剑指offer题解
数组中重复的数字
题目描述:在一个长度为n的数组里面的所有数字都在0~n-1的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但是不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次,请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是重复的数字2或者3.
解题思路:
1.先把输入的数组排序,从排序的数组中找出重复的数字是一件很容易的事,只需从头到尾扫描排序后的数组就可以了。排序一个长度为n的数组需要O(nlogn)的时间。
2.可以利用哈希表来解决,从头到尾按顺序扫描数组的每个数字,每扫描到一个数字的时候,都可以用O(1)的时间判断哈希表里面是否已经包含了该数字。如果哈希表里面还没有这个数字,就把他加入哈希表,如果已经存在了该数字,就找到一个重复的数字,算法的时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度为O(n),
3.假设重排这个数组,如果数组中没有重复的数字,那么当数组排序后,数字i将出现在下标为i的位置。由于数组中有重复的数字,那有些位置可能存在多个数字,有些位置可能没有数字。
现在重排这个数组,从头打到尾依次扫描这个数组中的每个数字。当扫描到下标为i的数字时,首先比较这个数字m是不是等于i,如果是,则接着扫描下一个数字;如果不是,那么拿它和第m个数字进行比较。如果它和第m个数字相等,就找到了一个重复的数字;如果它和第m个数字不相等,就把第i个数字和第m个数字交换,把m放在属于它的位置,接下来重复这个比较交换的过程,直到发现第一个重复数字。
以 (2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5) 为例:
position-0 : (2,3,1,0,2,5) // 2 <-> 1
(1,3,2,0,2,5) // 1 <-> 3
(3,1,2,0,2,5) // 3 <-> 0
(0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-1 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-2 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-3 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // already in position
position-4 : (0,1,2,3,2,5) // nums[i] == nums[nums[i]], exit
遍历到位置 4 时,该位置上的数为 2,但是第 2 个位置上已经有一个 2 的值了,因此可以知道 2 重复。
例题:
题目描述
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。 例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
public class Solution {
// Parameters:
// numbers: an array of integers
// length: the length of array numbers
// duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number,length of duplication array is 1,so using duplication[0] = ? in implementation;
// Here duplication like pointor in C/C++, duplication[0] equal *duplication in C/C++
// 这里要特别注意~返回任意重复的一个,赋值duplication[0]
// Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number
// otherwise false
public boolean duplicate(int numbers[],int length,int [] duplication) {
if (numbers == null || numbers.length == 0) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
while (numbers[i] != i) {
if (numbers[i] == numbers[numbers[i]]) {
duplication[0] = numbers[i];
return true;
}
swap(numbers, i, numbers[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
public void swap(int[] numbers, int i, int j) {
int temp = numbers[i];
numbers[i] = numbers[j];
numbers[j] = temp;
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
不修改数组找出重复的数字
题目描述:在一个长度为n+1的数组里面的所有数字都在1~n的范围内,所以数组中至少有一个数字是重复的,请找出数组当中任意一个重复的数字,但不能修改输入的数组。例如输入长度为8的数组{2,3,5,4,3,2,6,7},那么对应的输出是重复的数字2或者3。
解题思路:
1.可以创建一个长度为n+1上午辅助数组,然后逐一把原数组的每个数字复制到辅助数组。如果原数组中被复制的数字是m,则把它复制到辅助数组中下标为m的位置,这样很容易就能发现哪个数字是重复的,这样需要O(n)的辅助空间。
2.可以把1~n的数字从中间的数字m分为两部分,前面一半为1~m,后面一半为m+1~n。如果1~m的数字的数目超过m,那么这一版的区间里面一定包含重复数字,否则另一半区间里面肯定包含重复数字。我们可以继续吧包含重复数字的区间一分为二,直到找到一个重复的数字,类似二分法。
例题:
633. 寻找重复的数
给出一个数组 nums 包含 n + 1 个整数,每个整数是从 1 到 n (包括边界),保证至少存在一个重复的整数。假设只有一个重复的整数,找出这个重复的数。 样例
给出 nums = [5,5,4,3,2,1],返回 5.
