[SinGuLaRiTy] 高级搜索算法
【SinGuLaRiTy-1039】 Copyright (c) SinGuLaRiTy 2017. All Rights Reserved.
迭代加深搜索(ID)
迭代加深搜索,实质上就是限定下界的深度优先搜索。即首先允许深度优先搜索K层搜索树,若没有发现可行解,再将K+1后重复以上步骤搜索,直到搜索到可行解。
在迭代加深搜索的算法中,连续的深度优先搜索被引入,每一个深度约束逐次加1,直到搜索到目标为止。
迭代加深搜索算法就是仿广度优先搜索的深度优先搜索。既能满足深度优先搜索的线性存储要求,又能保证发现一个最小深度的目标结点。
从实际应用来看,迭代加深搜索的效果比较好,并不比广度优先搜索慢很多,但是空间复杂度却与深度优先搜索相同,比广度优先搜索小很多。
<伪代码>
- dfs(int depth,int maxdepth)
- {
- if(depth>maxdepth)
- return;
- if(找到答案)
- 输出答案;
- for each(当前节点的儿子节点)
- dfs(depth+,maxdepth);
- }
- int main()
- {
- for(int i=mindepth;;i++)
- dfs(,i);
- }
eg.埃及分数
Click HERE to get to the problem.
在古埃及,人们使用单位分数的和(形如1/a的,a是自然数)表示一切有理数。如:2/3=1/2+1/6,但不允许2/3=1/3+1/3,因为加数中有相同的。
对于一个分数a/b,表示方法有很多种,但是哪种最好呢?首先,加数少的比加数多的好,其次,加数个数相同的,最小的分数越大越好。如:
19/45=1/3 + 1/12 + 1/180
19/45=1/3 + 1/15 + 1/45
19/45=1/3 + 1/18 + 1/30
19/45=1/4 + 1/6 + 1/180
19/45=1/5 + 1/6 + 1/18.
最好的是最后一种,因为1/18比1/180,1/45,1/30,1/180都大。
给出a,b(0<a<b<1000),编程计算最好的表达方式。
解析
很明显这道题是一道搜索题。
我们首先来描述它对应的隐式搜索树:这是一个k叉树,k几乎无穷大,而且层数也是无穷大的。
如果直接使用DFS,有可能遇到一个“无底洞”——即第一个可行解的层次可能非常大。即使加上剪枝,仍然会超时;而如果使用BFS,则需要用队列保存节点,而每层的节点理论上有无穷多个,根本无法用队列存储。
这个时候,我们就可以用IDDFS。
Code
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cstdlib>
- #include<cmath>
- #define INF 0x7fffffff
- using namespace std;
- int error[];
- int res[];
- int temp[];
- int a,b,k;
- int gcd(int a,int b)
- {
- return (b ? gcd(b,a%b) : a);
- }
- bool IDDFS(int cur,int limit,int a,int b,int last)
- {
- if(cur==)memset(temp,,sizeof(temp));
- if(cur==limit-)
- {
- if(a!=||b<=last)
- return false;
- for(int i=;i<=k;i++)
- if(b==error[i])
- return false;
- temp[limit]=b;
- if(res[])
- {
- for(int i=limit;i>=;i--)
- {
- if(temp[i]<res[i])
- {
- for(int j=;j<=limit;j++)
- res[j]=temp[j];
- break;
- }
- else if(temp[i]>res[i])
- break;
- }
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- for(int j=;j<=limit;j++)
- res[j]=temp[j];
- return true;
- }
- }
- if(a==)
- return false;
- bool flag=false;
- for(int i=max(last+,b/a);i<=INF/b&&i<=(limit-cur)*b/a;i++)
- {
- bool check=false;
- for(int j=;j<=k;j++)
- if(error[j]==i)
- check=true;
- if(check==true)
- continue;
- int a1=a*i-b,b1=b*i;
- int x=gcd(a1,b1);
- a1/=x,b1/=x;
- temp[cur+]=i;
- if(IDDFS(cur+,limit,a1,b1,i))flag=true;
- }
- return flag;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int T;
- int cases=;
- scanf("%d",&T);
- while(T--)
- {
- memset(res,,sizeof(res));
- memset(temp,,sizeof(temp));
- scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&k);
- for(int i=;i<=k;i++)
- scanf("%d",&error[i]);
- int x=;
- while()
- {
- if(IDDFS(,x,a,b,))
- break;
- else
- x++;
- }
- printf("Case %d: %d/%d=1/%d",++cases,a,b,res[]);
- for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
- printf("+1/%d",res[i]);
- printf("\n");
- }
- return ;
- }
eg.加法链
Click HERE to get to the problem.
