Zygote启动及其作用
目录
1、Zygote简介
2、Zygote进程如何启动
2.1 init.zygote64_32.rc文件
2.2 查看ps信息
2.3 启动
3、Zygote作用
3.1 启动system_server
3.2 查看与验证Zygote启动systemserver
3.3 Zygote启动其他子进程
4、总结
1、Zygote简介
- 1.1 系统启动流程
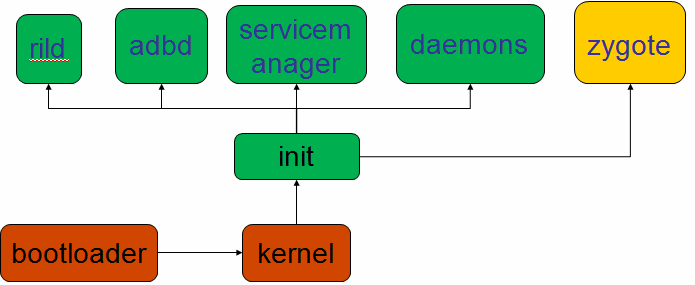
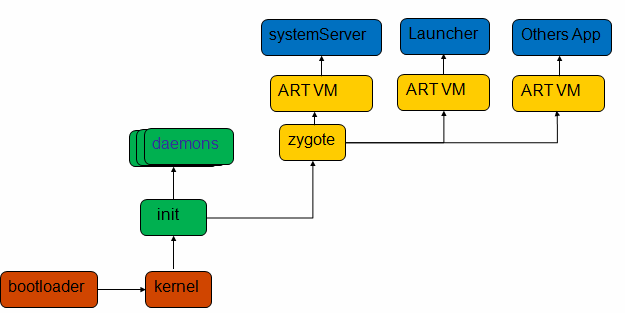
从按下电源到看到launcher,手机的启动是一个非常复杂的过程。
bootloader是手机上电之后第一个运行的程序,其作用是硬件的初始化,其作用类似于PC机的bios。
bootloader完成其工作后,将 Linux kernel镜像拷贝到内存中。完成剩余的与硬件平台相关的初始化工作,比如文件系统,驱动模块。最后启动第一个用户进程-init 进程并等待用户进程的执行。
用户空间的第一个进程init
- 1.2 zygote理解
- 在Android系统中,所有的应用程序进程以及系统服务进程SystemServer都是由Zygote进程孕育(fork)出来的。由于Zygote进程在Android系统中有着如此重要的地位,本文将详细分析它的启动过程。---老罗
- android系统中创建java世界的盘古 创建新进程的女娲。 ---邓凡平
2、Zygote进程如何启动
- 2.1 init.zygote64_32.rc文件
- system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64_32.rc文件内容

1 service zygote /system/bin/app_process32 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
2 class main
3 socket zygote stream 660 root system
4 onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
5 onrestart write /sys/power/state on
6 onrestart restart media
7 onrestart restart netd
8
9 service zygote_secondary /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --socket-name=zygote_secondary
10 class main
11 socket zygote_secondary stream 660 root system
12 onrestart restart zygote
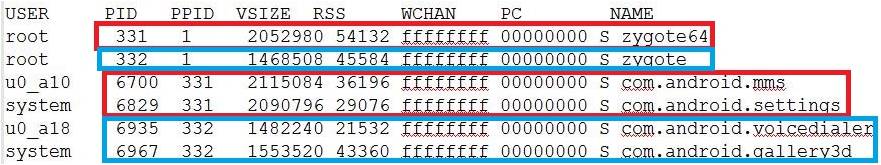
- 2.2 查看ps信息

Zygote64、Zygote是在init.rc中定义的服务进程,由init进程启动,PPID均为1。其中比较关键的vold、rild、surfaceflinger等关键进程也都是通过init进程启动的。
LOCAL_MULTILIB: Android.mk中用来设置编译为32位或者64位的apk,so等
- 2.3 启动

- Zygote process main(frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp)

1 int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
2 {
3 ...
121 if (zygote) {
122 runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args);
123 } else if (className) {
124 runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args);
125 } else {
126 fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
127 app_usage();
128 LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
129 return 10;
130 }
131 }
- 将init.rc中指定的-Xzygote参数传给JVM将进程的名字改为zygote(可以回答前面的问题)执行AppRuntime类的start()方法,runtime.start(“com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit”, true);


