【JDK】JDK源码分析-TreeMap(1)
概述
前面数据结构与算法笔记对红黑树进行了分析,而 TreeMap 内部就是基于红黑树实现的。示意图:
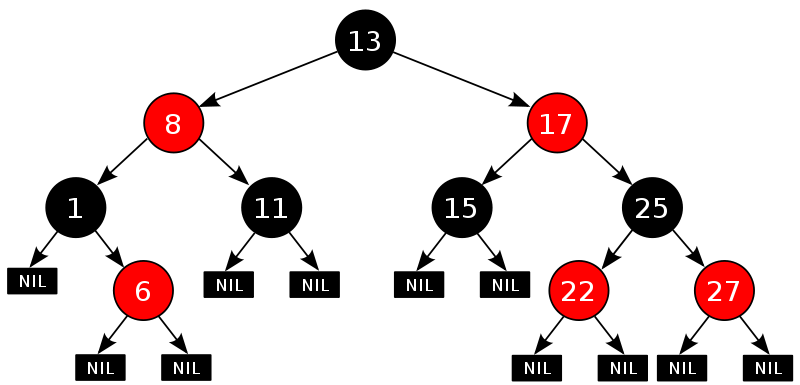
它的查找、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度均为 O(logn)。
TreeMap 类的继承结构如下:
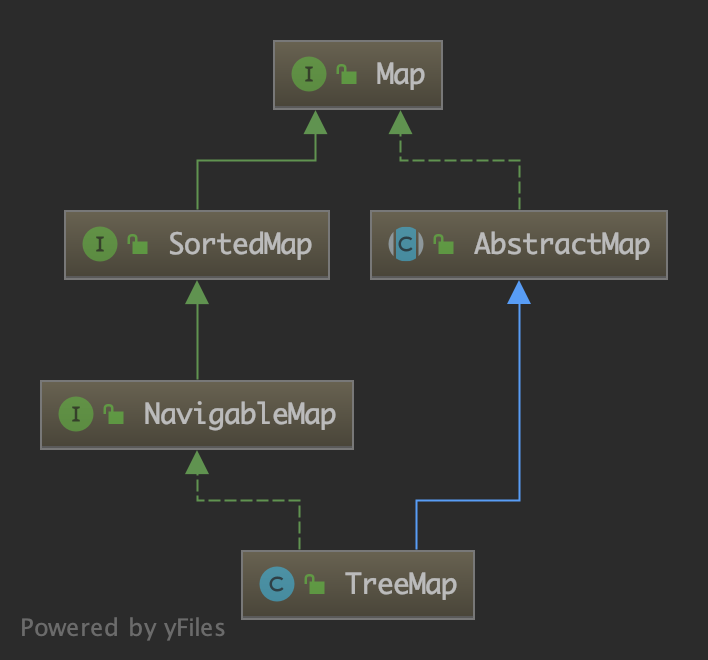
类签名:
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
TreeMap 实现了 Map 接口,其内部数据格式是“键-值对”的形式(Entry),排列顺序是按照键的顺序进行的。
代码分析
成员变量
/**
* The comparator used to maintain order in this tree map, or
* null if it uses the natural ordering of its keys.
*
* TreeMap 内部的比较器,若为空,则为自然顺序
*/
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; // 根节点
private transient Entry<K,V> root; /**
* The number of entries in the tree
*/
private transient int size = 0; /**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
构造器
TreeMap 有四个构造器,分别如下:
构造器一:无参构造器
/**
* 无参构造器。使用 key 的自然顺序排列(key 要实现 Comparable 接口)
*/
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
构造器二:
/**
* 使用指定的 Comparator(比较器)构造一个空的 TreeMap
*/
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
构造器三:
/**
* 使用给定的 Map 构造一个 TreeMap
*/
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
构造器四:
/**
* 使用给定的 SortedMap 构造一个 TreeMap
*(使用 SortedMap 的顺序)
*/
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
常用方法
查找某个 key
// 判断 TreeMap 是否包含某个 key
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
} // 查找 TreeMap 中某个 key 对应的 value(若不存在返回 null)
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
由于这两个方法内部都是通过 getEntry 方法实现,因此放在一起分析,如下:
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
当 Comparator 不为空时,使用如下方法查找:
/**
* Version of getEntry using comparator. Split off from getEntry
* for performance. (This is not worth doing for most methods,
* that are less dependent on comparator performance, but is
* worthwhile here.)