一个n的加法链是指符合下面4个条件的整数数列:
1.a0=1
2.am=n
3.a0<a1<a2<……<am-1<am
4.对每个ak(1<k<=m),都存在ai和aj,(i,j可以相同),满足ak=ai+aj
给你一个整数n,你的任务是构造一个n的加法链,使得链的长度最短。如果有多个答案,则任意输出一个即可。
例如,<1,2,4,5>是一种满足条件的5的加法链;<1,2,4,8,9,17,34,68,77>是一种满足条件的77的加法链。
解析
首先可以求出最少需要几个元素可以达到n。按照贪心的策略,对于每个元素的值,都选择让它等于一个数的两倍,即对于每个Ai = Ai-1 + Ai-1,当Ai>=n时就跳出循环,得到最少元素个数。
然后从最少步数开始迭代加深搜索,再用上一些剪枝技巧即可。
<关于这些“剪枝技巧”>
1.当前深度要填的数 肯定来自于它前几位中,较大的两位组成,且其和 要小于等于末端值n 又要大于前一位的值(序列严格递增)。即a[k-1]<a[i]+a[j]<=n
2.对于当前要填的值 temp,由于已经确定了深搜的深度,那么 我们按最大的取值(i,j都取前一位,即a[k-1]*2)延伸到 最大深度时候的temp,如果其值都比n小(能取的最大值都比n小),意味着在这趟搜索中它永远不可能达到n,所以剪掉这支。
Code
- #include<iostream>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<stdio>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<stdlib>
- using namespace std;
- int a[]={};
- int n=,depth=,flag=;
- int DFS(int len,int depth)
- {
- if(flag)
- return();
- if(len==depth&&a[len-]==n)
- {
- flag=;
- return();
- }
- else
- {
- for(int i=len-;i>=;i--)
- for(int j=i;j>=;j--)
- if(a[i]+a[j]<=n&&a[i]+a[j]>a[len-])
- {
- a[len]=a[i]+a[j];
- int temp=a[len];
- int k=;
- for(k=len+;k<=depth;k++)
- temp*=;
- if(temp<n)
- continue;
- DFS(len+,depth);
- if(flag)
- return ;
- }
- }
- return ;
- }
- int main()
- {
- while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF&&n>)
- {
- a[]=;
- depth=;
- int temp=;
- while(temp<n)
- {
- depth++;
- temp*=;
- }
- depth++;
- flag=;
- while(!flag)
- {
- DFS(,depth);
- if(!flag)
- depth++;
- }
- printf("%d",a[]);
- for(int i=;i<=depth-;i++)
- printf(" %d",a[i]);
- printf("\n");
- }
- return ;
- }
双向BFS搜索
双向BFS即从开始状态和结束状态同时往中间搜,当两端的路径交会于同一个顶点时,则最短路径就找到了。
一般的BFS,如果搜索树的深度为L,度为K,则搜索的最坏时间复杂度为K^L;而如果我们采用双向BFS,时间复杂度则降为2*K^(L/2),自然可以极大的提高搜索速度。
双向BFS本质上还是BFS,只是从两端同时搜索而已,我们可以采用两个队列来实现它。
双向BFS搜索,可以使用两个队列,交替进行搜索,每个方向搜完一层再换另一个方向,即逐层交替搜索。可以使用两个标记数组,一个用于标记正向搜索已经访问的节点,一个用于反向搜索已经访问的节点。如果正向搜索和反向搜索都访问到同一个节点,则表示已经找到了一条由起点到终点的路径。
<伪代码>
- while(!queue.empty())
- {
- t=queue.front();
- queue.pop();
- foreach(t下一个状态next)
- {
- if(当前是正向搜索)
- {
- if(vis2[next]==)
- {
- 处理结果,搜索结束;
- }
- if(vis1[next]==)
- {
- queue.push(next);
- }
- }
- else//当前是反向搜索
- {
- if(vis1[next]==)
- {
- 处理结果,搜索结束;
- }
- if(vis2[next]==)
- {
- queue.push(next);
- }
- }
- }
- }
eg.8数码问题
Click HERE to get to the problem.
如下如所示,a,b分别表示两种状态,每个九宫格中的数字都是0~8共9个数字的任意一种排列,现在要把算出a状态移动到b状态的最佳步骤(移动步数最少)。移动的规则是0方块与上下左右任意一块互换位置。
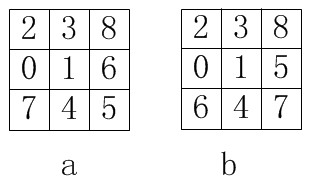
解析
本题其实可以采用双向搜索算法: 因为初始状态和目标状态都是确定的,要求的是最短路径。
Code
这是来自zy691357966的代码,他对这个问题的分析与展开也很棒。
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstdlib>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<ctime>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<iostream>
- #include<sstream>
- #include<string>
- #include<queue>
- #define oo 0x13131313
- using namespace std;
- struct node
- {
- int operator[](int index) const
- {
- return A[index];
- }
- int& operator[](int index)
- {
- return A[index];
- }
- int A[];
- int xnum;
- int deep;
- int Contor;
- void JSContor()
- {
- int temp=,p=;
- for(int i=;i>=;i--)
- {
- int tot=;
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- if(A[j]<A[i]) tot++;
- temp+=(A[i]-tot-)*p;
- p=p*(-i);
- }
- Contor=temp+;
- }
- };
- int visit[][];
- int dist[][];
- int DEEP[][];
- int dANS[][];
- char f[]={'u','d','l','r'};
- int fx[]={-,+,,};
- int fy[]={,,-,+};
- queue <node> Q[];
- node start;
- node End;
- char AAA[];
- void input()
- {
- memset(visit,,sizeof(visit));
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- if(AAA[i]=='x')
- {
- start[i]=;
- start.xnum=i;
- }
- else start[i]=AAA[i]-'';
- End[i]=i+;
- }
- End.xnum=;
- End.deep=;
- start.deep=;
- }
- void csh()
- {
- while(Q[].empty()!=) Q[].pop();
- start.JSContor();
- visit[][start.Contor]=;
- Q[].push(start);
- while(Q[].empty()!=) Q[].pop();
- End.JSContor();
- visit[][End.Contor]=;
- Q[].push(End);
- }
- int GAN(int pos)
- {
- node s,t;
- int x,y,p;
- s=Q[pos].front();
- Q[pos].pop();
- if(visit[pos^][s.Contor]==)
- return s.Contor;
- s.deep++;
- x=s.xnum/;y=s.xnum%;
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- {
- t=s;
- if(x+fx[i]<=&&x+fx[i]>=&&y+fy[i]<=&&y+fy[i]>=)
- {
