C++二叉树的实现
啥是二叉查找树
在数据结构中,有一个奇葩的东西,说它奇葩,那是因为它重要,这就是树。而在树中,二叉树又是当中的贵族。二叉树的一个重要应用是它们在查找中的应用,于是就有了二叉查找树。 使二叉树成为一颗二叉查找树,需要满足以下两点:
- 对于树中的每个节点X,它的左子树中所有项的值都要小于X中的项;
- 对于树中的每个节点Y,它的右子树中所有项的值都要大于Y中的项。
二叉查找树的基本操作
以下是对于二叉查找树的基本操作定义类,然后慢慢分析是如何实现它们的。
template<class T>
class BinarySearchTree
{
public:
// 构造函数,初始化root值
BinarySearchTree() : root(NULL){} // 析构函数,默认实现
~BinarySearchTree() {} // 查找最小值,并返回最小值
const T &findMin() const; // 查找最大值,并返回最大值
const T &findMax() const; // 判断二叉树中是否包含指定值的元素
bool contains(const T &x) const; // 判断二叉查找树是否为空
bool isEmpty() const { return root ? false : true; } // 打印二叉查找树的值
void printTree() const; // 向二叉查找树中插入指定值
void insert(const T &x); // 删除二叉查找树中指定的值
void remove(const T &x); // 清空整个二叉查找树
void makeEmpty() const; private:
// 指向根节点
BinaryNode<T> *root; void insert(const T &x, BinaryNode<T> *&t) const;
void remove(const T &x, BinaryNode<T> *&t) const;
BinaryNode<T> *findMin(BinaryNode<T> *t) const;
BinaryNode<T> *findMax(BinaryNode<T> *t) const;
bool contains(const T &x, BinaryNode<T> *t) const;
void printTree(BinaryNode<T> *t) const;
void makeEmpty(BinaryNode<T> *&t) const;
};
findMin和findMax实现
根据二叉查找树的性质:
- 对于树中的每个节点X,它的左子树中所有项的值都要小于X中的项;
- 对于树中的每个节点Y,它的右子树中所有项的值都要大于Y中的项。
我们可以从root节点开始:
- 一直沿着左节点往下找,直到子节点等于
NULL为止,这样就可以找到最小值了; - 一直沿着右节点往下找,直到子节点等于
NULL为止,这样就可以找到最大值了。
如下图所示: 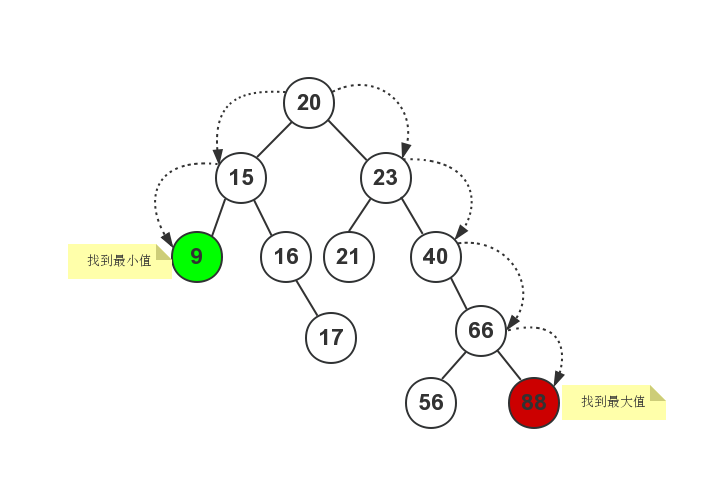
在程序中实现时,有两种方法:
- 使用递归实现;
- 使用非递归的方式实现。
对于finMin的实现,我这里使用递归的方式,代码参考如下:
BinaryNode<T> *BinarySearchTree<T>::findMin(BinaryNode<T> *t) const
{
if (t == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
else if (t->left == NULL)
{
return t;
}
else
{
return findMin(t->left);
}
}
在findMin()的内部调用findMin(BinaryNode<T> *t),这样就防止了客户端知道了root根节点的信息。上面使用递归的方式实现了查找最小值,下面使用循环的方式来实现findMax。
template<class T>
BinaryNode<T> *BinarySearchTree<T>::findMax(BinaryNode<T> *t) const
{
if (t == NULL)
{
return NULL;
} while (t->right)
{
t = t->right;
}
return t;
}
在很多面试的场合下,面试官一般都是让写出非递归的版本;而在对树进行的各种操作,很多时候都是使用的递归实现的,所以,在平时学习时,在理解递归版本的前提下,需要关心一下对应的非递归版本。
contains实现
contains用来判断二叉查找树是否包含指定的元素。代码实现如下:
template<class T>
bool BinarySearchTree<T>::contains(const T &x, BinaryNode<T> *t) const
{
if (t == NULL)
{
return false;
}
