LeetCode 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复(C++/Java)
题目:
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in averageO(1) time.
Note: Duplicate elements are allowed.
insert(val): Inserts an item val to the collection.remove(val): Removes an item val from the collection if present.getRandom: Returns a random element from current collection of elements. The probability of each element being returned is linearly related to the number of same value the collection contains.
Example:
// Init an empty collection.
RandomizedCollection collection = new RandomizedCollection(); // Inserts 1 to the collection. Returns true as the collection did not contain 1.
collection.insert(1); // Inserts another 1 to the collection. Returns false as the collection contained 1. Collection now contains [1,1].
collection.insert(1); // Inserts 2 to the collection, returns true. Collection now contains [1,1,2].
collection.insert(2); // getRandom should return 1 with the probability 2/3, and returns 2 with the probability 1/3.
collection.getRandom(); // Removes 1 from the collection, returns true. Collection now contains [1,2].
collection.remove(1); // getRandom should return 1 and 2 both equally likely.
collection.getRandom();
分析:
这道题是leetcode380的进阶版,也就是允许出现重复的元素。这里附上380的题解LeetCode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素(C++/Java)。
同样使用HashMap来支持插入和移除操作,利用数组来支持对数据的随机访问。只不过hashmap中val对应的是一个存放该元素在数组中索引的数组,当删除操作时,可以快速定位到该元素在数组的位置。
而数组中不只存放val,而是将val和该val在hashmap中对应的数组的索引,用来支持
我们来配合例子看一下:
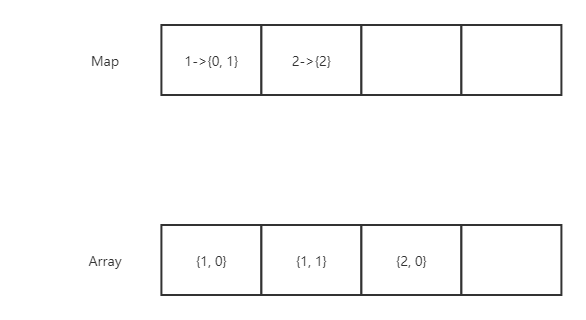
依次执行
insert(1);insert(1);insert(2);
此时存储的情况如图:
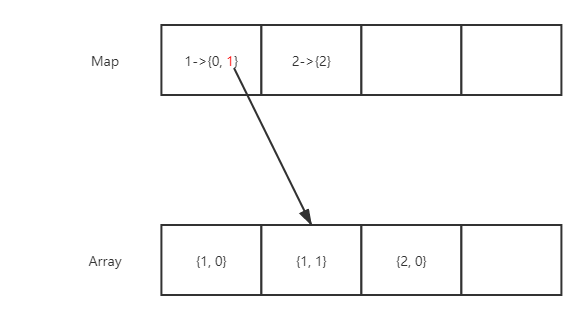
此时我们执行remove(1)的操作,我们首先通过map找到1这个元素对应的数组,取出数组中最后一个元素,表示的便是1这个元素在Array数组中的索引。
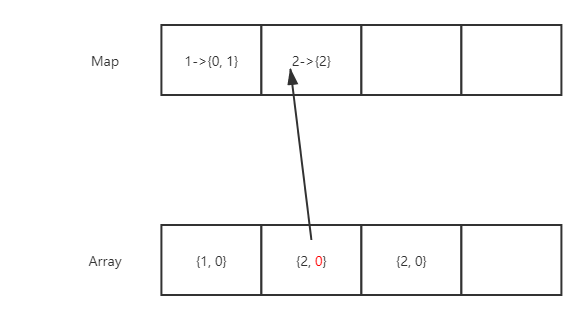
由于数组删除最后一个元素的时间复杂度为O(1)(不考虑扩容这种情况),我们将要删除的位置和数组中最后一个元素置换,或者是覆盖都可以。
然后我们再根据当前位置的这个元素去修改Map中数据,Array中元素的第二个值表示这个val在map中val对应的数组中的索引,此时我们要修改这个索引的值,改为array中调整后的索引值。最后在将无用的数据删除掉即可。
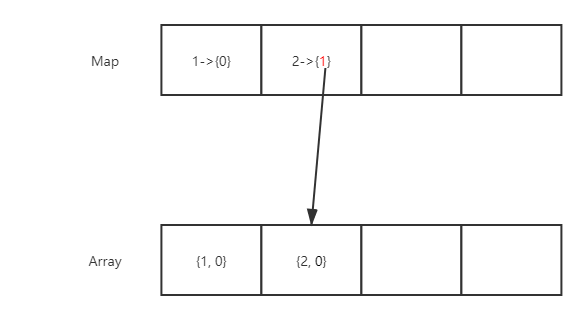
说着确实有些繁琐,不过通过实例配合图片过一遍应该比较好理解!