- p=(x+fx[i])*+y+fy[i];
- swap(t[t.xnum],t[p]);
- t.xnum=p;
- t.JSContor();
- if(visit[pos][t.Contor]==)
- {
- Q[pos].push(t);
- visit[pos][t.Contor]=;
- dist[pos][t.Contor]=s.Contor;
- dANS[pos][t.Contor]=i;
- DEEP[pos][t.Contor]=t.deep;
- }
- }
- }
- return ;
- }
- void twobfs()
- {
- void print(int ok1);
- csh();
- int ok1=,ok2=;
- while(Q[].empty()!=&&Q[].empty()!=)
- {
- ok1=GAN();
- if(ok1!=)
- break;
- ok2=GAN();
- if(ok2!=)
- {ok1=ok2;break;}
- }
- print(ok1);
- }
- char ANS[];
- void print(int ok1)
- {
- int tot=;
- for(int p=ok1;p!=start.Contor;p=dist[][p])
- {
- ANS[tot]=f[dANS[][p]];
- tot++;
- }
- for(int i=tot-;i>=;i--)
- printf("%c",ANS[i]);
- tot=;
- for(int p=ok1;p!=End.Contor;p=dist[][p])
- {
- ANS[tot]=f[dANS[][p]^];
- tot++;
- }
- for(int i=;i<tot;i++)
- printf("%c",ANS[i]);
- printf("\n");
- }
- int OK=;
- int JZyj()
- {
- int tot1=;
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- if(start[i]!=&&start[j]!=)
- if(start[i]<start[j])
- tot1++;
- if(tot1%==)
- return ;
- else
- return ;
- }
- int main()
- {
- while(scanf("%c %c %c %c %c %c %c %c %c\n",&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[],&AAA[])!=EOF)
- {
- input();
- if(JZyj())
- twobfs();
- else
- printf("unsolvable\n");
- }
- return ;
- }
其实,8数码难题还有一个更快的解法:A*算法
A*算法
在学习A*算法之前,我们来了解一下什么是启发式搜索。我们知道,DFS和BFS在展开子结点时均属于盲目型搜索,也就是说,它不会考虑哪个结点在下一次搜索中更优而去选择该结点进行下一步的搜索。在运气不好的情形中,均需要试探完整个解集空间。而启发式搜索,与DFS和BFS这类盲目型搜索最大的不同,就在于选择下一步要搜索的结点时,可以通过一个启发函数来进行选择,选择代价最少的结点作为下一步搜索的结点(遇到有一个以上代价最少的结点,不妨选距离当前搜索点最近一次展开的搜索点进行下一步搜索)。一个经过仔细设计的启发函数,往往在很快的时间内就可得到一个搜索问题的最优解,对于NP问题,亦可在多项式时间内得到一个较优解。
A*算法,作为启发式算法中很重要的一种,被广泛应用在最优路径求解和一些策略设计的问题中。而A*算法最为核心的部分,就在于它的一个估值函数的设计上:
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
其中f(n)是每个可能试探点的估值,它有两部分组成:一部分为g(n),它表示从起始搜索点到当前点的代价(通常用某结点在搜索树中的深度来表示)。另一部分,即h(n),它表示启发式搜索中最为重要的一部分,即当前结点到目标结点的估值,h(n)设计的好坏,直接影响着具有此种启发式函数的启发式算法的是否能称为A*算法。
一种具有f(n)=g(n)+h(n)策略的启发式算法能成为A*算法的充分条件是:
1) 搜索树上存在着从起始点到终点的最优路径。
2) 问题域是有限的
3) 所有结点的子结点的搜索代价值>0。
4) h(n)<=h*(n) h*(n)为实际问题的代价值
当此四个条件都满足时,该启发式算法才能成为A*算法,并一定能找到最优解。
对于一个搜索问题,显然,条件1,2,3都是很容易满足的,而条件4——h(n)<=h*(n)是需要精心设计的,由于h*(n)显然是无法知道的。
所以,一个满足条件4的启发策略h(n)就来的难能可贵了。不过,对于图的最优路径搜索和八数码问题,有些相关策略h(n)不仅很好理解,而且已经在理论上证明是满足条件4)的,从而为这个算法的推广起到了决定性的作用。不过h(n)距离h*(n)的呈度不能过大,否则h(n)就没有过强的区分能力,算法效率并不会很高。对一个好的h(n)的评价是:h(n)在h*(n)的下界之下,并且尽量接近h*(n).
<8数码难题的A*算法思路>
带有注释的该算法代码:
- #pragma warning(disable:4786)
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <set>
- #include <utility>
- #include <ctime>
- #include <cassert>
- #include <cstring>
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- /*item记录搜索空间中一个结点
- state 记录用整数形式表示的8数码格局
- blank 记录当前空格位置,主要用于程序优化,
- 扩展时可不必在寻找空格位置
- g, h 对应g(n), h(n)
- pre 记录当前结点由哪个结点扩展而来 */
- struct item
- {
- int state;
- int blank;
- int g;
- int h;
- int pre;
- };
- const int MAXSTEPS = ;
- const int MAXCHAR = ;
- char buf[MAXCHAR][MAXCHAR]; //open表
- item open[MAXSTEPS];
- //vector<item> open;
- int steps = ;
- //closed表,已查询状态只要知道该状态以及它由哪个结点扩展而来即可,用于输出路径
- //每次只需得到对应f值最小的待扩展结点,用堆实现提高效率
- pair<int, int> closed[MAXSTEPS];
- //读入,将8数码矩阵格局转换为整数表示
- bool read(pair<int,int> &state)
- {
- if (!gets(buf[]))
- return false;
- if (!gets(buf[]))
- return false;
- if (!gets(buf[]))
- return false;
- //cout << strlen(buf[0]) << ' ' << strlen(buf[1]) << ' ' << strlen(buf[2]) << endl;
- assert(strlen(buf[]) == && strlen(buf[]) == && strlen(buf[]) == );
- // astar.in中的每行数据长度必须为5
- state.first = ;
- for (int i = , p = ; i < ; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = ; j < ; j += )
- {
- if (buf[i][j] == '')
- state.second = i * + j / ; // state.second为0(空格)在节点中的位置
- else
- state.first += p * (buf[i][j] - '');
- p *= ;
- }
- }
- /* 若初试节点为:
- 1 2 3
- 8 0 4
- 7 6 5
- 则state.first为567408321,state.second为4
- */
- return true;
- }
- //计算当前结点距目标的距离
- int calculate(int current, int target) // return h=the sum of distances each block have to move to the right position,这里的each block不包括空格
- {
- int c[], t[];
- int i, cnt = ;
- for (i = ; i < ; ++i)
- {
- c[current % ] = t[target % ] = i;
- current /= ;
- target /= ;
- }
- for (i = ; i < ; ++i)