else if (x > t->element)
{
return contains(x, t->right);
}
else if (x < t->element)
{
return contains(x, t->left);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
算法规则如下:
- 首先判断需要查找的值与当前节点值的大小关系;
- 当小于当前节点值时,就在左节点中继续查找;
- 当大于当前节点值时,就在右节点中继续查找;
- 当找到该值时,直接返回true。
insert实现
insert函数用来向二叉查找树中插入新的元素,算法处理如下:
- 首先判断需要插入的值与当前节点值得大小关系;
- 当小于当前节点值时,就在左节点中继续查找插入点;
- 当大于当前节点值时,就在右节点中继续查找插入点;
- 当等于当前节点值时,什么也不干。
代码实现如下:
template<class T>
void BinarySearchTree<T>::insert(const T &x, BinaryNode<T> *&t) const
{
if (t == NULL)
{
t = new BinaryNode<T>(x, NULL, NULL);
}
else if (x < t->element)
{
insert(x, t->left);
}
else if (x > t->element)
{
insert(x, t->right);
}
}
remove实现
remove函数用来删除二叉查找树中指定的元素值,这个处理起来比较麻烦。在删除子节点时,需要分以下几种情况进行考虑(结合下图进行说明): 如下图所示: 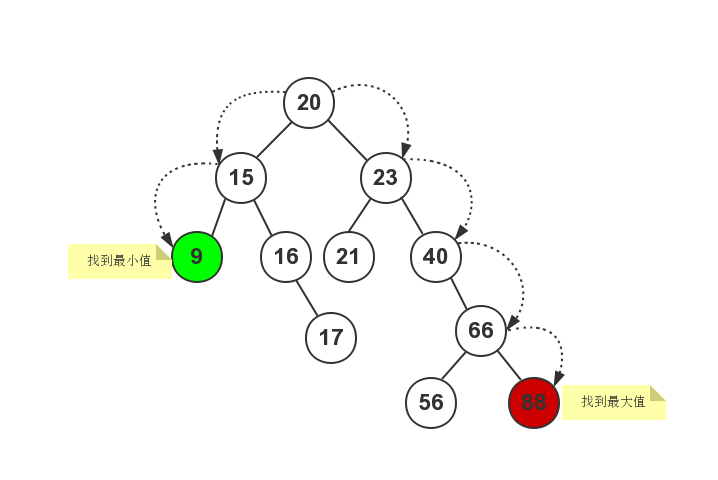
- 需要删除的子节点,它没有任何子节点;例如图中的节点9、节点17、节点21、节点56和节点88;这些节点它们都没有子节点;
- 需要删除的子节点,只有一个子节点(只有左子节点或右子节点);例如图中的节点16和节点40;这些节点它们都只有一个子节点;
- 需要删除的子节点,同时拥有两个子节点;例如图中的节点66等。
对于情况1,直接删除对应的节点即可;实现起来时比较简单的;
对于情况2,直接删除对应的节点,然后用其子节点占据删除掉的位置;
对于情况3,是比较复杂的。首先在需要被删除节点的右子树中找到最小值节点,然后使用该最小值替换需要删除节点的值,然后在右子树中删除该最小值节点。
假如现在需要删除包含值23的节点,步骤如下图所示: 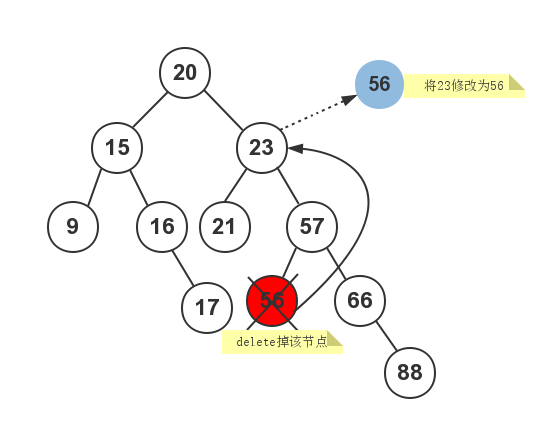
代码实现如下:
template<class T>
void BinarySearchTree<T>::remove(const T &x, BinaryNode<T> *&t) const
{
if (t == NULL)
{
return;
} if (x < t->element)
{
remove(x, t->left);
}
else if (x > t->element)
{
remove(x, t->right);
}
else if (t->left != NULL && t->right != NULL)
{
// 拥有两个子节点
t->element = findMin(t->right)->element;
remove(t->element, t->right);
}
else if (t->left == NULL && t->right == NULL)
{
// 没有子节点,直接干掉
delete t;
t = NULL;
}
else if (t->left == NULL || t->right == NULL)
{
// 拥有一个子节点
BinaryNode *pTemp = t;
t = (t->left != NULL) ? t->left : t->right;
delete pTemp;
}
}
makeEmpty实现
makeEmpty函数用来释放整个二叉查找树占用的内存空间,同理,也是使用的递归的方式来实现的。具体代码请下载文中最后提供的源码。
转载:http://www.jellythink.com/archives/692
@2017-03-29 20:25:17 测试通过:
/*!
* \file 二叉搜索树的实现.cpp
*
* \author ranjiewen
* \date 2017/03/29 17:13
*
*
*/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> typedef int ELementType;
typedef struct BSTreeNode* BSTree; struct BSTreeNode //不可以typedef;然后再次typedef;
{
ELementType Data;
BSTree Left;
BSTree Right;
}; //typedef BSTreeNode* Position;
