IPC之PIPE
管道是一种只允许用在有亲属关系的进程间通信的方式,由函数pipe创建一个管道,read,write进行读写操作。
- #include <unistd.h>
- int pipe(int pipefd[]);
参数pipefd[2]数组返回打开的读写描述符,pipefd[0]为读,pipefd[1]为写。
第一个问题:文件描述符怎么会出现一个只能读,一个只能写呢?猜想是对一个文件打开了2次,一个以只读打开,一个以只写打开。使用fcntl来验证下:
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
- F_GETFL (void)
- Get the file access mode and the file status flags; arg is ignored.
cmd为F_GETFL时,最后一个参数arg被忽略。测试代码:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- int main(void)
- {
- int flags;
- int fd[];
- if (pipe(fd) < )
- {
- perror("pipe error");
- }
- flags = fcntl(fd[], F_GETFL,);
- if ( flags < )
- {
- perror("fcntl");
- close(fd[]);
- close(fd[]);
- }
- switch (flags & O_ACCMODE)
- {
- case O_RDONLY:
- printf("read only\n");
- break;
- case O_WRONLY:
- printf("write only\n");
- break;
- case O_RDWR:
- printf("read write\n");
- break;
- default:
- printf("unknown access mode\n");
- }
- flags = fcntl(fd[], F_GETFL,);
- if ( flags < )
- {
- perror("fcntl");
- close(fd[]);
- close(fd[]);
- }
- switch (flags & O_ACCMODE)
- {
- case O_RDONLY:
- printf("read only\n");
- break;
- case O_WRONLY:
- printf("write only\n");
- break;
- case O_RDWR:
- printf("read write\n");
- break;
- default:
- printf("unknown access mode\n");
- }
- close(fd[]);
- close(fd[]);
- exit();
- }
运行结果:
- read only
- write only
与猜想相符。
数据的流向:

从图中可以看出,进程可以以pipefd[1]写完,然后以pipefd[0]读,自己写自己读,这条数据流是通的。 验证:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #define MAXLINE 4096
- int main(void)
- {
- int flags;
- int fd[], n;
- char buf[MAXLINE];
- if (pipe(fd) < )
- {
- perror("pipe error");
- }
- n = write(fd[], "hello world\n", MAXLINE);
- if ( n < )
- {
- perror("write");
- goto end;
- }
- n = read(fd[],buf, n);
- if ( n < )
- {
- perror("read");
- goto end;
- }
- printf("read:%s\n",buf);
- end:
- close(fd[]);
- close(fd[]);
- exit();
- }
输出:
- read:hello world
既然是进程间通信,那么管道在同一个进程中读写基本是没什么意义的,管道常用的方式是,先创建一个管道,然后fork,父子进程就共享了这个管道了。数据流向如图:

这样,管道的写端有2个进程操作,读端有2个进程操作。但是这样一来就出现了一个问题,假设父进程读,那么这个数据是它自己写进去的呢?还是子进程写进去的?无法区分。通常一个进程关闭它的读,另一个进程关闭它的写,这样,数据流向就只有一个方向了,数据来自谁就显而易见了。如图:
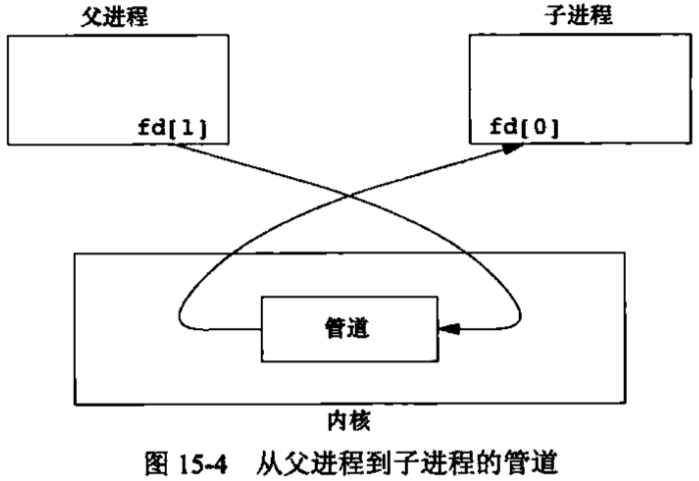
测试代码:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define MAXLINE 4096
- int main(void)
- {
- int n;
- int fd[];
- pid_t pid;
- char line[MAXLINE];
- if (pipe(fd) < )
- perror("pipe error");
- if ((pid = fork()) < )
- {
- perror("fork error");
- }
- else if (pid > ) /* parent */
- {
- close(fd[]);
- write(fd[], "hello world\n", );
- }
- else /* child */
- {
- close(fd[]);
- n = read(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
- write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n);
- }
- exit();
- }
结果:
- hello world
读一个空的管道或者写一个满的管道都将导致阻塞,不过可以通过fcntl的F_SETFL设置为O_NONBLOCK,从而不阻塞。
当管道一端被关闭后,有下列2条规则:
1.当读一个写端所有文件描述符引用都已被关闭的管道时,在所有数据被读完后,read将返回0。表示无数据可读。
2.当写一个读端所有文件描述符引用都已被关闭的管道时,将产生SIGPIPE信号,write返回-1。
混淆的东西,管道的容量和管道的缓冲区大小。
管道的容量:指管道满时装的字节数,自2.6.11内核后,容量为64k。管道满了就会导致写操作产生阻塞。
管道缓冲区大小:由PIPE_BUF指定,指的是保证管道写操作为原子操作的最大值,如果一次写入的内容超过这个值,那么这次的写操作就不是原子的。什么意思呢?就是指,可能存在多个进程写同一个管道,如果一次写入的字节数大于缓冲区大小,则可能会出现A进程写入的内容中插入了B进程写入的内容。
下面是出现这种情况的代码:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define MAXLINE 4096+100
- int main(void)
- {
- int n;
- int fd[];
- pid_t pid;
- char line[MAXLINE];
- if (pipe(fd) < )
- {
- perror("pipe error");
- }
- if ((pid = fork()) < )
- {
- perror("fork error");
- }
- else if (pid > ) /* parent */
- {
- close(fd[]);
- while ( )
- {
- n = read(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
- write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n);
- write(STDOUT_FILENO, "\n\n\n", );
- }
- }
- else /* child */
- {
- if ((pid = fork()) < )
- {
- perror("fork error");
- }
- else if (pid > )
- {
- close(fd[]);
- while ()
- {
- memset(line, 'a',MAXLINE);
- write(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
- }
- }
- else
- {
- close(fd[]);
- while ( )
- {
- memset(line, 'b',MAXLINE);
- write(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
- }
- }
- }
- exit();
- }
IPC之PIPE的更多相关文章
- Linux IPC BSD Pipe
mkfifo() //创建有名管道(FIFO special file),创建完了就像普通文件一样open(),再读写,成功返回0,失败返回-1设errno.VS$man 3 mkfifo #incl ...
