Python语言程序设计(3)--实例2-python蟒蛇绘制-turtle库
1.

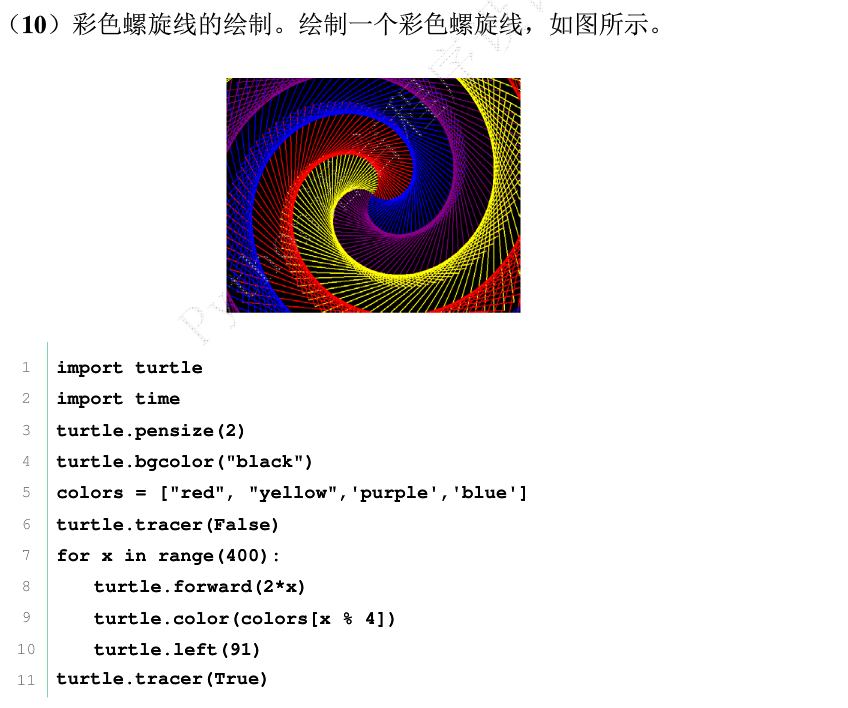
2.


3.了解turtle库
Turtle,也叫海龟渲染器,使用Turtle库画图也叫海龟作图。Turtle库是Python语言中一个很流行的绘制图像的函数库。海龟渲染器,和各种三维软件都有着良好的结合。功能强大,使用方便。该渲染器的特色在于其渲染速度可以优海龟渲染器,
和各种三维软件都有着良好的结合。功能强大,使用方便。化得非常快,相比起mental ray来说,这是他的一大优点。尤其是在全局光与final gather联用的时候效果更是明显。海龟渲染器在渲染大场景时非常有效,其对于光线的处理和色彩的鲜艳程度都要更胜三维软件自带的渲染器。其缺点在于对于三维软件的程序纹理贴图的支持不够,很多情况下并不能对它的材质球使用程序纹理贴图,这不能不说是一个遗憾。