typedef BSTree Position; Position Find(ELementType x, BSTree BST); //返回所在节点的地址
Position FindMin(BSTree BST);
Position FinMax(BSTree BST);
BSTree Insert(ELementType x, BSTree BST);
BSTree Delete(ELementType x, BSTree BST); //查找的效率取决于树的高度,和树的组织方法有关
Position Find(ELementType x, BSTree BST)
{
if (!BST)
{
return NULL;
}
if (x > BST->Data)
{
return Find(x, BST->Right); //尾递归都可以用循环的实现
}
else if (x < BST->Data)
{
return Find(x, BST->Left);
}
else //x==BST->Data
{
return BST;
}
} //非递归的执行效率高,可将“尾递归”函数改为迭代函数实现
Position IterFinde(ELementType x, BSTree BST)
{
while (BST)
{
if (x > BST->Data)
{
BST = BST->Right;
}
else if (x < BST->Data)
{
BST = BST->Left;
}
else
{
return BST;
}
}
return NULL;
} //递归实现
Position FindMin(BSTree BST)
{
if (!BST)
{
return NULL;
}
else if (!BST->Left)
{
return BST; //找到最左叶节点并返回
}
else
{
return FindMin(BST->Left);
}
} Position FinMax(BSTree BST)
{
if (!BST)
{
return NULL;
}
while (BST->Right)
{
BST = BST->Right; //沿右分支继续查找,直到最右节点
}
return BST;
} //关键是要找到元素应该插入的位置,可以采用与Find类似的方法
BSTree Insert(ELementType x, BSTree BST)
{
if (!BST)
{
BST = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTreeNode));
BST->Data = x;
BST->Left = NULL;
BST->Right = NULL;
}
else //开始找到要插入元素的位置
{
if (x < BST->Data)
{
BST->Left = Insert(x, BST->Left); //将子树的根节点挂在父节点下
}
else if (x > BST->Data)
{
BST->Right = Insert(x, BST->Right);
}
//else x已经存在
}
return BST;
} //删除节点的三种情况:
// 1.要删除的是叶节点:直接删除,并修改其父节点为NULL
// 2.要删除的结点只有一个孩子结点: 将其父结点的指针指向要删除结点的孩子结点
// 3.要删除的结点有左、右两棵子树: 用另一结点替代被删除结点:右子树的最小元素 或者 左子树的最大元素 BSTree Delete(ELementType x, BSTree BST)
{
Position temp;
if (!BST)
{
printf("要删除的元素未找到...\n");
}
else if (x < BST->Data)
{
BST->Left = Delete(x, BST->Left);
}
else if (x > BST->Data)
{
BST->Right = Delete(x, BST->Right);
}
else //找到要删除的节点
{
if (BST->Left&&BST->Right) /*被删除的节点有左右两个子节点*/
{
temp = FindMin(BST->Right); BST->Data = temp->Data;
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Data, BST->Right);
}
else //被删除节点有一个或者无子节点 //这里的理解:已经到尾节点了,只有一个元素了
{
temp = BST;
if (!BST->Left) //有右孩子
{
BST = BST->Right;
}
else if (!BST->Right)
{
BST = BST->Left;
}
free(temp);
}
}
return BST;
} BSTree CreateBST(BSTree BST)
{
int N = ;
