为什么KVM计算机点无故重启?
一.故障1:机器hangs
本地一台cloudstack计算节点无故连不上了,cloudstack也坏了,后查看有一台系统虚拟机在这台计算节点上,导致cs挂了。去找到这台机器后,发现这台机器卡住了,重启后卡在starting udev,等好久也不行,即使进入单用户也是一样,重启很多次也是卡在这。最后查到一篇文章,原话:
Remove quiet from the kernel command line and you should get enough output to see the cause of the hang.
然后进入系统菜单,在编辑kernel行,quiet静默模式。相当于设置"loglevel=4"(WARNING)。将quiet删除后,等待进入系统。大概一个小时后,进去系统了,能ssh了,问题解决了一个,得查一下机器为什么重启。
二.故障2:kvm计算机点为什么无故重启
通过查看cloudstack-agent的日志。
- [root@kvm204 ~]# tail -1000f /var/log/cloudstack/agent/cloudstack-agent.out

看到了这里有报警,并且执行了reboot命令。继续往上面翻,又看到一条信息,如下:
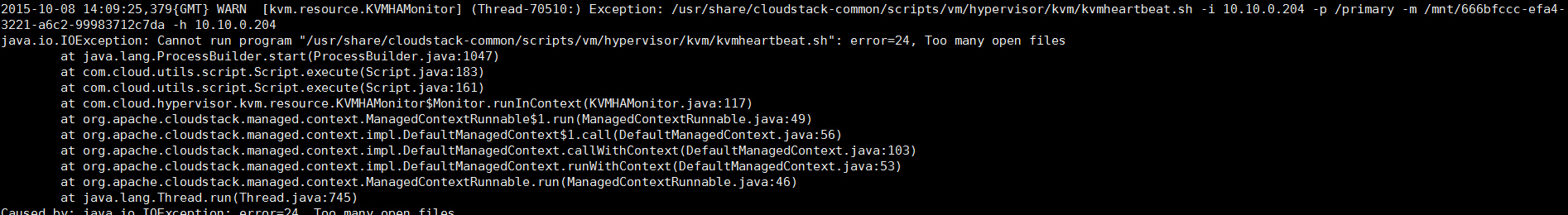
看到很多这样的报错,但最后一次报错是下面这个,可能是它导致了kvm检测脚本执行了reboot命令,然后就出现了本文第一张图片日志里reboot the host。

现在知道了是谁重启了电脑,但kvm为什么会重启这台计算节点呢?带着疑问,我去查看了一下那个脚本,也就是kvmheartbeat.sh脚本。内容如下:
- #!/bin/bash
- # Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
- # or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
- # distributed with this work for additional information
- # regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
- # to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
- # "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
- # with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
- #
- # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- #
- # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
- # software distributed under the License is distributed on an
- # "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
- # KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
- # specific language governing permissions and limitations
- # under the License.
- help() {
- printf "Usage: $0
- -i nfs server ip
- -p nfs server path
- -m mount point
- -h host
- -r write/read hb log
- -c cleanup
- -t interval between read hb log\n"
- exit
- }
- #set -x
- NfsSvrIP=
- NfsSvrPath=
- MountPoint=
- HostIP=
- interval=
- rflag=
- cflag=
- while getopts 'i:p:m:h:t:rc' OPTION
- do
- case $OPTION in
- i)
- NfsSvrIP="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- p)
- NfsSvrPath="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- m)
- MountPoint="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- h)
- HostIP="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- r)
- rflag=
- ;;
- t)
- interval="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- c)
- cflag=
- ;;
- *)
- help
- ;;
- esac
- done
- if [ -z "$NfsSvrIP" ]
- then
- exit
- fi
- #delete VMs on this mountpoint
- deleteVMs() {
- local mountPoint=$
- vmPids=$(ps aux| grep qemu | grep "$mountPoint" | awk '{print $2}' > /dev/null)
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- return
- fi
- if [ -z "$vmPids" ]
- then
- return
- fi
- for pid in $vmPids
- do
- kill - $pid &> /dev/null
- done
- }
- #checking is there the same nfs server mounted under $MountPoint?
- mounts=$(cat /proc/mounts |grep nfs|grep $MountPoint)
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- # remount it
- mount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath $MountPoint -o sync,soft,proto=tcp,acregmin=,acregmax=,acdirmin=,acdirmax=,noac,timeo=,retrans= &> /dev/null
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- printf "Failed to remount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath under $MountPoint"
- exit
- fi
- if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
- then
- deleteVMs $MountPoint
- fi
- fi
- hbFolder=$MountPoint/KVMHA/
- hbFile=$hbFolder/hb-$HostIP
- write_hbLog() {
- #write the heart beat log
- stat $hbFile &> /dev/null
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- # create a new one
- mkdir -p $hbFolder &> /dev/null
- touch $hbFile &> /dev/null
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- printf "Failed to create $hbFile"
- return
- fi
- fi
- timestamp=$(date +%s)
- echo $timestamp > $hbFile
- return $?