1 void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options)
2 {
3 ...
30 //const char* kernelHack = getenv("LD_ASSUME_KERNEL");
31 //ALOGD("Found LD_ASSUME_KERNEL='%s'\n", kernelHack);
32
33 /* start the virtual machine */
34 JniInvocation jni_invocation;
35 jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
36 JNIEnv* env;
37 if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
38 return;
39 }
40 onVmCreated(env);
41
42 /*
43 * Register android functions.
44 */
45 if (startReg(env) < 0) {
46 ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
47 return;
48 }
49
50 /*
51 * We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
52 * At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
53 * Create an array to hold them.
54 */
55 jclass stringClass;
56 jobjectArray strArray;
57 jstring classNameStr;
58
59 stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
60 assert(stringClass != NULL);
61 strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
62 assert(strArray != NULL);
63 classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
64 assert(classNameStr != NULL);
65 env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
66
67 for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
68 jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
69 assert(optionsStr != NULL);
70 env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
71 }
72
73 /*
74 * Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
75 * not return until the VM exits.
76 */
77 char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
78 jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
79 if (startClass == NULL) {
80 ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
81 /* keep going */
82 } else {
83 jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
84 "([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
85 if (startMeth == NULL) {
86 ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
87 /* keep going */
88 } else {
89 env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
90
91 #if 0
92 if (env->ExceptionCheck())
93 threadExitUncaughtException(env);
94 #endif
95 }
96 }
97 free(slashClassName);
98
99 ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
100 if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
101 ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
102 if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
103 ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
104 }
- runtime.start函数,即在frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp文件中
- AndroidRuntime::startVm()中,设置一些虚拟机的参数后,通过JNI_CreateJavaVM()启动虚拟机。
- StartReg()注册JNI 函数
- env->CallStaticVoidMethod,调用ZygoteInit类的main()方法,正式进入到Java世界.
- frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java

public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
....
registerZygoteSocket(socketName);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis()); // Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot(); // Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc(); // Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false); if (startSystemServer) {
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
} Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
runSelectLoop(abiList); closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
registerZygoteSocket,创建Socket服务端对象sServerSocket
preload方法预加载类,资源等
调用startSystemServer方法启动系统服务system_server
runSelectLoopMode监听和处理sServerSocket的Socket请求
- 3、Zygote作用
- 3.1 启动system_server
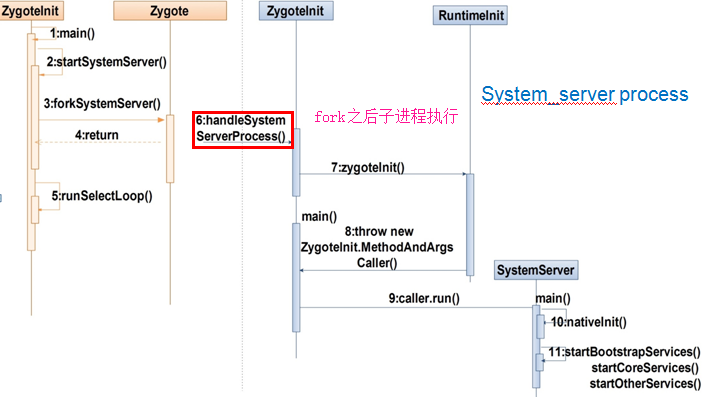

1 /**
2 * Prepare the arguments and fork for the system server process.
3 */
4 private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName)
5 throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
6 ...
31 int pid;
32
33 try {
34 parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
35 ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
36 ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
37
38 /* Request to fork the system server process */
39 pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
40 parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
41 parsedArgs.gids,
42 parsedArgs.debugFlags,
43 null,
44 parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
45 parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
46 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
47 throw new RuntimeException(ex);
48 }
49
50 /* For child process */
51 if (pid == 0) {//子进程进入
52 if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
53 waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
54 }
55
56 handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
57 }
58
59 return true;
60 }
- forkSystemServer,调用Native方法fork子进程通过forkSystemServer方法返回的值,进入两个分支处理:父进程返回子进程pid值,进入到ZygoteInit类中的main方法继续处理;而子进程调用handleSystemServerProcess方法,最终会运行system_server。

1 /**
2 * Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
3 */
4 private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
5 ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
6 throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
7
8 closeServerSocket();//子进程已经不是服务器了,所以关掉。
9
10 // set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
11 Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
12
13 if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
14 Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
15 }
16
17 final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
18 if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
19 performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
20 }
21
22 if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
23 String[] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;
24 // If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
25 // existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
26 // correctly when we exec a new process.
27 if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
28 String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
29 amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
30 amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
31 System.arraycopy(parsedArgs.remainingArgs, 0, amendedArgs, 2, parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length);
32 }
33
34 WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
35 parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
36 null, args);
37 } else {
38 ClassLoader cl = null;
39 if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
40 cl = new PathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
41 Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
42 }
43
44 /*
45 * Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
46 */
47 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
48 }
49
50 /* should never reach here */
51 }
- frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java