- cnt += abs(c[i] / - t[i] / ) + abs(c[i] % - t[i] % );
- return cnt;
- }
- //open表中结点间选择时的规则 f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
- class cmp
- {
- public: inline bool operator()(item a, item b)
- {
- return a.g + a.h > b.g + b.h;
- }
- };
- //将整数形式表示转换为矩阵表示输出
- void pr(int state)
- {
- memset(buf, ' ', sizeof(buf));
- for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
- {
- for (int j = ; j < ; j += )
- {
- if (state % )
- buf[i][j] = state % + '';
- state /= ;
- }
- buf[i][] = '\0';
- puts(buf[i]);
- }
- }
- //用于判断当前空格是否可以向对应方向移动
- inline bool suit(int a, int b) //空格移动后的坐标为(a,b)
- {
- return (a >= && a < && b >= && b < );
- }
- //递归输出搜索路径
- void path(int index)
- {
- if (index == )
- {
- pr(closed[index].first);
- puts("");
- return;
- }
- path(closed[index].second);
- pr(closed[index].first); //将整数形式表示转换为矩阵表示输出
- puts("");
- ++steps;
- }
- int getNixuNum( int state ) //求节点的逆序对数
- {
- int sum = ;
- int result[];
- memset( result, , sizeof(result) );
- //cout << result[8] << result[7] << endl;
- char buf[];
- itoa( state, buf, );
- //cout << buf << endl;
- int k = ;
- while( buf[k] != '\0' )
- {
- result[-k-] = buf[k] - '';
- k++;
- }
- for( int i = ; i < ; i++ )
- {
- for( int j = i + ; j < ; j++ )
- {
- if( result[i] && result[j] && result[i] > result[j] )
- {
- sum++;
- }
- }
- }
- return sum; //返回3*3方格数组的逆序对数
- }
- int main()
- {
- //cout << getNixuNum(87654321);
- //open.resize(MAXSTEPS);
- unsigned int t1 = clock();
- //cout << open.size() << endl;
- if( freopen("astar.in", "r", stdin) == NULL )
- {
- cout << "file not find\n";
- exit();
- };
- freopen("astar2.out", "w", stdout);
- set<int>states;
- char tmp[];
- int i, x, y, a, b, nx, ny, end, next, index, kase = ;
- pair<int,int> start, target;
- item head; //4个方向移动时的偏移量
- const int xtran[] = {-, , , };
- const int ytran[] = {, , , -};
- const int p[] = {, , , , , , , , , };
- while (read(start)) // 读取初试状态节点
- {
- unsigned int t2 = clock();
- printf("Case %d:\n\n", ++kase);
- gets(tmp);
- read(target); // 读取目标状态节点
- gets(tmp);
- int targetNixuNum = getNixuNum(target.first);
- //若两者的逆序对数不是同为奇数或同为偶数,则无解
- if( !(getNixuNum(start.first)& && targetNixuNum& || !(getNixuNum(start.first)&) && !(targetNixuNum&)) )
- {
- cout << "无法从初始节点到终态节点\n";
- exit();
- }
- //初始化open表,将初始状态加入
- open[].state = start.first;
- open[].h = calculate(start.first, target.first); // 计算当前节点到目标节点的估计距离
- open[].blank = start.second;
- open[].pre = -; // 初始节点无父节点
- open[].g = ; // 初始节点的g为0
- index = ;
- states.insert(start.first); // 扩展过节点保存在states中,即出现过的状态保存在states中,states为set<int>类型,其中的states中的元素唯一
- //提取open表中f值最小元素放入closed表,并对该结点进行扩展
- for (end = ; end > ; ++index) // end为open表中的元素个数,一直循环到open表为空
- {
- assert(index < MAXSTEPS);
- //临时存储
- head = open[]; // 由于使用pop_heap函数和push_heap函数,所以open[0]为g+h最小的元素
- //放入closed表记录当前格局和由哪个结点扩展而来(该结点肯定已在closed表中)
- closed[index].first = open[].state; //放入close表中,表示已经扩展完的节点,下面的for循环会扩展其节点
- closed[index].second = open[].pre; // index表示当前close表中当前扩展节点的下标
- //从open表中删除该结点
- pop_heap(open, open + end, cmp());//为algorithm文件中的函数,第一个参数指定开始位置,第二个指定结束,第三个指定比较函数
- --end;
- //得到结果,递归输出路径
- if (head.state == target.first)
- {
- path(index);
- break;
- }
- x = head.blank / ;
- y = head.blank % ; //空格在3*3方格中的x,y坐标
- /*
- |2 0 3|
- A = |1 8 4|
- |7 6 5| // 看成3*3的数组
- 则head.blank=1
- x=0,y=1,即空格的在3*3的数组中下标为(0,1)
- */
- for (i = ; i < ; ++i)
- {
- nx = x + xtran[i];
- ny = y + ytran[i];
- /*
- i=0时:(nx,ny)为当前空格向上移动一格后的坐标
- i=1时:(nx,ny)为当前空格向右移动一格后的坐标
- i=2时:(nx,ny)为当前空格向下移动一格后的坐标
- i=3时:(nx,ny)为当前空格向左移动一格后的坐标
- */
- if (suit(nx, ny)) // 判断是否能够移动
- {
- a = head.blank; // 空格当前位置,以上面矩阵A为例,a=1
- b = nx * + ny; // 空格移动后的新位置,开始是能够向右边移动,故b=0*3+2=2
- //调换十进制表示整数对应两个数字位
- next = head.state + ((head.state % p[a + ]) / p[a] - (head.state % p[b + ]) / p[b]) * p[b] + ((head.state % p[b + ]) / p[b] - (head.state % p[a + ]) / p[a]) * p[a];
- // 如head.state=567481302,空格向右移动一次后,next=567481032,即为移动后的节点
- // 判断能否由当前节点到达目标节点
- if( ( getNixuNum(next)& && targetNixuNum& ) || ( !(getNixuNum(next)&) && !(targetNixuNum&) ) )
- {
- //判断是否已经扩展过,即已经出现过
