree->left);
postOrder(tree->right);
cout<< tree->key << " " ;
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::postOrder()
{
postOrder(mRoot);
} /*
* (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const
{
if (x==NULL || x->key==key)
return x; if (key < x->key)
return search(x->left, key);
else
return search(x->right, key);
} template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search(T key)
{
search(mRoot, key);
} /*
* (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const
{
while ((x!=NULL) && (x->key!=key))
{
if (key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else
x = x->right;
} return x;
} template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch(T key)
{
iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
} /*
* 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::minimum(BSTNode<T>* tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL; while(tree->left != NULL)
tree = tree->left;
return tree;
} template <class T>
T BSTree<T>::minimum()
{
BSTNode<T> *p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != NULL)
return p->key; return (T)NULL;
} /*
* 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::maximum(BSTNode<T>* tree)
{
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL; while(tree->right != NULL)
tree = tree->right;
return tree;
} template <class T>
T BSTree<T>::maximum()
{
BSTNode<T> *p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != NULL)
return p->key; return (T)NULL;
} /*
* 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::successor(BSTNode<T> *x)
{
// 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。
if (x->right != NULL)
return minimum(x->right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。
BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent;
while ((y!=NULL) && (x==y->right))
{
x = y;
y = y->parent;
} return y;
} /*
* 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::predecessor(BSTNode<T> *x)
{
// 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。
if (x->left != NULL)
return maximum(x->left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。
BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent;
while ((y!=NULL) && (x==y->left))
{
x = y;
y = y->parent;
} return y;
} /*
* 将结点插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 插入的结点
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::insert(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z)
{
BSTNode<T> *y = NULL;
BSTNode<T> *x = tree; // 查找z的插入位置
while (x != NULL)
{
y = x;
if (z->key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else
x = x->right;
} z->parent = y;
if (y==NULL)
tree = z;
else if (z->key < y->key)
y->left = z;
else
y->right = z;
} /*
* 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::insert(T key)
{
BSTNode<T> *z=NULL; // 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if ((z=new BSTNode<T>(key,NULL,NULL,NULL)) == NULL)
return ; insert(mRoot, z);
} /*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
template <class T>
BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::remove(BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z)
{
BSTNode<T> *x=NULL;
BSTNode<T> *y=NULL; if ((z->left == NULL) || (z->right == NULL) )
y = z;
else
y = successor(z); if (y->left != NULL)
x = y->left;
else
x = y->right; if (x != NULL)
x->parent = y->parent; if (y->parent == NULL)
tree = x;
else if (y == y->parent->left)
y->parent->left = x;
else
y->parent->right = x; if (y != z)