printf("请输入创建二叉搜索树的元素个数:\n");
scanf("%d", &N);
int data = ;
for (int i = ; i < N; i++)
{
//scanf("%d", data);
BST=Insert(i + , BST);//
}
return BST;
} void PrintBST(BSTree BST) //考虑怎么可视化的输出
{
if (BST) //中序打印
{
PrintBST(BST->Left);
printf("%3d", BST->Data);
PrintBST(BST->Right);
}
} int main()
{
BSTree root = NULL;
//CreateBST(root);void 不行,要考虑怎么将节点传出来; 1.根据返回值 2.用传指针的方式,所有函数形参改为指针的指针&root root = CreateBST(root);
PrintBST(root);
printf("\n"); BSTree temp;
temp = Find(, root);
if (temp)
{
printf("search success!,search data is %d.\n", temp->Data);
}
else
{
printf("search failed!\n");
} temp = IterFinde(, root);
if (temp)
{
printf("search success!,search data is %d.\n", temp->Data);
}
else
{
printf("search failed!\n");
} root=Insert(, root);
PrintBST(root);
printf("\n"); root=Delete(, root);
PrintBST(root);
printf("\n"); return ;
}
补充:今天做了一个实验,感觉删除操作没有理解
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> typedef struct node {
int key;
struct node *LChild, *RChild; //孩子指针
}BSTNode, *BSTree; //定义二叉树----查找树 void CreatBST(BSTree *bst);
BSTree SearchBST(BSTree bst, int key);
void InsertBST(BSTree *bst, int key);
BSTNode * DelBST(BSTree t, int k);//以上是函数的声明 void print_bst(BSTree t) //打印
{
if (t)//中序顺序打印
{
print_bst(t->LChild);
printf("%d\t", t->key);
print_bst(t->RChild);
}
}
const int n = ;
/*创建树*/
void CreatBST(BSTree *bst)
{
printf("请输入%d个数创建二叉搜索树:",n);
int i;
int key;
*bst = NULL;
for (i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &key);
InsertBST(bst, key); //创建
};
}
/*寻找*/
BSTree SearchBST(BSTree bst, int key)
{
if (!bst)
return nullptr; //bst为空
else if (bst->key == key)
{
printf("查找成功!");
return bst; //找到,返回节点
}
else if (key < bst->key)
return SearchBST(bst->LChild, key); //左孩子递归调用查找
else
return SearchBST(bst->RChild, key); //右孩子递归
}
/*插入*/
void InsertBST(BSTree *bst, int key)
{
BSTree t;
if (*bst == NULL)
{
t = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode)); //树为空,申请空间
t->key = key;
t->LChild = NULL;
t->RChild = NULL;
*bst = t; //插入
//printf("插入成功!");
}
else if (key <(*bst)->key)
InsertBST(&((*bst)->LChild), key); //插到左子树
else if (key>(*bst)->key)
InsertBST(&((*bst)->RChild), key); //插到右子树
}
/*删除*/ //有问题?没有理解!