- Unix IPC之pipe
pipe创建函数: #include <unistd.h> /* Create a one-way communication channel (pipe). If successful, ...
- linux IPC的PIPE
一.PIPE(无名管道) 函数原型: #include <unistd.h> ]); 通常,进程会先调用pipe,接着调用fork,从而创建从父进程到子进程的IPC通道. 父进程和子进程之 ...
- CVE-2017-7494 Linux Samba named pipe file Open Vul Lead to DLL Execution
catalogue . 漏洞复现 . 漏洞代码原理分析 . 漏洞利用前提 . 临时缓解 && 修复手段 1. 漏洞复现 . SMB登录上去 . 枚举共享目录,得到共享目录/文件列表,匿 ...
- 【APUE】Chapter16 Network IPC: Sockets & makefile写法学习
16.1 Introduction Chapter15讲的是同一个machine之间不同进程的通信,这一章内容是不同machine之间通过network通信,切入点是socket. 16.2 Sock ...
- 高级IPC DBus
What is IPC IPC [Inter-Process Communication] 进程间通信,指至少两个进程或线程间传送数据或信号的一些技术或方法.在Linux/Unix中,提供了许多IPC ...
- (转)解决 ORA-12514: TNS: 监听程序当前无法识别连接描述符中请求的服务
下面操作默认在安装Oralce数据库的服务器上运行. 1)确保Oracle 基本服务都已启动 OracleDBConsoleorcl OracleOraDb11g_home1TNSListener O ...
- python高级之多进程
python高级之多进程 本节内容 多进程概念 Process类 进程间通讯 进程同步 进程池 1.多进程概念 multiprocessing is a package that supports s ...
- oracle 监听启动、停止、查看命令
1.su oracle 然后启动监听器 1.lsnrctl start 会看到启动成功的界面; 1.lsnrctl stop 停止监听器命令. 1.lsnrctl status 查看监听器命令. ...
随机推荐
- .NET开发 正则表达式中的 Bug
又发现了一个 .net 的 bug!最近在使用正则表达式的时候发现:在忽略大小写的时候,匹配值从 0xff 到 0xffff 之间的所有字符,正则表达式竟然也能匹配两个 ASCII 字符:i(code ...
- BI之SSAS完整实战教程4 -- 部署至SSAS进行简单分析
上一篇已经创建了多维数据集的结构. 接下来我们将多维数据集的架构定义发送到Analysis Services实例,部署到AS上去. 文章提纲 部署和浏览多维数据集 SSMS使用简介 总结 一.部署和浏 ...
- ThreadLocal解决线程安全问题
一.线程安全问题产生的原因 线程安全问题都是由全局变量及静态变量引起的 二.线程安全问题 SimpleDateFormate sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();使用sdf.pa ...
- 依赖于spring 4.x的spring组件
1.Spring Data MongoDB 1.6.x开始依赖于spring 4.x: 2.@Conditional注解: 3.spring-data-redis 1.4.x开始依赖于spring 4 ...
- IOS网络编请求响应之URL结构
资料均来自互联网,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任. 人魔七七:http://www.cnblogs.com/qiqibo/ 对于我们IOS开发者来说 ...
- ASP.NET检测到有潜在危险的 Request.Form 值解决方案汇总
ASP.NET检测到有潜在危险的 Request.Form 值解决方案汇总 当我们在网站中使用CKEditor等富文本编辑器时,大多都会遇到这样的到警告 这是因为ASP.NET默认开启对页面提交内容的 ...
- 如何查询拥有执行某个Tcode权限所有人员
方法很简单,如下 一:Tcode:S_BCE_68001400二:输入你想查询的Tcode,例如:SE38 打开如下图所示,然后执行即可 三:AUTH(关于权限的控制),打开如下图所示.上图“ ...
- Spark中的RDD操作简介
map(func) 对数据集中的元素逐一处理,变为新的元素,但一个输入元素只能有一个输出元素 scala> pairData.collect() res6: Array[Int] = Array ...
- 高性能JS笔记1——加载执行
一.脚本位置 1.Script标签尽可能放到Body底部,以减少脚本文件下载对整个页面UI渲染的影响. 2.Script标签永远不要紧跟Link标签后面. 二.组织脚本 1.合并多个文件在一个Scri ...
- 安装sql server managerment studio报错"The instance id is required but it is missing"
问题描述: 今天在安装sql server managerment studio的时候提示报错"The instance id is required but it is missing&q ...
