201871010134-周英杰《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十四周学习总结
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
|
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
|
|
作业学习目标 |
(1)掌握GUI布局管理器用法; (2)掌握Java Swing文本输入组件用途及常用API; (3)掌握Java Swing选择输入组件用途及常用API。 |
第一部分:总结第十二章本周理论知识
(1)GUI布局管理器用法;
一>FlowLayout(流式布局)
1>特点:
a、流式布局会将组件按照顺序从左到右添加;
b、当一行排满后会自动换行。
2>构造方法:
FlowLayout( );
FlowLayout( int aligh );
FlowLayOut(int aligh,int hgap,int vgap);
其中,参数aligh决定组件在容器中的对其方式,可选的值为:
CENTER:居中对齐(默认方式);
LEFT:左对齐;
RIGHT:右对齐;
LEADING:与容器方向的开始边对齐;
TRAILING:与容器方向的结束边对齐;
二>BorderLayout(边界布局)
1>特点:
a、边界布局将容器划分为五个区域,分别为东(EAST)、南(SOUTH)、西(WEST)、北(NORTH)、中(CENTER);
b、容器大小调整时,边界布局NORTH和SOUTH区域高度不变长度跟随变化,EAST和WEST长度不变高度跟随变化;
c、容器添加组件时,需调用add(Component comp,Object constraints)方法,constraints可选值为BorderLayout类的五个常数:EAST、WEST、SOUTH、NORTH、CENTER;
2>构造方法:
BorderLayout( );
BorderLayout(int hgap ,int vgap);
参数hgap和vgap分别设定组件之间的水平和垂直间隙,默认值为5像素。
三>CardLayout(卡片布局)
1>特点:
a、卡片布局管理器将容器中的每个组件看作一张卡片,任何时候一次只能看到一张卡片,这张卡片占据整个容器;
b、卡片的顺序由组件对象本身在容器内部的顺序决定;
c、通过调用previous(Container parent),next(Container parent),show(Container parent,String name)方法来切换卡片。其中name参数可通过调用add(Component comp,Object constraints)方法来设定。
2>构造方法:
CardLayout( );
CardLayout(int hgap ,int vgap);
参数hgap和vgap分别设定组件之间的水平和垂直间隙,默认值为5像素。
四>GridLayout(网格布局)
1>特点:
a、网格布局将容器划分为n行m列大小相等的网格,一个网格只能放置一个组件,且各组件大小一样;
b、通过构造方法设定行数和列数为非零值时,指定的列数将被忽略,列数通过指定的行数和布局中的组件总数来确定;
c、网格布局添加组件的默认顺序为从左到右,从上到下;
2>构造方法:
GridLayout( );
GridLayout( int rows ,int cols );
GridLayOut(int rows , int cols,int hgap , int vgap);
参数rows和cols分别指定网格布局的行数和列数,参数hgap和vgap分别设定组件之间的水平和垂直间隙;
(2)Java Swing文本输入组件用途及常用API;
1>文本框(JTextField和JPasswordField)
JTextField组件用于创建文本框。文本框是用来接收用户的单行文本信息输入的区域。通常文本框用于接收用户信息或其他文本信息的输入。当用户输入文本信息后,如果为JTextField对象添加了事件处理,按回车键后就会触发一定的操作。
JPasswordField是JTextField的子类,是一种特殊的文本框,也是用来接收单行文本信息输入的区域,但是会用回显字符串代替输入的文本信息。因此,JPasswordField组件也称为密码文本框。JPasswordField默认的是回显字符是”*”,用户可以自行设置回显字符。
JTextField的常见构造方法有如下几种:
- JTextField():创建一个空文本框。
- JTextField(String text):创建一个具有出事文本信息text的文本框。
- JTextField(String text,int columns):创建一个具有出事文本信息text以及制定列数的文本框。
JTextField的常用方法:
- void setText(String):设置显示内容。
- String getText():获取显示内容。
JPasswordField的构造方法有如下几种:
- JPasswordField():创建一个空的密码文本框。
- JPasswordField(String text):创建一个指定初始文本信息的密码文本框。
- JPasswordField(String text,int columns):创建一个指定文本和列数的密码文本框。
- JPasswordField(int columns):创建一个指定列数的密码文本框。
JPasswordField是JTextField的子类,因此JPasswordField也具有与JTextField类似的名称和功能的方法,此外,它还具有与JTextField类似的名称和功能的方法,此外,它还具有自己的独特方法:
- boolean echoCharIsSet():获取设置回显字符的状态。
- void setEchoChar(char):设置回显字符。
- void getEchoChar():获取回显字符。
- char[] getPassword():获取组件的文本。
(3)掌握Java Swing选择输入组件用途及常用API。
