Spring 学习记录3 ConversionService
ConversionService与Environment的关系
通过之前的学习(Spring 学习记录2 Environment),我已经Environment主要是负责解析properties和profile...但是它虽然实现了相关的接口,但是具体工作并不是由它本身处理,而是委托了其他的类来帮忙..properties相关的接口方法最终主要是通过PropertySourcesPropertyResolver这个类来处理的..(它们实现了相同的接口)
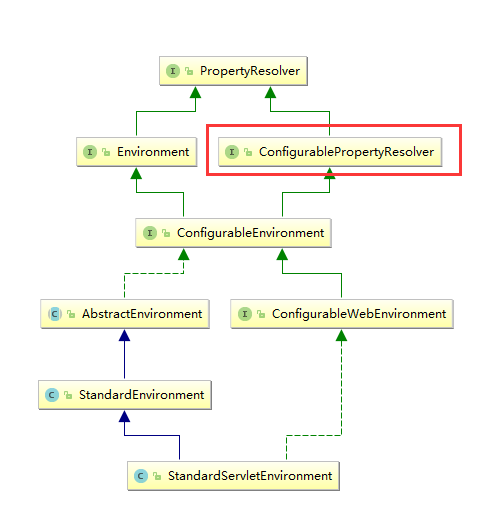
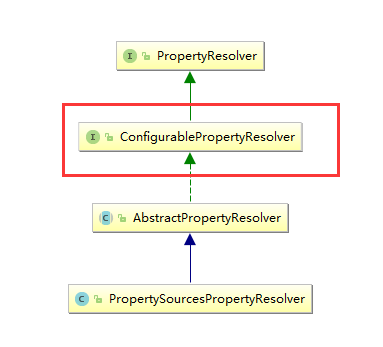
在通过Environment使用properties相关的方法中,有一些方法是带泛型参数的,比如
org.springframework.core.env.PropertyResolver
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or {@code null}
* if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
得到properties以后肯定要通过一些类型转换,才能从String类型得到T类型.那么这个类型转换.其实用的就是ConversionService以及其相关的一套类.
properties文件中的所有值都是String类型的,而java内存里都是对象.所以需要一些工具将String(或者其他类型)转化成我们需要的java类型..(ConversionService是一套通用的转化方案,并不只是在这里用到,任何需要类型转化的地方都可以用)
ConversionService
实验1
properties文件 list=a,b,c,1,2,3
/**
* 测试ConversionService
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:test-application-context.xml")
public class PropertySourcesPropertyResolverTest implements EnvironmentAware { StandardEnvironment standardEnvironment; @Test
public void testPropertySourcesPropertyResolver() {
List<String> list = standardEnvironment.getProperty("list", List.class);
System.out.println(list); // [a, b, c, 1, 2, 3]
} @Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
standardEnvironment = (StandardEnvironment) environment;
}
}
通过Environment的相关properties方法获取属性值并转化成List对象.
追踪断点发现:

PropertySourcesPropertyResolver内部得到属性值a,b,c,1,2,3以后通过conversionService去convert成List类型.
所以让我们来研究下ConversionService吧
ConversionService的结构
public abstract class AbstractPropertyResolver implements ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
protected ConfigurableConversionService conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
............
.............
}
conversionService是定义在AbstractPropertyResolver中的.也就是PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的父抽象类中.
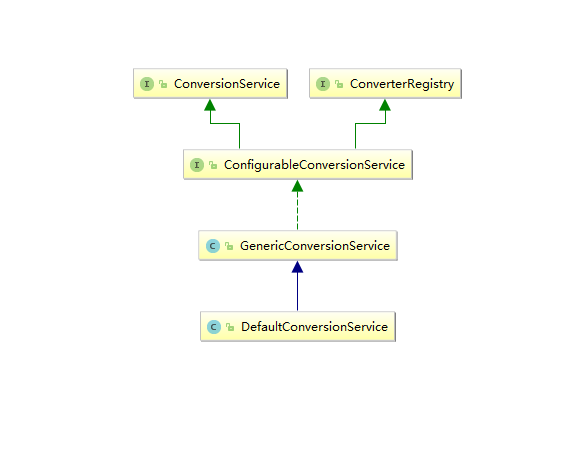
/*
* Copyright 2002-2013 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert; /**
* A service interface for type conversion. This is the entry point into the convert system.
