记录下这周的mysql调优工作
这周一至周四基本都在做mysql的测试和调优工作,包括erlang端对mysql的写入测试,到今天为止暂且告一段落,下周先做下其他的开发。
测试环境
使用的测试环境是aliyun的杭州节点,
CPU:8核
内存:8GB
带宽:5MB
数据盘:100GB
Erlang版本:OTP18
mysql版本:mysql 5.7.11
测试工具:sysbench,mysqlslap
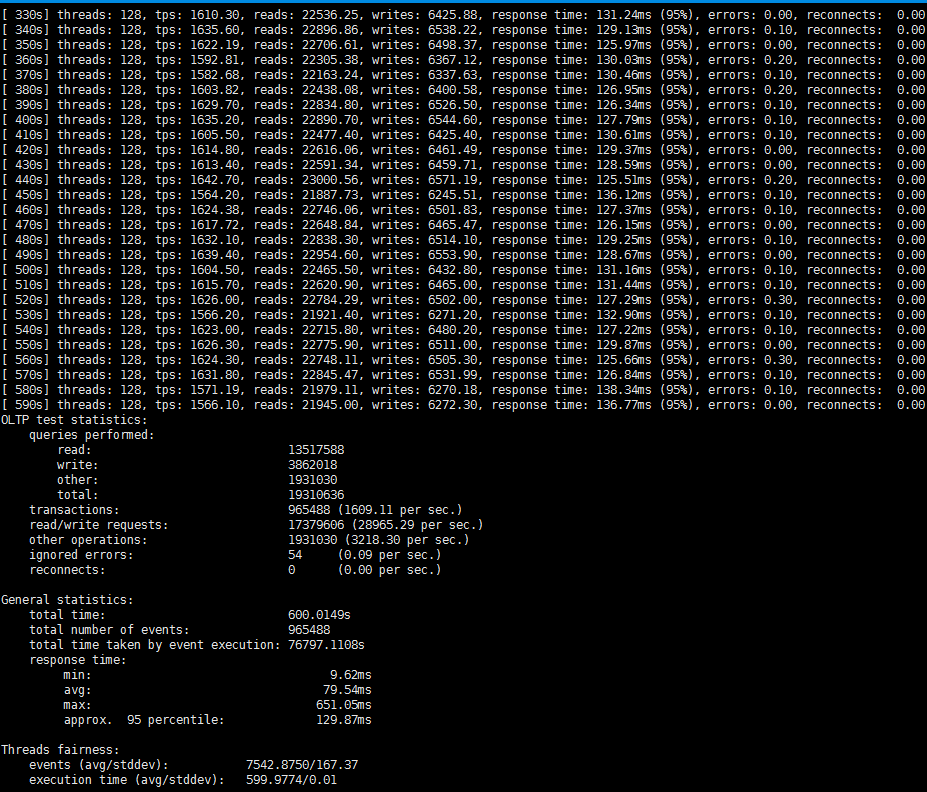
Sysbench部分测试:
prepare的语句:
./sysbench --test=/root/sysbench/tests/db/oltp.lua --oltp_tables_count=10 --oltp-table-size=800000 --db-driver=mysql --mysql-socket=/data/mysql/mysql.sock --mysql-user=自己的用户名 --mysql-password='自己的密码' --mysql-db=test_qps prepare
run的语句:
./sysbench --test=/root/sysbench/tests/db/oltp.lua --oltp_tables_count=10 --oltp-table-size=800000 --oltp-read-only=off --max-requests=0 --num-threads=128 --oltp-dist-type=uniform --max-time=600 --report-interval=10 --db-driver=mysql --mysql-socket=/data/mysql/mysql.sock --mysql-user=自己的用户名 --mysql-password='自己的密码' --mysql-db=test_qps run > test_result.log
mysqlslap的简单测试
测试表的sql:
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL default '', `name` varchar(250) default NULL, `password` varchar(250) default NULL, `last_login_time` int(11) NOT NULL default '', PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;

总感觉我不太会用mysqlslap,这样测试的结果有不少问题。还是倾向于用sysbench进行测试。
Erlang写的测试代码,用于测试emysql效率:
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
%%% @author Administrator
%%% @copyright (C) 2016, <COMPANY>
%%% @doc
%%%
%%% @end
%%% Created : 14. 四月 2016 16:28
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
-module(multi_thread_test).
-author("Administrator").
%% API
-export([start/2,run/3,run_sql/2,recv/1]).
-record(state,{running=0,start_time,total_count_all,sql_count_each_process}).