BSTNode * DelBST(BSTree t, int k) //根据LR为0或1,删除T中p所指结点的左或右子树
{
BSTNode *p, *f, *s, *q;
p = t;
s = t;//
f = NULL;
while (p) //树非空,先找到key的位置
{
if (p->key == k) //根节点等于K
break;
f = p; //f记录k所在的节点的 双亲节点
if (p->key > k) //向左子树方向
p = p->LChild;
else
p = p->RChild; //右
}
if (p == NULL) //为空
return t;
if (p->LChild == nullptr) //左空 ,下边就是删除过程
{
if (f == NULL)
t = p->RChild;
else if (f->LChild == p)
f->LChild = p->RChild;
else
f->RChild = p->LChild;
free(p); //释放空间
}
else //右,下边就是删除过程
{
q = p;
s = s->LChild;
while (s->RChild)
{
q = s;
s = s->RChild;
}
if (q == p)
q->LChild = s->LChild;
else
q->RChild = s->LChild;
p->key = s->key;
free(s); //释放空间
}
return t;
} int main()
{
BSTNode * root=nullptr;
int loop, i, data;
loop = true;
while (loop)
{
printf("\n***************二叉树操作菜单**************\n");
printf(" 1.创建\n");
printf(" 2.查找\n");
printf(" 3.插入\n");
printf(" 4.删除\n");
printf(" 5.打印\n");
printf(" 0.退出\n");
scanf("%d", &i);
switch (i)
{
case :
{
loop = false;
break;
}
case :
{
CreatBST(&root);
}break;
case :
{
printf("Please input the data you want search.\n");
scanf("%d", &data);
SearchBST(root, data); }break;
case :
{ printf("Please input the data you want insert.\n");
scanf("%d", &data);
InsertBST(&root, data);
printf("插入成功!");
}break;
case :
{
printf("Please input the data you want delete.\n");
scanf("%d", &data);
root = DelBST(root, data);
}break;
case :{
printf("\n");
if (root != NULL)
printf("The BSTree's root is:%d\n", root->key);
print_bst(root);
break;
}
}
}
}
//C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std; typedef int KeyType;
#define NUM 11 class BinStree;
class BinSTreeNode
{
public:
KeyType key;
BinSTreeNode *lchild;
BinSTreeNode *rchild;
BinSTreeNode()
{
lchild = NULL;
rchild = NULL;
}
}; class BinSTree
{
public:
BinSTreeNode *root;
BinSTree()
{
root = NULL;
}
~BinSTree()
{
//delete root;
}
BinSTreeNode *BSTreeSearch(BinSTreeNode *bt, KeyType k, BinSTreeNode *&p);
void BSTreeInsert(BinSTreeNode *&bt, KeyType k);
int BSTreeDelete(BinSTreeNode *&bt, KeyType k);
void BSTreePreOrder(BinSTreeNode *bt);
bool IsEmpty()
{
return root == NULL;
}
}; /**
* 二叉树排序查找算法
* 在根指针为bt的二叉排序树中查找元素k的节点,若查找成功,则返回指向该节点的指针
* 参数p指向查找到的结点,否则返回空指针,参数p指向k应插入的父结点
*/
BinSTreeNode* BinSTree::BSTreeSearch(BinSTreeNode *bt, KeyType k, BinSTreeNode *&p)