- if (states.find(next) == states.end()) //没出现就保存一下,也存入open表
- {
- states.insert(next);
- open[end].pre = index; //扩展后的子节点,其父节点为当前扩展节点
- open[end].blank = b;
- open[end].state = next;
- open[end].h = calculate(next,target.first);
- open[end].g = head.g + ;
- ++end; //open表中元素加1
- push_heap(open, open + end, cmp()); //压入堆中
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- if (end <= )
- puts("No solution");
- else
- {
- printf("Num of steps: %d\n", steps);
- printf("Num of expanded: %d\n", index);
- printf("Num of generated: %d\n", index + end);
- printf("Time consumed: %d\n\n", clock() - t2);
- }
- states.clear();
- steps = ;
- }
- printf("Total time consumed: %d\n", clock() - t1);
- return ;
- }
设F(N)=G(N)+H(N). G(N)为当前走过的步数,即当前节点的深度。 H(N)为估算还要走的步数,即从当前节点达到目标节点的步数。保证H(N)<=H*(N). H*(N)表示还要走的实际步数。 问题是我们根本不知道H*(N),那么如何确定H(N). 是有办法的。 定义H(n)为当前状态与目标状态处于不同位置的数字个数(数字不包含0,0其实是我们自己设定用来代表空格的。九宫格中其实没有0)。 显然,每一步最多能把1个数字移动到正确位置上,如果有H(N)个数字不在正确位置,至少需要移动H(N)步的。所以,可以保证H(N)<=H*(N). 现在定义一个优先队列,使得F值最小的节点先出队列。程序的结构类似于BFS。当队列为空或者搜索到目标节点,则返回解。可以保证搜索到的第一个目标节点必然是最少步数达到的。
但该启发函数其实是很简陋的。我们可以定义不在目标位置的数(不考虑0)的曼哈顿距离为H函数。所谓曼哈顿距离是指两点的横坐标之间距离与纵坐标的距离之和。曼哈顿距离必定也是小于等于H*的。所以仍然满足A*的性质。比起前面的H函数,现在的H函数要大得多,所以性能会好些。
A*算法最为核心的过程,就在每次选择下一个当前搜索点时,是从所有已探知的但未搜索过点中(可能是不同层,亦可不在同一条支路上),选取f值最小的结点进行展开。而所有“已探知的但未搜索过点”可以通过一个按f值升序的队列(即优先队列)进行排列。这样,在整体的搜索过程中,只要按照类似广度优先的算法框架,从优先队列中弹出队首元素(f值),对其可能子结点计算g、h和f值,直到优先队列为空(无解)或找到终止点为止。 A*算法与广度优先和深度优先的联系就在于,当g(n)=0时,该算法类似于DFS,当h(n)=0时,该算法类似于BFS , 这一点,可以通过上面的A*搜索树的具体过程中将h(n)设为0或将g(n)设为0而得到。
<核心代码>
- while(!myq.empty())
- {
- t=myq.top();
- myq.pop();
- if(t.step+t.diff>h[kangtuo(t.str)])
- continue;
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- step=t.step;
- temp=kangtuo(t.str);
- strcpy(tmps,t.str);
- pos_0=t.pos;
- if(pos_0+d[i]>=&&pos_0+d[i]<&&((pos_0+d[i])/==pos_0/||(pos_0+d[i])%==pos_0%))
- {
- swap(tmps[pos_0],tmps[pos_0+d[i]]);
- temp=kangtuo(tmps);
- if(strcmp(tmps,goal)==)
- {
- solution=;
- printf("%d",step+);
- return;
- }
- int gcnt=g(tmps);
- if(gcnt+step+<h[temp])
- {
- h[temp]=gcnt+step+;
- myq.push(node(tmps,pos_0+d[i],step+,gcnt));
- }
- }
- }
- }
eg.第k短路
Click HERE to get to the problem.
给出一个N个节点M条边的有向图(1<=N<=1000,0<=M<=100000)。求点s到点t 的第k短路。
注意:本题如果s==t,最短路不是0,即他需要从其他点绕过来。
解析
使用优先队列,每次取出队列中dis最小的。通过它去更新邻接点的dis,并将能更新的且不在队列中的新的节点压入队列。当队列为空时,所有节点的距离源点的最短距离就求出来了。
现在,我们可以在此基础上加以改进。仍然使用优先队列,每个元素是一个结构体。结构体有3个成员(id,cnt,dis),其中id表示节点编号,cnt表示当前出队次数,dis表示节点到起点的距离。优先队列中,仍然是dis值最小的先出队列,通过它求出其他节点的dis值,压入队列。节点入队列时不再判重,在cnt成员中记录该节点出队的次数。当某个点第i次出队列时,其dis则表示则可求出它到起点的第i短距离。若要输出第k短路径,则在结构体中再增加一个变量,表示它的上一个节点即可。
接下来介绍如何利用A*来改进。设f(n)=g(n)+h(n)。h(n)为估算每个点到终点的目标距离,在此即取该点到终点的最短距离。g(n)则取起点到当前节点的实际距离。每个点到终点的最小距离可以首先通过dijkstra或spfa预处理出来。在优先队列中,每次取f(n)值最小的出队列。同样,当终点第k次出队列时,k短路也就求出来了。
Code
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstdlib>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<queue>
- using namespace std;
- #define inf 0x7ffffff
- #define MAXN 1010
- #define MAXM 100005
- struct Edge
- {
- int u;//反向图的终止边
- int v;//终止点
- int c;//边权值
- int next;//下一个节点
- int next1;//反向边下一个节点
- Edge(){}
- Edge(int u,int v,int c):u(u),v(v),c(c){}
- }p[MAXM];
- int head[MAXN];//链表头
- int head1[MAXN];//反向
- int e; //邻接表中边总数
- int st,en,k;//起点,终点,第k短路
- int n,m;
- int dis[MAXN];//dis[v]表示的是终点到v的距离,即估价函数g
- bool vis[MAXN];
- struct pro
- {
- int v,c;//v是终点,c是起点到v的距离
- pro(){}
- pro(int v,int c):v(v),c(c){}
- bool operator < (const pro& a) const
- {
- return c+dis[v]>a.c+dis[a.v];//最小值优先队列
- }
- };
- void clear()
- {
- memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
- memset(head1,-,sizeof(head1));
- e=;
- }
- void addEdge(int u,int v,int c)
- {
- p[e]=Edge(u,v,c);
- p[e].next1=head1[v];head1[v]=e;
- p[e].next=head[u];head[u]=e++;
- }
- priority_queue<pro> que;
- void dij(int src)//求估价函数
- {
- memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- dis[i]=inf;
- dis[src]=;
- while(!que.empty())
- que.pop();
- que.push(pro(src,));
- while(!que.empty())
- {
- pro cur=que.top();
- que.pop();
- if(vis[cur.v])
- continue;
- vis[cur.v]=;
- for(int i=head1[cur.v];i+;i=p[i].next1)
- {
- if(dis[p[i].u]>dis[cur.v]+p[i].c)