%% 启动ProcessCount个进程,每个进程执行SqlCountEachProcess次sql 操作
start(TotalCount,SqlCountEachProcess)->
emysql:execute(default,<<"delete from account">>),
CurrentTime=time_utility:longunixtime(),
spawn_link(?MODULE,run,[TotalCount,SqlCountEachProcess,#state{start_time=CurrentTime,
total_count_all=TotalCount,
sql_count_each_process=SqlCountEachProcess}]).
recv(#state{running=0,start_time=StartTime, total_count_all=ProcessCount, sql_count_each_process=SqlCountEachProcess})->
CurrentTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
Usedtime = CurrentTime-StartTime,
io:format("process_count:~p sql count each process:~p used time:~p~n",[ProcessCount,SqlCountEachProcess,Usedtime]);
recv(#state{running=Running}=State)->
receive
done->
recv(State#state{running=Running-1})
end.
run(0,_SqlCountEachProcess,#state{}=State)->
recv(State);
run(TotalCount,SqlCountEachProcess,#state{running=Running}=State) when (TotalCount>0) ->
Parent =self(),
spawn(fun()-> run_sql(SqlCountEachProcess,Parent)end),
run(TotalCount-SqlCountEachProcess,SqlCountEachProcess,State#state{running=Running+1}).
run_sql(0,Parent)->
Parent!done;
run_sql(SqlCountEachProcess,Parent) ->
L = lists:seq(1,SqlCountEachProcess),
[test2() || _<-L],
run_sql(SqlCountEachProcess-SqlCountEachProcess ,Parent).
test_prepare()->
Rand = util:rand(1,10000),
emysql:execute(default,account_replace,[Rand]).
test1()->
Rand = util:rand(1,10000),
Sql = io_lib:format(<<"REPLACE INTO account(id) values (~p)">>,[Rand]).
test2()->
emysql:execute(default,<<"REPLACE INTO account(id) values (floor(RAND()*10000));">>).
运行结果:

是mysqlslap效率的二分之一。
本周测试用的部分代码:
game_db_writer.erl
这个文件实现的是一个队列性质的mysql写入器,做的操作是redis队列中取需要写入的sql,然后一条条的写入mysql
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
%%% @author 李世铭
%%% @copyright (C) April 1st,2016, <COMPANY>
%%% @doc
%%% 负责redis->mysql同步的写线程
%%% @end
%%% Created : 01. 四月 2016 15:02
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
-module(game_db_writer).
-author("Administrator"). -behaviour(gen_fsm).
-include("db_config.hrl").
-include("error_log.hrl").
-include("config_keys.hrl"). %% API
-export([start_link/0]). -export([write_sql/0]). %% gen_fsm callbacks
-export([init/1,
writing/2,
writing/3,
handle_event/3,
handle_sync_event/4,
handle_info/3,
terminate/3,
code_change/4]). -define(SERVER, ?MODULE).
-define(MAX_PACKET,4096).%%mysql5.6默认允许的最大的包上限
-define(TIMEOUT_SPAN, 1000).%%休眠间隔
-define(ZERO_SPAN,0).%%立即执行 -record(state, {try_times=0}).%%重试次数 %%%===================================================================
%%% API
%%%===================================================================
%%写一条sql语句
write_sql()->
StartTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Start Writing Time is ~p!~n",[StartTime]),
gen_fsm:send_event(?MODULE,{write_a_sql}). %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @doc
%% Creates a gen_fsm process which calls Module:init/1 to
%% initialize. To ensure a synchronized start-up procedure, this
%% function does not return until Module:init/1 has returned.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(start_link() -> {ok, pid()} | ignore | {error, Reason :: term()}).
start_link() ->
gen_fsm:start_link({local, ?SERVER}, ?MODULE, [], []). %%%===================================================================
%%% gen_fsm callbacks
%%%=================================================================== %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Whenever a gen_fsm is started using gen_fsm:start/[3,4] or
%% gen_fsm:start_link/[3,4], this function is called by the new
%% process to initialize.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(init(Args :: term()) ->
{ok, StateName :: atom(), StateData :: #state{}} |
{ok, StateName :: atom(), StateData :: #state{}, timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term()} | ignore).
init([]) ->
io:format("db_writer is ready!~n"),
{ok, writing, #state{},?ZERO_SPAN}.
