[Python] 09 - Multi-processing
前言
资源
Ref: Python3 多线程
Ref: Python3之多进程 # python中的多线程无法利用多核优势
更多的提高效率的策略,请参见:[Pandas] 01 - A guy based on NumPy
多线程
一、认识线程
与进程的区别
线程在执行过程中与进程还是有区别的。 1. 每个独立的线程有一个程序运行的入口、顺序执行序列和程序的出口。 2. 但是线程不能够独立执行,必须依存在应用程序中,由应用程序提供多个线程执行控制。 3. 每个线程都有他自己的一组CPU寄存器,称为线程的上下文,该上下文反映了线程上次运行该线程的CPU寄存器的状态。 4. 指令指针 和 堆栈指针寄存器 是线程上下文中两个最重要的寄存器,线程总是在进程得到上下文中运行的,这些地址都用于标志拥有线程的进程地址空间中的内存。
获取CPU信息
Ref: https://github.com/giampaolo/psutil
from multiprocessing import cpu_count
print(cpu_count())
二、创建线程
Python3 通过两个标准库 _thread 和 threading 提供对线程的支持。
_thread 提供了低级别的、原始的线程以及一个简单的锁,它相比于 threading 模块的功能还是比较有限的。
低级别:创建 _thread
提供了低级别,原始的线程以及一个简单的锁。
#!/usr/bin/python3 import _thread
import time # 为线程定义一个函数
def print_time( threadName, delay):
count = 0
while count < 5:
time.sleep(delay)
count += 1
print ("%s: %s" % ( threadName, time.ctime(time.time()) ))
----------------------------------------------------------------
# 创建两个线程,参数是:函数名 以及对应的参数
try:
_thread.start_new_thread( print_time, ("Thread-1", 2, ) )
_thread.start_new_thread( print_time, ("Thread-2", 4, ) )
except:
print ("Error: 无法启动线程")
# 让主线程不要提前结束
while 1:
pass
高级别:创建 threading
采用了线程类的手法,该方法比较 engineering。
#!/usr/bin/python3 import threading
import time exitFlag = 0
# 线程类
class myThread (threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadID, name, counter):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadID = threadID
self.name = name
self.counter = counter
def run(self):
print ("开始线程:" + self.name)
print_time(self.name, self.counter, 5)
print ("退出线程:" + self.name)
----------------------------------------------------------------
def print_time(threadName, delay, counter):
while counter:
if exitFlag:
threadName.exit()
time.sleep(delay)
print ("%s: %s" % (threadName, time.ctime(time.time())))
counter -= 1
----------------------------------------------------------------
# (1) 创建新 线程'类‘
thread1 = myThread(1, "Thread-1", 1)
thread2 = myThread(2, "Thread-2", 2) # (2) 启动新线程
thread1.start()
thread2.start() # (3) 等待所有线程结束
thread1.join()
thread2.join()
print ("退出主线程")
三、线程同步(锁)
使用 Thread 对象的 Lock 和 Rlock 可以实现简单的线程同步,这两个对象都有 acquire 方法和 release 方法;
对于那些需要每次只允许一个线程操作的数据,可以将其操作放到 acquire 和 release 方法之间。
#!/usr/bin/python3 import threading
import time class myThread (threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadID, name, counter):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadID = threadID
self.name = name
self.counter = counter
def run(self):
print ("开启线程: " + self.name)
-------------------------------------------------------
threadLock.acquire() # <----
print_time(self.name, self.counter, 3)
threadLock.release() # <----
------------------------------------------------------- # 作为线程共享资源
def print_time(threadName, delay, counter):
while counter:
time.sleep(delay)
print ("%s: %s" % (threadName, time.ctime(time.time())))
counter -= 1 threadLock= threading.Lock()
threads = []
# (1) 创建新线程
thread1 = myThread(1, "Thread-1", 1)
thread2 = myThread(2, "Thread-2", 2) # (2) 开启新线程
thread1.start()
thread2.start() # (3) 等待线程
threads.append(thread1)
threads.append(thread2)
for t in threads:
t.join()
print ("退出主线程")
四、守护线程
setDaemon 设置
不添加setDaemon时,主线程和子线程分别在执行,约在主线程执行完5秒后子线程也执行完毕。
添加setDaemon的话,主进程执行完后不会等待 “作为守护线程” 的子进程,如下代码中,不会给child thread留有运行的机会。
import threading
import time
from datetime import datetime class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, id):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.id = id def run(self):
time.sleep(5)
print "子线程动作",threading.current_thread().name, datetime.now() if __name__ == "__main__":
t1 = MyThread(999)
t1.setDaemon(True) # 添加守护线程!
