CompletableFuture异步优化代码
CompletableFuture异步编排优化代码
我们在项目开发中,有可能遇到一个接口需要调用N个服务的接口。比如用户请求获取订单信息,需要调用用户信息、商品信息、物流信息等接口,最后再汇总数据统一返回。如果使用串行的方法按照顺序挨个调用接口,这样接口的响应的速度就很慢。如果并行调用接口,同时调用就会节省很多时间。下面就介绍一个好用的异步编排工具CompletableFuture
简介
CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 中新增的一个异步编程工具类,它是基于 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口构建的,可以与 Java 8 中的 Stream API 配合使用,也能够与 Java 9 中的 Reactive Stream API 进行交互。
主要用于异步执行任务并返回结果,实现异步计算和操作组合。它提供了一种灵活、可组合的方式来实现异步计算,同时也提供了异常处理、取消、超时等特性。在CompletableFuture中,我们可以通过回调函数来处理任务的结果,也可以使用其它方法来组合多个CompletableFuture对象,以构建更复杂的异步操作流水线。
创建异步任务
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier){..}
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor){..}
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable){..}
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor){..}
supplyAsync
supplyAsync是创建有返回值的异步任务。它有两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法
// 有返回值,默认线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
// 带返回值的异步,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
代码示例
@Test
public void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 执行耗时任务,返回结果
return "使用默认线程池";
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}
@Test
public void test1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建一个固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 执行耗时任务,返回结果
return "使用自定义线程池";
},executor);
System.out.println(future.get());
}
runAsync
用于异步执行一个没有返回值的任务,有两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法
// 不带返回值的异步,默认线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
// 不带返回值的异步,可以自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
代码示例
@Test
public void testrunAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsyncVoid = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 执行耗时任务,返回结果
System.out.println("使用runAsync创建异步任务");
});
System.out.println("runAsyncVoid:" + runAsyncVoid.get());
}
@Test
public void testrunAsyncExecutors() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建一个固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsyncVoid = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 执行耗时任务,返回结果
System.out.println("使用runAsync创建异步任务");
},executor);
System.out.println("runAsyncVoid:" + runAsyncVoid.get());
}
运行结果
获取任务结果
CompletableFuture提供了不同的方法来获取异步任务的结果。以下是几种常用的获取结果的方法:
get()方法
该方法用于阻塞地获取异步任务的结果,返回结果的类型是泛型参数指定的类型。
get()方法会阻塞当前线程,直到异步任务完成并返回结果,或者抛出异常。因此,在使用get()方法时需要注意处理中断和异常
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 执行异步任务,返回结果
return 42;
});
try {
int result = future.get();
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
// 处理异常
}
join()方法
与get()方法类似,也是用于获取异步任务的结果,但是不会抛出InterruptedException和ExecutionException异常,而是将它们包装在RuntimeException中抛出
