栈帧示意图:stack pointer、frame pointer
更多参考:http://www.embeddedrelated.com/usenet/embedded/show/31646-1.php
一:
The calling convention described in this section is the one used by gcc, not the native MIPS compiler, which uses a more complex convention that is slightly faster.
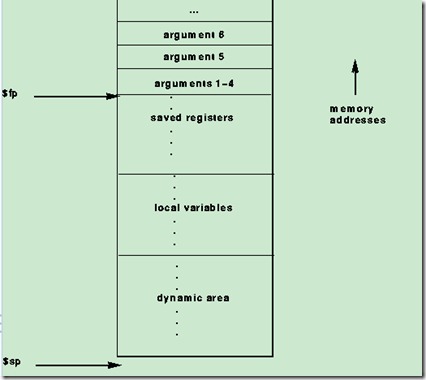
Figure 6: Layout of a stack frame. The frame pointer points just below the last argument passed on the stack. The stack pointer points to the first word after the frame.
Figure 6 shows a diagram of a stack frame. A frame consists of the memory between the frame pointer ($fp), which points to the word immediately after the last argument passed on the stack, and the stack pointer ($sp), which points to the first free word on the stack. As typical of Unix systems, the stack grows down from higher memory addresses, so the frame pointer is above stack pointer.
The following steps are necessary to effect a call:
- Pass the arguments. By convention, the first four arguments are passed in registers $a0-$a3 (though simplier compilers may choose to ignore this convention and pass all arguments via the stack). The remaining arguments are pushed on the stack.
- Save the caller-saved registers. This includes registers $t0-$t9, if they contain live values at the call site.
- Execute a jal instruction.
Within the called routine, the following steps are necessary:
- Establish the stack frame by subtracting the frame size from the stack pointer.
- Save the callee-saved registers in the frame. Register $fp is always saved. Register $ra needs to be saved if the routine itself makes calls. Any of the registers $s0- $s7 that are used by the callee need to be saved.
- Establish the frame pointer by adding the stack frame size to the address in $sp.
Finally, to return from a call, a function places the returned value into $v0 and executes the following steps:
- Restore any callee-saved registers that were saved upon entry (including the frame pointer $fp).
- Pop the stack frame by adding the frame size to $sp.
- Return by jumping to the address in register $ra.
二:
Here's how I diagram the conventional PDP-11 stack layout.
| | higher addresses
+---------------+
| argN |
| ... |
| arg0 | <- FP+4
+---------------+
| link reg | <- FP+2 = SP after JSR
+===============+
| saved FP | <- FP after prologue
+---------------+
/ | locals | <- FP-2
framesize \ | ... |
+---------------+
| saved regs |
| ... | <- SP after prologue
+---------------+
| | lower addresses
Note that local function arguments are at positive offsets from FP,
local variables are at negative offsets. Also note that the frame
pointer itself is among the callee-saved registers.
See here for a survey of subroutine linkage conventions:
http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~mark/subroutines.html
http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~mark/subroutines/pdp11.html (PDP-11
specific)
and here http://cm.bell-labs.com/cm/cs/who/dmr/clcs.html (original
PDP-11 C)
栈帧示意图:stack pointer、frame pointer的更多相关文章
- Java-JVM 栈帧(Stack Frame)
一.概述 栈帧位置 JVM 执行 Java 程序时需要装载各种数据到内存中,不同的数据存放在不同的内存区中(逻辑上),这些数据内存区称作运行时数据区(Run-Time Data Areas). 其中 ...
- frame pointer及其用途
1 什么是frame pointer frame pointer指向本函数栈帧顶,通过它可以找到本函数在进程栈中的位置.有专门的寄存器保存该值. 2 frame pointer有什么用 主要是back ...
- C函数调用过程原理及函数栈帧分析(转)
在x86的计算机系统中,内存空间中的栈主要用于保存函数的参数,返回值,返回地址,本地变量等.一切的函数调用都要将不同的数据.地址压入或者弹出栈.因此,为了更好地理解函数的调用,我们需要先来看看栈是怎么 ...