1>单选按钮(JRadioButton)
JRadioButton组件实现的是一个单选按钮。JRadioButton类可以单独使用,也可以与ButtonGroup类联合使用,当单独使用时,该单选按钮可以被选定和取消选定;当与ButtonGroup类联合使用,需要使用add()方法将JRadioButton添加到ButtonGroup中,并组成一个单选按钮组。此时用户只能选定按钮组中的一个单选按钮。
JRadioButton组件的常用方法:
- setText(String text):设置单选按钮的标签文本。
- setSelected(boolean b):设置单选按钮的状态,默认情况下未被选中,当设为true时表示单选按钮被选中。
- add(AbatractButton b):添加按钮到按钮组中。
- remove(AbatractButton b):从按钮组中移除按钮。
- getButtonCount():返回按钮组中包含按钮的个数,返回值为int型。
- getElements():返回一个Enumeration类型的对象,通过该对象可以遍历按钮组中包含的所有按钮对象。
- isSelected():返回单选按钮的状态,当设为true时为选中。
- setSelected(boolean b):设定单选按钮的状态。
2>复选框(JCheckBox)
使用复选框可以完成多项选择。Swing中的复选框与awt中的复选框相比,优点是Swing复选框中可以添加图片。复选框可以为每一次的单击操作添加一个事件。
复选框的构造方法如下。
- JCheckBox(Icon icon):创建一个有图标,但未被选中的复选框。
- JCheckBox(Icon icon,boolean selected):创建一个有图标复选框,并且制定是否被选中。
- JCheckBox(String text):创建一个有文本,但未被选中的复选框。
- JCheckBox(String text,boolean selected):创建一个有文本复选框,并且制定是否被选中。
- JCheckBox(String text,Icon icon):创建一个指定文本和图标,但未被选中的复选框。
- JCheckBox(String text,Icon icon,boolean selected):创建一个指定文本和图标,并且制定是否被选中的复选框。
常用方法:
- public boolean isSelected():返回复选框状态,true时为选中。
- public void setSelected(boolean b):设定复选框状态。
3>组合框(JComboBox)
JComboBox组件用来创建组合框对象。通常,根据组合框是否可编辑的状态,可以将组合框分成两种常见的外观。可编辑状态外观可视为文本框和下拉列表的组合,不可编辑状态的外观可视为按钮和下拉列表的组合。在按钮或文本框的右边有一个带三角符号的下拉按钮,用户可以单击该下拉按钮,便可出现一个内容列表,这也是组合框的得名。组合框通常用于从列表的”多个项目中选择一个”的操作。
JComboBox的构造方法有如下几种:
- JComboBox():创建一个默认模型的组合框。
- JComboBox(ComboBoxModel aModel):创建一个指定模型的组合框。
JComboBox(Object[] items):创建一个具有数组定义列表内容的组合框。
第二部分:实验部分
实验1:测试程序1
测试代码:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A panel with calculator buttons and a result display.
*/
public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel
{
private JButton display;
private JPanel panel;
private double result;
private String lastCommand;
private boolean start; public CalculatorPanel()
{
setLayout(new BorderLayout()); result = 0;
lastCommand = "=";
start = true; // add the display display = new JButton("0");
display.setEnabled(false);
add(display, BorderLayout.NORTH); var insert = new InsertAction();
var command = new CommandAction(); // add the buttons in a 4 x 4 grid panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4));
panel.setLocation(200, 300);; addButton("7", insert);
addButton("8", insert);
addButton("9", insert);
addButton("/", command); addButton("4", insert);
addButton("5", insert);
addButton("6", insert);
addButton("*", command); addButton("1", insert);
addButton("2", insert);
addButton("3", insert);
addButton("-", command); addButton("0", insert);
addButton(".", insert);
addButton("=", command);
addButton("+", command); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
} /**
* Adds a button to the center panel.
