[LeetCode] 885. Spiral Matrix III 螺旋矩阵之三
On a 2 dimensional grid with `R` rows and `C` columns, we start at `(r0, c0)` facing east.
Here, the north-west corner of the grid is at the first row and column, and the south-east corner of the grid is at the last row and column.
Now, we walk in a clockwise spiral shape to visit every position in this grid.
Whenever we would move outside the boundary of the grid, we continue our walk outside the grid (but may return to the grid boundary later.)
Eventually, we reach all R * C spaces of the grid.
Return a list of coordinates representing the positions of the grid in the order they were visited.
Example 1:
Input: R = 1, C = 4, r0 = 0, c0 = 0
Output: [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]
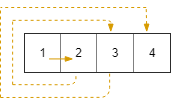
Example 2:
Input: R = 5, C = 6, r0 = 1, c0 = 4
Output: [[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]
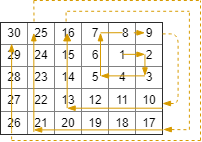
Note:
1 <= R <= 1001 <= C <= 1000 <= r0 < R0 <= c0 < C
这道题给了我们一个二维矩阵,还给了其中一个位置,让从这个位置开始搓一个螺旋丸,哦不,是螺旋打印矩阵。具体怎么螺旋打印呢,题目中给了例子,又给了示例图,真的是很贴心呢。可以看出来,首先是打印给定的位置,然后向右走一位,打印出来,再向下方走一位打印,再向左边走两位打印,再向上方走三位打印,以此类推,螺旋打印。那仔细观察,可以发现,刚开始只是走一步,后来步子越来越大,若只看每个方向走的距离,可以得到如下数组 1,1,2,2,3,3... 步长有了,下面就是方向了,由于确定了起始是向右走,那么方向就是 右->下->左->上 这样的循环。方向和步长都分析清楚了,现在就可以尝试进行遍历了。由于最终是会遍历完所有的位置的,那么最后结果 res 里面的位置个数一定是等于 RxC 的,所以循环的条件就是当结果 res 中的位置数小于 R*C。我们还需要一个变量 step 表示当前的步长,初始化为1。在循环中,首先要想右走 step 步,一步一步走,走到一个新的位置上,要进行判断,若当前位置没有越界,才能加入结果 res 中,由于每次都要判断,所以把这部分抽取出来,放到一个子函数中。由于是向右走,每走一步之后,c0 都要自增1。右边走完了之后,再向下方走 step 步,同理,每走一步之后,要将 r0 自增1。再向左边走之前,要将步数增1,不然无法形成正确的螺旋,同理,再完成向上方走 step 步之后,step 要再增1,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> spiralMatrixIII(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
int step = 1;
while (res.size() < R * C) {
for (int i = 0; i < step; ++i) add(R, C, r0, c0++, res);
for (int i = 0; i < step; ++i) add(R, C, r0++, c0, res);
++step;
for (int i = 0; i < step; ++i) add(R, C, r0, c0--, res);
for (int i = 0; i < step; ++i) add(R, C, r0--, c0, res);
++step;
}
return res;
}
void add(int R, int C, int x, int y, vector<vector<int>>& res) {
if (x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C) res.push_back({x, y});
}
};
上面的方法 for 循环太多,看的很木乱,可以用两个数组 dirX 和 dirY 来控制下一个方向,就像迷宫遍历中的那样,这样只需要一个变量 cur,来分别到 dirX 和 dirY 中取值,初始化为0,表示向右的方向。从螺旋遍历的机制可以看出,每当向右或者向左前进时,步长就要加1,那么我们只要判断当 cur 为0或者2的时候,step 就自增1。由于 cur 初始化为0,所以刚开始 step 就会增1,那么就可以将 step 初始化为0,同时还需要把起始位置提前加入结果 res 中。此时在 while 循环中只需要一个 for 循环即可,朝当前的 cur 方向前进 step 步,r0 加上 dirX[cur],c0 加上 dirY[cur],若没有越界,则加入结果 res 中即可。之后记得 cur 要自增1,为了防止越界,对4取余,就像循环数组一样的操作,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> spiralMatrixIII(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {
vector<vector<int>> res{{r0, c0}};
vector<int> dirX{0, 1, 0, -1}, dirY{1, 0, -1, 0};
int step = 0, cur = 0;
while (res.size() < R * C) {
if (cur == 0 || cur == 2) ++step;
for (int i = 0; i < step; ++i) {
r0 += dirX[cur]; c0 += dirY[cur];
if (r0 >= 0 && r0 < R && c0 >= 0 && c0 < C) res.push_back({r0, c0});
}
cur = (cur + 1) % 4;
}
return res;
}
};
我们也可以不使用方向数组,若仔细观察 右->下->左->上 四个方向对应的值 (0, 1) -> (1, 0) -> (0, -1) -> (-1, 0), 实际上,下一个位置的x值是当前的y值,下一个位置的y值是当前的-x值,因为两个方向是相邻的两个方向是垂直的,由向量的叉乘得到 (x, y, 0) × (0, 0, 1) = (y, -x, 0)。所以可以通过当前的x和y值,来计算出下一个位置的值。同理,根据之前的说的步长数组 1,1,2,2,3,3...,可以推出通项公式为 n/2 + 1,这样连步长变量 step 都省了,不过需要统计当前已经遍历的位置的个数,实在想偷懒,也可以用 res.size() 来代替,参见代码如下:
解法三:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> spiralMatrixIII(int R, int C, int r0, int c0) {
vector<vector<int>> res{{r0, c0}};
int x = 0, y = 1, t = 0;
for (int k = 0; res.size() < R * C; ++k) {
for (int i = 0; i < k / 2 + 1; ++i) {
r0 += x; c0 += y;
if (r0 >= 0 && r0 < R && c0 >= 0 && c0 < C) res.push_back({r0, c0});
}
t = x; x = y; y = -t;
}
return res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/885
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix-iii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix-iii/discuss/158970/C%2B%2BJavaPython-112233-Steps
[LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)](https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4606334.html)
[LeetCode] 885. Spiral Matrix III 螺旋矩阵之三的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 59. Spiral Matrix II 螺旋矩阵 II
Given an integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to n^2 in spiral order. For ...
- LeetCode 54. Spiral Matrix(螺旋矩阵)
Given a matrix of m x n elements (m rows, n columns), return all elements of the matrix in spiral or ...
- LeetCode 885. Spiral Matrix III
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix-iii/ 题目: On a 2 dimensional grid with R rows and ...
- 885. Spiral Matrix III
On a 2 dimensional grid with R rows and C columns, we start at (r0, c0) facing east. Here, the north ...
- [LeetCode] Spiral Matrix II 螺旋矩阵之二
Given an integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to n2 in spiral order. For ...
- [Leetcode] spiral matrix ii 螺旋矩阵
Given an integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to n 2 in spiral order. For ...
- PAT 1105 Spiral Matrix[模拟][螺旋矩阵][难]
1105 Spiral Matrix(25 分) This time your job is to fill a sequence of N positive integers into a spir ...
- [leetcode]59. Spiral Matrix II螺旋遍历矩阵2
Given a positive integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to n^2 in spiral or ...
- 【LeetCode】885. Spiral Matrix III 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 日期 题目地址:https://leetcode.c ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode1——两数之和
最近在家拧三阶魔方,把初级的玩法掌握了,也就是可以还原六个面了,速度不快,但是也很兴奋.三阶魔方的初级玩法按照套路拧就可以了,每一步需要完成的任务,该步骤转动的方法基本都是固定的,而且变化也并不是特别 ...
- Appium swipe实现屏幕滑动
在 Appium 中提供 swipe() 方法来模拟用户滑动屏幕. swipe() 实现过程 是先通过在屏幕上标记两个坐标,然后再从开始坐标移动到结束坐标. 先看下 swipe 方法定义: def s ...
- tornado的使用-日志篇
tornado的使用-日志篇
- 一小段 Dapper 的简单示例
关于 Dapper 的介绍,请参考:Dapper - 一款轻量级对象关系映射(ORM)组件,DotNet 下 using System; using System.Collections.Generi ...
- Spring源码系列 — 构造和初始化上下文
探索spring源码实现,精华的设计模式,各种jdk提供的陌生api,还有那么点黑科技都是一直以来想做的一件事!但是读源码是一件非常痛苦的事情,需要有很大的耐心和扎实的基础. 在曾经读两次失败的基础上 ...
- [ICP]手推SVD方法
该方法源于<Least-Squares Rigid Motion Using SVD>,原文推导十分详细,这里自己也仔细推导了一遍,有些地方加以注释整理. 问题定义 假设我们有两个点云集合 ...
- Asp.Net SignalR 使用记录
工作上遇到一个推送消息的功能的实现.本着面向百度编程的思想.网上百度了一大堆.主要的实现方式是原生的WebSocket,和SignalR,再次写一个关于Asp.Net SignalR 的demo 这里 ...
- Python - 数据结构 - 第十五天
Python 数据结构 本章节我们主要结合前面所学的知识点来介绍Python数据结构. 列表 Python中列表是可变的,这是它区别于字符串和元组的最重要的特点,一句话概括即:列表可以修改,而字符串和 ...
- Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel 读取 excel 中的 checkbox 和 radio
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; Excel.Application excelapp = new Excel.Application(); ...
- Docker install in Linux
install command sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 sudo yum-config-man ...
