Entity Framework Code-First(11):Configure One-to-One
Configure One-to-Zero-or-One Relationship:
Here, we will configure One-to-Zero-or-One relationship between two entities, e.g. Entity1 can be associated with zero or only one instance of Entity2.
Take an example of the following Student and StudentAddress entities.
public class Student
{
public Student() { } public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress
{
public int StudentAddressId { get; set; } public string Address1 { get; set; }
public string Address2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public int Zipcode { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; } public virtual Student Student { get; set; }
}
Visit Entity Relationship section to understand how EF manages one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships.
Now, let's configure Student and StudentAddress entities for One-to-Zero-or-One relationship where Student can have zero or maximum one StudentAddress.
As you may know, a one-to-zero-or-one relationship happens when the primary key of one table becomes PK & FK in another table in relational database such as SQL Server. So, we need to configure above entities in such a way that EF creates Students and StudentAddresses table in the DB where it will make StudentId in Student table as PK and StudentAddressId column in StudentAddress table as PK and FK both.
Configure one-to-zero-or-one relationship using DataAnnotations:
Here, we will apply DataAnnotations attributes on Student and StudentAddress entities to establish one-to-zero-or-one relationship.
The Student entity follows the default code-first convention as it includes StudentId property which will be key property. So we don't need to apply any attributes on it because EF will create Students table and make StudentId as a primary key in the DB.
For the StudentAddress entity, we need to configure StudentAddressId as PK & FK both. StudentAddressId property follows the default convention for primary key. So we don't need to apply any attribute for PK. However, we also need to make it a foreign key which points to StudentId. So, apply [ForeignKey("Student")] on StudentAddressId property which will make it foreign key for Student entity as shown below.
public class Student
{
public Student() { } public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress
{
[ForeignKey("Student")]
public int StudentAddressId { get; set; } public string Address1 { get; set; }
public string Address2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public int Zipcode { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; } public virtual Student Student { get; set; }
}
Thus, Student and StudentAddress entities has One-to-Zero-or-One relationship.
When StudentAddress entity does not follow conventions:
If, for example, StudentAddress entity does not follow the convention for PK i.e. different name for Id property then you need to configure it for PK as well. Consider the following StudentAddress entity which has property name StudentId instead of StudentAddressId.
public class Student
{
public Student() { } public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress
{
[Key, ForeignKey("Student")]
public int StudentId { get; set; } public string Address1 { get; set; }
public string Address2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public int Zipcode { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; } public virtual Student Student { get; set; }
}
In the above example, we need to configure StudentId property as Key as well as ForeignKey. This will make StudentId property in StudentAddress entity as PK and FK both.
Note: Student include StudentAddress navigation property and StudentAddress includes Student navigation property. With one-to-zero-or-one relationship, Student can be saved without StudentAddress but StudentAddress entity cannot be saved without Student entity. EF will throw an exception if you try to save StudentAddress entity without Student entity.
Configure One-to-Zero-or-One relationship using Fluent API:
Here, we will use Fluent API to configure Student and StudentAddress entities. Please note that we will not apply any DataAnnotations attributes in Student and StudentAddress entities because we will use Fluent API to configure them.
When Student and StudentAddress follow the conventions:
Student and StudentAddress entities follow the default code-first convention for PrimaryKey. So, we don't need to configure them to define their PrimaryKeys. We only need to configure StudentAddress entity where StudentAddressId should be ForeignKey.
The following example sets one-to-zero or one relationship between Student and StudentAddress using Fluent API.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{ // Configure Student & StudentAddress entity
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.HasOptional(s => s.Address) // Mark Address property optional in Student entity
.WithRequired(ad => ad.Student); // mark Student property as required in StudentAddress entity. Cannot save StudentAddress without Student }
In the above example, Student entity is configured using HasOptional() method which indicates that the StudentAddress navigation property in Student entity is an optional (not required when saving Student entity). Then, WithRequired() method configures StudentAddress entity and make Student navigation property of StudentAddress as required (required when saving StudentAddress entity. It will throw an exception when StudentAddress entity is saving without Student navigation property). This will make StudentAddressId as ForeignKey also.
Thus, you can configure One-to-Zero-or-one relationship between two entities where Student entity can be saved without attaching StudentAddress object to it but StudentAddress entity cannot be saved without attaching an object of Student entity. This makes one end required.
When StudentAddress entity do not follow conventions:
Now, let's take an example of StudentAddress entity where it does not follow primary key convention i.e. have different Id property name than <type name>Id. Consider the following Student and StudentAddress entities.
public class Student
{
public Student() { } public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress
{
public int StudentId { get; set; } public string Address1 { get; set; }
public string Address2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public int Zipcode { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; } public virtual Student Student { get; set; }
}
So now, we need to configure StudentId property of StudentAddress for PrimaryKey of StudentAddress as well as ForeignKey as shown below.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// Configure StudentId as PK for StudentAddress
modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>()
.HasKey(e => e.StudentId); // Configure StudentId as FK for StudentAddress
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.HasOptional(s => s.Address)
.WithRequired(ad => ad.Student); }
Configure One-to-One relationship using Fluent API:
We can configure One-to-One relationship between entities using Fluent API where both ends are required, meaning Student entity object must include StudentAddress entity object and StudentAddress entity must include Student entity object in order to save it.
Note:One-to-one relationship is technically not possible in MS SQL Server. It will always be one-to-zero or one. EF forms One-to-One relationships on entities not in DB.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// Configure StudentId as PK for StudentAddress
modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>()
.HasKey(e => e.StudentId); // Configure StudentId as FK for StudentAddress
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.HasRequired(s => s.Address)
.WithRequiredPrincipal(ad => ad.Student); }
In the above example, modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().HasRequired(s => s.Address) makes Address property of StudentAddress is required. .WithRequiredPrincipal(ad => ad.Student) makes Student property of StudentAddress entity as required. Thus it configures both ends required. So now, when you try to save Student entity without address or StudentAddress entity without Student, it will throw an exception.