t1.start()
for i in range(5):
print "主线程动作",threading.current_thread().name, datetime.now()
join() 方法
只是添加了join函数一行代码,我们发现主线程和子线程执行的顺序就改变了。
主线程会等待子线程。
if __name__ == "__main__":
t1 = MyThread(999)
t1.start()
t1.join() # 添加join函数!
for i in range(5):
print "主线程动作",threading.current_thread().name, datetime.now()
Output: 等待child执行完,再执行join()之后main thread的内容。
child thread Thread-4 2019-09-26 17:50:16.049128
main thread MainThread 2019-09-26 17:50:16.050622
main thread MainThread 2019-09-26 17:50:16.050930
main thread MainThread 2019-09-26 17:50:16.051079
main thread MainThread 2019-09-26 17:50:16.051915
main thread MainThread 2019-09-26 17:50:16.05206
守护线程 + join函数
主线程一直等待全部的子线程结束之后,主线程自身才结束,程序退出。(其实守护线程的设置就没用了)
if __name__ == "__main__":
t1 = MyThread(999)
t1.setDaemon(True) # 添加守护线程!
t1.start()
t1.join() # 添加join函数!
for i in range(5):
print "主线程动作",threading.current_thread().name, datetime.now()
多进程
一、伪并行 - GIL
GIL 的全名是 the Global Interpreter Lock (全局解释锁),是常规 python 解释器(当然,有些解释器没有)的核心部件。
GIL 是 Python 解释器正确运行的保证,Python 语言本身没有提供任何机制访问它。但在特定场合,我们仍有办法降低它对效率的影响。
使用多进程
通过cpython启动多进程,能 "绕过" GIL。
from multiprocessing import Process
def spawn_n_processes(n, target):
threads = []
for _ in range(n):
thread = Process(target=target)
thread.start()
threads.append(thread)
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
通过 cpython 执行以上程序。
def test(target, number=10, spawner=spawn_n_threads):
"""
分别启动 1, 2, 3, 4 个控制流,重复 number 次,计算运行耗时
""" for n in (1, 2, 3, 4, ): start_time = time()
for _ in range(number):
spawner(n, target)
end_time = time() print('Time elapsed with {} branch(es): {:.6f} sec(s)'.format(n, end_time - start_time)) test(fib, spawner=spawn_n_processes)
线程优先级队列
一、Queue模块
写在前面
操作性质
Python 的 “Queue 模块” 中提供了同步的、线程安全的队列类,包括
- FIFO(先入先出)队列Queue,
- LIFO(后入先出)队列LifoQueue,
- 优先级队列 PriorityQueue。
操作方法
三种队列均提供如下方法:
这些队列都实现了锁原语,能够在多线程中直接使用,可以使用队列来实现线程间的同步。
Queue 模块中的常用方法:
import Queue
- Queue.qsize() 返回队列的大小
- Queue.empty() 如果队列为空,返回True,反之False
- Queue.full() 如果队列满了,返回True,反之False
- Queue.full 与 maxsize 大小对应
- Queue.get([block[, timeout]]) 获取队列,timeout等待时间
- Queue.get_nowait() 相当Queue.get(False)
- Queue.put(item) 写入队列,timeout等待时间
- Queue.put_nowait(item) 相当Queue.put(item, False)
- Queue.task_done() 在完成一项工作之后,Queue.task_done()函数向任务已经完成的队列发送一个信号
- Queue.join() 实际上意味着等到队列为空,再执行别的操作
(1) FIFO队列先进先出
From: python多线程-queue队列类型优先级队列,FIFO,LIFO
默认队列:Queue.Queue()
#coding=utf8
import Queue queuelist = Queue.Queue() for i in range(5):
if not queuelist.full():
queuelist.put(i)
print "put list : %s ,now queue size is %s "%(i,queuelist.qsize()) while not queuelist.empty():
print "get list : %s , now queue size is %s"%(queuelist.get(),queuelist.qsize())
Output:
put list : 0 ,now queue size is 1
put list : 1 ,now queue size is 2
put list : 2 ,now queue size is 3
put list : 3 ,now queue size is 4
put list : 4 ,now queue size is 5
get list : 0 , now queue size is 4
get list : 1 , now queue size is 3
get list : 2 , now queue size is 2
get list : 3 , now queue size is 1
get list : 4 , now queue size is 0
(2) LIFO队列先进后出
本来是个stack,非要叫成是LIFO队列,汗~
#coding=utf8
import Queue queuelist = Queue.LifoQueue() for i in range(5):
if not queuelist.full():
queuelist.put(i)
print "put list : %s ,now queue size is %s "%(i,queuelist.qsize()) while not queuelist.empty():
print "get list : %s , now queue size is %s"%(queuelist.get(),queuelist.qsize())
Output:
put list : 0 ,now queue size is 1
put list : 1 ,now queue size is 2
put list : 2 ,now queue size is 3