与get()方法不同,join()方法不需要显式处理异常,但如果异步任务抛出了异常,join()方法将抛出CompletionException异常并包含原始异常作为其原因。
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 执行异步任务,返回结果
return 42;
});
int result = future.join();
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
一共有如下获取结果的方法
// 这个方法用于阻塞地获取异步任务的结果。如果任务已经完成,它将返回结果;如果任务尚未完成,它将阻塞当前线程直到任务完成。如果任务抛出异常,get()方法将抛出ExecutionException异常,并将原始异常作为其getCause()方法的返回值。
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
// 这个方法与上面的get()方法类似,但是增加了一个超时参数。它会阻塞当前线程,等待指定的时间,如果在超时时间内任务完成,则返回结果;如果超时时间到达而任务仍未完成,则抛出TimeoutException异常。
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException:
// 这个方法用于获取异步任务的结果,类似于get()方法。但是与get()方法不同的是,它不会抛出受检查异常(如InterruptedException和ExecutionException),而是将它们包装在一个运行时异常(即CompletionException)中抛出。
public T join()
// 这个方法用于在异步任务尚未完成时立即返回一个默认值。如果异步任务已经完成,则返回任务的结果;如果尚未完成,则返回指定的默认值。
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
// 这个方法用于手动地将异步任务标记为已完成,并设置结果值为指定的值。如果任务已经完成或已经被取消,则返回false;否则,返回true。
public boolean complete(T value)
// 这个方法用于手动地将异步任务标记为已完成,并设置异常结果为指定的异常。如果任务已经完成或已经被取消,则返回false;否则,返回true
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex)
异步回调方法
thenRun/thenRunAsync
执行完第一个任务在执行第二个任务,第二个任务无返回值
@Test
public void thenRunTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 第一个任务....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println( "第二个任务获取第一个任务的结果:" + cf1.join() );
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 第二个任务....");
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
// thenRunAsync 和上面的方法一致,方法名换一个即可
thenRun 和thenRunAsync区别
如果你执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池:
- 调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务是共用同一个线程池。
- 调用
thenRunAsync执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池。
后面介绍的thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它们之间的区别也是这个
thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该第一个任务的执行结果,作为参数传递到回调方法中,无返回值
@Test
public void thenAcceptTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 第一个任务....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAccept((result) -> {
System.out.println( "第二个任务获取第一个任务的结果:" + result );
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 第二个任务....");
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
// thenAcceptAsync代码和上面一致,方法名换一个即可
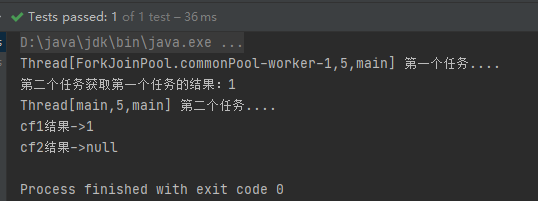
thenApply/thenApplyAsync
表示第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。
@Test
public void thenApplyTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 第一个任务....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApply((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " 第二个任务...");
result += 1;
return result;
});
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
// thenApplyAsync代码和上面一致,方法名换一个即可
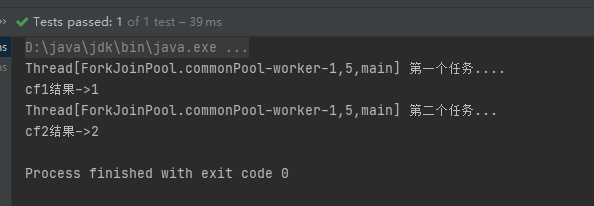