给出 nums = [5,4,4,3,2,1],返回 4. 注意事项
1.不能修改数组(假设数组只能读)
2.只能用额外的O(1)的空间
3.时间复杂度小于O(n^2)
4.数组中只有一个重复的数,但可能重复超过一次
解法:
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nums: an array containing n + 1 integers which is between 1 and n
* @return: the duplicate one
*/
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
// write your code here
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int start = 1;
int end = nums.length - 1;
while (end >= start) {
int mid = ((end - start) >> 1) + start;
int count = countRange(nums, start, mid);
if (end == start) {
if (count > 1) {
return start;
} else {
break;
}
}
//前半部分数字在数组中出现的次数大于前半部分数字的个数
if (count > (mid - start + 1)) {
end = mid;
} else {
start = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 统计nums数组中某个范围当中的数字出现的次数
**/
public int countRange(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] >= start && nums[i] <= end) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
二维数组中的查找
在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。
请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
Consider the following matrix:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
] Given target = 5, return true.
Given target = 20, return false.
public class Solution {
/**
* 从左下角开始查找,复杂度:O(M + N) + O(1)
**/
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0 || array[0] == null || array[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int row = array.length;
int col = array[0].length;
int i = row - 1;
int j = 0;
while (i >= 0 && j < col) {
if (target == array[i][j]) {
return true;
} else if (target > array[i][j]) {
j++;
} else {
i--;
}
}
return false;
}
}
-------------------------------------------
替换空格
题目描述
请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。
解题思路
在字符串尾部填充任意字符,使得字符串的长度等于替换之后的长度。因为一个空格要替换成三个字符(%20),因此当遍历到一个空格时,需要在尾部填充两个任意字符。 令 P1 指向字符串原来的末尾位置,P2 指向字符串现在的末尾位置。P1 和 P2从后向前遍历,当 P1 遍历到一个空格时,就需要令 P2 指向的位置依次填充 02%(注意是逆序的),否则就填充上 P1 指向字符的值。 从后向前遍是为了在改变 P2 所指向的内容时,不会影响到 P1 遍历原来字符串的内容。
public class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
int oldLen = str.length() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < oldLen + 1; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == ' ') {
str.append(" ");
}
}
int newLen = str.length() - 1;
while (oldLen >= 0 && newLen > oldLen) {
char temp = str.charAt(oldLen--);
if (temp == ' ') {
str.setCharAt(newLen--, '0');
str.setCharAt(newLen--, '2');
str.setCharAt(newLen--, '%');
} else {
str.setCharAt(newLen--, temp);
}
}
return str.toString();
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------
从头到尾打印链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
/**
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
*
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
//使用栈
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.push(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res.add(stack.pop());
}
return res;
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
重建二叉树
根据前序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
题目描述
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
解题思路
前序遍历的第一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。
递归的调用,实现功能。
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < in.length; i++) {
map.put(in[i], i);
}
TreeNode root = helper(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1, map);
return root;
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] pre, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] in, int inStart, int inEnd, Map<Integer, Integer> inMap) {
if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[preStart]);
int index = inMap.get(root.val);
int leftNums = index - inStart;