* @param label the button label
* @param listener the button listener
*/
private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener)
{
var button = new JButton(label);
button.addActionListener(listener);
panel.add(button);
} /**
* This action inserts the button action string to the end of the display text.
*/
private class InsertAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String input = event.getActionCommand();
if (start)
{
display.setText("");
start = false;
}
display.setText(display.getText() + input);
}
} /**
* This action executes the command that the button action string denotes.
*/
private class CommandAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String command = event.getActionCommand(); if (start)
{
if (command.equals("-"))
{
display.setText(command);
start = false;
}
else lastCommand = command;
}
else
{
calculate(Double.parseDouble(display.getText()));
lastCommand = command;
start = true;
}
}
} /**
* Carries out the pending calculation.
* @param x the value to be accumulated with the prior result.
*/
public void calculate(double x)
{
if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x;
display.setText("" + result);
}
}
运行结果:
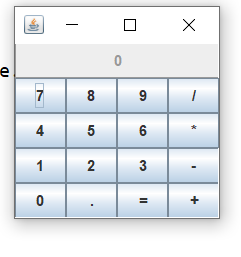
实验1:测试程序2
实验代码:
运行结果:

实验1:测试程序3
实验代码:
package checkBox; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A frame with a sample text label and check boxes for selecting font
* attributes.
*/
public class CheckBoxFrame extends JFrame
{
private JLabel label;
private JCheckBox bold;
private JCheckBox italic;
private static final int FONTSIZE = 24; public CheckBoxFrame()
{
// add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, FONTSIZE));
add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // this listener sets the font attribute of
// the label to the check box state ActionListener listener = event -> {
int mode = 0;
if (bold.isSelected()) mode += Font.BOLD;
if (italic.isSelected()) mode += Font.ITALIC;
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", mode, FONTSIZE));
}; // add the check boxes var buttonPanel = new JPanel(); bold = new JCheckBox("Bold");
bold.addActionListener(listener);
bold.setSelected(true);
buttonPanel.add(bold); italic = new JCheckBox("Italic");
italic.addActionListener(listener);
buttonPanel.add(italic); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
}
CheckBoxFrame
运行结果:
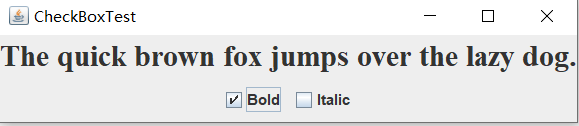
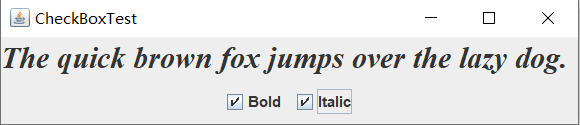
实验1:测试程序4
运行代码:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A frame with a sample text label and radio buttons for selecting font sizes.
*/
public class RadioButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private ButtonGroup group;
private JLabel label;
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 36; public RadioButtonFrame()
{
// add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));
add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // add the radio buttons buttonPanel = new JPanel();
group = new ButtonGroup(); addRadioButton("Small", 8);
addRadioButton("Medium", 12);
addRadioButton("Large", 18);
addRadioButton("Extra large", 36); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
} /**
* Adds a radio button that sets the font size of the sample text.
* @param name the string to appear on the button
* @param size the font size that this button sets
*/
public void addRadioButton(String name, int size)
{
boolean selected = size == DEFAULT_SIZE;
var button = new JRadioButton(name, selected);
group.add(button);
buttonPanel.add(button); // this listener sets the label font size ActionListener listener = event -> label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, size)); button.addActionListener(listener);
}
}
RadioButtonFrame
运行结果:
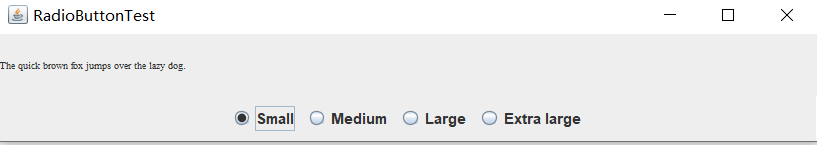

实验1:测试程序5
实验代码:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.*; /**
* A frame with radio buttons to pick a border style.