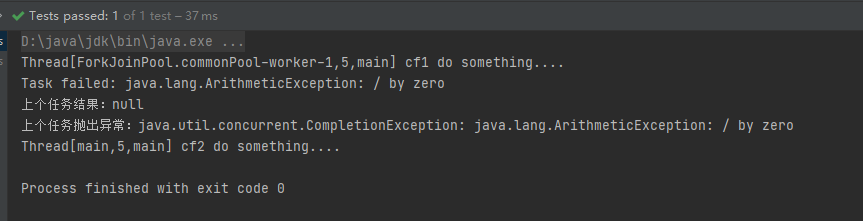
whenComplete/whenCompleteAsync
用于在异步任务完成后执行指定的操作,并且可以访问任务的结果或异常信息,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常
@Test
public void whenCompleteTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((result, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
System.out.println("Task failed: " + e.getMessage());
} else {
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
}
System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);
System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
}
运行结果
whenCompleteAsync()方法使用了默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池来执行指定的操作。如果需要自定义线程池,可以使用带有Executor参数的重载方法。whenComplete()和whenCompleteAsync()方法都可以访问任务的结果或异常信息,并在任务完成后执行指定的操作。它们的区别在于任务的执行方式和线程使用情况,根据具体需求选择合适的方法。
多任务组合
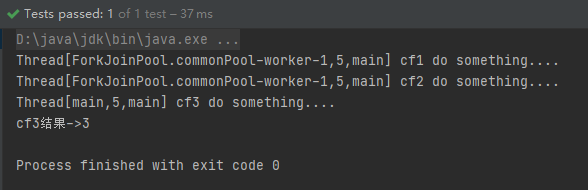
thenCombine/thenAcceptBoth /runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,将只有两个任务都正常完成时,才进行下阶段任务,通俗讲就是当任务一和任务二都完成再执行任务三
区别:
- 「thenCombine」:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
- 「thenAcceptBoth」: 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值
- 「runAfterBoth」 不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值
@Test
public void thenCombineTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf3 = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (a, b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
return a + b;
});
System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
@Test
public void thenAcceptBothTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2, (a, b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
System.out.println(a + b);
});
System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
@Test
public void runAfterBothTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
return 2;
});
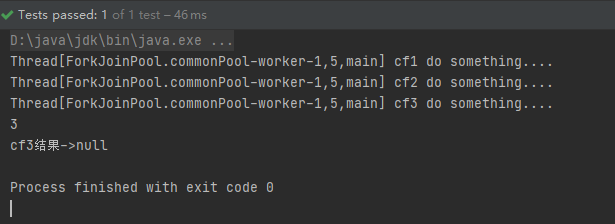
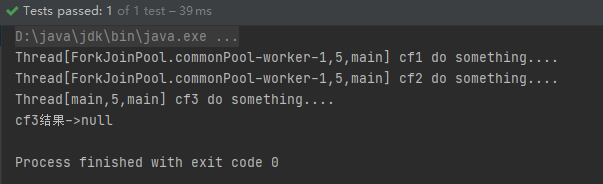
CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2, () -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
});
System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
运行结果:
applyToEither/acceptEither/runAfterEither
这三个方法和上面一样也是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,但是当有一个任务正常完成时,就会进行下阶段任务。
两个任务,只要有一个任务完成,就执行任务三
区别在于:
- 「runAfterEither」:不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值
- 「acceptEither」: 会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值
- 「applyToEither」:会将已经执行完成的任务,作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值
@Test
public void applyToEitherTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
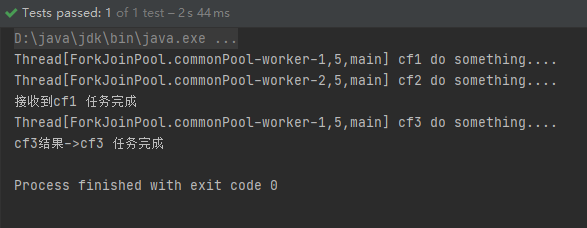
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = cf1.applyToEither(cf2, (result) -> {
System.out.println("接收到" + result);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