{
BinSTreeNode *q = NULL;
q = bt;
while (q)
{
p = q;
if (q->key == k)
{
return(p);
}
if (q->key > k)
q = q->lchild;
else
q = q->rchild;
}
return NULL;
} /**
* 二叉排序树的插入节点算法
* bt指向二叉排序树的根结点,插入元素k的结点
*/
void BinSTree::BSTreeInsert(BinSTreeNode *&bt, KeyType k)
{
BinSTreeNode *p = NULL, *q;
q = bt;
if (BSTreeSearch(q, k, p) == NULL)
{
BinSTreeNode *r = new BinSTreeNode;
r->key = k;
r->lchild = r->rchild = NULL;
if (q == NULL)
{
bt = r; //被插入节点做为树的根节点
}
if (p && k < p->key)
p->lchild = r;
else if (p)
p->rchild = r;
}
}
/**
* 先序遍历
*/
void BinSTree::BSTreePreOrder(BinSTreeNode *bt)
{
if (bt != NULL)
{
cout << bt->key << " ";
BSTreePreOrder(bt->lchild);
BSTreePreOrder(bt->rchild);
}
}
/**
* 二叉排序树的删除结点算法
* 在二叉排序树中删除元素为k的结点,*bt指向二叉排序树的根节点
* 删除成功返回1,不成功返回0.
*/
int BinSTree::BSTreeDelete(BinSTreeNode *&bt, KeyType k)
{
BinSTreeNode *f, *p, *q, *s;
p = bt;
f = NULL;
//查找关键字为k的结点,同时将此结点的双亲找出来
while (p && p->key != k)
{
f = p; //f为双亲
if (p->key > k)
p = p->lchild;
else
p = p->rchild;
}
if (p == NULL) //找不到待删除的结点时返回
return ;
if (p->lchild == NULL) //待删除结点的左子树为空
{
if (f == NULL) //待删除结点为根节点
bt = p->rchild;
else if (f->lchild == p) //待删结点是其双亲结点的左节点
f->lchild = p->rchild;
else
f->rchild = p->rchild; //待删结点是其双亲结点的右节点
delete p;
}
else //待删除结点有左子树,相当于有二个节点
{
q = p;
s = p->lchild;
while (s->rchild) //在待删除结点的左子树中查找最右下结点
{
q = s;
s = s->rchild; //找左子树的最大值
}
if (q == p)
q->lchild = s->lchild;
else
q->rchild = s->lchild; p->key = s->key;
delete s;
}
return ;
}
int main(void)
{
int a[NUM] = { , , , , , , , , , , };
int i;
BinSTree bst;
BinSTreeNode *pBt = NULL, *p = NULL, *pT = NULL; for (i = ; i < NUM; i++)
{
bst.BSTreeInsert(pBt, a[i]); //创建二叉排序树
}
pT = bst.BSTreeSearch(pBt, , p); //搜索排序二叉树
bst.BSTreePreOrder(pBt);
cout << endl;
bst.BSTreeDelete(pBt, ); //删除无左孩子的情况
bst.BSTreePreOrder(pBt);
cout << endl;
bst.BSTreeDelete(pBt, ); //删除有左孩子的情况
bst.BSTreePreOrder(pBt);
cout << endl;
return ;
}
C++二叉树的实现的更多相关文章
- [数据结构]——二叉树(Binary Tree)、二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)及其衍生算法
二叉树(Binary Tree)是最简单的树形数据结构,然而却十分精妙.其衍生出各种算法,以致于占据了数据结构的半壁江山.STL中大名顶顶的关联容器--集合(set).映射(map)便是使用二叉树实现 ...
- 二叉树的递归实现(java)
这里演示的二叉树为3层. 递归实现,先构造出一个root节点,先判断左子节点是否为空,为空则构造左子节点,否则进入下一步判断右子节点是否为空,为空则构造右子节点. 利用层数控制迭代次数. 依次递归第二 ...