%%{ok,writing,#state{}}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% There should be one instance of this function for each possible
%% state name. Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:send_event/2, the instance of this function with the same
%% name as the current state name StateName is called to handle
%% the event. It is also called if a timeout occurs.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(writing(Event :: term(), State :: #state{}) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{}} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), NewState :: #state{}}).
writing(timeout,State)->
do_write(State);
writing(_Event, State) ->
do_write(State). %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% There should be one instance of this function for each possible
%% state name. Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:sync_send_event/[2,3], the instance of this function with
%% the same name as the current state name StateName is called to
%% handle the event.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(writing(Event :: term(), From :: {pid(), term()},
State :: #state{}) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{}} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{reply, Reply, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{}} |
{reply, Reply, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: normal | term(), NewState :: #state{}} |
{stop, Reason :: normal | term(), Reply :: term(),
NewState :: #state{}}).
writing(_Event, _From, State) ->
Reply = ok,
{reply, Reply, writing, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:send_all_state_event/2, this function is called to handle
%% the event.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(handle_event(Event :: term(), StateName :: atom(),
StateData :: #state{}) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: #state{}} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), NewStateData :: #state{}}).
handle_event(_Event, StateName, State) ->
{next_state, StateName, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:sync_send_all_state_event/[2,3], this function is called
%% to handle the event.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(handle_sync_event(Event :: term(), From :: {pid(), Tag :: term()},
StateName :: atom(), StateData :: term()) ->
{reply, Reply :: term(), NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{reply, Reply :: term(), NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term(),
timeout() | hibernate} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term(),
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), Reply :: term(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), NewStateData :: term()}).
handle_sync_event(_Event, _From, StateName, State) ->
Reply = ok,
{reply, Reply, StateName, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% This function is called by a gen_fsm when it receives any
%% message other than a synchronous or asynchronous event
%% (or a system message).
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(handle_info(Info :: term(), StateName :: atom(),
StateData :: term()) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term(),
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: normal | term(), NewStateData :: term()}).
handle_info(_Info, StateName, State) ->
{next_state, StateName, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% This function is called by a gen_fsm when it is about to
%% terminate. It should be the opposite of Module:init/1 and do any
%% necessary cleaning up. When it returns, the gen_fsm terminates with
%% Reason. The return value is ignored.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(terminate(Reason :: normal | shutdown | {shutdown, term()}
| term(), StateName :: atom(), StateData :: term()) -> term()).
terminate(_Reason, _StateName, _State) ->
ok. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Convert process state when code is changed
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(code_change(OldVsn :: term() | {down, term()}, StateName :: atom(),
StateData :: #state{}, Extra :: term()) ->
{ok, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: #state{}}).
code_change(_OldVsn, StateName, State, _Extra) ->
{ok, StateName, State}. %%%===================================================================
%%% Internal functions
%%%===================================================================
%%进行实际的写操作
do_write(State)->
case State#state.try_times>0 of
true->
%%说明上次的消息未写入成功,从中转区取消息
Result = redis:get(?CURR_WRITING_MSG),
case Result of
{ok,SzMsg} ->
Msg = db_utility:unpack_data(SzMsg);
_->
{ok,Msg} = game_db_queue:dequeue(?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST),
?LOG_ERROR("REDIS SYSTEM ERROR!!!Cannot load Msg from game_frame:mysql_writing_msg")
end;
_->
{ok,Msg} = game_db_queue:dequeue(?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST)
end,
case Msg of
%%队列已空
undefined->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("end writing test time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime}]),
{next_state,writing,#state{},?TIMEOUT_SPAN};
_->
do_write(Msg,State)
end. do_write(Msg,State)->
%%先将取出来的消息存入中转区
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG,db_utility:pack_data(Msg)),
IsPrepare = Msg#db_queue_msg.prepare,
case IsPrepare of
true->
%%如果预编译过
SqlId = Msg#db_queue_msg.prepare_atom,
SqlArgs = Msg#db_queue_msg.prepare_param,
PoolId = Msg#db_queue_msg.poolid,
Result = mysql:run_prepare(PoolId,SqlId,SqlArgs);
_->
%%如果没有
PoolId = Msg#db_queue_msg.poolid,
Sql = Msg#db_queue_msg.sql,
Result = mysql:execute(PoolId,Sql)
end,
case Result of
{ok,_}->
%%写入成功后标记数据过期时间
Redis_expir_time = game_config:lookup_keys([?CF_DB_QUEUE, <<"redis_expir_time">>]),
redis:expire(Msg#db_queue_msg.redis_key, integer_to_list(util:floor(3600 * Redis_expir_time))),
%%然后中转区标记为<<"successful">>,表示写成功
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG,<<"successful">>),
{next_state,writing,#state{},?ZERO_SPAN};
_->
RetryTimes = State#state.try_times,
case RetryTimes>=?MAX_MYSQL_RETRY_TIME of
true->
%% 如果写代码次数超过上限
%% 单独写一个log,方便查找log
?LOG_ERROR("Max MySQL retry times reached, Msg is: ~p",
[[Msg]]),
{next_state,writing,#state{},?ZERO_SPAN};
_->
{next_state,writing,#state{try_times=RetryTimes + 1},?ZERO_SPAN}
end
end.