root.left = helper(pre, preStart + 1, preStart + leftNums, in, inStart, index - 1, inMap);
root.right = helper(pre, preStart + leftNums + 1, preEnd, in, index + 1, inEnd, inMap);
return root;
}
}
根据后序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the tree. For example, given inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
Return the following binary tree: 3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
解题思路
后序遍历的最后一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。
递归的调用,实现功能。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if (inorder == null || postorder == null || inorder.length != postorder.length) {
return null;
}
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
TreeNode root = helper(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1, map);
return root;
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd, Map<Integer, Integer> map) {
if (inStart > inEnd || postStart > postEnd) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postEnd]);
int index = map.get(root.val);
int leftNums = index - inStart;
root.left = helper(inorder, inStart, index - 1, postorder, postStart, postStart + leftNums - 1, map);
root.right = helper(inorder, index + 1, inEnd, postorder, postStart + leftNums, postEnd - 1, map);
return root;
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
二叉树的下一个节点
题目描述
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
解题思路
① 如果一个节点的右子树不为空,那么该节点的下一个节点是右子树的最左节点;

② 否则,向上找第一个左链接指向的树包含该节点的祖先节点。

/*
public class TreeLinkNode {
int val;
TreeLinkNode left = null;
TreeLinkNode right = null;
TreeLinkNode next = null; TreeLinkNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode)
{
if (pNode == null) {
return null;
}
if (pNode.right != null) {
TreeLinkNode node = pNode.right;
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
} else {
while (pNode.next != null) {
TreeLinkNode p = pNode.next;
if (p.left == pNode) {
return p;
}
pNode = pNode.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
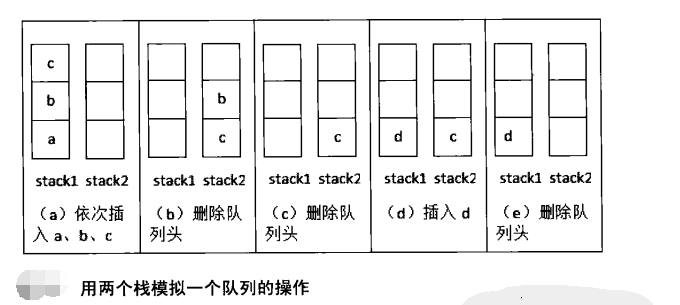
两个栈实现队列
题目描述
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
解题思路:
声明两个栈,stack1,stack2
进入队列的时候,都push到stack1中
从队列中出去的时候,从stack2中pop,如果stack2为空,
那么将stack1中的元素pop后压入stack2中,如果stack2还是为空,
那么抛出异常。
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() throws Exception{
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("queue is empty");
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
两个队列实现栈
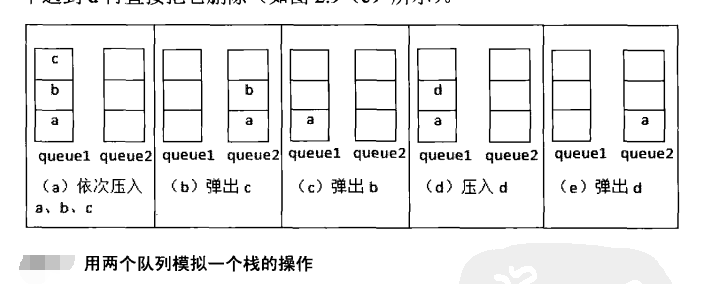
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue; public class Demo08 {
Queue<Integer> queue1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
Queue<Integer> queue2 = new ArrayDeque<>(); public void push(int node) {
//两个栈都为空时,优先考虑queue1
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()) {
queue1.add(node);
return;
} //如果queue1为空,queue2有元素,直接放入queue2
if (queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.add(node);
return;
} if (queue2.isEmpty()) {
queue1.add(node);
return;
} } public int pop() {
//两个栈都为空时,没有元素可以弹出
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()) {
try {
throw new Exception("stack is empty");
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
//如果queue1为空,queue2有元素, 将queue2的元素依次放入queue1中,直到最后一个元素,我们弹出。
if (queue1.isEmpty()) {
while (queue2.size()>1) {
queue1.add(queue2.poll());
}
return queue2.poll();
} if (queue2.isEmpty()) {
while (queue1.size()>1) {
queue2.add(queue1.poll());
}
return queue1.poll();
} return (Integer) null;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo08 demo08 = new Demo08();
demo08.push(1);
demo08.push(2);
demo08.push(3);
demo08.push(4);
System.out.println(demo08.pop());
System.out.println(demo08.pop());
demo08.push(5);
System.out.println(demo08.pop());
