爬虫获取搜狐汽车的配置信息 和swf动态图表的销量数据-------详细教学
前情提要:需要爬取搜狐汽车的所有配置信息,具体配置对应的参数. 以及在动态图表上的历史销量。
比如: 一汽奥迪旗下Q5L 的《40 TFSI 荣享进取型 国VI 》的历史销量和该配置的参数信息。
因此整体分两个大块,一个是配置参数,一个是历史销量。
下面开始正文
第一步:
首先观察网页:http://db.auto.sohu.com/home/
在搜狐汽车主页查看源代码,找到对应的配置信息链接所在DIV:
(可以任选一个汽车的配置信息页比如奥迪A4 发现链接为 http://db.auto.sohu.com/yiqiaudi/2374
而其配置信息的页面为 http://db.auto.sohu.com/yiqiaudi/2374/trim.html .
故需要找的是主页内每一款车的具体链接所在的div模块 ,有了这个每次加上trim.html 进行循环爬取即可。)
对应DIV模块为:

因此利用xpath定位到具体的 a标签下 class="model-a"即可锁定所有车型的链接,代码如下:
import requests
import pandas as pd
import re
from lxml import etree
import numpy as np
import collections
import pickle
# 总页面的根据字母提取子url和对应品牌
# treeNav brand_tit
url_all='https://db.auto.sohu.com/home/'
req_all=requests.get(url_all)
wb_all=req_all.text; #网页源码
html_all = etree.HTML(wb_all) # model-a 先获取所有车型链接反推建立上层 或根据链接分析建立(英文不推荐)
js=html_all.xpath('//a[@class="model-a"]')
h=[]
for i in js:
h.append(i.xpath('@href')[0])
所得到的h 即为所有子链接的list;
第二步:
观察某一个车型子链接下配置页面的源代码, 寻找配置的具体参数命名和具体参数的值。 如下图
<table id="trimArglist" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr id="SIP_C_102">
<th class="th1">
<div class="th1_div">
<a href="http://db.auto.sohu.com/baike/244.shtml" target="_blank">厂商指导价</a>:
</div>
</th>
<td class="th2"></td>
<td class="th3"> </td>
<td class="th4"> </td>
<td class="th5"> </td>
</tr>
<tr id="SIP_C_101" class="new-energy-car">
<th class="th1">补贴后售价: </th>
<td class="th2"></td>
<td class="th3"> </td>
<td class="th4"> </td>
<td class="th5"> </td>
</tr>
<tr id="SIP_C_103">
<th class="th1">
<a href="http://db.auto.sohu.com/baike/247.shtml" target="_blank">4S店报价</a>:
</th>
<td class="th2"> </td>
<td class="th3"> </td>
<td class="th4"> </td>
<td class="th5"> </td>
</tr>
<tr id="ttr_0">
<th colspan="60" class="colSpan6" style="border-top: 0px">
<span>车辆基本参数</span>
<span class="sqsq">收起</span>
</th>
</tr> <tr id="SIP_C_105">
<th class="th1">
<a href="http://db.auto.sohu.com/baike/249.shtml" target="_blank">级别</a>:
</th>
<td class="th2"> </td>
<td class="th3"> </td>
<td class="th4"> </td>
<td class="th5"> </td>
</tr>
<tr id="SIP_C_109">
<th class="th1">