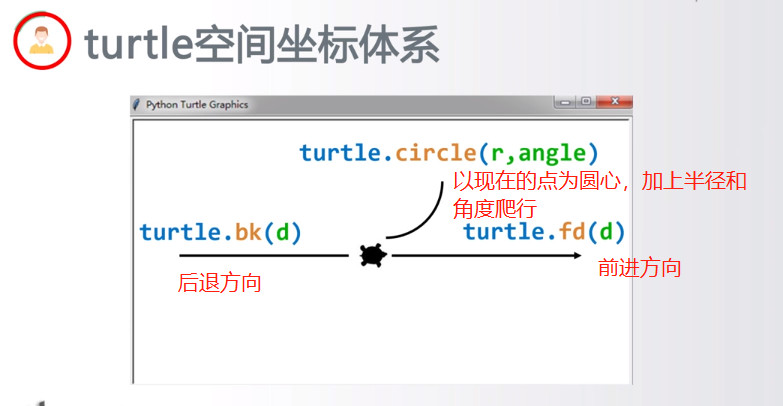


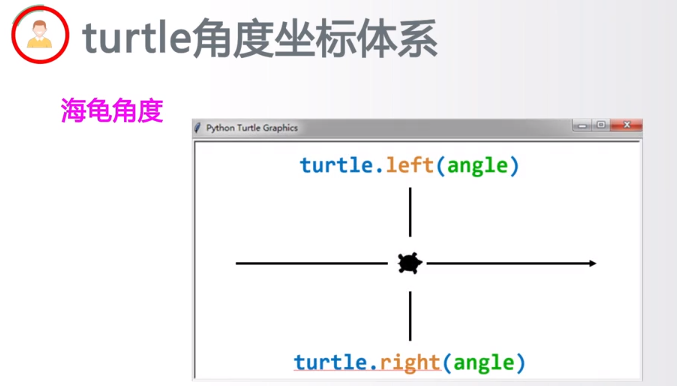
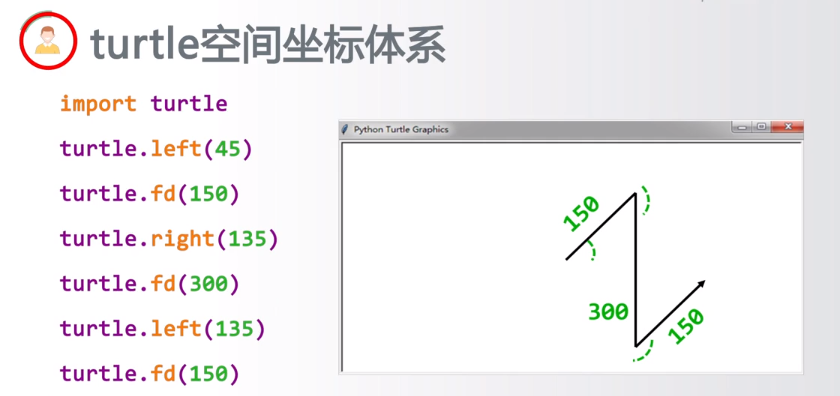

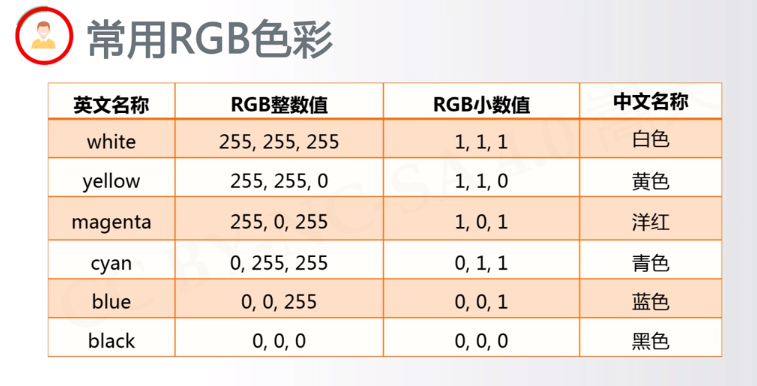

4.编写代码
#pythondraw.py
import turtle #引用 绘制(海龟)库
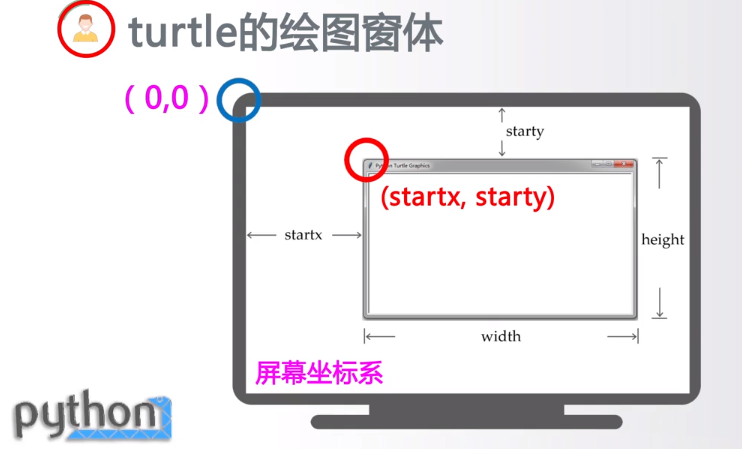
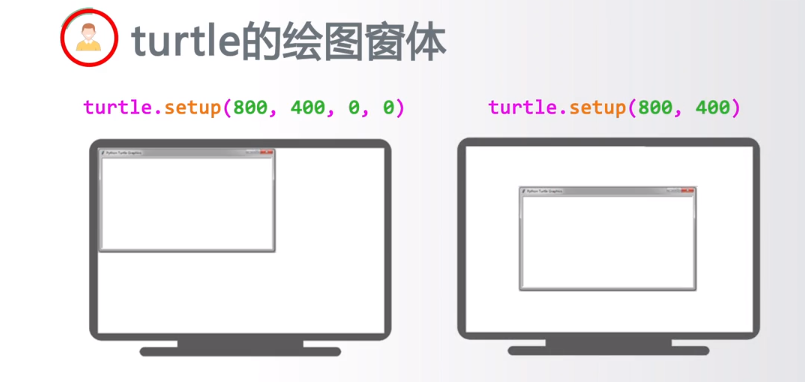
turtle.setup(650,350,200,200) #启动窗体,宽650,高350
turtle.penup() #抬起画笔
turtle.fd(-250) #倒退250像素
turtle.pendown() #落下画笔
turtle.pensize(25) #画笔宽度是25像素
turtle.pencolor('purple') #画笔颜色是紫色
turtle.seth(-40) #调整方向为绝对40度
for i in range(4): #循环4次,走曲线,r为40像素,角度为80
turtle.circle(40,80)
turtle.circle(-40,80)
turtle.circle(40,80/2) #继续走曲线
turtle.fd(40) #向前走40像素
turtle.circle(16,180)
turtle.fd(40 * 2/3)
turtle.done() #结束绘制,不会主动退出;如果想绘图结束就关闭窗口,就去掉这一行