* Call {@link #convert(Object, Class)} to perform a thread-safe type conversion using this system.
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 3.0
*/
public interface ConversionService { /**
* Return {@code true} if objects of {@code sourceType} can be converted to the {@code targetType}.
* <p>If this method returns {@code true}, it means {@link #convert(Object, Class)} is capable
* of converting an instance of {@code sourceType} to {@code targetType}.
* <p>Special note on collections, arrays, and maps types:
* For conversion between collection, array, and map types, this method will return {@code true}
* even though a convert invocation may still generate a {@link ConversionException} if the
* underlying elements are not convertible. Callers are expected to handle this exceptional case
* when working with collections and maps.
* @param sourceType the source type to convert from (may be {@code null} if source is {@code null})
* @param targetType the target type to convert to (required)
* @return {@code true} if a conversion can be performed, {@code false} if not
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code targetType} is {@code null}
*/
boolean canConvert(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType); /**
* Return {@code true} if objects of {@code sourceType} can be converted to the {@code targetType}.
* The TypeDescriptors provide additional context about the source and target locations
* where conversion would occur, often object fields or property locations.
* <p>If this method returns {@code true}, it means {@link #convert(Object, TypeDescriptor, TypeDescriptor)}
* is capable of converting an instance of {@code sourceType} to {@code targetType}.
* <p>Special note on collections, arrays, and maps types:
* For conversion between collection, array, and map types, this method will return {@code true}
* even though a convert invocation may still generate a {@link ConversionException} if the
* underlying elements are not convertible. Callers are expected to handle this exceptional case
* when working with collections and maps.
* @param sourceType context about the source type to convert from
* (may be {@code null} if source is {@code null})
* @param targetType context about the target type to convert to (required)
* @return {@code true} if a conversion can be performed between the source and target types,
* {@code false} if not
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code targetType} is {@code null}
*/
boolean canConvert(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); /**
* Convert the given {@code source} to the specified {@code targetType}.
* @param source the source object to convert (may be null)
* @param targetType the target type to convert to (required)
* @return the converted object, an instance of targetType
* @throws ConversionException if a conversion exception occurred
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if targetType is null
*/
<T> T convert(Object source, Class<T> targetType); /**
* Convert the given {@code source} to the specified {@code targetType}.
* The TypeDescriptors provide additional context about the source and target locations
* where conversion will occur, often object fields or property locations.
* @param source the source object to convert (may be null)
* @param sourceType context about the source type to convert from
* (may be {@code null} if source is {@code null})
* @param targetType context about the target type to convert to (required)
* @return the converted object, an instance of {@link TypeDescriptor#getObjectType() targetType}
* @throws ConversionException if a conversion exception occurred
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if targetType is {@code null},
* or {@code sourceType} is {@code null} but source is not {@code null}
*/
Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); }
查看ConversionService接口里的方法得知,这个类主要就是判断是否能够类型转化,可以的话就转化.
/*
* Copyright 2002-2009 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert.converter; /**
* For registering converters with a type conversion system.
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
*/
public interface ConverterRegistry { /**
* Add a plain converter to this registry.
* The convertible sourceType/targetType pair is derived from the Converter's parameterized types.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the parameterized types could not be resolved
*/
void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter); /**
* Add a plain converter to this registry.
* The convertible sourceType/targetType pair is specified explicitly.
* Allows for a Converter to be reused for multiple distinct pairs without having to create a Converter class for each pair.
* @since 3.1
*/
void addConverter(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType, Converter<?, ?> converter); /**
* Add a generic converter to this registry.
*/
void addConverter(GenericConverter converter); /**
* Add a ranged converter factory to this registry.
* The convertible sourceType/rangeType pair is derived from the ConverterFactory's parameterized types.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the parameterized types could not be resolved.
*/
void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> converterFactory); /**
* Remove any converters from sourceType to targetType.