game_db_writer2:
这个文件是上面那个文件的升级版,区别是一次性取一定数量(宏定义现在是100)的sql语句,自行进行sql拼接一次性写入,写入失败的语句会重新拼接进行写入,效率比上面那种方法能提高不少,但是如果多个mysql节点的话处理起来会比较麻烦
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
%%% @author 李世铭
%%% @copyright (C) April 1st,2016, <COMPANY>
%%% @doc
%%% 负责redis->mysql同步的写线程
%%% @end
%%% Created : 01. 四月 2016 15:02
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
-module(game_db_writer2).
-author("Administrator"). -behaviour(gen_fsm).
-include("db_config.hrl").
-include("error_log.hrl").
-include("config_keys.hrl"). %% API
-export([start_link/0]). -export([write_sql/0]). %% gen_fsm callbacks
-export([init/1,
writing/2,
writing/3,
handle_event/3,
handle_sync_event/4,
handle_info/3,
terminate/3,
code_change/4]). -define(SERVER, ?MODULE).
-define(MAX_PACKET,4096).%%mysql5.6默认允许的最大的包上限
-define(TIMEOUT_SPAN, 1000).%%休眠间隔
-define(ZERO_SPAN,0).%%立即执行 -record(state, {try_times=0}).%%重试次数 %%%===================================================================
%%% API
%%%===================================================================
%%写一条sql语句
write_sql()->
StartTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Start Writing Time is ~p!~n",[StartTime]),
gen_fsm:send_event(?MODULE,{write_a_sql}). %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @doc
%% Creates a gen_fsm process which calls Module:init/1 to
%% initialize. To ensure a synchronized start-up procedure, this
%% function does not return until Module:init/1 has returned.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(start_link() -> {ok, pid()} | ignore | {error, Reason :: term()}).
start_link() ->
gen_fsm:start_link({local, ?SERVER}, ?MODULE, [], []). %%%===================================================================
%%% gen_fsm callbacks
%%%=================================================================== %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Whenever a gen_fsm is started using gen_fsm:start/[3,4] or
%% gen_fsm:start_link/[3,4], this function is called by the new
%% process to initialize.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(init(Args :: term()) ->
{ok, StateName :: atom(), StateData :: #state{}} |
{ok, StateName :: atom(), StateData :: #state{}, timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term()} | ignore).
init([]) ->
io:format("db_writer is ready!~n"),
{ok, writing, #state{},?ZERO_SPAN}.
%%{ok,writing,#state{}}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% There should be one instance of this function for each possible
%% state name. Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:send_event/2, the instance of this function with the same
%% name as the current state name StateName is called to handle
%% the event. It is also called if a timeout occurs.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(writing(Event :: term(), State :: #state{}) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{}} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), NewState :: #state{}}).
writing(timeout,State)->
do_write(State);
writing(_Event, State) ->
do_write(State). %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% There should be one instance of this function for each possible
%% state name. Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:sync_send_event/[2,3], the instance of this function with
%% the same name as the current state name StateName is called to
%% handle the event.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(writing(Event :: term(), From :: {pid(), term()},
State :: #state{}) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{}} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{reply, Reply, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{}} |
{reply, Reply, NextStateName :: atom(), NextState :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: normal | term(), NewState :: #state{}} |
{stop, Reason :: normal | term(), Reply :: term(),
NewState :: #state{}}).
writing(_Event, _From, State) ->
Reply = ok,
{reply, Reply, writing, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:send_all_state_event/2, this function is called to handle
%% the event.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(handle_event(Event :: term(), StateName :: atom(),
StateData :: #state{}) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: #state{}} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: #state{},
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), NewStateData :: #state{}}).
handle_event(_Event, StateName, State) ->
{next_state, StateName, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Whenever a gen_fsm receives an event sent using
%% gen_fsm:sync_send_all_state_event/[2,3], this function is called
%% to handle the event.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(handle_sync_event(Event :: term(), From :: {pid(), Tag :: term()},
StateName :: atom(), StateData :: term()) ->
{reply, Reply :: term(), NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{reply, Reply :: term(), NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term(),
timeout() | hibernate} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term(),
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), Reply :: term(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{stop, Reason :: term(), NewStateData :: term()}).
handle_sync_event(_Event, _From, StateName, State) ->
Reply = ok,
{reply, Reply, StateName, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% This function is called by a gen_fsm when it receives any
%% message other than a synchronous or asynchronous event
%% (or a system message).