- {
- dis[p[i].u]=dis[cur.v]+p[i].c;
- que.push(pro(p[i].u,));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int a_star(int src)
- {
- while(!que.empty())
- que.pop();
- que.push(pro(src,));
- while(!que.empty())
- {
- pro cur=que.top();
- que.pop();
- if(cur.v==en)
- {
- if(k>)//相当于求k次最短路
- k--;
- else
- return cur.c;
- }
- for(int i=head[cur.v];i+;i=p[i].next)//将所有与u相连接的点都加入队列
- que.push(pro(p[i].v,cur.c+p[i].c));
- }
- return -;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int u,v,c;
- while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
- {
- clear();
- while(m--)
- {
- scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&c);
- addEdge(u,v,c);
- }
- scanf("%d%d%d",&st,&en,&k);
- dij(en);
- if(dis[st]==inf)
- {
- puts("-1");
- continue;
- }
- if(st==en)
- k++;
- printf("%d\n",a_star(st));
- }
- return ;
- }
看了ID和A*算法,下面让我们来认识一下IDA*算法:
IDA*算法
IDA*算法嘛,就是ID算法+A*算法啦,算是两种搜索的结合吧~
先来看看代码框架:
- dfs(int start,int depth)
- {
- if(start==solution)
- {
- flag=;
- return;
- }
- if(depth+start.h>limit)
- return;//关键,利用A*剪枝
- for each(start.everyson)
- {
- dfs(start.oneson,depth+);
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- flag=;
- while(flag==)
- {
- limit++;
- dfs(start,);
- }
- }
我们其实可以发现:与IDA相比,IDA*算法其实只是在ID的基础上加上了A*来进行剪枝优化。 与A*算法相比,A*算法本质上是广搜,但采用了估价函数来改变队列中节点的顺序,而IDA*则把A*由广搜的形式变成了深搜的形式。
下面给出一些例题,同时附上简单的思路和代码——毕竟网上的题解那么多,就不再一一赘述了。
eg.循环游戏
Click HERE to get to the problem.
旋转游戏是在一个'#'棋盘中进行的,它有24个格子组成,每个格子中有一个数字,数字只能是1~3中的一个,并且每个数字刚好出现8次。
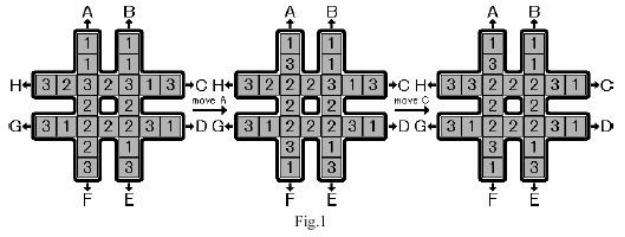
开始时,这些数字是随机分布在棋盘中。你的任务是移动这些格子,使得中心的8个格子是同一个数字。你只能循环移动最长的两行和最长的两列。具体来讲,对于每一行,你可以向左循环移动,也可以向右循环移动;对于每一列,你可以向上循环移动,也可以向下循环移动。总共有8种移动方式,分别用A~G来表示,如图所示,通过操作A和操作C,则可以将棋盘从初始状态变成目标状态,中间的格子全部是2. 给出初始棋盘,求你最少需要多少次操作才能完成任务。
解析
因为要求最少步数。可以采用A*.因为每次移动只能有一个数字进入中间八个格子。所以,可以设计h为8-max(cnt[1],cnt[2],cnt[3])。其中cnt[i]表示在中间8个格子中的i的个数。
(当然,暴力一点的做法可以分类讨论:假设目标状态为中间的数全是X,把X以外的数当作同一个数来进行搜索)
Code
- #include<iostream>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstdlib>
- using namespace std;
- int map[][],step;
- char road[];
- int hash1[]={,,,,,,,};
- void TurnCOL(int c,int flag)
- {
- int t;
- if(flag)
- {
- t=map[][c];
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- map[i-][c]=map[i][c];
- map[][c]=t;
- }
- else {
- t=map[][c];
- for(int i=;i>=;i--)
- map[i+][c]=map[i][c];
- map[][c]=t;
- }
- }
- void TurnROW(int r,int flag)
- {
- int t;
- if(flag)
- {
- t=map[r][];
- for(int i=;i>=;i--)
- map[r][i+]=map[r][i];
- map[r][]=t;
- }
- else
- {
- t=map[r][];
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- map[r][i-]=map[r][i];
- map[r][]=t;
- }
- }
- int check()
- {
- int num[]={};
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- {
- num[map[][i]]++;
- num[map[][i]]++;
- }
- num[map[][]]++;
- num[map[][]]++;
- int t=max(num[],max(num[],num[]));
- return t;
- }
- bool dfs(int cnt)
- {
- int t=check();
- if(t==&&cnt==step)
- return true;
- if(cnt+(-t)>step)
- return false;
- char c;
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- c=i+'A';
- road[cnt]=c;
- if(c=='A'||c=='B')
- {
- TurnCOL(hash1[i],);
- if(dfs(cnt+))
- return true;
- TurnCOL(hash1[i],);
- }
- else if(c=='F'||c=='E')
- {
- TurnCOL(hash1[i],);
- if(dfs(cnt+))
- return true;
- TurnCOL(hash1[i],);
- }
- else if(c=='C'||c=='D')
- {
- TurnROW(hash1[i],);
- if(dfs(cnt+))
- return true;
- TurnROW(hash1[i],);
- }
- else
- {
- TurnROW(hash1[i],);
- if(dfs(cnt+))
- return true;
- TurnROW(hash1[i],);
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int a,b;
- while(scanf("%d",&a)==&&a)
- {
- scanf("%d",&b);
- memset(map,,sizeof(map));
- map[][]=a;
- map[][]=b;
- for(int i=;i<=;i++)
- {
- if(i==||i==)
- {
- for(int j=;j<=;j++)
- scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);
- continue;
- }
- scanf("%d %d",&map[i][],&map[i][]);
- }
- if(check()==)
- {
- puts("No moves needed");
- printf("%d\n",map[][]);
- continue;
- }
- step=;
- while(true)
- {
- if(dfs())
- break;
- step++;
- }
- road[step]='\0';
- puts(road);
- printf("%d\n",map[][]);
- }
- return ;
- }
eg.Escape from Tetris
Click HERE to get to the problem.