- IDA Pro 权威指南学习笔记(十) - 栈帧
栈帧(stack frame)是在程序的运行时栈中分配的内存块,用于特定的函数调用 如果一个函数没有执行则不需要内存,当函数被调用时就需要用到内存 1.传给函数的参数的值需要存储到函数能够找到它们的位 ...
- 深入理解java虚拟机(十) Java 虚拟机运行时栈帧结构
运行时栈帧结构 栈帧(Stack Frame) 是用于虚拟机执行时方法调用和方法执行时的数据结构,它是虚拟栈数据区的组成元素.每一个方法从调用到方法返回都对应着一个栈帧入栈出栈的过程. 每一个栈帧在编 ...
- Java虚拟机之栈帧
写在前面的话:Java虚拟机是一门学问,是众多Java大神们的杰作,由于我个人水平有限,精力有限,不能保证所有的东西都是正确的,这里内容都是经过深思熟虑的,部分引用原著的内容,讲的已经很好了,不在累述 ...
- java 栈和栈帧
文章转载自:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/URZrMnb jvm为每个新创建的线程都分配一个堆栈.堆栈以帧为单位保存线程的状态.jvm对堆栈只进行两种操作:以帧为单位 ...
- 详细解析Java虚拟机的栈帧结构
欢迎关注微信公众号:万猫学社,每周一分享Java技术干货. 什么是栈帧? 正如大家所了解的,Java虚拟机的内存区域被划分为程序计数器.虚拟机栈.本地方法栈.堆和方法区.(什么?你还不知道,赶紧去看看 ...
- 【转载】深入理解Java虚拟机笔记---运行时栈帧结构
栈帧(Stack Frame)是用于支持虚拟机进行方法调用和方法执行的数据结构,它是虚拟机运行时数据区的虚拟机栈(Virtual Machine Stack)的栈元素.栈帧存储了方法的局部变量表,操作 ...
随机推荐
- 【转】 关于IDEA javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 不存在 解决方案
昨天从eclipse导入了一个web项目到idea,想运行一下,结果发现 servlet报红... 没有包,第一反应就是eclipse需要设置Targeted Runtimes,但是idea的设置是啥 ...
- bzoj1934 Vote 善意的投票 最小割(最大匹配)
题目传送门 题目大意:很多小朋友,每个小朋友都有自己的立场,赞成或者反对,如果投了和自己立场不同的票会得到一个能量.又有很多朋友关系,如果一个人和他的一个朋友投的票不同,也会得到一个能量,现在问,通过 ...
- mac 系统配置(一)
1.终端颜色配置 文件 .bash_profile下添加环境变量如下: export CLICOLOR=1 export LSCOLORS=gxfxaxdxcxegedabagacad 环境变量生效: ...
- C++ GUI Qt4编程(02)-1.2quit
1. 根据C++ GUI Qt4编程(第二版)整理2. 系统:centos7: Qt版本:5.5.13. 程序:quit.cpp #include <QApplication> #inc ...
- Linux kvm虚拟机的基本操作命令
Linux 虚拟化kvm virsh常用命令篇 1.创建虚拟机 virsh define damo.xml //创建的虚拟机不是活动的 virsh create damo.xml //创建的虚拟机是活 ...
- BankNote
# coding=utf-8 import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn import cross_validation import te ...
- Hash算法总结
1. Hash是什么,它的作用 先举个例子.我们每个活在世上的人,为了能够参与各种社会活动,都需要一个用于识别自己的标志.也许你觉得名字或是身份证就足以代表你这个人,但是这种代表性非常脆弱,因为重名的 ...
- GreenPlum 大数据平台--web监控
一,安装web监控界面 01,准备 下载greenplum cc包,>> 解压缩 02,安装前配置 vim /greenplum/data/master/gpseg-/pg_hba.con ...
- 使用 Ninject
在[ASP.NET MVC 小牛之路]系列上一篇文章(依赖注入(DI)和Ninject)的末尾提到了在ASP.NET MVC中使用Ninject要做的两件事情,续这篇文章之后,本文将用一个实际的示例来 ...
- SecureCRT 连接 CentOS虚拟机
SecureCRT 连接 CentOS虚拟机 1.安装SecureCRT SecureCRT是一款支持SSH等协议的终端仿真软件,可以在windows下登录Linux服务器,这样大大方便了开发工作.安 ...