43 public class RuntimeInit {
44 。。。
197 private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
198 throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
199 。。。
232 throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
233 }
267 public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
268 throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
269 if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
270
271 redirectLogStreams();
272
273 commonInit();
274 nativeZygoteInit();
275
276 applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
277 }
297 private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
298 throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
299 。。。
308 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
309 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
310
311 。。。
320 // Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
321 invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
322 }
363 public static final IBinder getApplicationObject() {
364 return mApplicationObject;
365 }
425 }

1 public static void main(String argv[]) {
2 try {
3 。。。
42 if (startSystemServer) {
43 startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
44 }
45 。。。//然而并没有机会进入循环
50 } catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
51 caller.run();
52 } catch (RuntimeException ex) {
53 Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
54 closeServerSocket();
55 throw ex;
56 }
57 }
- 这个函数会执行两个操作,一个是调用zygoteInitNative函数来执行一个Binder进程间通信机制的初始化工作,这个工作完成之后,这个进 程中的Binder对象就可以方便地进行进程间通信了,另一个是调用上面传进来的com.android.server.SystemServer类的main函数。
- 3.2 查看与验证Zygote启动systemserver

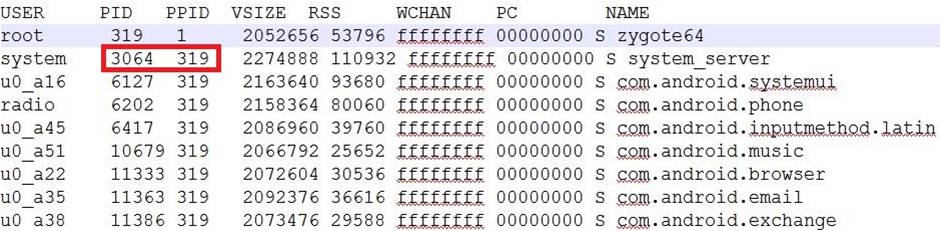
- ps进程信息,验证system_server是Zygote的分裂出的第一个子进程.
- 3.3 Zygote启动其他子进程
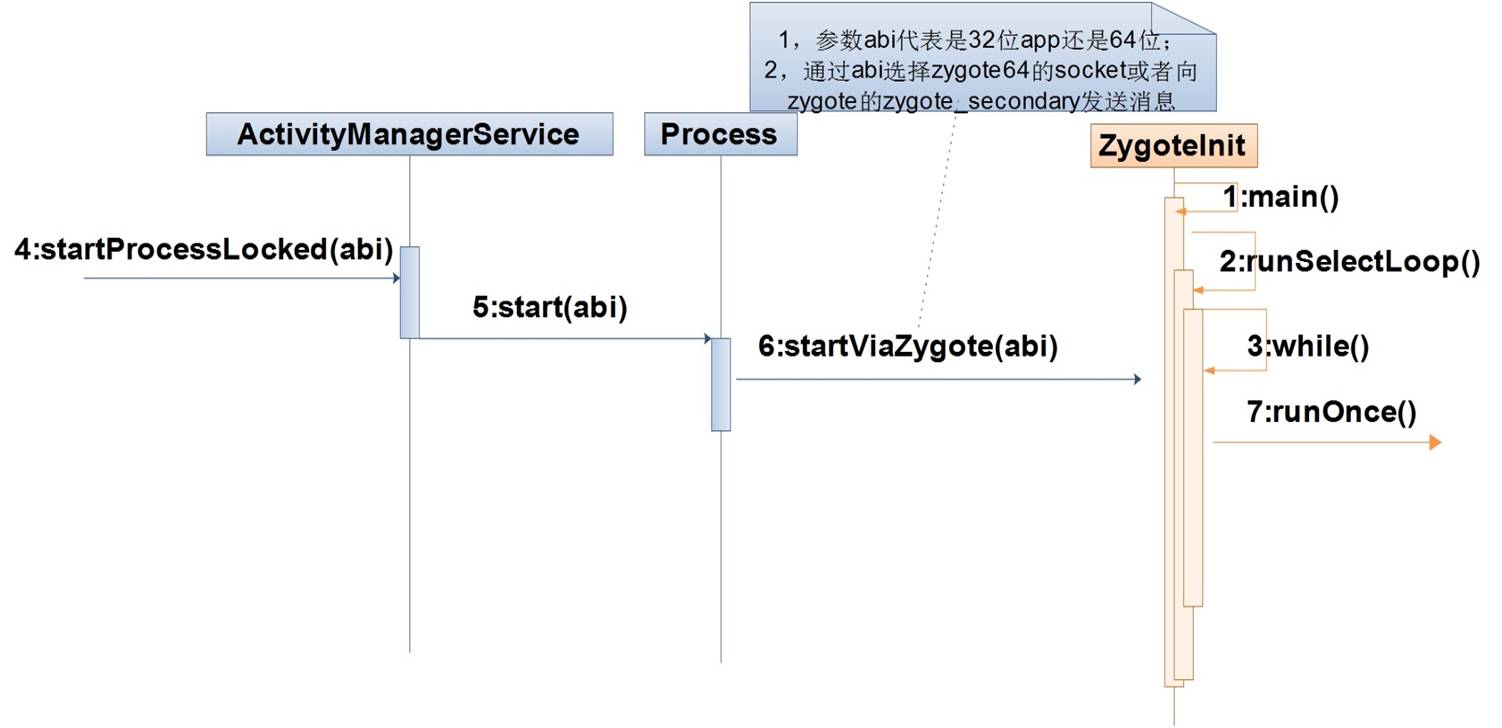