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(handle_info(Info :: term(), StateName :: atom(),
StateData :: term()) ->
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term()} |
{next_state, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: term(),
timeout() | hibernate} |
{stop, Reason :: normal | term(), NewStateData :: term()}).
handle_info(_Info, StateName, State) ->
{next_state, StateName, State}. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% This function is called by a gen_fsm when it is about to
%% terminate. It should be the opposite of Module:init/1 and do any
%% necessary cleaning up. When it returns, the gen_fsm terminates with
%% Reason. The return value is ignored.
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(terminate(Reason :: normal | shutdown | {shutdown, term()}
| term(), StateName :: atom(), StateData :: term()) -> term()).
terminate(_Reason, _StateName, _State) ->
ok. %%--------------------------------------------------------------------
%% @private
%% @doc
%% Convert process state when code is changed
%%
%% @end
%%--------------------------------------------------------------------
-spec(code_change(OldVsn :: term() | {down, term()}, StateName :: atom(),
StateData :: #state{}, Extra :: term()) ->
{ok, NextStateName :: atom(), NewStateData :: #state{}}).
code_change(_OldVsn, StateName, State, _Extra) ->
{ok, StateName, State}. %%%===================================================================
%%% Internal functions
%%%===================================================================
%%进行实际的写操作
do_write(State)->
case State#state.try_times>0 of
true->
%%说明上次的消息未写入成功,从中转区取消息
Result = redis:get(?CURR_WRITING_MSG_MULT),
case Result of
{ok,SzMsg} ->
MsgList = db_utility:unpack_data(SzMsg);
_->
{ok,MsgList} = game_db_queue:dequeue(?MYSQL_MULTI_WRITE_NUM,?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST_MULT),
?LOG_ERROR("REDIS SYSTEM ERROR!!!Cannot load Msg from game_frame:mysql_writing_msg")
end;
_->
{ok,MsgList} = game_db_queue:dequeue(?MYSQL_MULTI_WRITE_NUM,?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST_MULT)
end,
case MsgList of
%%队列已空
[]->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("end writing test time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime}]),
{next_state,writing,#state{},?TIMEOUT_SPAN};
_->
do_write(MsgList,State)
end. do_write(MsgList,State)->
%%先将取出来的消息存入中转区
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG_MULT,db_utility:pack_data(MsgList)),
F = fun(X,{_,FinalSql})->
Sql = X#db_queue_msg.sql,
PoolId = X#db_queue_msg.poolid,
%%之所以逆序是因为取出来的时候逆序存放
{PoolId,<<Sql/binary,";",FinalSql/binary>>}
end,
{PoolId,Sql} = lists:foldr(F,{default,<<>>},MsgList),
Result = emysql:execute(PoolId,Sql),
Result1 = lists:zip(MsgList,Result),
F1 = fun({Msg,ETM}, Res) ->
case ETM of
{ok_packet,_,_,NID,_,_,_}->
Res;
{result_packet,_,_,RS,_} ->
Res;
{error_packet,_,_,_,DB_ERROR_MSG} ->
Res ++ [Msg]
end
end,
if
is_list(Result)->
LeftMsgList = lists:foldl(F1, [], Result1);
true->
LeftMsgList = lists:foldl(F1, [], [Result1])
end,
case LeftMsgList of
[]->
%%写入成功后标记数据过期时间
Redis_expir_time = game_config:lookup_keys([?CF_DB_QUEUE, <<"redis_expir_time">>]),
[redis:expire(Msg#db_queue_msg.redis_key, integer_to_list(util:floor(3600 * Redis_expir_time))) || Msg<-MsgList],
%%然后中转区标记为<<"successful">>,表示写成功
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG_MULT,<<"successful">>),
{next_state,writing,#state{},?ZERO_SPAN};
_->
RetryTimes = State#state.try_times,
case RetryTimes>=?MAX_MYSQL_RETRY_TIME of
true->
%% 如果写代码次数超过上限
%% 单独写一个log,方便查找log
?LOG_ERROR("Max MySQL retry times reached, Msg is: ~p",
[[MsgList]]),
{next_state,writing,#state{},?ZERO_SPAN};
_->
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG_MULT,LeftMsgList),
{next_state,writing,#state{try_times=RetryTimes + 1},?ZERO_SPAN}
end
end.
game_db_writer3:
这个放弃了状态机的方式,之前我对前两种的效率很不满意,怀疑是gen_fsm内部的超时机制消耗了大量的事情,才写了这个非otp的写入,但经测试发现,otp内部消耗的时间基本可以忽略不计。
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
%%% @author Administrator
%%% @copyright (C) 2016, <COMPANY>
%%% @doc
%%%
%%% @end
%%% Created : 14. 四月 2016 11:13
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
-module(game_db_writer3).