z->key = y->key; return y;
} /*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::remove(T key)
{
BSTNode<T> *z, *node; if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != NULL)
if ( (node = remove(mRoot, z)) != NULL)
delete node;
} /*
* 销毁二叉树
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::destroy(BSTNode<T>* &tree)
{
if (tree==NULL)
return ; if (tree->left != NULL)
return destroy(tree->left);
if (tree->right != NULL)
return destroy(tree->right); delete tree;
tree=NULL;
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::destroy()
{
destroy(mRoot);
} /*
* 打印"二叉查找树"
*
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::print(BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction)
{
if(tree != NULL)
{
if(direction==) // tree是根节点
cout << setw() << tree->key << " is root" << endl;
else // tree是分支节点
cout << setw() << tree->key << " is " << setw() << key << "'s " << setw() << (direction==?"right child" : "left child") << endl; print(tree->left, tree->key, -);
print(tree->right,tree->key, );
}
} template <class T>
void BSTree<T>::print()
{
if (mRoot != NULL)
print(mRoot, mRoot->key, );
} #endif
二叉查找树的C++测试程序(BSTreeTest.cpp)
/**
* C++ 语言: 二叉查找树
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2013/11/07
*/ #include <iostream>
#include "BSTree.h"
using namespace std; static int arr[]= {,,,,,};
#define TBL_SIZE(a) ( (sizeof(a)) / (sizeof(a[0])) ) int main()
{
int i, ilen;
BSTree<int>* tree=new BSTree<int>(); cout << "== 依次添加: ";
ilen = TBL_SIZE(arr);
for(i=; i<ilen; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] <<" ";
tree->insert(arr[i]);
} cout << "\n== 前序遍历: ";
tree->preOrder(); cout << "\n== 中序遍历: ";
tree->inOrder(); cout << "\n== 后序遍历: ";
tree->postOrder();
cout << endl; cout << "== 最小值: " << tree->minimum() << endl;
cout << "== 最大值: " << tree->maximum() << endl;
cout << "== 树的详细信息: " << endl;
tree->print(); cout << "\n== 删除根节点: " << arr[];
tree->remove(arr[]); cout << "\n== 中序遍历: ";
tree->inOrder();
cout << endl; // 销毁二叉树
tree->destroy(); return ;
}
关于二叉查找树的C++实现有两点需要补充说明的:
第1点:采用了STL模板。因此,二叉查找树支持任意数据类型。
第2点:将二叉查找树的"声明"和"实现"都位于BSTree.h中。这是因为,在二叉查找树的实现采用了模板;而C++编译器不支持对模板的分离式编译!
二叉查找树的C++测试程序
上面的BSTreeTest.c是二叉查找树树的测试程序,运行结果如下:
== 依次添加:
== 前序遍历:
== 中序遍历:
== 后序遍历:
== 最小值:
== 最大值:
== 树的详细信息:
is root
is 's right child
is 's left child
is 's left child
is 's left child
is 's right child == 删除根节点:
== 中序遍历:
下面对测试程序的流程进行分析!
(01) 新建"二叉查找树"root。
(02) 向二叉查找树中依次插入1,5,4,3,2,6 。如下图所示:

(03) 遍历和查找
插入1,5,4,3,2,6之后,得到的二叉查找树如下:

前序遍历结果: 1 5 4 3 2 6
中序遍历结果: 1 2 3 4 5 6
后序遍历结果: 2 3 4 6 5 1
最小值是1,而最大值是6。
(04) 删除节点4。如下图所示:

(05) 重新遍历该二叉查找树。
中序遍历结果: 1 2 4 5 6
二叉查找树(二)之 C++的实现的更多相关文章
- 二叉查找树(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要 本章先对二叉树的相关理论知识进行介绍,然后给出C语言的详细实现.关于二叉树的学习,需要说明的是:它并不难,不仅不难,而且它非常简单.初次接触树的时候,我也觉得它似乎很难:而之所产生这种感觉主要是 ...
- 二叉查找树(三)之 Java的实现
概要 在前面分别介绍了"二叉查找树的相关理论知识,然后给出了二叉查找树的C和C++实现版本".这一章写一写二叉查找树的Java实现版本. 目录 1. 二叉树查找树2. 二叉查找树的 ...
- C++数据结构之二叉查找树(BST)
C++数据结构之二叉查找树(BST) 二分查找法在算法家族大类中属于“分治法”,二分查找的过程比较简单,代码见我的另一篇日志,戳这里!因二分查找所涉及的有序表是一个向量,若有插入和删除结点的操作,则维 ...
- "《算法导论》之‘树’":二叉查找树
树的介绍部分摘取自博文二叉查找树(一).二叉查找树(二).二叉查找树. 1. 树的介绍 1.1 树的定义 树是一种数据结构,它是由n(n>=1)个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合. 把它叫做“ ...
- 【algo&ds】【吐血整理】4.树和二叉树、完全二叉树、满二叉树、二叉查找树、平衡二叉树、堆、哈夫曼树、B树、字典树、红黑树、跳表、散列表
本博客内容耗时4天整理,如果需要转载,请注明出处,谢谢. 1.树 1.1树的定义 在计算机科学中,树(英语:tree)是一种抽象数据类型(ADT)或是实作这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结 ...