System.out.println(demo08.pop());
System.out.println(demo08.pop());
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
菲波那切数列
题目描述
大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项(从0开始,第0项为0)。
n<=39
递归解法:
public class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
f[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
}
非递归解法:
public class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
//考虑到第 i 项只与第 i-1 和第 i-2 项有关,
//因此只需要存储前两项的值就能求解第 i 项,
//从而将空间复杂度由 O(N) 降低为 O(1)。
int pre = 0;
int p = 1;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
res = pre + p;
pre = p;
p = res;
}
return res;
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
青蛙跳台阶
题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
解题思路:
首先考虑最简答的情况,如果只有一级台阶,那么只有一种跳法
如果有两级台阶,那么就有两种跳法
我们把n级台阶时的跳法看成n的函数,即为f(n),
当n>2时,第一次跳的时候就有两种不同的选择:
第一种是第一次只跳一级,此时跳法数目等于后面剩下的n-1级台阶的跳法数目,即为f(n-1)
第二种是第一次跳两级,此时的跳法数目等于后面剩下的n-2级台阶的跳法数目,即为f(n-2)
因此,n级台阶的不同跳法的总数为f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)。
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if (target <= 0) {
return 0;
}
if (target >0 && target <= 2) {
return target;
}
int pre = 1;
int p = 2;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++) {
res = pre + p;
pre = p;
p = res;
}
return res;
}
}
变态跳台阶
题目描述
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
这个可以用数学来解释
F(n) = F(n-1)+F(n-2)+...+F(1)
F(n-1) = F(n-2)+F(n-3)+...+F(1)
两个式子相减,很容易得出F(n)=2F(n-1)
每个台阶都有跳与不跳两种情况(除了最后一个台阶),最后一个台阶必须跳。所以共用2^(n-1)中情况
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
if (target == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (target == 1) {
return 1;
}
return 2 * JumpFloorII(target - 1);
}
}
--------------------------------------------------
矩形覆盖
题目描述
我们可以用2*1的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个2*1的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
解题思路:
假设2*n的矩形的覆盖方法为f(8)
用第一个2x1的小矩形区覆盖大矩形的最左边有两种选择,竖着放或者横着放。当竖着放的时候,右边还剩2*(n-1)的区域,覆盖的方法有f(n-1)种。当横着放的税后,左下角也得横着放一个小矩形,右边还剩2*(n-2),覆盖的方法还有f(n-2).即f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)
public class Solution {
public int RectCover(int target) {
if (target <= 0) {
return 0;
}
if (target > 0 && target <= 2) {
return target;
}
int pre = 1;
int p = 2;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= target; i++) {
res = p + pre;
pre = p;
p = res;
}
return res;
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
旋转数组的最小数字
题目描述
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
这个题目分为有重复元素和没有重复元素两种情况,没有重复元素时,利用二分法,这个时候首先要判断nums[mid]>nums[high],如果是的话,最小值肯定在在mid和high之间,令low=mid+1;否则的话领high=mid,代码如下:
public class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null) {
return -1;
}
int low = 0;
int high = nums.length - 1;
if (nums[low] < nums[high]) {
return nums[low];
}
int mid;
while (low < high) {
mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] > nums[high]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid;
}
}
return nums[low];
}
}
那么判断nums[mid]>nums[high],如果是的话,那么最小值肯定在mid和high中间,然后判断nums[mid]<nums[low],如果是的话最小值肯定在low和mid中间;否则的话都有可能,这个时候只需要令high--,代码如下:
public class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int low = 0;
int high = nums.length - 1;
if (nums[low] < nums[high]) {
return nums[low];
}
int mid;
while (low < high) {
mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] > nums[high]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[high]) {
high = mid;
} else {
high--;
}
}
return nums[low];
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------
搜索旋转排序数组
描述
假设有一个排序的按未知的旋转轴旋转的数组(比如,0 1 2 4 5 6 7 可能成为4 5 6 7 0 1 2)。给定一个目标值进行搜索,如果在数组中找到目标值返回数组中的索引位置,否则返回-1。 你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。 您在真实的面试中是否遇到过这个题?