-author("Administrator").
-include("db_config.hrl").
-include("error_log.hrl").
-include("config_keys.hrl"). %% API
-export([write_sql/0]). write_sql()->
StartTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Start Writing Time is ~p!~n",[StartTime]),
do_write(0),
ok. %%进行实际的写操作
do_write(TryTimes)->
case TryTimes>0 of
true->
%%说明上次的消息未写入成功,从中转区取消息
Result = redis:get(?CURR_WRITING_MSG),
case Result of
{ok,SzMsg} ->
Msg = db_utility:unpack_data(SzMsg);
_->
{ok,Msg} = game_db_queue:dequeue(?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST),
?LOG_ERROR("REDIS SYSTEM ERROR!!!Cannot load Msg from game_frame:mysql_writing_msg")
end;
_->
{ok,Msg} = game_db_queue:dequeue(?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST)
end,
case Msg of
%%队列已空
undefined->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("end writing test time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime}]),
timer:sleep(1000);
%%do_write(0);
_->
do_write(Msg,TryTimes)
end. do_write(Msg,TryTimes)->
%%先将取出来的消息存入中转区
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG,db_utility:pack_data(Msg)),
IsPrepare = Msg#db_queue_msg.prepare,
case IsPrepare of
true->
%%如果预编译过
SqlId = Msg#db_queue_msg.prepare_atom,
SqlArgs = Msg#db_queue_msg.prepare_param,
PoolId = Msg#db_queue_msg.poolid,
Result = mysql:run_prepare(PoolId,SqlId,SqlArgs);
_->
%%如果没有
PoolId = Msg#db_queue_msg.poolid,
Sql = Msg#db_queue_msg.sql,
Result = mysql:execute(PoolId,Sql)
end,
case Result of
{ok,_}->
%%写入成功后标记数据过期时间
Redis_expir_time = game_config:lookup_keys([?CF_DB_QUEUE, <<"redis_expir_time">>]),
redis:expire(Msg#db_queue_msg.redis_key, integer_to_list(util:floor(3600 * Redis_expir_time))),
%%然后中转区标记为<<"successful">>,表示写成功
redis:set(?CURR_WRITING_MSG,<<"successful">>),
do_write(0);
_->
case TryTimes>=?MAX_MYSQL_RETRY_TIME of
true->
%% 如果写代码次数超过上限
%% 单独写一个log,方便查找log
?LOG_ERROR("Max MySQL retry times reached, Msg is: ~p",
[[Msg]]),
do_write(0);
_->
do_write(Msg,TryTimes+1)
end
end.
db_test.erl
这个主要是配合进行压测的erl,包括简单的单线程sql效率测试
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
%%% @author 李世铭
%%% @copyright (C) 2016, <COMPANY>
%%% @doc
%%% 测试数据库各种写方法的效率
%%% @end
%%% Created : 05. 四月 2016 16:48
%%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
-module(db_test).
-author("Administrator").
-include("db_config.hrl"). %% API
-export([test_db_multi_write/1,test_prepare_write/1,test_directly_write/1]).
-export([test_directly_select/1,test_prepare_select/1]).
-export([test_db_write/1,test_db_write_single/1]).