<a href="http://db.auto.sohu.com/baike/249.shtml" target="_blank">上市时间</a>:
</th>
<td class="th2"> </td>
<td class="th3"> </td>
<td class="th4"> </td>
<td class="th5"> </td>
</tr>
经过观察上图看到,具体的配置名称可以通过xpath定位到 table[@id="trimArglist"] 后提取内中所有 a标签的名称。 但是此处并未有具体配置的值信息。因此只是一个配置名称的集合。
而链接配置名称与配置参数值的枢纽是他的 tr id 比如上图 中 : 上市时间的表格 id
SIP_C_109 发现该值出现在js的一个参数里: 见下图

即调用js的参数对表格进行赋值。链接枢纽是表格id代表其物理意义。 然后我们即提取id 然后搜寻js的这个赋值参数即可。
因在js中所有配置的参数赋值本身就是字典形式,即var trim={SIP_C_103:xxx,SIP_C_104:xxx}
因此直接在python中执行这一js赋值语句即可得到一个字典,然后再将这些
id号比如SIP_C_103对应的网页div表格下a标签的中文进行替换即可 代码如下:
# 所有车
df={}
df=collections.OrderedDict()
for o in h:
############################################## 整车配置 #################################################
url='https:'+o+'/trim.html'
req=requests.get(url)
wb_data=req.text #网页源码 # xpath定位至其js赋给车辆页面参数的地方
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
js=html.xpath('//script[@type="text/javascript"]')
# 这里有很多js 寻找js内存在参数配置备注的这一条
k=[]
for i in range(len(js)):
if js[i].text!=None:
if len(re.findall('// 参数配置',js[i].text))!=0:
k.append(js[i]);
js=k.copy()
js=k.copy()
sss=js[0].text
# 定位到具体js的某一个变量 trimParam 顺便处理js赋值中TRUE 和false在python中会报错 因此定义为字符。
sss=sss[sss.find('trimParam'):]
sss=sss.replace('false','"false"')
sss=sss.replace('true','"true"')
# 直接调用js的赋值. 某些车辆停售或暂未发售无参数默认就继续循环执行(continue)
exec(sss)
if len(trimParam)==0:
continue
# js对参数赋值时对应的代号的物理意义:比如 SIP_C_103的意义可能是为 续航里程,把代号换掉
c=[]
TB=html.xpath('//table[@id="trimArglist"]')
for i in list(trimParam[0]['SIP_T_CONF'].keys()):
tbname=TB[0].xpath('//table//tr[@id=\"'+i+'\"]//th[@class="th1"]')
for j in range(len(trimParam)):
if len(tbname)!=0:
if tbname[0].text.replace(' ','')=='\n':
tbname=TB[0].xpath('//tr[@id=\"'+i+'\"]//th[@class="th1"]//a')
c.append(tbname[0].text)
trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text] = trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'].pop(i)
try:
trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]=trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]['v']
except:
trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]=''; #车辆没有的配置数据不进行记录