由于整日整夜地对着这个棋盘,Lele终于走火入魔。每天一睡觉,他就会梦到自己会被人被扔进一个棋盘中,一直找不到出路,然后从梦中惊醒。久而久之,Lele被搞得精神衰弱。梦境是否会成为现实,谁也说不准,不过不怕一万只怕万一。现在Lele每次看到一个棋盘,都会想象一下自己被关进去以后要如何逃生。
Lele碰到的棋盘都是正方形的,有N*N个格子(N<=9),其中有些格子是坏的,不可以走,剩下的都是可以走的。只要一走到棋盘的边沿(最外面的一圈),就算已经逃脱了。Lele梦见自己一定会被扔在一个可以走的格子里,但是不确定具体是哪一个,所以他要做好被扔在任意一个格子的准备。
现在Lele请你帮忙,对于任意一个棋盘,找出一个最短的序列,序列里可以包括"north"(地图里向上),"east"(地图里向右),"south"(地图里向下),"west"(地图里向左),这四个方向命令。不论Lele被扔在棋盘里的哪个好的格子里,都能按这个序列行走逃出棋盘。
逃脱的具体方法是:不论Lele被扔在哪里,Lele按照序列里的方向命令一个一个地走,每个命令走一格,如果走的时候会碰到坏的格子,则忽略这条命令。当然,如果已经逃脱了,就可以不考虑序列中剩下的命令了。
解析
可以采用IDA* 先用BFS求出迷宫内部的点走到边界的最小步数(为了后面的IDA*剪枝),因为有很多状态,不好表示,所以可以想到用IDA*算法,在dfs的时候每次内部的点安同一个方向走,当某个点走到边界或遇见墙时不变,其他的点还是继续走。
Code
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<queue>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstdlib>
- #define inf 0x7fffffff
- using namespace std;
- char map[][];
- char Dir[][]={"east","north","south","west"};
- int dir[][]={,,-,,,,,-};
- int dis[][],path[];
- int n,step;
- struct node
- {
- int x,y;
- };
- queue<node>q;
- bool isedge(int x,int y)
- {
- return x==||x==n-||y==||y==n-;
- }
- bool ismap(int i,int j)
- {
- return i>=&&i<n&&j>=&&j<n;
- }
- void bfs()
- {
- node head,tail;
- while(!q.empty())
- {
- head=q.front();
- q.pop();
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- tail.x=head.x+dir[i][];
- tail.y=head.y+dir[i][];
- if(!map[tail.x][tail.y])
- continue;
- if(!ismap(tail.x,tail.y))
- continue;
- if(dis[tail.x][tail.y]>dis[head.x][head.y]+)
- {
- dis[tail.x][tail.y]=dis[head.x][head.y]+;
- q.push(tail);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- void Init()
- {
- while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- for(int j=;j<n;j++)
- {
- dis[i][j]=inf;
- map[i][j]=map[i][j]==''?:;
- if(!map[i][j])
- continue;
- if(isedge(i,j))
- {
- dis[i][j]=;
- node pp;
- pp.x=i;
- pp.y=j;
- q.push(pp);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int get_h(char mat[][])
- {
- int Mx=;
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- for(int j=;j<n;j++)
- if(mat[i][j])
- Mx=max(Mx,dis[i][j]);
- return Mx;
- }
- bool dfs(char mat[][],int d)
- {
- if(d+get_h(mat)>step)
- return false;
- if(d==step)
- return true;
- char nxt[][];
- for(int k=;k<;k++)
- {
- memset(nxt,,sizeof(nxt));
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- for(int j=;j<n;j++)
- {
- if(isedge(i,j)||!mat[i][j])
- continue;
- int nx=i+dir[k][];
- int ny=j+dir[k][];
- if(!map[nx][ny])
- nxt[i][j]=;
- else
- nxt[nx][ny]=;
- }
- }
- path[d]=k;
- if(dfs(nxt,d+))
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int ca=;
- while(~scanf("%d",&n))
- {
- if(ca++) cout<<endl;
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- scanf("%s",map[i]);
- Init();
- bfs();
- step=;
- while()
- {
- if(dfs(map,)) break;
- step++;
- }
- for(int i=;i<step;i++)
- printf("%s\n",Dir[path[i]]);
- }
- return ;
- }
eg.DNA sequence
Click HERE to get to the problem.