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
可以看到,这两个方法都是二叉查找树的查找过程。
PS: 这里将 Comporator 和 Comparable 两个接口分开进行操作。注释说明是出于性能考虑,虽然大部分方法中不值得这样做,但这里值得。
查找某个 value
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
getFirstEntry() 方法是获取第一个 Entry 节点(中序遍历最左边的节点):
/**
* Returns the first Entry in the TreeMap (according to the TreeMap's
* key-sort function). Returns null if the TreeMap is empty.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
查找某个 Entry 的后继节点:
/**
* Returns the successor of the specified Entry, or null if no such.
*/
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
// 若右子树不为空,则后继节点就是右子树的最小节点
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
// 若右子树为空,则向上回溯
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
可以看到,这里判断 TreeMap 是否包含某个 value,是按照二叉查找树的中序遍历去比较是否存在与给定 value 相等的值。
lowerEntry / lowerKey: 查找比指定 key 小的最大 Entry / key
public Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getLowerEntry(key));
}
public K lowerKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getLowerEntry(key));
}
/**
* Returns the entry for the greatest key less than the specified key; if
* no such entry exists (i.e., the least key in the Tree is greater than
* the specified key), returns {@code null}.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getLowerEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
// 给定的key大于根节点,继续与右子节点比较
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else {
// 左子节点不为空,则为左子节点
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
// 左子节点为空,向父节点上溯
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}
higherEntry / higherKey: 查找比指定 key 大的最小 Entry / key
public Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getHigherEntry(key));
}
public K higherKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getHigherEntry(key));
}
getHigherEntry 方法与 getLowerEntry 方法实现类似,不同之处在于 left 和 right 相反,这里不再贴代码。
floorEntry / floorKey:
public Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getFloorEntry(key));
}
public K floorKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getFloorEntry(key));
}
/**
* Gets the entry corresponding to the specified key; if no such entry
* exists, returns the entry for the greatest key less than the specified
* key; if no such entry exists, returns {@code null}.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
// 与上述方法的区别
return p;
}
return null;
}
查找指定 key 关联的 Entry;若不存在,返回比该 key 小的最大 key 关联的 Entry;若这也不存在则返回 null。
PS: 该方法与上面的 getLowerEntry 方法仅相差 while 循环内部的一个 else。
ceilingEntry / ceilKey:
public Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
return exportEntry(getCeilingEntry(key));
}
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key));
}
getCeilingEntry 方法与 getFloorEntry 方法实现类似,也是 left 和 right 相反。就像上面 getLowerEntry 和 getHigherEntry的区别那样,这里不再贴代码。
查找指定 key 关联的 Entry;若不存在,返回比该 key 大的最小 key 关联的 Entry;若这也不存在则返回 null。
还有几个截取 TreeMap 一部分的方法,分别如下:
public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(this,
true, null, true,
false, toKey, inclusive);
}
public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(this,
false, fromKey, inclusive,
true, null, true);
}
public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
return new AscendingSubMap<>(this,
false, fromKey, fromInclusive,
false, toKey, toInclusive);
}
除此之外,最常用的插入和删除操作还未分析,这两部分比较复杂,因此留到后面单独分析。
小结
1. TreeMap 实现了 Map 接口,内部节点类型为 Entry;
2. 基于红黑树实现,具有红黑树的特点;
3. 有序,根据 Entry 的 key 排序;
4. 查找、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度均为 O(logn)。
相关阅读
Stay hungry, stay foolish.

PS: 本文首发于微信公众号【WriteOnRead】。
【JDK】JDK源码分析-TreeMap(1)的更多相关文章
- 【JDK】JDK源码分析-TreeMap(2)
前文「JDK源码分析-TreeMap(1)」分析了 TreeMap 的一些方法,本文分析其中的增删方法.这也是红黑树插入和删除节点的操作,由于相对复杂,因此单独进行分析. 插入操作 该操作其实就是红黑 ...
- JDK Collection 源码分析(2)—— List
JDK List源码分析 List接口定义了有序集合(序列).在Collection的基础上,增加了可以通过下标索引访问,以及线性查找等功能. 整体类结构 1.AbstractList 该类作为L ...
- JDK AtomicInteger 源码分析
@(JDK)[AtomicInteger] JDK AtomicInteger 源码分析 Unsafe 实例化 Unsafe在创建实例的时候,不能仅仅通过new Unsafe()或者Unsafe.ge ...