样例
给出[4, 5, 1, 2, 3]和target=1,返回 2 给出[4, 5, 1, 2, 3]和target=0,返回 -1 挑战
O(logN) time
解题思路
这个题目解得时候,首先查找mid下标元素的值,判断nums[mid]是否等于target,
如果是,返回1;如果不是的话就与low位置的值相比较,判断nums[low]<nums[mid],
如果是,那么这个范围内的数字是单调递增的,如果不是,那么这个范围内的数字不是单调的。
如果是单调递增的,那么判断这个nums[low]<=target<=nums[mid],是的话那么让high=mid,否则的话low=mid+1,;
如果不是单调递增的话,那么判断nums[mid]=<target<=nums[high],如果是的话,令low=mid,否则的话让high=mid-1。
由于区间是low+1<high,所以最后要对结果进行验证,判断low和high哪一个符合要求,具体代码如下:
public class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null) {
return -1;
}
int low = 0;
int high = nums.length - 1;
while(low + 1 < high) {
int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if (nums[mid] > nums[low]) {//前半部分是升序
if (target >= nums[low] && target <= nums[mid]) {//待查找的元素再升序子序列中
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[low]){//前半部分不是升序
if (target >= nums[mid] && target <= nums[high]) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
}
if (nums[low] == target) {
return low;
}
if (nums[high] == target) {
return high;
}
return -1;
}
}
另一种情况是旋转数组中存在重复元素的时候,这个时候与上面基本相似,就是加一个判断如果nums[mid]=nums[low]的话,就是让low++,具体代码如下:
public class Solution {
public boolean search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null) {
return false;
}
int low = 0;
int high = nums.length - 1;
while(low + 1 < high) {
int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return true;
}
if (nums[mid] > nums[low]) {//前半部分是升序
if (target >= nums[low] && target <= nums[mid]) {//待查找的元素再升序子序列中
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[low]){//前半部分不是升序
if (target >= nums[mid] && target <= nums[high]) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
} else {
low++;
}
}
if (nums[low] == target) {
return true;
}
if (nums[high] == target) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
二进制中1的个数
题目描述
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
解题思路:
n&(n-1)
该位运算去除 n 的位级表示中最低的1那一位。 n : 10110100
n-1 : 10110011
n&(n-1) : 10110000
时间复杂度:O(M),其中 M 表示 1 的个数。
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
while (n != 0) {
count++;
n &= n - 1;
}
return count++;
}
}
相关题目:
1.判断一个整数是不是2的整数次方。如果一个整数是2的整数次方,那么它的二进制表示中只有一位是1,
所以把这个整数减去1之后再和它自己做与运算,这个整数中唯一的1就会变成0. 2.输入两个整数m,n,计算需要改变m的二进制表示中的多少位才能得到n。比如10的二进制为1010,13的二进制为1101,
需要改变1010中3为才能得到1101.分为两步解决,第一步求这连个数的异或;第二步统计异或结果中1的位数。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
数值的整数次方
题目描述
给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
思路分析:
就是求解一个数的幂级数并返回,这道题的一个思路就是利用二分法,判断n的值,
如果n=0,直接返回1,如果n=1,返回x,否则的话判断n的奇偶性,
如果n是偶数,那么x的n次方就可以分解成两个x的n/2次方相乘,然后继续分解;
如果是奇数,那么直接分解成两个x的n/2次方相乘再乘以x,然后递归的调用分解函数就行,具体代码如下;
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if (exponent == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (exponent == 1) {
return base;
}
if (exponent > 0) {
return pow(base, exponent);
} else {
return 1 / pow(base, -exponent);
}
}
public double pow(double x, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return x;
}
double half = pow(x, n >>> 1);
if (n % 2 == 0) {
return half * half;
} else {
return half * half * x;
}
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------
调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目描述
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0) {
return;
}
int oddCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] % 2 == 1) {
oddCnt++;
}
}
int[] copy = array.clone();
int i = 0, j = oddCnt;
for (int num : copy) {
if (num % 2 == 1) {
array[i++] = num;
} else {