- 数据结构中的树(二叉树、二叉搜索树、AVL树)
数据结构动图展示网站 树的概念 树(英语:tree)是一种抽象数据类型(ADT)或是实作这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合.它是由n(n>=1)个有限节点组成一个具有 ...
- Java实现二叉搜索树
原创:转载需注明原创地址 https://www.cnblogs.com/fanerwei222/p/11406176.html 尝试一下用Java实现二叉搜索树/二叉查找树,记录自己的学习历程. 1 ...
- 平衡二叉树(AVL Tree)
在学习算法的过程中,二叉平衡树是一定会碰到的,这篇博文尽可能简明易懂的介绍下二叉树的相关概念,然后着重讲下什么事平衡二叉树. (由于作图的时候忽略了箭头的问题,正常的树一般没有箭头,虽然不影响描述的过 ...
- mysql高级教程(一)-----逻辑架构、查询流程、索引
mysql逻辑架构 和其它数据库相比,MySQL有点与众不同,它的架构可以在多种不同场景中应用并发挥良好作用.主要体现在存储引擎的架构上,插件式的存储引擎架构将查询处理和其它的系统任务以及数据的存储提 ...
随机推荐
- Android图片处理-相机、相处简单调用
安卓开发中,常常需要使用到手机相机拍照.或者相册上传头像等等.通过使用Intent,我们很方便地获得相机.相册里面的图片: 1.相机调用,通过设置File文件路径和文件名,可以将拍照得到的图片保存下来 ...
- Oracle 查看哪个表被锁定,并获取对应的sessionID
SELECT A.OWNER,A.OBJECT_NAME,B.XIDUSN,B.XIDSLOT,B.XIDSQN,B.SESSION_ID,B.ORACLE_USERNAME, B.OS_USER_N ...
- 《Windows核心编程》学习笔记(9)– 在win7或者vista系统下提升一个进程的运行权限
win7或者vista默认运行程序是在受限制的环境下运行的,以减轻病毒对于系统的破坏.那么我们怎样才能提升一个进程的权限以至让它在 管理员模式下运行.当然CreateProcess函数没有提供这个功能 ...
- 關於imagick不得不說的一些事
PHP建圖通常都用GD庫,因為是內置的不需要在服務器上額外安裝插件,所以用起來比較省心,但是如果你的程序主要的功能就是處理圖像,那麼就不建議用GD了,因為GD不但低效能而且能力也比較弱,佔用的系統資源 ...
- JVM中的Stack和Frame
JVM执行Java程序时需要装载各种数据,比如类型信息(Class).类型实例(Instance).常量数据(Constant).本地变量等.不同的数据存放在不同的内存区中,这些数据内存区称作“运行时 ...
- 努力学习 HTML5 (4)—— 浏览器对语义元素的支持情况
经过上一节学习,我们已经建立一个结构良好的页面,如果在旧版的 IE 浏览器中浏览可能这些语义元素无法显示. 毕竟这些语义元素什么也不做,要支持它们,只要让浏览器把它们当做普通的 <div> ...
- StringBuffer&StringBuilder区别详解
序言 StringBuffer与StringBuilder是java.lang包下被大家熟知的两个类.其异同为:一.长度都是可扩充的:二.StringBuffer是线程安全的,StringBuilde ...
- 通过生产者消费者模式例子讲解Java基类方法wait、notify、notifyAll
wait(),notify()和notifyAll()都是Java基类java.lang.Object的方法. 通俗解释wait():在当前线程等待其它线程唤醒.notify(): 唤醒一个线程正在等 ...
- Java关键字--static
在Java中,将关键字static分为三部分进行讨论,分别为Java静态变量.Java静态方法.Java静态类 Java Static Variables Java instance variable ...
- Ubuntu上安装和使用SSH,Xming+PuTTY在Windows下远程Linux主机使用图形界面的程序
自:http://blog.csdn.net/neofung/article/details/6574002 Ubuntu上安装和使用SSH 网上有很多介绍在Ubuntu下开启SSH服务的文章,但大 ...