* @param sourceType the source type
* @param targetType the target type
*/
void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType); }
查看ConverterRegistry接口里的方法得知,这个类主要就是增加Converter用的.
那么既实现了ConversionService又实现了ConverterRegistry的DefaultConversionService用处就是
1.允许添加类型转化器Converter.
2.允许调用相关方法进行类型转化.
/*
* Copyright 2002-2013 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert.support; import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.UUID; import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConverterRegistry;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils; /**
* A specialization of {@link GenericConversionService} configured by default with
* converters appropriate for most environments.
*
* <p>Designed for direct instantiation but also exposes the static
* {@link #addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry)} utility method for ad hoc use against any
* {@code ConverterRegistry} instance.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
*/
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService { /** Java 8's java.util.Optional class available? */
private static final boolean javaUtilOptionalClassAvailable =
ClassUtils.isPresent("java.util.Optional", DefaultConversionService.class.getClassLoader()); /** Java 8's java.time package available? */
private static final boolean jsr310Available =
ClassUtils.isPresent("java.time.ZoneId", DefaultConversionService.class.getClassLoader()); /**
* Create a new {@code DefaultConversionService} with the set of
* {@linkplain DefaultConversionService#addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry) default converters}.
*/
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
} // static utility methods /**
* Add converters appropriate for most environments.
* @param converterRegistry the registry of converters to add to (must also be castable to ConversionService,
* e.g. being a {@link ConfigurableConversionService})
* @throws ClassCastException if the given ConverterRegistry could not be cast to a ConversionService
*/
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry); converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
if (jsr310Available) {
Jsr310ConverterRegistrar.registerZoneIdConverters(converterRegistry);
} converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
if (javaUtilOptionalClassAvailable) {
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}
} // internal helpers private static void addScalarConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new NumberToNumberConverterFactory()); converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToNumberConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Number.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter()); converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCharacterConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Character.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter()); converterRegistry.addConverter(new NumberToCharacterConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new CharacterToNumberFactory()); converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToBooleanConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Boolean.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter()); converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToEnumConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Enum.class, String.class,
new EnumToStringConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry)); converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToLocaleConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Locale.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter()); converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToPropertiesConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new PropertiesToStringConverter()); converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToUUIDConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(UUID.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
} private static void addCollectionConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
ConversionService conversionService = (ConversionService) converterRegistry; converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToArrayConverter(conversionService)); converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new MapToMapConverter(conversionService)); converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToStringConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToArrayConverter(conversionService)); converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToObjectConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToArrayConverter(conversionService)); converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToStringConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCollectionConverter(conversionService)); converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToObjectConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
} /**
* Inner class to avoid a hard-coded dependency on Java 8's {@code java.time} package.
*/
private static final class Jsr310ConverterRegistrar { public static void registerZoneIdConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeToCalendarConverter());
}
} }
查看DefaultConversionService的代码得知,它的构造方法里添加了一堆Converter,这些converter是Spring已经帮助我们实现的.通过这些Converter我们可以进行很多通用类型的转化.比如之前的string->list的类型转化.
Converter接口
/*
* Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert.converter; /**
* A converter converts a source object of type S to a target of type T.
* Implementations of this interface are thread-safe and can be shared.
*
* <p>Implementations may additionally implement {@link ConditionalConverter}.
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @since 3.0
* @param <S> The source type
* @param <T> The target type
*/
public interface Converter<S, T> { /**
* Convert the source of type S to target type T.
* @param source the source object to convert, which must be an instance of S (never {@code null})
* @return the converted object, which must be an instance of T (potentially {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the source could not be converted to the desired target type
*/
T convert(S source); }
Converter接口很简单,就是把S类型转化成T类型.