程序:
C++
class RandomizedCollection {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
RandomizedCollection() {
}
/** Inserts a value to the collection. Returns true if the collection did not already contain the specified element. */
bool insert(int val) {
m[val].push_back(v.size());
v.emplace_back(val, m[val].size() - );
return true;
}
/** Removes a value from the collection. Returns true if the collection contained the specified element. */
bool remove(int val) {
if(!m.count(val))
return false;
int lIndex = m[val].back();
auto entry = v.back();
v[lIndex] = entry;
m[entry.first][entry.second] = lIndex;
v.pop_back();
m[val].pop_back();
if(m[val].empty())
m.erase(val);
return true;
}
/** Get a random element from the collection. */
int getRandom() {
int index = rand() % v.size();
return v[index].first;
}
private:
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> m;
vector<pair<int, int>> v;
};
Java
class RandomizedCollection {
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public RandomizedCollection() {
}
/** Inserts a value to the collection. Returns true if the collection did not already contain the specified element. */
public boolean insert(int val) {
List<Integer> l = map.getOrDefault(val, new ArrayList<Integer>());
l.add(list.size());
map.put(val, l);
list.add(new Pair<>(val, l.size()-1));
return true;
}
/** Removes a value from the collection. Returns true if the collection contained the specified element. */
public boolean remove(int val) {
if(!map.containsKey(val))
return false;
List<Integer> l = map.get(val);
int lastIndex = l.get(l.size()-1);
Pair<Integer, Integer> p = list.get(list.size()-1);
list.set(lastIndex, p);
List<Integer> cl = map.get(p.getKey());
cl.set(p.getValue(), lastIndex);
map.put(p.getKey(), cl);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
l.remove(l.size()-1);
if(l.size() == 0)
map.remove(val);
return true;
}
/** Get a random element from the collection. */
public int getRandom() {
Random r = new Random();
int index = r.nextInt(list.size());
return list.get(index).getKey();
}
private HashMap<Integer, List> map = new HashMap<>();
private ArrayList<Pair<Integer, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
}
LeetCode 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复(C++/Java)的更多相关文章
- 381 Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复
设计一个支持在平均 时间复杂度 O(1) 下, 执行以下操作的数据结构.注意: 允许出现重复元素. insert(val):向集合中插入元素 val. remove(val):当 val ...
- [LeetCode] 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed 插入删除和获得随机数O(1)时间 - 允许重复
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- [LeetCode] 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed 常数时间内插入删除和获得随机数 - 允许重复
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- LeetCode 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-delete-getrandom-o1-duplicates-allowed/?tab=Description ...
- LeetCode 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed (插入删除和获得随机数 常数时间 允许重复项)
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- [leetcode]381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed常数时间插入删除取随机值
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- leetcode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 、381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed
380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 实现插入.删除.获得随机数功能,且时间复杂度都在O(1).实际上在插入.删除两个功能中都包含了查找功能,当然查找也必须是O(1). ...
- 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed允许重复的设计1数据结构
[抄题]: Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Dup ...
随机推荐
- 页面显示jsp源码问题
问题错误在于WEB.XML 将/*改为*即可
- appium启动app(android)
android Appium 启动APP至少需要5个参数 'platformVersion','deviceName'.'appPackage'.'appActivity'.'platform ...
- DEVOPS技术实践_01:jenkins集成平台
一.准备环境 准备三台机器 角色 IP地址 用户名 密码 jenkins-master 172.25.254.130 admin meiyoumima gitlab 172.25.254 ...
- 微服务实战——微服务架构选型SpringCloud / Dubbo / K8S比较(一)
## 说在前面 大概是三年前,因一些原因公司原项目最初为单体结构部署,所有业务模块都在一个项目里面,而后随着业务的不断膨胀以及模块之间的耦合,导致后面增加或修改一些简单业务时的成本都会变的极大.新入职 ...
- 力扣142——环形链表 II
原题 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点. 如果链表无环,则返回 null. 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始). 如果 pos ...
- selenium模块的基本使用
一.selenium库与requests库的区别 - selenium请求库: - 本质上是一个自动化测试模块; ---> 主要用于测试 UI界面 - selenium除了可以做自动化测试,还可 ...
- 1069 微博转发抽奖 (20分)C语言
小明 PAT 考了满分,高兴之余决定发起微博转发抽奖活动,从转发的网友中按顺序每隔 N 个人就发出一个红包.请你编写程序帮助他确定中奖名单. 输入格式: 输入第一行给出三个正整数 M(≤ 1000). ...
- mysql 执行计划查看
使用explain关键字可以模拟优化器执行SQL查询语句,从而知道MySQL是如何处理你的SQL语句的,分析你的查询语句或是表结构的性能瓶颈.explain执行计划包含的信息 其中最重要的字段为:id ...
- 解决httpclient设置代理ip之后请求无响应的问题
httpclient这个工具类对于大家来说应该都不陌生吧,最近在使用过程中出现了碰到一个棘手的问题,当请求的接口地址由http变成https之后,程序执行到 httpClient.execute(ht ...
- bootstrapValidator JS修改内容无法验证
需求: form表单输入中有坐标,坐标可以输入也可以从地图中获取,验证插件使用的是 bootstrapValidator 问题: 当输入错误的值时会触发验证,有错误提示.当在地图上选择坐标,通过js修 ...