-export([test_eprof_start/0,test_eprof_end/0]). test_db_multi_write(N)->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(), L = lists:seq(1,N),
F = fun(X,Res)->
Rand = util:rand(1,1000000),
Sql = mysql:make_insert_sql(account,["id"],[Rand]),
SzSql = list_to_binary(Sql),
case Res==<<"">> of
true->
SzSql;
_->
<<Res/binary,";",SzSql/binary>>
end
end,
FinalSql = lists:foldl(F,<<>>,L),
Result = emysql:execute(default,FinalSql),
EndTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Cost time is:~w~n",[{EndTime - CurrTime}]). test_prepare_write(N)->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
L = lists:seq(1,N),
F = fun(X)->
Rand = util:rand(1,10000),
emysql:execute(default,account_replace,[Rand])
end,
[F(X) || X<-L],
EndTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Cost time is:~w~n",[{EndTime - CurrTime}]). test_directly_write(N)->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
L = lists:seq(1,N),
F = fun(X)->
Rand = util:rand(1,10000),
Sql = mysql:make_replace_sql(account,["id"],[Rand]),
emysql:execute(default,Sql)
end,
[F(X) || X<-L],
EndTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Cost time is:~w~n",[{EndTime - CurrTime}]). test_directly_select(N)->
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
L = lists:seq(1,N),
F = fun(X)->
Sql = io_lib:format(<<"select * from account where id=~p">>,[X]),
emysql:execute(default,Sql)
end,
[F(X) || X<-L],
EndTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Cost time is:~w~n",[{EndTime - CurrTime}]). test_prepare_select(N)->
emysql:prepare(account_select,"select * from account where id=?"),
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
L = lists:seq(1,N),
F = fun(X)->
emysql:execute(default,account_select,[X])
end,
[F(X) || X<-L],
EndTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("Cost time is:~w~n",[{EndTime - CurrTime}]). test_db_write()->
Rand = util:rand(1,100000),
Sql = mysql:make_replace_sql(account,["id"],[Rand]),
SzSql = conversion_utility:to_binary(Sql),
State = #db_queue_msg{redis_key = <<"TEST_HINCR">>,sql = SzSql},
%%State = #db_queue_msg{redis_key = <<"TEST_HINCR">>,prepare = true,prepare_atom = account_replace,prepare_param = [Rand]},
game_db_queue:enqueue(State,?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST_MULT). test_db_write(N)->
test_eprof_start(),
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("enqueue start time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime}]),
L = lists:seq(1,N),
[test_db_write() || X<-L],
CurrTime1 = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("enqueue end time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime1}]),
test_eprof_end(),
ok. test_db_write_single()->
Rand = util:rand(1,100000),
Sql = mysql:make_replace_sql(account,["id"],[Rand]),
SzSql = conversion_utility:to_binary(Sql),
State = #db_queue_msg{redis_key = <<"TEST_HINCR">>,sql = SzSql},
%%State = #db_queue_msg{redis_key = <<"TEST_HINCR">>,prepare = true,prepare_atom = account_replace,prepare_param = [Rand]},
game_db_queue:enqueue(State,?MYSQL_WRITE_LIST). test_db_write_single(N)->
test_eprof_start(),
CurrTime = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("enqueue start time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime}]),
L = lists:seq(1,N),
[test_db_write_single() || X<-L],
CurrTime1 = time_utility:longunixtime(),
io:format("enqueue end time is:~w~n",[{CurrTime1}]),
test_eprof_end(),
ok. test_eprof_start()->
eprof:start(),
eprof:start_profiling([self()]). test_eprof_end()->
eprof:stop_profiling(),
eprof:log(test_match),
eprof:analyze(),
eprof:stop().
个人感觉:
1.队列方式进行写入的时候无法充分的利用cpu,因为队列必然是单线程,800%CPU只能使用50%的时候mysql的效率一定不高。
2.批量写入并不见得一定好用,会带来很多其它的问题,如果不是特殊需求,没必要非得批量写入。
3.尽量购买rdb而不是自己搭建mysql服务器,20倍的iops差距真的很坑。
最后附上我自己测试用的my.cnf
# For advice on how to change settings please see
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
# *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the
# *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you
# *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL.
[mysqld] # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data
# cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%. # Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging
# changes to the binary log between backups. # These are commonly set, remove the # and set as required.
basedir = /usr
datadir = /data/mysql
socket = /data/mysql/mysql.sock
pid-file = /data/mysql/mysql_pidfile.pid
log-error = /data/mysql/mysql_errorlog.err
# port = .....
server_id = 1
# socket = ..... # Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers.
# The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs.
# Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values.
# join_buffer_size = 128M
# sort_buffer_size = 2M
# read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M log_bin = /data/binlog/mysql_binlog
sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES max_connections=4000
key_buffer_size=200M
low_priority_updates=1
table_open_cache = 8000
back_log=1500
query_cache_type=0
query_cache_limit = 1M
query_cache_size=256M
table_open_cache_instances=16 # files
innodb_file_per_table = ON
innodb_log_file_size=1024M
innodb_log_files_in_group = 3
innodb_open_files=4000 # buffers
innodb_buffer_pool_size=4096M
innodb_buffer_pool_instances=32
innodb_log_buffer_size=64M
join_buffer_size=32K
sort_buffer_size=32K # innodb
innodb_checksums=0
innodb_doublewrite=0
innodb_support_xa=0
innodb_thread_concurrency=0
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=2
innodb_max_dirty_pages_pct=50
innodb_use_native_aio=1
innodb_stats_persistent = 1 # perf special
innodb_adaptive_flushing = 1
innodb_flush_neighbors = 0
innodb_read_io_threads = 4
innodb_write_io_threads = 4
innodb_io_capacity = 4000
innodb_purge_threads=1
innodb_adaptive_hash_index=0 # monitoring
innodb_monitor_enable = '%'
performance_schema=OFF
记录下这周的mysql调优工作的更多相关文章
- mysql调优 基础
MySQL调优可以从几个方面来做: 1. 架构层:做从库,实现读写分离: 2.系统层次:增加内存:给磁盘做raid0或者raid5以增加磁盘的读写速度:可以重新挂载磁盘,并加上noatime参数,这样 ...