实验2
利用ConversionService进行类型转化
@Test
public void testConversionService1() {
String s = conversionService.convert(false, String.class);
System.out.println(s); // false
Boolean b = conversionService.convert("true", Boolean.class);
System.out.println(b); // true
} @Before
public void setup() {
conversionService = standardEnvironment.getConversionService();
}
boolean -> string 用到的是ObjectToStringConverter
string -> boolean 用到的是StringToBooleanConverter
这些都是内置的.同时我们也可以发现1个converter也可以进行N种转化.因为ObjectToStringConverter不止可以转化String.任何类型转化成String都可以用这个Converter..内部是直接调用toString()方法...
ConverterFactory和GenericConverter
Converter接口在绝大多数情况下可能都是专门进行S->T类型的转化.也就是1对1的.Spring还提供了一些其他接口来帮我们进行类型转化.比如ConverterFactory和GenericConverter
/*
* Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert.converter; /**
* A factory for "ranged" converters that can convert objects from S to subtypes of R.
*
* <p>Implementations may additionally implement {@link ConditionalConverter}.
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @since 3.0
* @see ConditionalConverter
* @param <S> the source type converters created by this factory can convert from
* @param <R> the target range (or base) type converters created by this factory can convert to;
* for example {@link Number} for a set of number subtypes.
*/
public interface ConverterFactory<S, R> { /**
* Get the converter to convert from S to target type T, where T is also an instance of R.
* @param <T> the target type
* @param targetType the target type to convert to
* @return A converter from S to T
*/
<T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType); }
看源代码可以发现ConverterFactory更像是1对N的转化.
可以从S->各种R的各种子类型T..因为平时处理业务上面的各种转化基本上都是很特殊的1:1的专门的converter去转化.所以可能ConverterFactory和GenericConverter不太用得到.因此主要看看Spring是怎么用这些Converter的吧.
实验3
/**
* 测试ConverterFactory StringToNumberConverterFactory
*/
@Test
public void testConversionService2() {
double d = conversionService.convert("1.2", double.class);
System.out.println(d); //1.2 int i = conversionService.convert("2", int.class);
System.out.println(i); // Byte b = conversionService.convert("0x10", Byte.class);
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b)); //
}
这里用到了StringToNumberConverterFactory把String转化成了Number的各个子类型.
@Override
public T convert(String source) {
if (source.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
return NumberUtils.parseNumber(source, this.targetType);
}
StringToNumberConverterFactory通过NumberUtils的static方法进行转化
public static <T extends Number> T parseNumber(String text, Class<T> targetClass) {
Assert.notNull(text, "Text must not be null");
Assert.notNull(targetClass, "Target class must not be null");
String trimmed = StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(text);
if (targetClass.equals(Byte.class)) {
return (T) (isHexNumber(trimmed) ? Byte.decode(trimmed) : Byte.valueOf(trimmed));
}
else if (targetClass.equals(Short.class)) {
return (T) (isHexNumber(trimmed) ? Short.decode(trimmed) : Short.valueOf(trimmed));
}
else if (targetClass.equals(Integer.class)) {
return (T) (isHexNumber(trimmed) ? Integer.decode(trimmed) : Integer.valueOf(trimmed));
}
else if (targetClass.equals(Long.class)) {
return (T) (isHexNumber(trimmed) ? Long.decode(trimmed) : Long.valueOf(trimmed));
}
else if (targetClass.equals(BigInteger.class)) {
return (T) (isHexNumber(trimmed) ? decodeBigInteger(trimmed) : new BigInteger(trimmed));
}
else if (targetClass.equals(Float.class)) {
return (T) Float.valueOf(trimmed);
}
else if (targetClass.equals(Double.class)) {
return (T) Double.valueOf(trimmed);
}
else if (targetClass.equals(BigDecimal.class) || targetClass.equals(Number.class)) {
return (T) new BigDecimal(trimmed);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot convert String [" + text + "] to target class [" + targetClass.getName() + "]");
}
}
parseNumber方法里面各种ifelse判断需要的是哪种类型的Number然后再转化.
同理,GenericConverter应该是N:N的转化
/*
* Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert.converter; import java.util.Set; import org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor;
import org.springframework.util.Assert; /**
* Generic converter interface for converting between two or more types.
*
* <p>This is the most flexible of the Converter SPI interfaces, but also the most complex.