- 注意:重复的不再涉及,我们只是分析一下7-12吧。
- frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java

1 /**
2 * Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
3 * they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
4 * worth at a time.
5 *
6 * @throws MethodAndArgsCaller in a child process when a main() should
7 * be executed.
8 */
9 private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
10 。。。
18 while (true) {
19 。。。
38 try {
39 fdArray = fds.toArray(fdArray);
40 index = selectReadable(fdArray);
41 } catch (IOException ex) {
42 throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()", ex);
43 }
44
45 if (index < 0) {
46 throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()");
47 } else if (index == 0) {
48 ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
49 peers.add(newPeer);
50 fds.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
51 } else {
52 boolean done;
53 done = peers.get(index).runOnce();
54
55 if (done) {
56 peers.remove(index);
57 fds.remove(index);
58 }
59 }
60 }
61 }
- runSelectLoopMode中while(true)循环,接收到Socket请求后,会fork出子进程,子进程调用handleChildProc方法,最终抛出RuntimeInit.invokeStaticMain异常,退出while(true)循环(与fork Systemserver不一样,后者没有进入循环),进入到android.app.ActivityThread类的main方法执行;父进程调用handleParentProc方法,再次进入runSelectLoopMode中while(true)循环,准备接收下一个的请求事件。
- frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java

1 boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
...
37 try {
38 ...
105 pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
106 parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
107 parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, parsedArgs.instructionSet,
108 parsedArgs.appDataDir);
109 checkTime(startTime, "zygoteConnection.runOnce: postForkAndSpecialize");
110 } catch (IOException ex) {
111 logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
112 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
113 logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
114 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
115 logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
116 } catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
117 logAndPrintError(newStderr,
118 "Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
119 }
120
121 try {
122 if (pid == 0) {
123 // in child
124 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
125 serverPipeFd = null;
126 handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
127
128 // should never get here, the child is expected to either
129 // throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
130 return true;
131 } else {
132 // in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
133 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
134 childPipeFd = null;
135 return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
136 }
137 } finally {
138 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
139 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
140 }
141 }
- 10和11略过,只是返回而已。我们现在进入子进程的handleChildProc。