推荐使用:

画笔控制函数:



turtle.fillcolor(colorstring):绘制图形的填充颜色
turtle.color(color1, color2):同时设置pencolor=color1, fillcolor=color2
turtle.filling():返回当前是否在填充状态
turtle.begin_fill():准备开始填充图形
turtle.end_fill():填充完成
turtle.hideturtle():隐藏画笔的turtle形状
turtle.showturtle():显示画笔的turtle形状
运动控制函数:



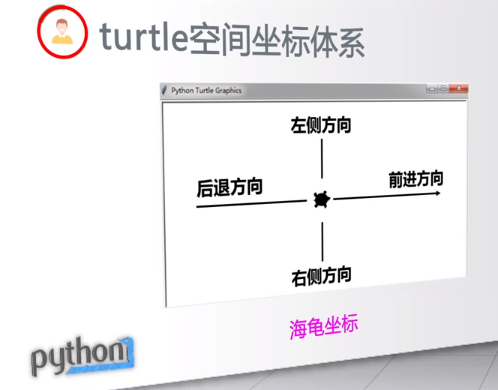
turtle.forward(distance):向当前画笔方向移动distance像素长度
turtle.backward(distance):向当前画笔相反方向移动distance像素长度
turtle.right(degree):顺时针移动degree°
turtle.left(degree):逆时针移动degree°
turtle.pendown():移动时绘制图形,缺省时也为绘制
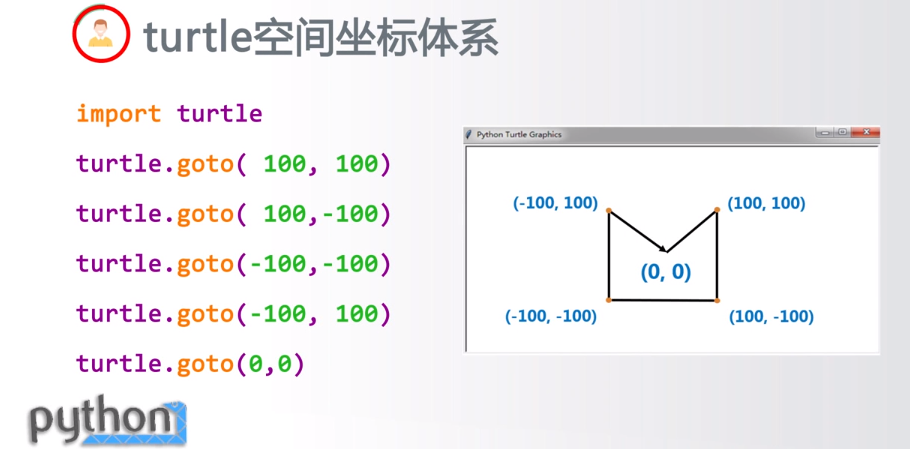
turtle.goto(x,y):将画笔移动到坐标为x,y的位置
turtle.penup():提起笔移动,不绘制图形,用于另起一个地方绘制
turtle.circle():画圆,半径为正(负),表示圆心在画笔的左边(右边)画圆
setx( ):将当前x轴移动到指定位置
sety( ):将当前y轴移动到指定位置
setheading(angle):设置当前朝向为angle角度
home():设置当前画笔位置为原点,朝向东。
dot(r):绘制一个指定直径和颜色的圆点
方向控制函数:



循环与range函数:

 print里加了逗号,输出时文字与参数会加一个空格
print里加了逗号,输出时文字与参数会加一个空格

全局控制命令:
turtle.clear():清空turtle窗口,但是turtle的位置和状态不会改变
turtle.reset():清空窗口,重置turtle状态为起始状态
turtle.undo():撤销上一个turtle动作
turtle.isvisible():返回当前turtle是否可见
stamp():复制当前图形
turtle.write(s [,font=("font-name",font_size,"font_type")]):写文本,s为文本内容,font是字体的参数,分别为字体名称,大小和类型;font为可选项,font参数也是可选项
其他命令:

网上找的示例:
使用turtle绘制七段数码管,显示当前日期
#SevenDigitsDrawV2.py
import turtle, time
def drawGap(): #绘制数码管间隔
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(5)
def drawLine(draw): #绘制单段数码管
drawGap()
turtle.pendown() if draw else turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(40)
drawGap()
turtle.right(90)
def drawDigit(d): #根据数字绘制七段数码管
drawLine(True) if d in [2,3,4,5,6,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,2,3,5,6,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,2,6,8] else drawLine(False)
turtle.left(90)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,4,5,6,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,2,3,5,6,7,8,9] else drawLine(False)
drawLine(True) if d in [0,1,2,3,4,7,8,9] else drawLine(False)
turtle.left(180)
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(20)
def drawDate(date):
turtle.pencolor("red")
for i in date: #根据设置的符号分隔年月日
if i == '-':
turtle.write('年',font=("Arial", 18, "normal"))
turtle.pencolor("green")
turtle.fd(40)
elif i == '=':
turtle.write('月',font=("Arial", 18, "normal"))
turtle.pencolor("blue")
turtle.fd(40)
elif i == '+':
turtle.write('日',font=("Arial", 18, "normal"))
else:
drawDigit(eval(i))
def main():
turtle.setup(800, 350, 200, 200) #设置画布窗口大小以及位置
turtle.penup()
turtle.fd(-350)
turtle.pensize(5)
t=time.gmtime() #获取系统当前时间
drawDate(time.strftime('%Y-%m=%d+',t)
turtle.hideturtle()
turtle.done()
main()
画个时钟:
# coding=utf-8 import turtle
from datetime import * # 抬起画笔,向前运动一段距离放下
def Skip(step):
turtle.penup()
turtle.forward(step)
turtle.pendown() def mkHand(name, length):
# 注册Turtle形状,建立表针Turtle
turtle.reset()
Skip(-length * 0.1)
# 开始记录多边形的顶点。当前的乌龟位置是多边形的第一个顶点。
turtle.begin_poly()
turtle.forward(length * 1.1)
# 停止记录多边形的顶点。当前的乌龟位置是多边形的最后一个顶点。将与第一个顶点相连。
turtle.end_poly()
# 返回最后记录的多边形。
handForm = turtle.get_poly()
turtle.register_shape(name, handForm) def Init():
global secHand, minHand, hurHand, printer
# 重置Turtle指向北
turtle.mode("logo")
# 建立三个表针Turtle并初始化
mkHand("secHand", 135)
mkHand("minHand", 125)
mkHand("hurHand", 90)
secHand = turtle.Turtle()
secHand.shape("secHand")
minHand = turtle.Turtle()
minHand.shape("minHand")
hurHand = turtle.Turtle()
hurHand.shape("hurHand") for hand in secHand, minHand, hurHand:
hand.shapesize(1, 1, 3)
hand.speed(0) # 建立输出文字Turtle
printer = turtle.Turtle() # 隐藏画笔的turtle形状
printer.hideturtle()
printer.penup() def SetupClock(radius):
# 建立表的外框
turtle.reset()
turtle.pensize(7)
turtle.pencolor("#ff5500")
turtle.fillcolor("green") for i in range(60):
Skip(radius)
if i % 5 == 0:
turtle.forward(20)
Skip(-radius - 20) Skip(radius + 20)
if i == 0:
turtle.write(int(12), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
elif i == 30:
Skip(25)
turtle.write(int(i / 5), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
Skip(-25)
elif (i == 25 or i == 35):
Skip(20)
turtle.write(int(i / 5), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
Skip(-20)
else:
turtle.write(int(i / 5), align="center", font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
Skip(-radius - 20)
else:
turtle.dot(5)
Skip(-radius)
turtle.right(6) def Week(t):
week = ["星期一", "星期二", "星期三",
"星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日"]
return week[t.weekday()] def Date(t):
y = t.year
m = t.month
d = t.day
return "%s-%d-%d" % (y, m, d) def Tick():
# 绘制表针的动态显示
t = datetime.today()
second = t.second + t.microsecond * 0.000001
minute = t.minute + second / 60.0
hour = t.hour + minute / 60.0
secHand.setheading(6 * second)
minHand.setheading(6 * minute)
hurHand.setheading(30 * hour) turtle.tracer(False) printer.forward(65)
printer.write(Week(t), align="center",
font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
printer.back(130)
printer.write(Date(t), align="center",
font=("Courier", 14, "bold"))
printer.home()
turtle.tracer(True) # 100ms后继续调用tick
turtle.ontimer(Tick, 100) def main():
# 打开/关闭龟动画,并为更新图纸设置延迟。
turtle.tracer(False)
Init()
SetupClock(160)
turtle.tracer(True)
Tick()
turtle.mainloop() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()