return "cf3 任务完成";
});
System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
@Test
public void acceptEither() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
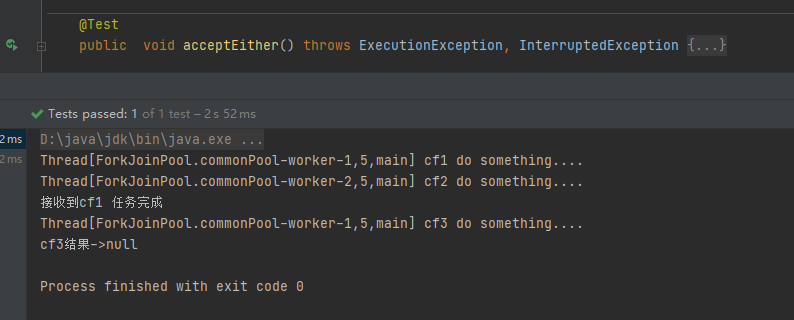
CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.acceptEither(cf2, (result) -> {
System.out.println("接收到" + result);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
});
System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
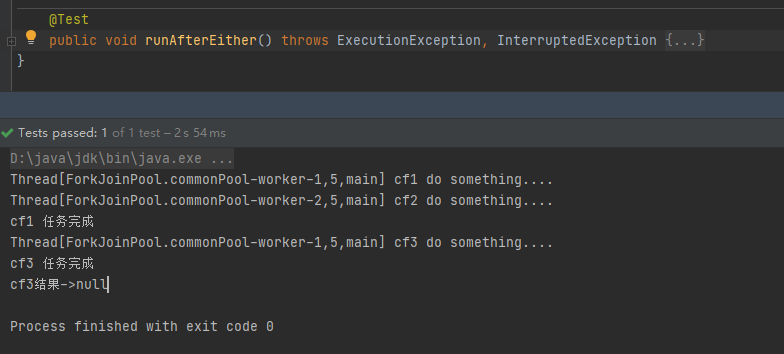
@Test
public void runAfterEither() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterEither(cf2, () -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");
});
System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}
运行结果
allOf / anyOf
- 「allOf」:等待所有任务完成。只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null
- 「anyOf」:只要有一个任务完成,就执行后续的操作
// allOf
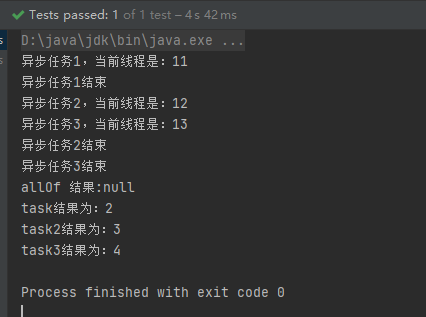
@Test
public void testCompletableAallOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");
return "cf3 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cfAll = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);
System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}
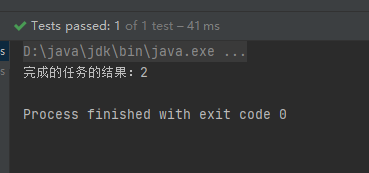
@Test
public void testCompletableAnyOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//开启异步任务1
CompletableFuture<Integer> task = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 1 + 1;
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 1 + 2;
return result;
}, executorService);
//开启异步任务3
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 1 + 3;
return result;
}, executorService);
//任务组合
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(task, task2, task3);
//只要有一个有任务完成
Object o = anyOf.get();
System.out.println("完成的任务的结果:" + o);
}
实际应用代码
public SkuItemVo item(Long skuId) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
SkuItemVo skuItemVo = new SkuItemVo();
CompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> infoFutrue = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//1 sku基本信息
SkuInfoEntity info = getById(skuId);
skuItemVo.setInfo(info);
return info;
}, executor);
// 无需获取返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> imageFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
//2 sku图片信息
List<SkuImagesEntity> images = imagesService.getImagesBySkuId(skuId);
skuItemVo.setImages(images);
}, executor);
// 在1之后
CompletableFuture<Void> saleAttrFuture =infoFutrue.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
//3 获取spu销售属性组合 list
List<ItemSaleAttrVo> saleAttrVos = skuSaleAttrValueService.getSaleAttrsBuSpuId(res.getSpuId());
skuItemVo.setSaleAttr(saleAttrVos);
},executor);
// 在1之后
CompletableFuture<Void> descFuture = infoFutrue.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