* It is flexible in that a GenericConverter may support converting between multiple source/target
* type pairs (see {@link #getConvertibleTypes()}. In addition, GenericConverter implementations
* have access to source/target {@link TypeDescriptor field context} during the type conversion
* process. This allows for resolving source and target field metadata such as annotations and
* generics information, which can be used influence the conversion logic.
*
* <p>This interface should generally not be used when the simpler {@link Converter} or
* {@link ConverterFactory} interfaces are sufficient.
*
* <p>Implementations may additionally implement {@link ConditionalConverter}.
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
* @see TypeDescriptor
* @see Converter
* @see ConverterFactory
* @see ConditionalConverter
*/
public interface GenericConverter { /**
* Return the source and target types which this converter can convert between. Each
* entry is a convertible source-to-target type pair.
* <p>For {@link ConditionalConverter conditional} converters this method may return
* {@code null} to indicate all source-to-target pairs should be considered.
*/
Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes(); /**
* Convert the source to the targetType described by the TypeDescriptor.
* @param source the source object to convert (may be null)
* @param sourceType the type descriptor of the field we are converting from
* @param targetType the type descriptor of the field we are converting to
* @return the converted object
*/
Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType); /**
* Holder for a source-to-target class pair.
*/
public static final class ConvertiblePair { private final Class<?> sourceType; private final Class<?> targetType; /**
* Create a new source-to-target pair.
* @param sourceType the source type
* @param targetType the target type
*/
public ConvertiblePair(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType) {
Assert.notNull(sourceType, "Source type must not be null");
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type must not be null");
this.sourceType = sourceType;
this.targetType = targetType;
} public Class<?> getSourceType() {
return this.sourceType;
} public Class<?> getTargetType() {
return this.targetType;
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (other == null || other.getClass() != ConvertiblePair.class) {
return false;
}
ConvertiblePair otherPair = (ConvertiblePair) other;
return (this.sourceType.equals(otherPair.sourceType) && this.targetType.equals(otherPair.targetType));
} @Override
public int hashCode() {
return (this.sourceType.hashCode() * 31 + this.targetType.hashCode());
} @Override
public String toString() {
return (this.sourceType.getName() + " -> " + this.targetType.getName());
}
} }
1个GenericConverter支持转化的所有类型都写在了属性Set<ConvertiblePair>内.
实验四
/**
* 测试GenericConverter CollectionToCollectionConverter
*/
@Test
public void testConversionService3() {
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Set<String> set1 = conversionService.convert(list1, Set.class); // Set<Integer>
System.out.println(set1); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
System.out.println(set1.toArray()[0].getClass()); // class java.lang.Integer
}
这里用到了CollectionToCollectionConverter
/*
* Copyright 2002-2014 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.core.convert.support; import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set; import org.springframework.core.CollectionFactory;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConditionalGenericConverter; /**
* Converts from a Collection to another Collection.
*
* <p>First, creates a new Collection of the requested targetType with a size equal to the
* size of the source Collection. Then copies each element in the source collection to the
* target collection. Will perform an element conversion from the source collection's
* parameterized type to the target collection's parameterized type if necessary.
*
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
*/
final class CollectionToCollectionConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter { private final ConversionService conversionService; public CollectionToCollectionConverter(ConversionService conversionService) {
this.conversionService = conversionService;
} @Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(Collection.class, Collection.class));
} @Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return ConversionUtils.canConvertElements(
sourceType.getElementTypeDescriptor(), targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor(), this.conversionService);
} @Override
public Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
if (source == null) {
return null;
}
Collection<?> sourceCollection = (Collection<?>) source; // Shortcut if possible...
boolean copyRequired = !targetType.getType().isInstance(source);
if (!copyRequired && sourceCollection.isEmpty()) {
return source;
}
TypeDescriptor elementDesc = targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor();
if (elementDesc == null && !copyRequired) {
return source;
} // At this point, we need a collection copy in any case, even if just for finding out about element copies...