1 private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
2 FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
3 throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
4
5 /**
6 * By the time we get here, the native code has closed the two actual Zygote
7 * socket connections, and substituted /dev/null in their place. The LocalSocket
8 * objects still need to be closed properly.
9 */
10
11 closeSocket();
12 ZygoteInit.closeServerSocket();
13
14 。。。
55 if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
56 WrapperInit.execStandalone(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
57 parsedArgs.classpath, className, mainArgs);
58 } else {
59 ClassLoader cloader;
60 if (parsedArgs.classpath != null) {
61 cloader = new PathClassLoader(parsedArgs.classpath,
62 ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
63 } else {
64 cloader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
65 }
66
67 try {
68 ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain(cloader, className, mainArgs);
69 } catch (RuntimeException ex) {
70 logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Error starting.", ex);
71 }
72 }
73 。。。
74 }
- 剩余的就和上面雷同了,这里不再分析。
- 3.1 启动system_server
4、总结
- 系统启动时init进程会创建Zygote进程,Zygote进程负责后续Android应用程序框架层的其它进程的创建和启动工作。(可以使用ps查看)
Zygote进程会首先创建一个SystemServer进程,SystemServer进程负责启动系统的关键服务,如包管理服务PackageManagerService和应用程序组件管理服务ActivityManagerService。
当我们需要启动一个Android应用程序时,ActivityManagerService会通过Socket进程间通信机制,通知Zygote进程为这个应用程序创建一个新的进程。
Zygote启动及其作用的更多相关文章
- Android系统进程Zygote启动过程的源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6768304 在Android系统中,所有的应用 ...
- Android 8.1 源码_启动篇(二) -- 深入研究 zygote(转 Android 9.0 分析)
前言 在Android中,zygote是整个系统创建新进程的核心进程.zygote进程在内部会先启动Dalvik虚拟机,继而加载一些必要的系统资源和系统类,最后进入一种监听状态.在之后的运作中,当其他 ...
- Zygote及System进程启动
1. init 根据init.rc 运行 app_process, 并携带‘--zygote' 和 ’--startSystemServer' 参数. 2. AndroidRuntime.cpp: ...
- Android Zygote进程启动分析
dvm,app进程,linux进程三者关系 DVM指 dalivk 的虚拟机.每一个 Android 应用程序都在它自己的进程中运行,都拥有一个独立的 Dalvik 虚拟机实例.而每一个 DVM 都是 ...
- 图解Android - Zygote, System Server 启动分析
Init 是所有Linux程序的起点,而Zygote于Android,正如它的英文意思,是所有java程序的'孵化池'(玩过星际虫族的兄弟都晓得的).用ps 输出可以看到 >adb shell ...
- 笔记:Zygote和SystemServer进程启动过程
简述 Android设备启动过程中,先是Linux内核加载完,接着Android中的第一个进程init启动,它会启动一些需要开机启动的进程. Zygote就是进程init启动起来的.Android中所 ...
- Android系统启动流程(二)解析Zygote进程启动过程
1.Zygote简介 在Android系统中,DVM(Dalvik虚拟机).应用程序进程以及运行系统的关键服务的SystemServer进程都是由Zygote进程来创建的,我们也将它称为孵化器.它通过 ...
- Zygote和System进程的启动过程
##init脚本的启动 +------------+ +-------+ +-----------+ |Linux Kernel+--> |init.rc+-> |app_process| ...
- Zygote和System进程的启动过程、Android应用进程启动过程
1.基本过程 init脚本的启动Zygote Zygote进程的启动 System进程的启动 Android应用进程启动过程 2.init脚本的启动 +------------+ +-------+ ...
随机推荐
- 一些 SQLite技巧
SQLite自增ID自段 使用方法为 INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT 如: CREATE TABLE 21andy ( id INTEGER PRIMA ...
- 二十三、mysql索引管理详解
一.索引分类 分为聚集索引和非聚集索引. 聚集索引 每个表有且一定会有一个聚集索引,整个表的数据存储在聚集索引中,mysql索引是采用B+树结构保存在文件中,叶子节点存储主键的值以及对应记录的数据,非 ...
- Spark运行原理【史上最详细】
https://blog.csdn.net/lovechendongxing/article/details/81746988 Spark应用程序以进程集合为单位在分布式集群上运行,通过driver程 ...
- oracle 设置归档日模式
首先关闭ORACLE SQL> shutdown immediate 把ORACLE启动为MOUNT模式 SQL:>startup mount sql:> alter databas ...
- CentOS7- ABRT has detected 1 problem(s). For more info run: abrt-cli list --since 1548988705
CentOS7重启后,xshell连接,后出现ABRT has detected 1 problem(s). For more info run: abrt-cli list --since 1548 ...
- kubernetes集群的认证、授权、准入控制
一.kubernetes集群安全架构 用户使用kubectl.客户机或通过REST请求访问API.可以授权用户和Kubernetes服务帐户进行API访问.当一个请求到达API时,它会经历几个阶段,如 ...
- 数据库PDO简介
php简介,php历史,php后端工程师职业前景,php技术方向,php后端工程师职业体系介绍. php是世界上使用最广泛的web开发语言,是超文本预处理器,是一种通用的开源脚本语言,语法吸收了c语言 ...
- Flink原理(二)——资源
前言 本文主要是想简要说明Flink在集群部署.任务提交.任务运行过程中资源情况,若表述有误欢迎大伙留言分享,非常感谢! 一.集群部署阶段 集群部署这里指的是Flink standalone模式,因为 ...
- sqlite3入门之sqlite3_mprintf
sqlite3_mprintf sqlite3_mprintf()函数原型: char *sqlite3_mprintf(const char*,...); sqlite3_mprintf()的作用是 ...
- 用java刷剑指offer(平衡二叉树)
题目描述 输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树. 牛客网链接 java代码 import java.lang.Math; public class Solution { public bool ...