if (trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]=='-') | (trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]==''): # 车辆配置里-代表车无此配置厂商也无法进行安装此配置
del trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]
else:
# 某些配置在js中没有参数进行赋值,发现是一些复写的参数比如已有长宽高的信息和参数值,但是存在名字为长的信息但没有赋值,因此不要
c.append(np.nan)
del trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][i] trimParam_dict={}
for i in range(len(trimParam)):
trimParam_dict[trimParam[i]['SIP_T_NAME']]=trimParam[i]; # 反推建立数据字典
if trimParam[0]['brandName'] not in df.keys():
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']]={}
if trimParam[0]['subbrandName'] not in df[trimParam[0]['brandName']].keys():
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']][trimParam[0]['modelName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']][trimParam[0]['modelName']]['配置参数']=trimParam_dict
最后反推建立字典是根据配置里的品牌,子品牌,车辆配置名称信息建立上层字典的key来定位自身。
至此配置信息的字典格式就完成了,因为访问每一个车型时都会进行数据处理,因此访问间隔不会太短导致被反爬机制封掉。
接下来是动态图表的销量信息 ,我们希望承接上文,在每一个子品牌的车型旗下直接新建一个key(本来只有上文的配置参数key),让他记录历史的销量信息。
首先动态图表的历史数据在网页源码上搜不到,那么我们调用浏览器的控制台来观察他在动态图表上显示数据的整个响应过程,通过这个来找图表调用的数据来源是什么。
打开控制台观察一个车型子链接的销量页面。见下图:

左侧为动态图表,右侧为控制台,现在我们点一下全部数据

响应的信息数据出现了,见右侧控制台xml参数,观察xml的header(当前是response返回的数据)
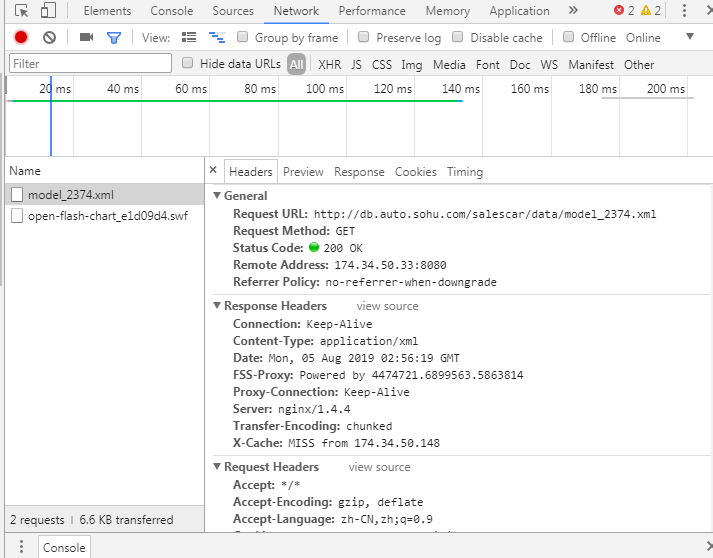
不难发现数据是从这个 链接得到的,如下图:
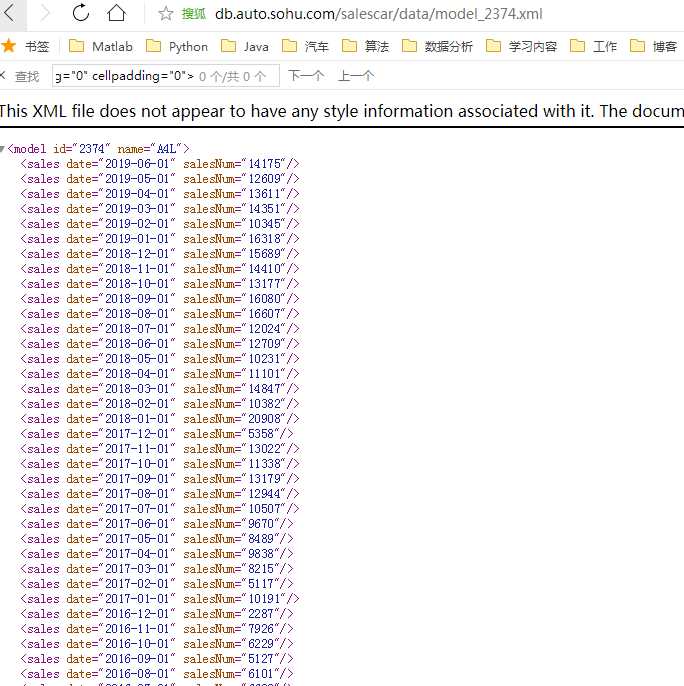
这跟我们车型的关系枢纽就是model后的那一串数字 即为车型id号的链接,那么每一款车型的id号知道了,就能获取每一个销量数据的链接,
车型id号 恰好我们在调用js赋值时发现是有的 那么在之前的循环中 提取id号 然后处理销量数据即可,代码如下面的销量数据部分:
for o in h:
############################################## 整车配置 #################################################
url='https:'+o+'/trim.html'
req=requests.get(url)
wb_data=req.text #网页源码 # xpath定位至其js赋给车辆页面参数的地方
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
js=html.xpath('//script[@type="text/javascript"]')
# 这里有很多js 寻找js内存在参数配置备注的这一条
k=[]
for i in range(len(js)):
if js[i].text!=None:
if len(re.findall('// 参数配置',js[i].text))!=0:
k.append(js[i]);
js=k.copy()
js=k.copy()
sss=js[0].text
# 定位到具体js的某一个变量 trimParam
sss=sss[sss.find('trimParam'):]
sss=sss.replace('false','"false"')
sss=sss.replace('true','"true"')