Note: Here, Principal entity is Student and dependent entity is StudentAddress.
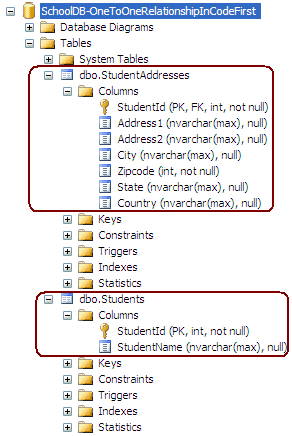
DataAnnotations and Fluent API example for one-to-zero or one relationship will create the following database:
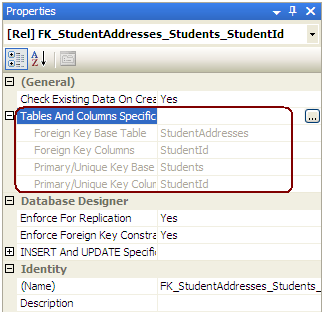
You can check the relationship between Student and StudentAddress in the database, as shown below:
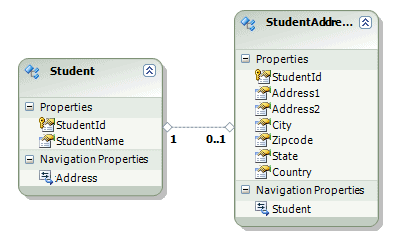
If you create an entity data model of a created database then it will appear like the diagram shown below:
Learn how to configure a one-to-many relationship in the next section.
Entity Framework Code-First(11):Configure One-to-One的更多相关文章
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(11):Code First
Code First development with Entity Framework: Entity Framework supports three different development ...
- Entity Framework Code first(转载)
一.Entity Framework Code first(代码优先)使用过程 1.1Entity Framework 代码优先简介 不得不提Entity Framework Code First这个 ...
- Entity Framework Code First (三)Data Annotations
Entity Framework Code First 利用一种被称为约定(Conventions)优于配置(Configuration)的编程模式允许你使用自己的 domain classes 来表 ...
- Entity Framework Code First (二)Custom Conventions
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- Entity Framework Code First (一)Conventions
Entity Framework 简言之就是一个ORM(Object-Relational Mapper)框架. Code First 使得你能够通过C#的类来描述一个模型,模型如何被发现/检测就是通 ...
- Entity Framework Code First (七)空间数据类型 Spatial Data Types
声明:本文针对 EF5+, Visual Studio 2012+ 空间数据类型(Spatial Data Types)是在 EF5 中引入的,空间数据类型表现有两种: Geography (地理学上 ...
- Entity Framework Code First (四)Fluent API - 配置属性/类型
上篇博文说过当我们定义的类不能遵循约定(Conventions)的时候,Code First 提供了两种方式来配置你的类:DataAnnotations 和 Fluent API, 本文将关注 Flu ...
- Entity Framework Code First (八)迁移 Migrations
创建初始模型和数据库 在开始使用迁移(Migrations)之前,我们需要一个 Project 和一个 Code First Model, 对于本文将使用典型的 Blog 和 Post 模型 创建一个 ...
- Entity Framework Code First (六)存储过程
声明:本文只针对 EF6+ 默认情况下,Code First 对实体进行插入.更新.删除操作是直接在表上进行的,从 EF6 开始你可以选择使用存储过程(Stored Procedures) 简单实体映 ...
- Entity Framework Code First (五)Fluent API - 配置关系
上一篇文章我们讲解了如何用 Fluent API 来配置/映射属性和类型,本文将把重点放在其是如何配置关系的. 文中所使用代码如下 public class Student { public int ...
随机推荐
- python操作mysql(一)原生模块pymysql
一.下载安装 pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同. 下载安装 C:\Users\Administrator>pip install pymysq ...
- curl 监控web
[root@rhel6 ~]# curl -I -s -w "%{http_code}\n" -o /dev/null http://127.0.0.1 [root@rhel6 ~ ...
- JavaScript的undefined与null、NaN的区别
Javascript的数据类型 在JavaScript中,有三种住数据类型.两种复合数据类型和两种特殊数据类型. 1.主数据类型(基元数据类型) 字符串 String数据类型: 字符串值是一个由零个或 ...
- Codeforces Round #335 (Div. 2) C. Sorting Railway Cars
C. Sorting Railway Cars time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- 表达式语句(EL)
EL的基本语法 ${expression} Expression:制定要输出的变了或字符串.或EL运算符组成的表达式. 禁用EL表达式: 1. 使用“\”符号禁用. \${expression} 2. ...
- 未测试 Delphi读写UTF-8、Unicode格式文本文件
// UTF-8文件写入函数 procedure SaveUTFFile(const FileName: string; S: string; WriteHeader: Boolean = True) ...
- priority_queue用法(转载)
关于priority_queue 1,关于STL中的priority_queue:确定用top()查看顶部元素时,该元素是具有最高优先级的一个元素. 调用pop()删除之后,将促使下一个元素进入该位置 ...
- Linux学习过程中的简单命令
1.su su- 与 sudo (1) 普通用户和root转换:su 用户名或root 不知道root密码的情况下:普通 -> root:sudo su roo ...
- HashMap,Hashtable,TreeMap ,Map
package com.wzy.list; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Hashtable; import java.util.Iterato ...
- leetcode 3 Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters(滑动窗口)
用滑动窗口的思想来做.用一个unordered_map来查询之前的char有没有在现在的窗口中. class Solution { public: int lengthOfLongestSubstri ...