绘制小猪佩奇:
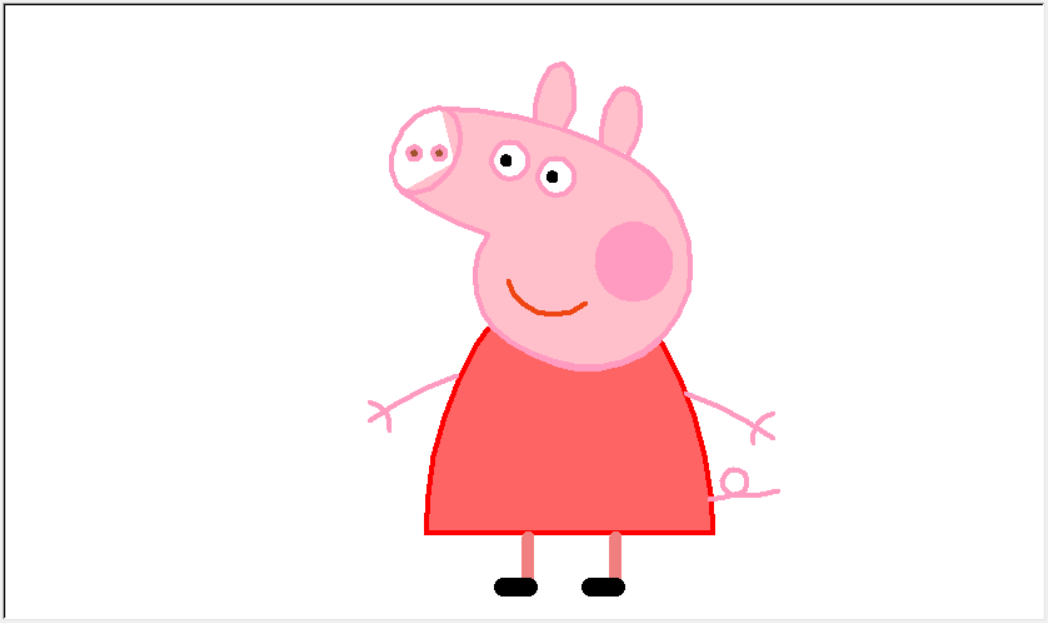

# coding:utf-8
import turtle as t
# 绘制小猪佩奇
# ======================================= t.pensize(4)
t.hideturtle()
t.colormode(255)
t.color((255, 155, 192), "pink")
t.setup(840, 500)
t.speed(10) # 鼻子
t.pu()
t.goto(-100,100)
t.pd()
t.seth(-30)
t.begin_fill()
a = 0.4
for i in range(120):
if 0 <= i < 30 or 60 <= i < 90:
a = a+0.08
t.lt(3) # 向左转3度
t.fd(a) # 向前走a的步长
else:
a = a-0.08
t.lt(3)
t.fd(a)
t.end_fill() t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(25)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(10)
t.pd()
t.pencolor(255, 155, 192)
t.seth(10)
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(5)
t.color(160, 82, 45)
t.end_fill() t.pu()
t.seth(0)
t.fd(20)
t.pd()
t.pencolor(255, 155, 192)
t.seth(10)
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(5)
t.color(160, 82, 45)
t.end_fill() # 头
t.color((255, 155, 192), "pink")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(41)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(0)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(180)
t.circle(300, -30)
t.circle(100, -60)
t.circle(80, -100)
t.circle(150, -20)
t.circle(60, -95)
t.seth(161)
t.circle(-300, 15)
t.pu()
t.goto(-100, 100)
t.pd()
t.seth(-30)
a = 0.4
for i in range(60):
if 0 <= i < 30 or 60 <= i <90:
a = a+0.08
t.lt(3) # 向左转3度
t.fd(a) # 向前走a的步长
else:
a = a-0.08
t.lt(3)
t.fd(a)
t.end_fill() # 耳朵
t.color((255, 155, 192), "pink")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-7)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(70)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(100)
t.circle(-50, 50)
t.circle(-10, 120)
t.circle(-50, 54)
t.end_fill() t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-12)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(30)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(100)
t.circle(-50, 50)
t.circle(-10, 120)
t.circle(-50, 56)
t.end_fill() #眼睛
t.color((255, 155, 192), "white")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-20)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-95)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(15)
t.end_fill() t.color("black")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(12)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-3)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(3)
t.end_fill() t.color((255, 155, 192), "white")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-25)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(40)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(15)