*/
public class BorderFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel demoPanel;
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private ButtonGroup group; public BorderFrame()
{
demoPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
group = new ButtonGroup(); addRadioButton("Lowered bevel", BorderFactory.createLoweredBevelBorder());
addRadioButton("Raised bevel", BorderFactory.createRaisedBevelBorder());
addRadioButton("Etched", BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());
addRadioButton("Line", BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.BLUE));
addRadioButton("Matte", BorderFactory.createMatteBorder(10, 10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE));
addRadioButton("Empty", BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder()); Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder();
Border titled = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched, "Border types");
buttonPanel.setBorder(titled); setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1));
add(buttonPanel);
add(demoPanel);
pack();
} public void addRadioButton(String buttonName, Border b)
{
var button = new JRadioButton(buttonName);
button.addActionListener(event -> demoPanel.setBorder(b));
group.add(button);
buttonPanel.add(button);
}
}
BorderFrame
运行结果:

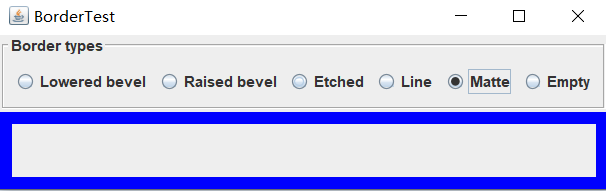
实验1:测试程序6
实验代码:
package comboBox; import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Font; import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel; /**
* A frame with a sample text label and a combo box for selecting font faces.
*/
public class ComboBoxFrame extends JFrame
{
private JComboBox<String> faceCombo;
private JLabel label;
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 24; public ComboBoxFrame()
{
// add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));
add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // make a combo box and add face names faceCombo = new JComboBox<>();
faceCombo.addItem("Serif");
faceCombo.addItem("SansSerif");
faceCombo.addItem("Monospaced");
faceCombo.addItem("Dialog");
faceCombo.addItem("DialogInput"); // the combo box listener changes the label font to the selected face name faceCombo.addActionListener(event ->
label.setFont(
new Font(faceCombo.getItemAt(faceCombo.getSelectedIndex()),
Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE))); // add combo box to a panel at the frame's southern border var comboPanel = new JPanel();
comboPanel.add(faceCombo);
add(comboPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
}
}
ComboBoxFrame
运行结果:
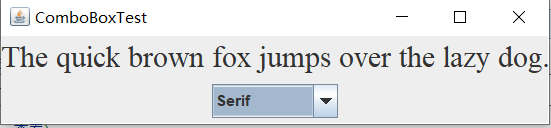

实验2:结对编程练习包含以下4部分:
1) 程序设计思路简述;
运用GridLayout布局,北边放JTextField(用以处理姓名和地址)以及JLabel,还有性别按钮(此为单选按钮用以处理性别选择)和爱好按钮(此为复选按钮用以处理爱好选择),南边放一个JTextArea(用以打印提交后的信息显示),总归就是把前几个示例代码糅合在一起写出来的。
2) 程序代码;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.BorderFactory;
import javax.swing.ButtonGroup;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JCheckBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JRadioButton;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.border.Border; public class GUIFrame extends JFrame{
public GUIFrame() {
setSize(500,380); JPanel northPanel = new JPanel(); //北面
add(northPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH);
//northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,4)); JLabel nameLabel = new JLabel("姓名:",JLabel.RIGHT);
JTextField nameText = new JTextField(8);
JLabel adressLabel = new JLabel("地址:",JLabel.RIGHT);
JTextField adressText = new JTextField(15);
northPanel.add(nameLabel);
northPanel.add(nameText);
northPanel.add(adressLabel);
northPanel.add(adressText); JPanel centerPanel = new JPanel();
centerPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,1));
add(centerPanel,BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel blankPanel = new JPanel();
centerPanel.add(blankPanel); JPanel choosePanel = new JPanel();
choosePanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
centerPanel.add(choosePanel);
choosePanel.setSize(100,100); JPanel sexPanel = new JPanel(); //性别按钮
choosePanel.add(sexPanel);
Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder();
Border titled1 = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched,"性别");
sexPanel.setBorder(titled1);
ButtonGroup sexGroup = new ButtonGroup();
JRadioButton manButton = new JRadioButton("男",true);
sexGroup.add(manButton);
JRadioButton womenButton = new JRadioButton("女",false);
sexGroup.add(womenButton);
sexPanel.add(manButton);
sexPanel.add(womenButton); JPanel hobbyPanel = new JPanel(); //爱好按钮
choosePanel.add(hobbyPanel);
Border titled2 = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched,"爱好");
hobbyPanel.setBorder(titled2);
JCheckBox read = new JCheckBox("阅读");
JCheckBox sing = new JCheckBox("唱歌");
JCheckBox dance = new JCheckBox("跳舞");
hobbyPanel.add(read);
hobbyPanel.add(sing);
hobbyPanel.add(dance); JPanel ButtonPanel = new JPanel();
centerPanel.add(ButtonPanel);
JButton submit = new JButton("提交");
JButton reset = new JButton("重置");
ButtonPanel.add(submit);
ButtonPanel.add(reset); JTextArea southText = new JTextArea("录入信息显示区!",6,10); //南面
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(southText); //滚动
southText.setLineWrap(true);
add(scrollPane,BorderLayout.SOUTH); submit.addActionListener(event->{ //按钮监听器
String hobby="";
if(read.isSelected())
hobby=hobby+"阅读 ";
if(sing.isSelected())
hobby=hobby+"唱歌 ";
if(dance.isSelected())
hobby=hobby+"跳舞 "; String sex="";
if(manButton.isSelected())
sex="男";
else
sex="女";
if(southText.getText().equals("录入信息显示区!")) //清空默认值
southText.setText("");
southText.append("姓名:"+nameText.getText()+" 地址:"+adressText.getText()+" 性别:"+sex+" 爱好:"+hobby+"\n");
}); reset.addActionListener(event->{
southText.setText("");
nameText.setText("");
adressText.setText("");
});
}
}
GUIFrame
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new GUIFrame();
frame.setTitle("UserGUITest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
main
3) 程序运行功能界面截图;
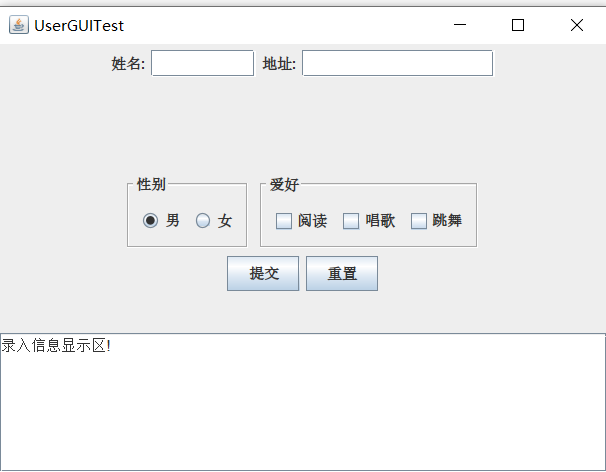
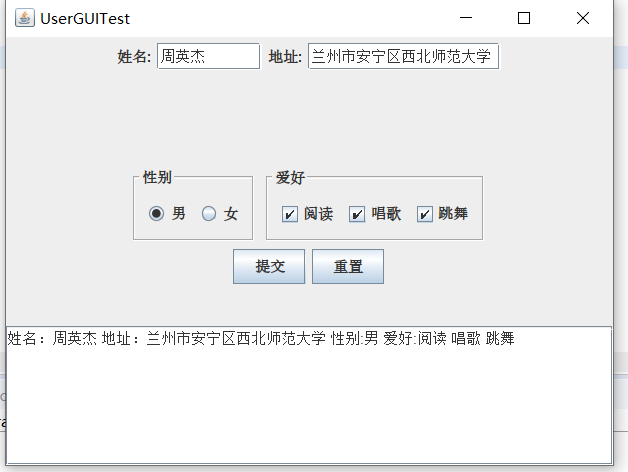
4) 结对过程描述及结对照片(非摆拍)。

实验总结:
通过上一周的学习我们学到了GUI布局管理器用法;和Java Swing文本输入组件用途及常用API;以及Java Swing选择输入组件用途及常用API。GUI布局管理器总共学了4种,分别是流式布局,边界布局,卡片布局以及网格布局;而在Java Swing文本输入组件中学到了TextFile以及PassWord;在Java Swing选择输入组件中学到了,单选按钮,复选框,组合框等;以及上面一改的用法都有了大致的了解;最后,在结对编程的题目中我将前面的测试程序糅合在一起写了这个程序,目前看来还是可以的,以后我要更加的努力了,争取把以前拉下的补回来。

201871010134-周英杰《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十四周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201521123061 《Java程序设计》第十四周学习总结
201521123061 <Java程序设计>第十四周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多数据库相关内容. 2. 书面作业 1. MySQL数据 ...