//4 获取spu介绍
SpuInfoDescEntity spuInfo = spuInfoDescService.getById(res.getSpuId());
skuItemVo.setDesc(spuInfo);
},executor);
// 在1之后
CompletableFuture<Void> baseAttrFuture = infoFutrue.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
//5 获取spu规格参数信息
List<SpuItemAttrGroup> attrGroups = attrGroupService.getAttrGroupWithAttrsBySpuId(res.getSpuId(), res.getCatalogId());
skuItemVo.setGroupAttrs(attrGroups);
}, executor);
// 6.查询当前sku是否参与秒杀优惠
CompletableFuture<Void> secKillFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
R skuSeckillInfo = seckillFeignService.getSkuSeckillInfo(skuId);
if (skuSeckillInfo.getCode() == 0) {
// 注意null的问题
SeckillSkuRedisTo data = skuSeckillInfo.getData(new TypeReference<SeckillSkuRedisTo>() {});
SeckillInfoVo seckillInfoVo = new SeckillInfoVo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(data,seckillInfoVo);
skuItemVo.setSeckillInfoVo(seckillInfoVo);
}
}, executor);
// 等待所有任务都完成再返回
CompletableFuture.allOf(imageFuture,saleAttrFuture,descFuture,baseAttrFuture,secKillFuture).get();
// CompletableFuture.allOf(imageFuture,saleAttrFuture,descFuture,baseAttrFuture).get();
return skuItemVo;
}
优点
异步编程能力:
CompletableFuture提供了强大的异步编程能力,可以方便地处理异步计算和组合多个异步操作。它支持链式操作、组合操作、转换操作等,使得异步编程更加灵活和便捷。非阻塞式调用:通过使用
CompletableFuture,可以实现非阻塞式的调用。在执行异步任务时,主线程不会被阻塞,可以继续执行其他任务或处理其他逻辑。异常处理:
CompletableFuture提供了丰富的异常处理机制。可以通过方法链中的异常处理方法来捕获和处理任务执行过程中产生的异常,使得异常处理更加灵活和方便。可组合性:
CompletableFuture支持多个任务之间的组合操作。可以通过方法链将多个异步任务串联起来,并在任务完成后进行后续处理。这种可组合性使得代码更加清晰、可读性更高。超时处理:使用
CompletableFuture可以方便地实现超时处理。可以设置超时时间,并在超时时间内等待任务完成,如果超时则执行相应的操作,例如返回默认值或执行备用逻辑。并发控制:
CompletableFuture提供了一些方法来控制并发执行的线程数,例如thenComposeAsync()和thenCombineAsync()等方法可以指定线程池来执行任务,从而实现对并发度的控制。可以与其他异步编程工具结合使用:
CompletableFuture可以与其他异步编程工具(如RxJava、Spring Reactor等)结合使用,以实现更复杂的异步编程需求。可以与函数式编程结合使用:
CompletableFuture支持函数式编程风格,可以使用Lambda表达式和方法引用来简化代码,并提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
CompletableFuture异步优化代码的更多相关文章
- 使用await写异步优化代码
使用promise: function readMsg(){ return dispatch=>{ axios.post('/msgList').then(res=>{ console.l ...
- 使用 CompletableFuture 异步组装数据
使用 CompletableFuture 异步组装数据 一种快捷.优雅的异步组装数据方式 实际项目中经常遇到这种情况: 从多个表中查找到数据然后拼装成一个VO返回给前端. 这个过程有可能会非常耗时.因 ...
- 如何解救在异步Java代码中已检测的异常
Java语言通过已检测异常语法所提供的静态异常检测功能非常实用,通过它程序开发人员可以用很便捷的方式表达复杂的程序流程. 实际上,如果某个函数预期将返回某种类型的数据,通过已检测异常,很容易就可以扩展 ...
- CompletableFuture异步编排
什么是CompletableFuture CompletableFuture是JDK8提供的Future增强类.CompletableFuture异步任务执行线程池,默认是把异步任务都放在ForkJo ...
- 为duilib的MenuDemo增加消息响应,优化代码和显示效果
转载请说明原出处,谢谢~~:http://blog.csdn.net/zhuhongshu/article/details/38253297 第一部分 我在前一段时间研究了怎么制作duilib的菜单, ...
- Webpack 4教程:为什么要优化代码
转载请注明出处:葡萄城官网,葡萄城为开发者提供专业的开发工具.解决方案和服务,赋能开发者.原文出处:https://wanago.io/2018/07/30/webpack-4-course-part ...