put list : 3 ,now queue size is 4
put list : 4 ,now queue size is 5
get list : 4 , now queue size is 4
get list : 3 , now queue size is 3
get list : 2 , now queue size is 2
get list : 1 , now queue size is 1
get list : 0 , now queue size is 0
(3) 优先队列
put方法的参数是个元组 (<优先级> ,<value>)。
#coding=utf8
import queue as Queue
import random queuelist = Queue.PriorityQueue() for i in range(5):
if not queuelist.full():
x=random.randint(1,20)
y=random.randint(1,20)
print x
queuelist.put((x,y)) while not queuelist.empty():
print "get list : %s , now queue size is %s"%(queuelist.get(),queuelist.qsize())
Output:
11
5
10
7
10
get list : (5, 10) , now queue size is 4
get list : (7, 10) , now queue size is 3
get list : (10, 10) , now queue size is 2
get list : (10, 10) , now queue size is 1
get list : (11, 10) , now queue size is 0
二、综合例子
栗子:模拟检票过程
内容:一个队,三个检票口 (三个线程)
锁机制:不能同时“取”,所以取的过程需要加“锁”。
#coding=utf8 import Queue
import threading
import time exitsingle = 0 class myThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadname, queuelist):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadname = threadname
self.queuelist = queuelist def run(self):
print "Starting queue %s"%self.threadname
queue_enter(self.threadname, self.queuelist) # 每一个线程从管道中”取数据“
time.sleep(1)
print "close " + self.threadname
def queue_enter(threadname, queuelist):
while not exitsingle:
queueLock.acquire()
if not workQueue.empty():
data = queuelist.get()
queueLock.release() # 取完就可以释放“锁”
print "%s check ticket %s" % (threadname, data)
else:
queueLock.release()
time.sleep(1)
####################################################
# 初始化
####################################################
threadList = ["list-1", "list-2", "list-3"]
queueLock = threading.Lock()
workQueue = Queue.Queue()
threads = [] queueLock.acquire()
for num in range(100001,100020):
workQueue.put(num) # 计入“票的编号”
queueLock.release()
print "start .."
# 三个线程从一个管道里取数据,但不能同时取
for name in threadList:
thread = myThread( name, workQueue)
thread.start()
threads.append(thread) while not workQueue.empty():
pass exitsingle = 1 for t in threads:
t.join()
print "stop enter.."
栗子:生产者消费者问题
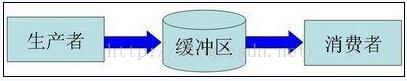
但这里貌似少了lock相关,具体可参考以上两个栗子。
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author :
# @File : text.py
# @Software : PyCharm
# @description : XXX from queue import Queue
import random
import threading
import time # Producer thread
class Producer(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, t_name, queue):
threading.Thread.__init__(self, name=t_name)
self.data = queue
def run(self):
for i in range(5):
print("%s: %s is producing %d to the queue!" % (time.ctime(), self.getName(), i))
self.data.put(i)
time.sleep(random.randrange(10) / 5)
print("%s: %s finished!" % (time.ctime(), self.getName())) # Consumer thread
class Consumer(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, t_name, queue):
threading.Thread.__init__(self, name=t_name)
self.data = queue
def run(self):
for i in range(5):
val = self.data.get()
print("%s: %s is consuming. %d in the queue is consumed!" % (time.ctime(), self.getName(), val))
time.sleep(random.randrange(10))
print("%s: %s finished!" % (time.ctime(), self.getName()))
# Main thread
def main():
queue = Queue()
producer = Producer('Pro.', queue)
consumer = Consumer('Con.', queue)
producer.start()
consumer.start()
producer.join()
consumer.join()
print('All threads terminate!') if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
End.