# 直接调用js的赋值.
exec(sss)
if len(trimParam)==0:
continue
# js对参数赋值时对应的代号的物理意义:比如 SIP_C_103的意义可能是为 续航里程,把代号换掉
c=[]
TB=html.xpath('//table[@id="trimArglist"]')
for i in list(trimParam[0]['SIP_T_CONF'].keys()):
tbname=TB[0].xpath('//table//tr[@id=\"'+i+'\"]//th[@class="th1"]')
for j in range(len(trimParam)):
if len(tbname)!=0:
if tbname[0].text.replace(' ','')=='\n':
tbname=TB[0].xpath('//tr[@id=\"'+i+'\"]//th[@class="th1"]//a')
c.append(tbname[0].text)
trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text] = trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'].pop(i)
try:
trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]=trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]['v']
except:
trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]=''; #车辆没有的配置数据不进行记录
if (trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]=='-') | (trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]==''): # 车辆配置里-代表车无此配置厂商也无法进行安装此配置
del trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][tbname[0].text]
else:
# 某些配置在js中没有参数进行赋值,发现是一些复写的参数比如已有长宽高的信息和参数值,但是存在名字为长的信息但没有赋值,因此不要
c.append(np.nan)
del trimParam[j]['SIP_T_CONF'][i] trimParam_dict={}
for i in range(len(trimParam)):
trimParam_dict[trimParam[i]['SIP_T_NAME']]=trimParam[i]; # 反推建立数据字典
if trimParam[0]['brandName'] not in df.keys():
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']]={}
if trimParam[0]['subbrandName'] not in df[trimParam[0]['brandName']].keys():
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']][trimParam[0]['modelName']]={}
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']][trimParam[0]['modelName']]['配置参数']=trimParam_dict ############################################## 销量数据 #################################################
vehicle_model_id= trimParam[0]['SIP_T_MODELID']
url='https://db.auto.sohu.com/cxdata/xml/sales/model/model'+str(vehicle_model_id)+'sales.xml'
req=requests.get(url)
wb_data=req.text #网页源码
sales=re.findall(r'(?<=<sales).*?(?=/>)',wb_data)
if len(sales)==0:
continue;
else:
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']][trimParam[0]['modelName']]['历史销量']={}
for i in sales:
df[trimParam[0]['brandName']][trimParam[0]['subbrandName']][trimParam[0]['modelName']]['历史销量'][re.findall(r'(?<=date=").*?(?=")',i)[0]]=int(re.findall(r'(?<=salesNum=").*?(?=")',i)[0])
print(trimParam[0]['subbrandName']+trimParam[0]['modelName']+'--num'+str(h.index(o))+'--total:'+str(len(h)))
至此整个字典就定义好了,最上层为品牌,其次是子品牌,然后是配置,最后分销量和配置信息。
接下来要么就已字典的格式利用pymongo存到mongodb里去,要么改成dataframe格式存入sql都可。 需要注意的是mongodb存入的过程中 字典key不可以出现" ."点的符号 因此需要替换。
给出一个替换函数供参考
# fix 字典内keys含有.并替换
def fix_dict(data, ignore_duplicate_key=True):
"""
Removes dots "." from keys, as mongo doesn't like that.
If the key is already there without the dot, the dot-value get's lost.
This modifies the existing dict! :param ignore_duplicate_key: True: if the replacement key is already in the dict, now the dot-key value will be ignored.
False: raise ValueError in that case.
"""
if isinstance(data, (list, tuple)):
list2 = list()
for e in data:
list2.append(fix_dict(e))
# end if
return list2
if isinstance(data, dict):
# end if
for key, value in data.items():
value = fix_dict(value)
old_key = key
if "." in key:
key = old_key.replace(".", "_")
if key not in data:
data[key] = value
else:
error_msg = "Dict key {key} containing a \".\" was ignored, as {replacement} already exists".format(
key=key_old, replacement=key)
if force:
import warnings
warnings.warn(error_msg, category=RuntimeWarning)
else:
raise ValueError(error_msg)
# end if
# end if
del data[old_key]
# end if
data[key] = value
# end for
return data
# end if
return data
# end def
df_2=fix_dict(df);
我这里做成一个首字母的key在品牌之前,然后按照pkl的格式保存到本地
#按照首字母检索的字典
for letter in range(65,91):
df2[chr(letter)]={}
for i in df.keys():
df2[lazy_pinyin(i)[0][0].upper()][i]=df[i] #本地文件保存
output = open('soho_vehicle.pkl', 'wb')
pickle.dump(df2, output)
output.close()
后续也可以再处理存到sql 并另存为csv或excel 用于查看。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pickle output = open('soho_vehicle.pkl', 'wb')
df=pickle.load(output)
output.close()
# 配置信息整理
a=[]
for o in df.keys():
for i in df[o].keys():
for j in df[o][i].keys():
for k in df[o][i][j]['配置参数'].keys():
df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_CONF']['子品牌']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['subbrandName']
df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_CONF']['品牌']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['brandName']
df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_CONF']['款式']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['modelName']
df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_CONF']['配置名称']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_NAME']
df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_CONF']['是否电动']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_C_ISELECTRIC']
a.append(pd.Series(df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['SIP_T_CONF'])) df_trim=pd.DataFrame(a) df_trim=df_trim.replace(np.nan,'---');
cols = list(df_trim)
for i in cols:
df_trim[i]=df_trim[i].str.strip();
df_trim[i]=df_trim[i].apply(lambda x:x.replace('m³','立方米'))
df_trim[i]=df_trim[i].apply(lambda x:x.replace('\xa0',' ')) #df_trim['配置名称']=df_trim['配置名称'].apply(lambda x:x.replace('m³','立方米'))