t.end_fill() t.color("black")
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(12)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-3)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(3)
t.end_fill() # 腮
t.color((255, 155, 192))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-95)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(65)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.circle(30)
t.end_fill() # 嘴
t.color(239, 69, 19)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(15)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-100)
t.pd()
t.seth(-80)
t.circle(30, 40)
t.circle(40, 80) # 身体
t.color("red", (255, 99, 71))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-20)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-78)
t.pd()
t.begin_fill()
t.seth(-130)
t.circle(100,10)
t.circle(300,30)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(230)
t.seth(90)
t.circle(300,30)
t.circle(100,3)
t.color((255,155,192),(255,100,100))
t.seth(-135)
t.circle(-80,63)
t.circle(-150,24)
t.end_fill() # 手
t.color((255,155,192))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-40)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-27)
t.pd()
t.seth(-160)
t.circle(300,15)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(15)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(0)
t.pd()
t.seth(-10)
t.circle(-20,90) t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(30)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(237)
t.pd()
t.seth(-20)
t.circle(-300,15)
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(20)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(0)
t.pd()
t.seth(-170)
t.circle(20,90) # 脚
t.pensize(10)
t.color((240,128,128))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(-75)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(-180)
t.pd()
t.seth(-90)
t.fd(40)
t.seth(-180)
t.color("black")
t.pensize(15)
t.fd(20) t.pensize(10)
t.color((240, 128, 128))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(40)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(90)
t.pd()
t.seth(-90)
t.fd(40)
t.seth(-180)
t.color("black")
t.pensize(15)
t.fd(20) # 尾巴
t.pensize(4)
t.color((255, 155, 192))
t.pu()
t.seth(90)
t.fd(70)
t.seth(0)
t.fd(95)
t.pd()
t.seth(0)
t.circle(70, 20)
t.circle(10, 330)
t.circle(70, 30)
t.done()
Python语言程序设计(3)--实例2-python蟒蛇绘制-turtle库的更多相关文章
- Python语言程序设计学习 之 了解Python