[Python] 09 - Multi-processing的更多相关文章
- python 09 数据包 异常处理
pickle模块操作文件 pickle.dump(obj, file[, protocol]) 序列化对象,并将结果数据流写入到文件对象中.参数protocol是序列化模式,默认值为0,表示以文本的形 ...
- 【Python 09】汇率兑换2.0-2(分支语句)
分支语句:根据判断条件选择程序执行路径 1.使用方法 if <条件1>: <语句块1> elif <条件2>: <语句块2> ... else: < ...
- python 09 文件操作
一 流程: #1. 打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量 #2. 通过句柄对文件进行操作 #3. 关闭文件 二 例子 #1. 打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量f=open('a.txt','r ...
- python 09
1.函数进阶: 函数动态参数: 动态位置参数 *args 动态关键字参数 **kwargs 位置 > 动态位置参数 > 默认(关键字)参数 > 动态关键字参数 2.命名空间 局部命名 ...
- python --- 09 初始函数 参数
函数 1.函数: 对代码块和功能的封装和定义 2.格式及语法 def 函数名() # 定义 函数体 函数名() # 调用 3. return ret ...
- python 09 函数
目录 函数初识 1. 函数定义: 2. 函数调用: 3. 函数的返回值: 4. () 4.1 位置传参: 4.2 关键字传参: 4.3 混合传参: 函数初识 1. 函数定义: def 函数名(): 函 ...
- Python 09 安装torch、torchvision
这个也是弄了我很久,百度了好多文章,其实像下面那样挺简单的,没那么复杂 1.进入torch的官网的下载页面,选择一下参数信息 地址:https://pytorch.org/get-started/lo ...
- python 09篇 操作Excel
一.往Excel中写数据 使用pip install xlwt安装xlwt模块,用xlwt模块进行对Excel进行写数据. import xlwt # book = xlwt.Workbook() # ...
- Python自然语言处理工具小结
Python自然语言处理工具小结 作者:白宁超 2016年11月21日21:45:26 目录 [Python NLP]干货!详述Python NLTK下如何使用stanford NLP工具包(1) [ ...
随机推荐
- maven学习(1)下载和安装和初步使用(手动构建项目和自动构建项目)
1:背景 关于项目的搭建,有些人使用开发工具搭建项目,然后将项目所依赖第三方jar 复制到类路径下面,上述搭建方式没有第三方类库的依赖关系,在导入一个jar包的时候,这个jar包还可能依赖其他jar包 ...
- 90002CAD相关操作
第一章 初识CAD 1.1 CAD能干什么 (1)绘制机械图/建筑图/装修图等二维复杂工程图的不二之选.二维设计软件的王者. (2)CAD可以绘制平面图.轴测图(二维线框表示三维图形).立体图(三 ...
- Comupter Tools 清单------包含但不限于此
- C++11——智能指针
1. 介绍 一般一个程序在内存中可以大体划分为三部分——静态内存(局部的static对象.类static数据成员以及所有定义在函数或者类之外的变量).栈内存(保存和定义在函数或者类内部的变量)和动态内 ...
- CF 551 D.Serval and Rooted Tree 树形DP
传送门:http://codeforces.com/contest/1153/problem/D 思路: 这道题想了一天,突发奇想,就是维护每个点两个值,第几大和第几小,就可以有传递性了. #incl ...
- P2774 方格取数问题 网络最大流 割
P2774 方格取数问题:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P2774 题意: 给定一个矩阵,取出不相邻的数字,使得数字的和最大. 思路: 可以把方格分成两个 ...
- HDU 5973 Aninteresting game 威佐夫博奕(Wythoff Game)
HDU 5973:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5975 题意: 有两堆石子,每次可以从一堆石子中取任意个,或者从两堆石子中取相同个数的石子.两个 ...
- hihocoder [Offer收割]编程练习赛18 C 最美和弦(dp)
题目链接:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1532 题解:一道基础的dp,设dp[i][j][k][l]表示处理到第几个数,当前是哪个和弦错了几次初始x ...
- Codeforces 729C Road to Cinema(二分)
题目链接 http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/729/C 题意:n个价格c[i],油量v[i]的汽车,求最便宜的一辆使得能在t时间内到达s,路途中有k个位 ...
- CodeForces 982 C Cut 'em all!
Cut 'em all! 题意:求删除了边之后,剩下的每一块联通块他的点数都为偶数,求删除的边最多能是多少. 题解:如果n为奇数,直接返回-1,因为不可能成立.如果n为偶数,随意找一个点DFS建树记录 ...