cols=list(pd.Series(cols).str.strip()); cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('保修政策')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('车联网:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('自动泊车入位')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('车身稳定控制')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('车载信息服务')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('车道保持辅助系统:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('车道偏离预警系统:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('倒车车侧预警系统:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('主动刹车/主动安全系统')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('中央差速器结构')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('底盘结构')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('转向助力')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('轮毂材料')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('进气形式:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('每缸气门数(个)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('气门结构')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('汽缸容积(cc)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('汽缸排列形式')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('最大马力(ps)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('最大扭矩(N·m/rpm)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('最大功率(kW/rpm)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('挡位个数')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('变速箱类型')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('变速箱')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('压缩比')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('发动机电子防盗')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('发动机型号')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('发动机启停技术')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('发动机')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('工信部油耗(L/100km)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('排放标准')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('供油方式')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('整车最大扭矩(N·m):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('整车最大功率(kW):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('轴距(mm)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('整备质量(kg)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('长x宽x高(mm)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('车体结构')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('官方最高车速(km/h)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('官方0-100加速(s)')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('快充时间(小时):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('快充电量(%):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('充电兼容性:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('充电方式:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电池种类:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电池容量(kWh):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电动机总功率(kW):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电动机总扭矩(N·m):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电动机总扭矩(N·m):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电机布局:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电机数:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('电机类型:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('上市时间')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('动力类型:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('驱动方式')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('补贴后售价:')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('4S店报价')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('厂商指导价')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('级别')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('百公里耗电量(kWh/100km):')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('是否电动')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('配置名称')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('款式')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('子品牌')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('品牌'))) df_trim = df_trim.ix[:, cols]
df_trim=df_trim.replace(np.nan,'---');
df_trim=df_trim.drop(['高度(mm)','长度(mm)','宽度(mm)'],axis=1)
df_trim=df_trim.drop(['车门数(个)','4S店报价'],axis=1)
df_trim.to_csv('soho_veh_trim_para.csv',encoding='gbk') #销量
a=[]
for o in df.keys():
for i in df[o].keys():
for j in df[o][i].keys():
try:
k=list(df[o][i][j]['配置参数'].keys())[0];
df[o][i][j]['销量']['子品牌']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['subbrandName']
df[o][i][j]['销量']['品牌']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['brandName']
df[o][i][j]['销量']['款式']=df[o][i][j]['配置参数'][k]['modelName']
a.append(pd.Series(df[o][i][j]['销量']))
except:
continue df_sales=pd.DataFrame(a) cols = list(df_sales)
cols.reverse()
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('款式')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('子品牌')))
cols.insert(0, cols.pop(cols.index('品牌')))
df_sales = df_sales.ix[:, cols]
df_sales=df_sales.fillna(0)
df_sales.to_csv('soho_veh_sales.csv',encoding='gbk') #存入 sql
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sqlalchemy.types import VARCHAR
host = '127.0.0.1'
port= 3306
db = 'soho_vehicle'
user = 'root'
password = 'twz1478963'
engine = create_engine(str(r"mysql+mysqldb://%s:" + '%s' + "@%s/%s?charset=utf8") % (user, password, host, db))
df_sales.to_sql('soho_veh_sales', con=engine, if_exists='append', index=False) #如量级过大使用chunksize
df_trim=df_trim.drop(['内饰可选颜色','车身可选颜色'],axis=1)
df_trim.to_sql('soho_veh_trim', con=engine, if_exists='append', index=False) #如量级过大使用chunksize

欢迎交流!
爬虫获取搜狐汽车的配置信息 和swf动态图表的销量数据-------详细教学的更多相关文章
- C/C++通过WMI和系统API函数获取获取系统硬件配置信息
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/renyuan/archive/2012/12/29/2838716.html 转载:http://blog.csdn.net/jhqin/arti ...
- C#程序中获取电脑硬件配置信息的一种方法
本文介绍获取cpu信息和内存信息的方法,根据本文所举例的代码可以举一反三获取更多信息. 获取cpu名称的方法: public string GetCpuInfo() { ManagementObjec ...
- System.getProperty()获取系统的配置信息
原文地址:http://www.jsjtt.com/java/Javajichu/105.html 此处记录备用. 1. 通过System.getProperty()可以获取系统的配置信息,Syste ...