Collection<Object> target = CollectionFactory.createCollection(targetType.getType(),
(elementDesc != null ? elementDesc.getType() : null), sourceCollection.size()); if (elementDesc == null) {
target.addAll(sourceCollection);
}
else {
for (Object sourceElement : sourceCollection) {
Object targetElement = this.conversionService.convert(sourceElement,
sourceType.elementTypeDescriptor(sourceElement), elementDesc);
target.add(targetElement);
if (sourceElement != targetElement) {
copyRequired = true;
}
}
} return (copyRequired ? target : source);
} }
conveter方法中如果source和target的collection是同一种类型的话是不需要转化的,直接返回source就OK了.
然后73行是我觉得很奇怪的一个地方
TypeDescriptor elementDesc = targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor();
因为泛型不同于数组,数组是协变的,泛型是编译期的功能,所以这行代码肯定返回的是null....不知道这里为什么还需要去判断是否是null....ArrayToCollection和其他一些converter都有自己的实现,似乎没走这个converter所以我这里也不是很懂什么时候elementDesc会不是null..看这个样子只有target是数组类才有可能,但是这样的话为什么会出现在CollectionToCollectionConverter中呢?很奇怪....
因为elementDesc是null,所以会进target.addAll(sourceCollection)这行,所以就是简单的把source的所有元素丢到target中了.因为没有对元素进行转化.所以Set之中仍然是Integer类型还不是String.
不过也可以理解.集合中的类型都不知道怎么能把每个元素转化成相应的其他类型呢...这是做不到的...这大概也是泛型的缺陷吧....
后面的操作
3种不同的converter在GenericConversionService类中都有对应的addConverter方法可以添加converter.通过ConverterAdapter或者ConverterFactoryAdapter最后都会转化成GenericConverter我想应该是因为这种converter是最通用的原因吧.
这些适配的GenericConverter会被添加到GenericConversionService的静态内部类Converters中,而不是List或者Map中去.可能是因为查找对应Converter方法的时候比较麻烦.
Converters中有属性converters
Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair> converters =