- 设计模式(十八)——观察者模式(JDK Observable源码分析)
1 天气预报项目需求,具体要求如下: 1) 气象站可以将每天测量到的温度,湿度,气压等等以公告的形式发布出去(比如发布到自己的网站或第三方). 2) 需要设计开放型 API,便于其他第三方也能接入气象 ...
- JDK Collection 源码分析(3)—— Queue
@(JDK)[Queue] JDK Queue Queue:队列接口,对于数据的存取,提供了两种方式,一种失败会抛出异常,另一种则返回null或者false. 抛出异常的接口:add,remove ...
- JDK Collection 源码分析(1)—— Collection
JDK Collection JDK Collection作为一个最顶层的接口(root interface),JDK并不提供该接口的直接实现,而是通过更加具体的子接口(sub interface ...
- 【JDK】JDK源码分析-HashMap(1)
概述 HashMap 是 Java 开发中最常用的容器类之一,也是面试的常客.它其实就是前文「数据结构与算法笔记(二)」中「散列表」的实现,处理散列冲突用的是“链表法”,并且在 JDK 1.8 做了优 ...
- JDK(七)JDK1.8源码分析【集合】TreeMap
本文转载自joemsu,原文链接 [JDK1.8]JDK1.8集合源码阅读——TreeMap(二) TreeMap是JDK中一种排序的数据结构.在这一篇里,我们将分析TreeMap的数据结构,深入理解 ...
- JDK源码分析—— ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue
JDK源码分析—— ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue 目的:本文通过分析JDK源码来对比ArrayBlockingQueue 和LinkedBlocki ...
随机推荐
- 设计模式之装饰器模式(decorator pattern)
装饰器模式主要对现有的类对象进行包裹和封装,以期望在不改变类对象及其类定义的情况下,为对象添加额外功能.是一种对象结构型模式.需要注意的是,该过程是通过调用被包裹之后的对象完成功能添加的,而不是直接修 ...
- PWN菜鸡入门之栈溢出 (2)—— ret2libc与动态链接库的关系
准备知识引用自https://www.freebuf.com/articles/rookie/182894.html 0×01 利用思路 ret2libc 这种攻击方式主要是针对 动态链接(Dynam ...
- 安装Flume——海量日志收集聚合系统
下载flume: 1.官方网站下载: http://flume.apache.org/download.html 2.百度网盘资源: apache-flume-1.9.0-bin.tar 链接:ht ...
- 【IDE】idea在debug模式启动非常慢,debug模式一直在启动中状态
现象:一直处于启动中状态,日志刷的很慢,非debug模式正常启动: 最终解决方式:下图按钮,取消所有打过的断点,问题解决
- oh-my-zsh自定义配置
oh-my-zsh主题配置 默认的zsh主题robbyrussell已经很棒了, 简洁高效, 能很好的显示git的相关信息, 比如branch信息, 修改, 删除, 添加等操作. 但是多用户的话就不能 ...
- Python基础(九) 常用模块汇总
3.8 json模块重点 json模块是将满足条件的数据结构转化成特殊的字符串,并且也可以反序列化还原回去. 不同语言都遵循的一种数据转化格式,即不同语言都使用的特殊字符串.(比如Python的一个列 ...
- 大白话5分钟带你走进人工智能-第31节集成学习之最通俗理解GBDT原理和过程
目录 1.前述 2.向量空间的梯度下降: 3.函数空间的梯度下降: 4.梯度下降的流程: 5.在向量空间的梯度下降和在函数空间的梯度下降有什么区别呢? 6.我们看下GBDT的流程图解: 7.我们看一个 ...
- RABC权限控制(二级菜单实现)
目前大部分系统由于用户体验,基本上菜单不会做的很深,以二级菜单为例,做了一个简单的权限控制实现,可精确到按钮级别(基于django),下面具体看看实现 1.表结构的设计 无论开发什么都需要先梳理清楚需 ...
- HDU 1584:蜘蛛牌(DFS)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1584 题意:要让小的牌放到大的牌上面最少移动的距离. 思路:看成让大的牌放在小的牌上面了...用一个标记数组vi ...
- vue.js 解决跨域问题
我们调试vue.js代码的时候一般都用chrome, 下载插件 进入chrome应用商店 搜索 重启chrome就可以解决跨域问题