- 数据库MySQL调优实战经验总结<转>
数据库MySQL调优实战经验总结 MySQL 数据库的使用是非常的广泛,稳定性和安全性也非常好,经历了无数大小公司的验证.仅能够安装使用是远远不够的,MySQL 在使用中需要进行不断的调整参数或优化设 ...
- MySQL 调优/优化的 100 个建议
MySQL 调优/优化的 100 个建议 MySQL是一个强大的开源数据库.随着MySQL上的应用越来越多,MySQL逐渐遇到了瓶颈.这里提供 101 条优化 MySQL 的建议.有些技巧适合特定 ...
- MySQL调优系列基础篇
前言 有一段时间没有写博客了,整天都在忙,上班,录制课程,恰巧最近一段时间比较清闲,打算弄弄MYSQL数据库. 关于MySQL数据库,这里就不做过多的介绍,开源.免费等特性深受各个互联网行业喜爱,尤其 ...
- MySQL调优 —— Using temporary
DBA发来一个线上慢查询问题. SQL例如以下(为突出重点省略部分内容): select distinct article0_.id, 等字段 from article_table article ...
- MySQL调优 优化需要考虑哪些方面
MySQL调优 优化需要考虑哪些方面 优化目标与方向定位 总体目标:使得响应时间更快,吞吐量更大. (throughout --- 吞吐量:单位时间内处理事务的数量) 如何找到需要优化的地方 使用 ...
- MySQL 调优基础(一) CPU与进程
一般而言,MySQL 的调优可以分为两个层面,一个是在MySQL层面上进行的调优,比如SQL改写,索引的添加,MySQL各种参数的配置:另一个层面是从操作系统的层面和硬件的层面来进行调优.操作系统的层 ...
- mysql调优最大连接数
一.mysql调优 1.1 报错: Mysql: error 1040: Too many connections 1.2 原因: 1.访问量过高,MySQL服务器抗不住,这个时候就要考虑增加从服务器 ...
- 面试官问我MySQL调优,我真的是
面试官:要不你来讲讲你们对MySQL是怎么调优的? 候选者:哇,这命题很大阿...我认为,对于开发者而言,对MySQL的调优重点一般是在「开发规范」.「数据库索引」又或者说解决线上慢查询上. 候选者: ...
随机推荐
- 【Lintcode】062.Search in Rotated Sorted Array
题目: Suppose a sorted array is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand. (i.e., 0 1 2 4 5 6 7 ...
- 异常:Error: Aesthetics must either be length one, or the same length as the dataProblems:AData
今天遇到一个异常,代码如下: set.seed(12345) require(ggplot2) AData <- data.frame(Glabel=LETTERS[1:7], A=rnorm( ...
- 创建maven parent project & module project
1.命令方式: 1)Create the top-level root: mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=org.codehaus.mojo.arc ...
- 使用superobject 解析Json数据
接口数据有如下规范{"error": 0, "msg": "", "data": ...} 其中数据data类型不确定. ...
- JSON 生成 C# Model
http://www.cnblogs.com/tianqiq/p/4309791.html
- Ubuntu 12.04 Eclipse设…
Ubuntu 12.04 Eclipse设置(黑色背景解决) 分类: ubuntu2012-11-21 10:47 252人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 eclipseEclipseubuntuUbu ...
- 微信小程序开发之日期组件
一: wxml: <view class="navbarlift" style="background:#ffffff;padding:20rpx"> ...
- 《剑指offer》面试题21—包含min函数的栈
题目:定义栈数据结构,并在该数据结构中实现一个能获得栈最小元素的函数min.要求push,min,pop时间都是O(1). 思路:要用一个辅助栈,每次有新元素压栈时辅助栈压入当前最小元素:min函数直 ...
- Unity中场景异步加载
引入命名空间 using UnityEngine.UI; using UnityEngine.SceneManagement; using System.Collections; using Syst ...
- C++类型起别名的方式
C++给类型起别名的方式: #include <iostream> using namespace std; #define DString std::string //! 不建议使用!t ...