20世纪是生物科技快速发展的世纪。我们知道基因由DNA组成。核苷酸DNA构建的碱基是A(腺嘌呤)、C(胞嘧啶)、G(鸟嘌呤)和T(胸腺嘧啶)。寻找DNA /蛋白质序列之间最长的公共子序列是现代计算分子生物学的基本问题之一。但这个问题有点不同。给定几个DNA序列,你要求一个最短的序列,使每一个给定的序列都是它的子序列。

比如给出的序列为"ACGT","ATGC","CGTT"和"CAGT",你可以构造一个这样的序列:"ACAGTGCT",它是最短的一个序列,但不是唯一的。
解析
迭代加深搜索加上A*剪枝。h函数即为每个串中还没有被匹配的最大长度值。剪枝即为当前的深度+最少还有加深的深度是否大于限制的长度,若是,则退回上一层状态。
Code
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<queue>
- #include<cstdlib>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cmath>
- using namespace std;
- int n;
- char ch[][];
- int len[],want;
- char dir[]= {'A','C','G','T'};
- int wei[];
- int get_h()
- {
- int t=;
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- t=max(t,len[i]-wei[i]);
- return t;
- }
- int IDA(int dep)
- {
- if(dep+get_h()>want)
- return ;
- if(dep==want)
- return ;
- int tmp[];
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- int flag=;
- memcpy(tmp,wei,sizeof(wei));
- for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
- {
- if(ch[j][wei[j]]==dir[i])
- {
- flag=;
- wei[j]++;
- }
- }
- if(flag)
- {
- if(IDA(dep+))
- return ;
- memcpy(wei,tmp,sizeof(tmp));
- }
- }
- return ;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int T;
- scanf("%d",&T);
- while(T--)
- {
- int Max=;
- scanf("%d",&n);
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- {
- scanf("%s",ch[i]);
- len[i]=strlen(ch[i]);
- if(len[i]>Max)
- Max=len[i];
- }
- memset(wei,,sizeof(wei));
- want=Max;
- while()
- {
- if(IDA())
- break;
- want++;
- }
- printf("%d\n",want);
- }
- return ;
- }
Time:2017-10-05
[SinGuLaRiTy] 高级搜索算法的更多相关文章
- 第3章:LeetCode--算法:strStr KMP算法
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-strstr/ 28. Implement strStr() 暴力算法: int ViolentMatch(char* ...
- ACM北大暑期课培训第四天
今天讲了几个高级搜索算法:A* ,迭代加深,Alpha-Beta剪枝 以及线段树 A*算法 启发式搜索算法(A算法) : 在BFS算法中,若对每个状态n都设定估价函数 f(n)=g(n)+h(n) ...
- 【高级算法】禁忌搜索算法解决3SAT问题(C++实现)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhoubin1992/article/details/46440389 近期梳理,翻出了当年高级算法课程做的题目.禁忌搜索算法解决3SAT问 ...
- 【转】ACM搜索算法总结 --By GreenHand
搜索是ACM竞赛中的常见算法,本文的主要内容就是分析它的 特点,以及在实际问题中如何合理的选择搜索方法,提高效率.文章的第一部分首先分析了各种基本的搜索及其各自的特点.第二部分在基本搜索方法的基础上提 ...
- [SinGuLaRiTy] 2017-03-27 综合性测试
[SinGuLaRiTy-1013] Copyright (c) SinGuLaRiTy 2017. All Rights Reserved. 这是 三道 USACO 的题...... 第一题:奶牛飞 ...
- [SinGuLaRiTy] 平衡树
[SinGuLaRiTy-1009] Copyright (c) SinGuLaRiTy 2017. All Rights Reserved. 二叉查找树 二叉查找树是指具有下列性质的非空二叉树: ⑴ ...
- [转载]ACM搜索算法总结(总结)
原文地址:ACM搜索算法总结(总结)作者:GreenHand 搜索是ACM竞赛中的常见算法,本文的主要内容就是分析它的 特点,以及在实际问题中如何合理的选择搜索方法,提高效率.文章的第一部分首先分析了 ...
- 《深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级特性与最佳实践》【PDF】下载
<深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级特性与最佳实践>[PDF]下载链接: https://u253469.pipipan.com/fs/253469-230062566 内容简介 作为一位 ...
- 【高级算法】遗传算法解决3SAT问题(C++实现)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhoubin1992/article/details/46910079 1 SAT问题描写叙述 命题逻辑中合取范式 (CNF) 的可满足性问 ...
随机推荐
- mybatis配置ehcache缓存
1:在spring配置文件中加载缓存配置文件 <!-- 使用ehcache缓存 --> <bean id="ehCacheManager" class=" ...
- SDRAM 之时序收敛(学习了特权老师)
到现在我还是不太理解SDRAM的时序设置,但是可能蒙对了.(呵呵) 开发环境: quartus II 13.0 板子: DE2 EP2C35F672C6N 时序约束step 1:create cl ...
- CVE-2017-11882复现配合koadic
项目地址:https://github.com/iBearcat/CVE-2017-11882 首先开启koadic,然后配置一下 复制这句代码 mshta http://192.168.220.13 ...
- WEB扫描器Atscan的安装和使用
项目地址:https://github.com/AlisamTechnology/ATSCAN root@sch01ar:/sch01ar# git clone https://github.com/ ...
- python's thirty-first day for me re模块
正则表达式: re 模块 可以读懂 你写的正则表达式,根据你写的表达式去执行任务. 正则表达式:字符串的操作. 使用一些规则来检测字符串是否符合我的要求 —— 表单验证 从一段字符串中找到符合我要 ...
- 第十六章 Java内存模型(待续)
········
- sql 2012先分离迁移mdf mlf 文件到别的机器后附加 数据库成只读的修复方法
SQL Server2008附加数据库之后显示为只读时解决方法 从本地分离的数据库文件放到远程服务器上,附加数据库出现数据库为(只读情况) 阅读了以下两篇文章: 第一篇:http://blog.c ...
- npm中npm install 始终出错解决办法
npm中npm install 始终出错解决办法 错误信息: C:\Windows\System32>npm install -g gulp npm ERR! Windows_NT 6.1.76 ...
- leetcode832
vector<vector<int>> flipAndInvertImage(vector<vector<int>>& A) { vector& ...
- For input String:"" 异常记录
开发中遇到 For input String:"" 这个异常,一般为在将字符串转换为数字类型时, 出现转换的异常,常见的比如输入的字符串为空串