Python简介 Python是一种面向对象的解释型计算机程序设计语言,由荷兰人Guido van Rossum于1989年发明,第一个公开发行版发行于1991年. Python是纯粹的自由软件,源代 ...
- Python语言程序设计(1)--实例1和基本知识点
记录慕课大学课程<Python语言程序设计>的学习历程. 实例1:温度转换 #温度转换TempStr = input("请输入带有符号的温度值:") #TempStr是 ...
- 【任务】Python语言程序设计.MOOC学习
[博客导航] [Python导航] 任务 18年11月29日开始,通过9周时间跨度,投入约50小时时间,在19年1月25日之前,完成中国大学MOOC平台上的<Python语言程序设计>课程 ...
- 全国计算机等级考试二级Python语言程序设计考试大纲
全国计算机等级考试二级Python语言程序设计考试大纲(2018年版) 基本要求 掌握Python语言的基本语法规则. 掌握不少于2个基本的Python标准库. 掌握不少于2个Python第三方库,掌 ...
- Python语言程序设计之二--用turtle库画围棋棋盘和正、余弦函数图形
这篇笔记依然是在做<Python语言程序设计>第5章循环的习题.其中有两类问题需要记录下来. 第一是如何画围棋棋盘.围棋棋盘共有19纵19横.其中,位于(0,0)的星位叫天元,其余8个星位 ...
- Python语言程序设计之一--for循环中累加变量是否要清零
最近学到了Pyhton中循环这一章.之前也断断续续学过,但都只是到了函数这一章就停下来了,写过的代码虽然保存了下来,但是当时的思路和总结都没有记录下来,很可惜.这次我开通了博客,就是要把这些珍贵的学习 ...
- Python语言程序设计之三--列表List常见操作和错误总结
最近在学习列表,在这里卡住了很久,主要是课后习题太多,而且难度也不小.像我看的这本<Python语言程序设计>--梁勇著,列表和多维列表两章课后习题就有93道之多.我的天!但是题目出的非常 ...
- 【笔记】嵩天.Python语言程序设计.完成两个简单实例(温度转换和绘图)
[博客导航] [Python相关] 目标 使用PyCharm,完成两个小实例的编写和运行.一个是温度转换,一个是蟒蛇图形绘制. 过程 1.先设置project目录,虽然命名不是很正式,主要不太习惯软件 ...
- 【学习笔记】PYTHON语言程序设计(北理工 嵩天)
1 Python基本语法元素 1.1 程序设计基本方法 计算机发展历史上最重要的预测法则 摩尔定律:单位面积集成电路上可容纳晶体管数量约2年翻倍 cpu/gpu.内存.硬盘.电子产品价格等都遵 ...
随机推荐
- PyCharm的安装方法及设置中文界面
pycharm官网下载安装包:https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/#section=windows 下载中文语言包:https://github.co ...
- PostgreSQL的参数优化
硬件和软件信息 CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2683 v3 @ 2.00GHz 2 sockets / 28 cores / 56 threads内存: 256GB of ...
- 查看LINUX进程内存占用情况及启动时间
可以直接使用top命令后,查看%MEM的内容.可以选择按进程查看或者按用户查看,如想查看oracle用户的进程内存使用情况的话可以使用如下的命令: (1) top top命令是Linux下常用的性能分 ...
- LeetCode 187. 重复的DNA序列(Repeated DNA Sequences)
187. 重复的DNA序列 187. Repeated DNA Sequences 题目描述 All DNA is composed of a series of nucleotides abbrev ...
- 08 Spring框架的概念、优势、体系结构、耦合性和IOC(反转控制)
1.spring介绍 Spring 是分层的 Java SE/EE 应用 full-stack 轻量级开源框架,以 IoC(Inverse Of Control: 反转控制)和 AOP(Aspect ...
- 不借助其他任何软件防止QQ被盗的小技巧
分享一个小技巧(防止QQ被盗号): 在登录的时候前面加个0,点击登录,如果显示账号不存在,是因为你没有在添加或注册账号这儿登录,也就是切换账号.PC端也可以,如下图: ...
- tcpdump网络调试
简介 用简单的话来定义tcpdump,就是:dump the traffic on a network,根据使用者的定义对网络上的数据包进行截获的包分析工具. tcpdump可以将网络中传送的数据包的 ...
- linux查看进程与结束进程
查看所有进程 ps -ef ps -ef | grep 查找的进程名 结束进程 ps -ef | grep 查找的进程名 | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xar ...
- Java基础系列3:多线程超详细总结
该系列博文会告诉你如何从入门到进阶,一步步地学习Java基础知识,并上手进行实战,接着了解每个Java知识点背后的实现原理,更完整地了解整个Java技术体系,形成自己的知识框架. 1.线程概述 几乎所 ...
- SQL Server 索引优化-----数据库引擎优化顾问
本文将根据“数据库引擎优化顾问”(DTA)来发现无用或缺失的索引. 要使用“数据库引擎优化顾问”,首先需要对数据库负载进行监控,为数据库负载分析准备数据.从SSMS的工具中,打开SQL Server ...