new LinkedHashMap<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair>(36);
ConvertiblePair是source的class与target的Class的封装
ConvertersForPair内部含有
LinkedList<GenericConverter> converters = new LinkedList<GenericConverter>();
所以是各种genericConvrter的封装.
因为GenericConverter可以转化N种source->target的配对.所以可以对应N个ConvertiblePair,也就是说N个ConvertiblePair对应的ConvertersForPair中的GenericConverter可以是同一个.(虽然我Spring中好像没有看到这样的..基本都是对应1个ConvertiblePair)
同样,多个GenericConverter也可以转化同一个source->target的配对,所以1个ConvertiblePair对应的ConvertersForPair中可以有多个GenericConverter.(虽然Spring中也很少出现我只发现了1个)
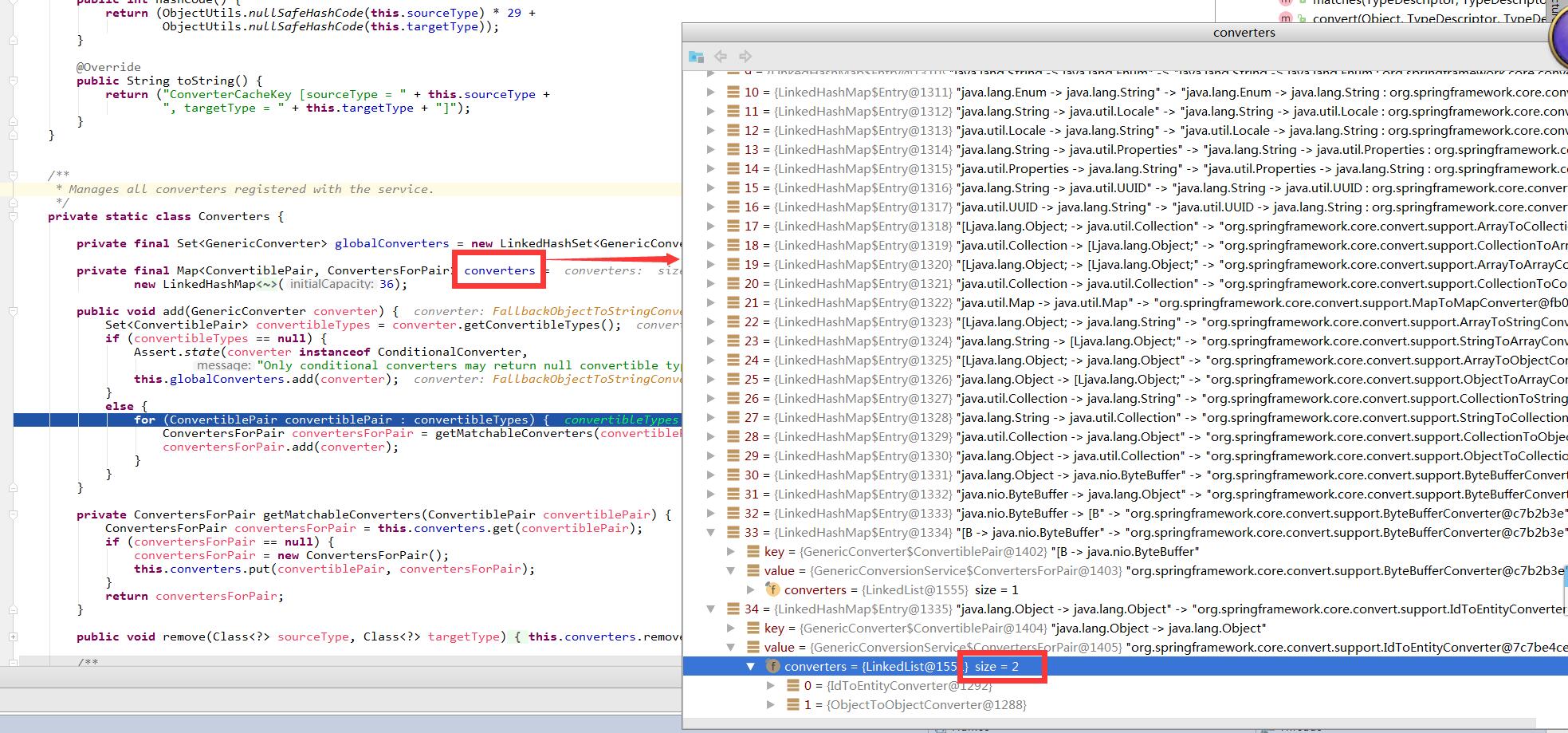
这样情况下如果要convert source->target是会使用前面的那个converter的...每次添加converter的时候都是向linkledlist调用addFirst方法..所以后面加的应该会放到最前面.
小结
1.Spring使用ConversionService来convert各种类型.默认提供的是DefaultConversionService.同时它实现了ConverterRegistry接口,所以也可以添加你自定义的converter.
2.Spring提供了3种converter接口,分别是Converter,ConverterFactory和GenericConverter.一般用于1:1, 1:N, N:N的source->target类型转化.
3.在DefaultConversionService内部3种converter都会转化成GenericConverter放到静态内部类Converters中.
4.接口ConvertiblePair是source的class与target的Class的封装.静态内部类ConvertersForPair是多个converter对应的LinkedList的封装..静态内部类Converters中含有1个Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair>用来储存所有converter.
1个GenericConverter可以对应N个ConvertiblePair,1个ConvertiblePair对应的ConvertersForPair中也可以有N个GenericConverter.
Spring 学习记录3 ConversionService的更多相关文章
- Spring 学习记录6 BeanFactory(2)
主题 除了Spring 学习记录5 BeanFactory 里写的几个接口外,BeanFactory的实现类还实现了一些其他接口,这篇文章主要介绍这些接口和实现类. 结构 DefaultListabl ...
- 我的Spring学习记录(二)
本篇就简单的说一下Bean的装配和AOP 本篇的项目是在上一篇我的Spring学习记录(一) 中项目的基础上进行开发的 1. 使用setter方法和构造方法装配Bean 1.1 前期准备 使用sett ...