- Android 性能优化:使用 Lint 优化代码、去除多余资源
前言 在保证代码没有功能问题,完成业务开发之余,有追求的程序员还要追求代码的规范.可维护性. 今天,以“成为优秀的程序员”为目标的拭心将和大家一起精益求精,学习使用 Lint 优化我们的代码. 什么是 ...
- Netty实现的一个异步Socket代码
本人写的一个使用Netty实现的一个异步Socket代码 package test.core.nio; import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ThreadF ...
- 如何优化代码中大量的if/else,switch/case?
前言 随着项目的迭代,代码中存在的分支判断可能会越来越多,当里面涉及到的逻辑比较复杂或者分支数量实在是多的难以维护的时候,我们就要考虑下,有办法能让这些代码变得更优雅吗? 正文 使用枚举 这里我们简单 ...
- 异步nodejs代码的同步样子写法样例
异步nodejs代码的同步样子写法样例 js的异步嵌套太深代码将不好看.尤其在用node的时候这种情况会大量出现. 这里用node连接redis,做一个用户注册的简单例子来说明.例如用redis做存储 ...
随机推荐
- 什么是hive的高级分组聚合,它的用法和注意事项以及性能分析
hive的高级分组聚合是指在聚合时使用GROUPING SETS.CUBE和ROLLUP的分组聚合. 高级分组聚合在很多数据库类SQL中都有出现,并非hive独有,这里只说明hive中的情况. 使用高 ...
- Java扩展Nginx之二:编译nginx-clojure源码
欢迎访问我的GitHub 这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 为什么要编译nginx-clojure源码 作为< ...
- [NOIP2011 提高组] 聪明的质监员【题解】
题目 小 T 是一名质量监督员,最近负责检验一批矿产的质量.这批矿产共有 \(n\) 个矿石,从 \(1\) 到 \(n\) 逐一编号,每个矿石都有自己的重量 \(w_i\) 以及价值 \(v_i\) ...
- IRF技术介绍及配置介绍
IRF技术介绍及配置介绍 IRF(Intelligent Resilient Framework,智能弹性架构)是 H3C 自主研发的软件虚拟化技术. 它的核心思想是将多台设备通过 IRF 物理端口连 ...
- 微信小程序+web数据库的开发实践
前言 生活中使用微信小程序的场景越来越多,它实现了用户对于应用"触手可及.用完即走"的理想需求.微信小程序的开发难度也低于APP的开发制作,使用它会更便利.低成本.高经济效益. 但 ...
- 【教程】AWD中如何通过Python批量快速管理服务器?
前言 很多同学都知道,我们常见的CTF赛事除了解题赛之外,还有一种赛制叫AWD赛制.在这种赛制下,我们战队会拿到一个或多个服务器.服务器的连接方式通常是SSH链接,并且可能一个战队可能会同时有多个服务 ...
- nodejs端模块化方式comomjs详解
nodejs端实现模块化的方式通常是通过commonjs,使用模块化可以复用js代码,使得逻辑结构更为清晰. commonjs的语法规则如下通过 module.exports 或者 exports 导 ...
- [oracle]用户与权限管理
创建用户 CREATE USER 用户名 IDENTIFIED BY 密码 DEFAULT TABLESPACE 表空间 TEMPORARY TABLESPACE 临时表空间 QUOTA 空间配额大小 ...
- 部署安装zookeeper集群
版本:3.7.0 节点IP: 172.50.13.103 172.50.13.104 172.50.13.105 获取安装包: wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/apac ...
- 基于C#的消息处理的应用程序 - 开源研究系列文章
今天讲讲基于C#里的基于消息处理的应用程序的一个例子. 我们知道,Windows操作系统的程序是基于消息处理的.也就是说,程序接收到消息代码定义,然后根据消息代码定义去处理对应的操作.前面有一个博文例 ...