- c 二叉树的使用
简单的通过一个寻找嫌疑人的小程序 来演示二叉树的使用 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h& ...
- Java 二叉树遍历右视图-LeetCode199
题目如下: 题目给出的例子不太好,容易让人误解成不断顺着右节点访问就好了,但是题目意思并不是这样. 换成通俗的意思:按层遍历二叉树,输出每层的最右端结点. 这就明白时一道二叉树层序遍历的问题,用一个队 ...
- 数据结构:二叉树 基于list实现(python版)
基于python的list实现二叉树 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- class BinTreeValueError(ValueError): ...
- [LeetCode] Path Sum III 二叉树的路径和之三
You are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value. Find the number of paths t ...
- [LeetCode] Find Leaves of Binary Tree 找二叉树的叶节点
Given a binary tree, find all leaves and then remove those leaves. Then repeat the previous steps un ...
- [LeetCode] Verify Preorder Serialization of a Binary Tree 验证二叉树的先序序列化
One way to serialize a binary tree is to use pre-oder traversal. When we encounter a non-null node, ...
- [LeetCode] Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal 二叉树的竖直遍历
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from top to bott ...
- [LeetCode] Binary Tree Longest Consecutive Sequence 二叉树最长连续序列
Given a binary tree, find the length of the longest consecutive sequence path. The path refers to an ...
随机推荐
- github不小心同步覆盖了本地文件
昨天不小心github的commit还没push就同步了,导致本地文件被覆盖,一度以为没救了. 后来得微博 @空非无和 @柳烟堆雪 指点,用git reflog 恢复了文件. 事情是这样的... 我在 ...
- 使用git建立本地仓储管理代码【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/airk000/article/details/7738231 Git是Linus大神的代码管理工具,简直说是开发者的超级福音,而作为屌丝的个人开发者, ...
- C# Server.MapPath()
./当前目录 /网站主目录../上层目录~/网站虚拟目录 如果当前的网站目录为E:\wwwroot 应用程序虚拟目录为E:\wwwroot\company 浏览的页面路径为E:\wwwroot\ ...
- GitHub的使用(上)—— 创建和更新
推荐一个属于自己的代码控制工具(或者是叫代码托管工具)——GitHub. 提起代码控制工具,很容易想到的就是CVS,SVN.这也是开发团队常用的.但如果想管理只属于自己的代码呢?那它们就不太合适了—— ...
- MySQL工具:管理员必备的10款MySQL工具
MySQL是一个复杂的的系统,需要许多工具来修复,诊断和优化它.幸运的是,对于管理员,MySQL已经吸引了很多软件开发商推出高品质的开源工具来解决MySQL的系统的复杂性,性能和稳定性,其中大部分是免 ...
- 7.cadence原理图后续[原创]
一.网表输出 1.自动编号 输出网表前,不能有问号 -- 效果: ---- -- 效果: 2.DRC检查 输出网表前需要DRC检查 3.网表输出 二.生成BOM表 法1: 法2: --- 点击OK: ...
- lightOJ 1366 Pair of Touching Circles(统计矩形内相切圆对)
题目链接:http://lightoj.com/volume_showproblem.php?problem=1366 题意:给出一个矩形,在内部画两个圆A和B使得AB都完全在矩形内且AB相切且AB的 ...
- SQL[连载1]简介
SQL[连载1]简介 SQL 教程 SQL 是用于访问和处理数据库的标准的计算机语言. 在本教程中,您将学到如何使用 SQL 访问和处理数据系统中的数据,这类数据库包括:MySQL.SQL Serve ...
- networking常用命令
nc -l 3000 将开一个临时的3000端口并且侦听,用于测试
- 【转】 ARM Linux 3.x的设备树(Device Tree)
1. ARM Device Tree起源 http://blog.csdn.net/21cnbao/article/details/8457546 Linus Torvalds在2011年3月1 ...