- 我的Spring学习记录(四)
虽然Spring管理这我们的Bean很方便,但是,我们需要使用xml配置大量的Bean信息,告诉Spring我们要干嘛,这还是挺烦的,毕竟当我们的Bean随之增多的话,xml的各种配置会让人很头疼. ...
- 我的Spring学习记录(五)
在我的Spring学习记录(四)中使用了注解的方式对前面三篇做了总结.而这次,使用了用户登录及注册来对于本人前面四篇做一个应用案例,希望通过这个来对于我们的Spring的使用有一定的了解. 1. 程序 ...
- Spring 学习记录8 初识XmlWebApplicationContext(2)
主题 接上文Spring 学习记录7 初识XmlWebApplicationContext refresh方法 refresh方法是定义在父类AbstractApplicationContext中的. ...
- Spring学习记录(九)---通过工厂方法配置bean
1. 使用静态工厂方法创建Bean,用到一个工厂类 例子:一个Car类,有brand和price属性. package com.guigu.spring.factory; public class C ...
- Spring学习记录(七)---表达式语言-SpEL
SpEL---Spring Expression Language:是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图表达式语言.使用#{...}作为定界符,为bean属性动态赋值提供了便利. ①对于普通的赋值,用Sp ...
- Spring 学习记录5 BeanFactory
主题 记录我对BeanFactor接口的简单的学习. BeanFactory我感觉就是管理bean用的容器,持有一堆的bean,你可以get各种bean.然后也提供一些bean相关的功能比如别名呀之类 ...
- Spring学习记录(十四)---JDBC基本操作
先看一些定义: 在Spring JDBC模块中,所有的类可以被分到四个单独的包:1.core即核心包,它包含了JDBC的核心功能.此包内有很多重要的类,包括:JdbcTemplate类.SimpleJ ...
随机推荐
- centos7.3安装zend guard loader3.3 for php5.6
1 下载zend guard loader 到这里选择自己的系统版本 我选择的64位 for php5.6.3 linux http://www.zend.com/en/products/load ...
- Xeon Phi 编程备忘
▶ 闲鱼的 Xeon Phi 3120A 配办公室的新 Xeon 服务器,记录一下环境安装过程. ● 原本尝试搭 Ubuntu 服务器,参考[https://software.intel.com/en ...
- 30. CentOS终端命令行显示中文乱码的解决方法
安装CentOS的时候选择了中文,结果在终端不能显示中文,都是乱码,解决方法:修改/etc/sysconfig/i18n,内容为 代码如下: LANG="zh_CN.GB18030&qu ...
- NPOI操作word文档1
1.首先进行XWPFDocument类的实例化,该类的实例对应一个word文档 XWPFDocument MyDoc = new XWPFDocument(); 2.设置页面的大小 CT_SectPr ...
- Linux批量查询替换字符串
Linux 批量查询替换文本文件中的字符串: 1.批量查找某个目下文件的包含的内容,例如: # grep -rn "要找查找的文本" ./ 2.批量查找并替换文件内容. # ...
- event 实现两个程序的交互
event.wait() 等待一定时间,或者当遇到event.set() 时,继续执行 event.clear() 清除信号 event.set() 设置信号 event.isset() 判断信号 例 ...
- Spring @Trasactionl 失效, JDK,CGLIB动态代理
@Transaction: http://blog.csdn.net/bao19901210/article/details/41724355 Spring上下文: http://blog.csd ...
- jdk免安装对应配置
通常我们不用配置jdk,tomcat和eclipse会选取系统的环境变量获取jdk,但有时一个系统中部署不同的项目,各版本又不一样,不能完全兼容. 因此就需要采用自己的jdk.将jdk安装后,将安装后 ...
- HIBERNATE知识复习记录2-继承关系
发现了一篇和我类似的学习尚硅谷视频写的文章,内容如下,比我说的详细全面,可以看一下: [原创]java WEB学习笔记87:Hibernate学习之路-- -映射 继承关系(subclass , jo ...
- redmine邮件配置
网上找了半天,有很多答案,最后自己测试找出一个解决办法. 1.找到安装位置 D:\Bitnami\redmine-2.5.2-2\apps\redmine\htdocs\config下的文件confi ...