array[j++] = num;
}
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
链表中倒数第k个结点
题目描述
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
解题思路
声明两个指针,第一个先后移k,然后两个指针同时后移,直到第一个到达最后。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if (head == null || k <= 0) {
return null;
}
ListNode p = head;
ListNode pre = head;
while (p != null && k != 0) {
p = p.next;
k--;
}
if (k > 0) {
return null;
}
while (p != null) {
p = p.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return pre; }
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
反转链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
有递归和非递归两种实现方式,对于非递归方式,
首先要定要三个指针,pre表示前驱节点,p表示当前节点,next表示下一个节点,
非递归的时候有非常固定的模式,
next=p.next,p.next=pre,pre=p,p=next;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode p = head.next;
ListNode next = null;
while (p != null) {
next = p.next;
p.next = pre;
pre = p;
p = next;
}
head.next = null;
return pre; }
}
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = ReverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead; }
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
将两个有序链表合并成一个有序链表,首先判断一下是否有一个为空,如果是的话返回另外一个,然后从头结点开始判断哪一个链表的节点值小,
将小的一个节点插入到新建的链表中,同时指针向后移动一个,最后知道有一个链表为空结束。最后还要判断哪一个链表没有结束,直接将新链表的next指向没有结束的链表即可.
另外还有一种递归的算法,直接比较两个链表的头结点大小,将小的一个作为新的头结点,然后递归的调用函数.
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
p.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
p.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = (list1 == null) ? list2 : list1;
return dummy.next;
}
}
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
list1.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
} else {
list2.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
删除链表中重复的结点
题目描述
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
把所有重复的元素都要删除,因为头结点可能也是重复元素,所以要声明新的头结点,同样这次要声明三个指针pre,p,next; pre初始化指向新生命的头结点,p初始化为头结点,要判断p和next的值是否相等,所以这两者都不能为空。直接判断p.val是否等于next.val,如果相等 将next后移直至不相等,然后pre.next = next,p = next,这样就将重复的元素都删除了,如果不想等的话直接将pre = p;p = p.next;然后继续执行循环,
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead)
{
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) {
return pHead;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = pHead;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode p = pHead;
ListNode next = null;
while (p != null && p.next != null) {
next = p.next;
if (p.val == next.val) {
while (next != null && next.val == p.val) {
next = next.next;
}
pre.next = next;
p = next;
} else {
pre = p;
p = p.next;
}
}
return dummy.next; }
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
链表中环的入口结点
题目描述
给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
利用快慢指针做,判断时主要有以下依据:


/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution { public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead)
{
if (pHead == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = pHead;
ListNode slow = pHead;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) {
slow = pHead;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
剑指offer题解的更多相关文章
- 剑指offer题解(Java版)
剑指offer题解(Java版) 从尾到头打印链表 题目描述 输入一个链表,按从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList. 方法1:用一个栈保存从头到尾访问链表的每个结点的值,然后按出栈顺序将各个值存入 ...
- 剑指Offer题解(Python版)
https://blog.csdn.net/tinkle181129/article/details/79326023# 二叉树的镜像 链表中环的入口结点 删除链表中重复的结点 从尾 ...
- 剑指Offer题解索引
数组 数组中重复的数字 二维数组中的查找 构建乘积数组 字符串 替换空格 字符流中第一个不重复的字符 表示数值的字符串 递归和循环 斐波那契数列 跳台阶 变态跳台阶 矩形覆盖 链表 从尾到头打印链表 ...