- }
- check_hbLog() {
- now=$(date +%s)
- hb=$(cat $hbFile)
- diff=`expr $now - $hb`
- if [ $diff -gt $interval ]
- then
- return
- fi
- return
- }
- if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
- then
- check_hbLog
- if [ $? == ]
- then
- echo "=====> ALIVE <====="
- else
- echo "=====> DEAD <======"
- fi
- exit
- elif [ "$cflag" == "" ]
- then
- reboot
- exit $?
- else
- write_hbLog
- exit $?
- fi
上面这个脚本是我们现在的计算节点上的版本。从上面可以看出,有判断reboot命令,也就是知道了为什么会重启。但这很坑爹呀,你检测检测,你还重启。。。。
下面这个脚本是我在github上看到的。而且版本已经更新。距离现在8月。应该是最新的,从下面看出,这个坑爹的reboot命令已经被修改了。
- #!/bin/bash
- # Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
- # or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
- # distributed with this work for additional information
- # regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
- # to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
- # "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
- # with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
- #
- # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- #
- # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
- # software distributed under the License is distributed on an
- # "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
- # KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
- # specific language governing permissions and limitations
- # under the License.
- help() {
- printf "Usage: $0
- -i nfs server ip
- -p nfs server path
- -m mount point
- -h host
- -r write/read hb log
- -c cleanup
- -t interval between read hb log\n"
- exit
- }
- #set -x
- NfsSvrIP=
- NfsSvrPath=
- MountPoint=
- HostIP=
- interval=
- rflag=
- cflag=
- while getopts 'i:p:m:h:t:rc' OPTION
- do
- case $OPTION in
- i)
- NfsSvrIP="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- p)
- NfsSvrPath="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- m)
- MountPoint="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- h)
- HostIP="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- r)
- rflag=
- ;;
- t)
- interval="$OPTARG"
- ;;
- c)
- cflag=
- ;;
- *)
- help
- ;;
- esac
- done
- if [ -z "$NfsSvrIP" ]
- then
- exit
- fi
- #delete VMs on this mountpoint
- deleteVMs() {
- local mountPoint=$
- vmPids=$(ps aux| grep qemu | grep "$mountPoint" | awk '{print $2}' > /dev/null)
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- return
- fi
- if [ -z "$vmPids" ]
- then
- return
- fi
- for pid in $vmPids
- do
- kill - $pid &> /dev/null
- done
- }
- #checking is there the same nfs server mounted under $MountPoint?
- mounts=$(cat /proc/mounts |grep nfs|grep $MountPoint)
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- # remount it
- mount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath $MountPoint -o sync,soft,proto=tcp,acregmin=,acregmax=,acdirmin=,acdirmax=,noac,timeo=,retrans= &> /dev/null
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- printf "Failed to remount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath under $MountPoint"
- exit
- fi
- if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
- then
- deleteVMs $MountPoint
- fi
- fi
- hbFolder=$MountPoint/KVMHA/
- hbFile=$hbFolder/hb-$HostIP
- write_hbLog() {
- #write the heart beat log
- stat $hbFile &> /dev/null
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- # create a new one
- mkdir -p $hbFolder &> /dev/null
- touch $hbFile &> /dev/null
- if [ $? -gt ]
- then
- printf "Failed to create $hbFile"
- return
- fi
- fi
- timestamp=$(date +%s)
- echo $timestamp > $hbFile
- return $?
- }
- check_hbLog() {
- now=$(date +%s)
- hb=$(cat $hbFile)
- diff=`expr $now - $hb`
- if [ $diff -gt $interval ]
- then
- return
- fi
- return
- }
- if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
- then
- check_hbLog
- if [ $? == ]
- then
- echo "=====> ALIVE <====="
- else
- echo "=====> DEAD <======"
- fi
- exit
- elif [ "$cflag" == "" ]
- then
- /usr/bin/logger -t heartbeat "kvmheartbeat.sh rebooted system because it was unable to write the heartbeat to the storage."
- sync &
- sleep
- echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger
- exit $?
- else
- write_hbLog
- exit $?
- fi
为什么KVM计算机点无故重启?的更多相关文章
- ACPI引起linux系统无故重启
新装机器无故重启多次. centos6 64bit uname -a Linux Eos 2.6.32-71.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri May 20 03:51:51 BST 201 ...