- System.getProperty()获取系统的配置信息(系统变量)
原文地址:http://www.jsjtt.com/java/Javajichu/105.html 此处记录备用. 1. 通过System.getProperty()可以获取系统的配置信息,Syste ...
- JAVA 获取jdbc.properties配置信息
Properties myProperty = new Properties();String jdbcPath = PathKit.getWebRootPath()+File.separator+& ...
- SpringBoot配置分析、获取到SpringBoot配置文件信息以及几种获取配置文件信息的方式
Spring入门篇:https://www.cnblogs.com/biehongli/p/10170241.html SpringBoot的默认的配置文件application.properties ...
- 教你如何利用分布式的思想处理集群的参数配置信息——spring的configurer妙用
引言 最近LZ的技术博文数量直线下降,实在是非常抱歉,之前LZ曾信誓旦旦的说一定要把<深入理解计算机系统>写完,现在看来,LZ似乎是在打自己脸了.尽管LZ内心一直没放弃,但从现状来看,需要 ...
- ASP.NET MVC 学习笔记-7.自定义配置信息(后续)
自定义配置信息的高级应用 通过上篇博文对简单的自定义配置信息的学习,使得更加灵活的控制系统配置信息.实际项目中,这种配置的灵活度往往无法满足项目的灵活度和扩展性. 比如,一个配置信息有三部分组成,而每 ...
- 应用SharedPreference保存程序的配置信息
SharedPreference: 1.用来保存应用程序的配置信息的XML文件,内部的数据形式为键值对 2.一般存在于/data/data/<包名>shared_prefs目录下 3.该对 ...
随机推荐
- python模块之:paramiko
1. 介绍: paramiko是一个用于做远程控制的模块,使用该模块可以对远程服务器进行命令或文件操作,值得一说的是,fabric和ansible内部的远程管理就是使用的paramiko来实现.安装: ...
- Fiddler如何自动修改请求和响应包
Charles的Map功能可以将某个请求进行重定向,用重定向的内容响应请求的内容.这个功能非常方便.在抓包过程当中,有时候为了调试方便,需要将线上的服务定位到内网.比如我们线上的服务器域名为 api. ...
- 设计模式-桥接模式(Bridge)
桥接模式是构造型模式之一.把抽象(Abstraction)与行为实现(Implementor)分离开来,从而可以保持各部分的独立性以及应对它们的功能扩展. 角色和职责: 1.抽象类(Abstracti ...
- 001-python3 初识
一.python的起源 python是一门 解释型弱类型编程语言. 特点: 简单.明确.优雅 二.python的解释器 CPython. 官方提供的. 内部使用c语言来实现 PyPy. 一次性把我们的 ...
- HDU 4283:You Are the One(区间DP)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4283 题意:有n个数字,不操作的情况下从左到右按顺序输出,但是可以先让前面的数字进栈,让后面的数字输出,然后栈里 ...
- CSU 1508:地图的四着色(DFS+剪枝)
http://acm.csu.edu.cn/OnlineJudge/problem.php?id=1508 题意:地图中四联通的块是一个国家,A和B每个人可以涂两种颜色,且B不能涂超过5次,相邻的国家 ...
- 关于红黑树(R-B tree)原理,看这篇如何
学过数据数据结构都知道二叉树的概念,而又有多种比较常见的二叉树类型,比如完全二叉树.满二叉树.二叉搜索树.均衡二叉树.完美二叉树等:今天我们要说的红黑树就是就是一颗非严格均衡的二叉树,均衡二叉树又是在 ...
- 从后端到前端之Vue(二)写个tab试试水
上一篇写了一下table,然后要写什么呢?当然是tab了.动态创建一个tab,里面放一个table,这样一个后台管理的基本功能(之一)就出来了. 好吧,这里其实只是试试水,感受一下vue的数据驱动可以 ...
- 【题解】【A % B Problem(P1865)】-C++
题目背景 题目名称是吸引你点进来的 实际上该题还是很水的 题目描述 区间质数个数 输入输出格式 输入格式: 一行两个整数 询问次数n,范围m 接下来n行,每行两个整数 l,r 表示区间 输出格式: 对 ...
- 理解 Spring 定时任务的 fixedRate 和 fixedDelay 的区别
用过 Spring 的 @EnableScheduling 的都知道,有三种方式,即 @Scheduled 注解的 fixedRate(fixedRateString), fixedDelay(fix ...