- 剑指offer题解02-10
02 单例模式 单例模式,是一种常用的软件设计模式.在它的核心结构中只包含一个被称为单例的特殊类.通过单例模式可以保证系统中,应用该模式的类一个类只有一个实例.即一个类只有一个对象实例. 从具体实现角 ...
- 【剑指offer】(第 2 版)Java 题解
[剑指offer](第 2 版)Java 题解 第一章 面试的流程 略... 第二章 面试需要的基础知识 面试题 1. 赋值运算符函数 面试题 2. 实现 Singleton 模式 Solution ...
- 《剑指offer》题解
有段时间准备找工作,囫囵吞枣地做了<剑指offer>提供的编程习题,下面是题解收集. 当初没写目录真是个坏习惯(-_-)||,自己写的东西都要到处找. 提交的源码可以在此repo中找到:h ...
- LeetCode题解汇总(包括剑指Offer和程序员面试金典,持续更新)
LeetCode题解汇总(持续更新,并将逐步迁移到本博客列表中) LeetCode题解分类汇总(包括剑指Offer和程序员面试金典) 剑指Offer 序号 题目 难度 03 数组中重复的数字 简单 0 ...
- LeetCode题解分类汇总(包括剑指Offer和程序员面试金典,持续更新)
LeetCode题解汇总(持续更新,并将逐步迁移到本博客列表中) 剑指Offer 数据结构 链表 序号 题目 难度 06 从尾到头打印链表 简单 18 删除链表的节点 简单 22 链表中倒数第k个节点 ...
- C++版 - 剑指offer 面试题23:从上往下打印二叉树(二叉树的层次遍历BFS) 题解
剑指offer 面试题23:从上往下打印二叉树 参与人数:4853 时间限制:1秒 空间限制:32768K 提交网址: http://www.nowcoder.com/practice/7fe2 ...
随机推荐
- scala 基础
1.scala一些预热操作 1.1 to 是一个方法,()可以进行 参数传递,map()把每一个元素取出来进行相应的操作, print(1.to(10).map(_*10)) 结果 Vector ...
- elasticsearch6.7 05. Document APIs(7)Update By Query API
6.Update By Query API _update_by_query 接口可以在不改变 source 的情况下对 index 中的每个文档进行更新.这对于获取新属性或其他联机映射更改很有用.以 ...
- 撩课-Java每天5道面试题第17天
116.说下Struts的设计模式 MVC模式: web应用程序启动时 就会加载并初始化ActionServler. 用户提交表单时, 一个配置好的ActionForm对象被创建, 并被填入表单相应的 ...
- 移动端meta整理
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http ...
- JavaScript有这几种测试
译者按: 也许你讨厌测试,但是你不得不面对它,所以至少区分一下单元测试.集成测试与功能测试?对吧... 原文: What are Unit Testing, Integration Testing a ...
- css清楚浮动的class
.clearfix:after { display: table; visibility: hidden; clear: both; height:; content: ''; } 直接在浮动元素的父 ...
- js之全选即点击全选标签可选择全部复选框
目标效果:网页全选功能,即点击全选标签可选择全部复选框 实现代码如下 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head&g ...
- ADB命令行控制界面开关
以下命令需要root权限: svc命令 这个脚本在/system/bin目录下,这个命令可以用来控制电源管理,wifi开关,数据开关(就是上网流量) svc power stayon [t ...
- dmesg七种用法
dmesg 命令的使用范例 ‘dmesg’命令设备故障的诊断是非常重要的.在‘dmesg’命令的帮助下进行硬件的连接或断开连接操作时,我们可以看到硬件的检测或者断开连接的信息.‘dmesg’命令在多数 ...
- centos7安装rabbitmq 总结
centos7下安装rabbitmq 折腾了三天最后做了以下总结 先查看一电脑名 :示例 #hostname name 查看一下hosts配置文件:如果如下结果,就要修改下 #cat /etc/ho ...