- centos7无故重启-内核升级
最近有一台物理服务器,centos7操作系统,无故重启,每天都会发生这种情况: 解决: 升级内核 CentOS 允许使用 ELRepo,这是一个第三方仓库,可以将内核升级到最新版本,使用ELRepo升 ...
- PowerShell工作流学习-4-工作流中重启计算机
关键点: a)工作流中重新启动计算机,请使用Restart-Computer的Wait参数,Wait参数不仅适用于本地计算机,也适用于远程计算机. b)重启运行工作流的计算机,手工恢复请使用Resum ...
- Win10自动重启原因怎么查Windows10无故自动重启
电脑偶尔自动重启,可能很少用户会在意,若电脑经常无故重启,那么应该怎么办,怎么查找电脑无故自动重启原因呢?下面就以Windows10系统自动重启为例,来查查WIN10无故重启是什么原因导致.百度经验: ...
- kvm 使用入门详解
kvm 是虚拟化技术的一个典型实现,功能非常强大,使用很方便.kvm 本身主要实现对 CPU 的虚拟化,内存和IO的虚拟化使用了开源软件 qemu,qemu 是纯软件层面的虚拟化,其实就是个模拟器.k ...
- Linux 修改计算机名
查看计算机名:在终端输入hostname 修改的话 hostname +计算机名(重启后失效) 要永久修改的话要修改配置文件/etc/sysconfig/network 修改hostname=你要改的 ...
- centos linux中怎么查看和修改计算机名/etc/sysconfig/network
centos linux中怎么查看和修改计算机名 查看计算机名:在终端输入hostname 修改的话 hostname +计算机名(重启后失效)要永久修改的话要修改配置文件/etc/sysconfig ...
- cmd 更改计算机名
bat 更改计算机名 不用重启电脑就生效^_^ @Echo off Color 0A title --更改计算机名 :A cls echo. echo. [0]退出 echo. echo. 不用重启 ...
- KVM之五:KVM日常管理常用命令
1.查看.编辑及备份KVM 虚拟机配置文件 以及查看KVM 状态: 1.1.KVM 虚拟机默认的配置文件在 /etc/libvirt/qemu 目录下,默认是以虚拟机名称命名的.xml 文件,如下,: ...
随机推荐
- 分水岭分割算法(watershed segmentation)的C++实现(法1)
运行环境:ubuntu16.04+Qt+opencv2.4.13 参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/u010741471/article/details/45193521 water ...
- React之状态(state)与生命周期
很多时候,我们的页面数据是动态的.所以,我们需要实时渲染页面: 一.用定时函数setInterval() 组件(输出当前时间): index.js: 这样每隔1秒页面就会重新渲染一次,这样传进去的时间 ...
- python3之环境搭建以及基础语法
早些时候,有一段时间吧,为了想免费下载网易云的收费音乐,也是翻了下python的教程的,语法方面没细致地去看,跟java.php.javascript这些都大同小异,也是面向对象的.那么,近期准备快速 ...
- Android6.0之后的权限机制对App开发的影响
随着Android系统的更新换代,每次重大更新的方面也逐步扩展,从4.*主要是增强功能,到5.*主要是美化界面,到6.*主要提高系统安全性,再到7.*和8.*主要支撑各种大屏设备,因此开发者需要对每个 ...
- 关于python的包
参考文献:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_615c388d01017b5o.html 注:本文大多对上连接的整理,仅用于学习,望博主见谅.转载请附上上述链接. 为什么要包 ...
- js获得分辨率
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/stri ...
- hdu1575 Tr A 矩阵初识
A为一个方阵,则Tr A表示A的迹(就是主对角线上各项的和),现要求Tr(A^k)%9973. Input数据的第一行是一个T,表示有T组数据. 每组数据的第一行有n(2 <= n <= ...
- Built(最小生成树+构图离散化)
个人心得:看了题目很明确,最小生成树,但是但是周赛卡住了,因为10W的点若一个一个找出距离很明显内存和时间都炸了, 静下心来,画了下图,仔细一想,任意一个点都只会在她左右俩边选择建立联系,那么我们只要 ...
- Windows常用配置和sublime快捷键
常用配置和快捷键 1.操作系统常用配置 (1)系统调整为最佳性能 (2)文件夹显示设置:显示文件类型.显示路径 (3)任务栏设置:锁定任务栏+使用小图标2.操作系统常用快捷键 win+数字键--快速打 ...
- Http中Get/Post请求区别
Http中Get/Post请求区别 (1)get是从服务器上获取数据,post是向服务器传送数据. (1) 在客户端,Get方式在通过URL提交数据,数据在URL中可以看到:POST方式,数据放置 ...