- 201521123072《java程序设计》第十四周学习总结
201521123072<java程序设计>第十四周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多数据库相关内容. 2. 书面作业 1. MySQL数据库 ...
- 201521123038 《Java程序设计》 第十四周学习总结
201521123038 <Java程序设计> 第十四周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多数据库相关内容. 接口: DriverManager ...
- 201521123122 《java程序设计》第十四周学习总结
## 201521123122 <java程序设计>第十四周实验总结 ## 1. 本周学习总结 1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多数据库相关内容. 2. 书面作业 1. M ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计Java》第四周总结学习
2019面向对象程序设计(Java)第4周学习指导及要求 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 <任课教师博客主页链接>https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ ...
- 汪慧和201771010123《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第四周实验总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.类 类(class)是具有相同属性和行为的一组对象的集合,是构造程序的基本单元,是构造对象的模板或蓝图. 2.对象 对象:即数据,对象有三个特性——1.行为 2.状态 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 201621123040《Java程序设计》第十四周学习总结
1.本周学习总结 1.1以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结与数据库相关内容. 显示所有数据库: show databases; 创建数据库: create database test; 删除数据 ...
随机推荐
- day54_9_18视图层某内部原理(fbv和cbv)与模板层
一.render内部原理. 在render中往往需要返回三个参数,request,模板和一些键值对. 键值对中存储的是需要对模板渲染的值. 如果手动实现可以如下: from django.templa ...
- C++ 回调函数 Callback 机制例程
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> #include <Windows.h> ...
- Python IO 模式
IO 模式 对于 Linux 的 network IO: 一次 IO 访问(以read举例),数据会先被拷贝到操作系统内核的缓冲区中,然后才会从操作系统内核的缓冲区 copy 到应用程序的地址空间.所 ...
- 2019 SDN上机第二次作业
2019 SDN上机第二次作业 1.利用mininet创建如下拓扑,要求拓扑支持OpenFlow 1.3协议,主机名.交换机名以及端口对应正确,请给出拓扑Mininet执行结果,展示端口连接情况 1. ...
- Oracle中如何创建数据库
Oracle数据库的物理结构与MySQL以及SQLServer有着很大的不同.在使用MySQL或SQLServer时,我们不需要去关心它们的逻辑结构和物理结构. 但是在使用Oracle的时候,我们必须 ...
- svn merge操作
使用SVN做Merge操作时,会包含6个选项,下面就这6个选项给出详细的说明: 1.Merge a range of revisions 此类型应用最为广泛,主要是把源分支中的修改合并到目标分支上来. ...
- (二十八)golang--二维数组
初始化: var array [2][3]int = [2][3]int{{0,0,0},{0,0,0}} var array [2][3]int = [...][3]int{{0,0,0},{0,0 ...
- 优雅的解决springboot Aop @Cacheable this不生效
问题描述:在同一个类中springAop不生效,例如在同一个类中没有 @Cacheable的方法调用本类有 @Cacheable的方法,则缓存不会设置. 原因:springaop基于java prox ...
- Worker Services的新项目模板
.NET Core3.0创建Worker Services2019-10-24 09:05 成天 阅读(1438) 评论(20) 编辑收藏 .NET CORE 3.0新增了Worker Ser ...
- springboot 1.4 CXF配置
启动类: package com.eshore.main; import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector; import org.apache.coyo ...
