曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
写在前面的话&&About me
网上写spring的文章多如牛毛,为什么还要写呢,因为,很简单,那是人家写的;网上都鼓励你不要造轮子,为什么你还要造呢,因为,那不是你造的。
我不是要造spring,我只是想把自己学习spring的一些感想,一些心得说出来,希望大家看到有不对的地方,请一定不吝赐教。
说说我自己,13年小本毕业,软件工程专业,校招去了最近疯传的牢厂总部里待了2年,15年越狱出来,某落魄互联网公司(PC时代风头无两)待了1年,慨叹深圳买房之艰难,遂于16年底回蓉。趁着热血未冷,去了一家创业公司,9个月后,欠薪3月,靠刷信用卡还贷,不得不含泪辞职;17年投奔国企,目前从事公共安全相关工作,趁着对技术还有一腔热情,没事写写文章,目前主要兴趣是:分布式、微服务等后端技术;对k8s等新技术保持关注;没事参加一些线下技术活动,欢迎大家和我交流。
本系列的源码讲解思路
本来,我是想分享一些 spring cloud 的东西,但后来发现,我自己在读spring cloud的过程中,有些东西也不是理解得很透彻,比如各种@Enable注解其实是用到了spring boot的东西,然后我觉得应该倒回去先看看spring boot,然后呢,看spring boot的过程中,发现spring 和 spring boot其实是一个深度融合,“你中有我,我中有你”的关系,比如spring boot启动时,不是会连带启动spring 容器吗,等等。
我就想着,干脆把spring boot系统研究一把算了,我在github上找了spring boot的工程,克隆到了码云上(速度要快得多),然后自己回退到了spring boot的第一个版本,时间大概是2013年4月,其实这第一个版本,基本的代码也已经成型了,我就拿这个版本的源码在本地idea里面看,配套的spring 版本是4.0.0,也还行。
我自己加了不少注释在工程里,工程地址在这:
https://gitee.com/ckl111/spring-boot-first-version-learn
工程结构如下:

这个工程我也会一直维护着,我觉得,spring 4.0.0的版本,暂时对我阅读代码来说,足够了,如果大家大概了解spring 每个版本的新特性的话,可以发现,spring 4.0开始,各种注解已经很完善了,现在虽然已经出到5.2版本了,但核心的东西也还是没有变化,所以,对我们研读源码,影响不大。如果真的把这个版本能读得差不多了,那想必对spring /spring boot的核心也理解差不多了,到时候再读新版本的源码也不迟,是吧。
总体来说:
spring boot 版本,2013年4月,first version。
配套的spring版本,4.0.0.BOOTSTRAP-SNAPSHOT
那时候的spring boot长什么样子,我这边给个地址(我这已经克隆到码云了)
https://gitee.com/ckl111/spring-boot/tree/fb6b2244707dd5dfad12d62cb6a3c396555270d1/
目前已更新的部分
曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
曹工说Spring Boot源码(6)-- Spring怎么从xml文件里解析bean的
曹工说Spring Boot源码(7)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(10)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:annotation-config 解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(11)-- context:component-scan,你真的会用吗(这次来说说它的奇技淫巧)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(12)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:component-scan完整解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(13)-- AspectJ的运行时织入(Load-Time-Weaving),基本内容是讲清楚了(附源码)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(14)-- AspectJ的Load-Time-Weaving的两种实现方式细细讲解,以及怎么和Spring Instrumentation集成
曹工说Spring Boot源码(15)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(context:load-time-weaver 完整解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(16)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(aop:config完整解析【上】)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(17)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(aop:config完整解析【中】)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(18)-- Spring AOP源码分析三部曲,终于快讲完了 (aop:config完整解析【下】)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(19)-- Spring 带给我们的工具利器,创建代理不用愁(ProxyFactory)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(20)-- 码网恢恢,疏而不漏,如何记录Spring RedisTemplate每次操作日志
曹工说Spring Boot源码(21)-- 为了让大家理解Spring Aop利器ProxyFactory,我已经拼了
曹工说Spring Boot源码(22)-- 你说我Spring Aop依赖AspectJ,我依赖它什么了
曹工说Spring Boot源码(23)-- ASM又立功了,Spring原来是这么递归获取注解的元注解的
曹工说Spring Boot源码(24)-- Spring注解扫描的瑞士军刀,asm技术实战(上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(25)-- Spring注解扫描的瑞士军刀,ASM + Java Instrumentation,顺便提提Jar包破解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(26)-- 学习字节码也太难了,实在不能忍受了,写了个小小的字节码执行引擎
曹工说Spring Boot源码(27)-- Spring的component-scan,光是include-filter属性的各种配置方式,就够玩半天了
spring思维导图(bean definition部分)
因为我这个系列,大概会按照思维导图的流程来走,然后思维导图太大了,我这里先直接贴前面这部分:
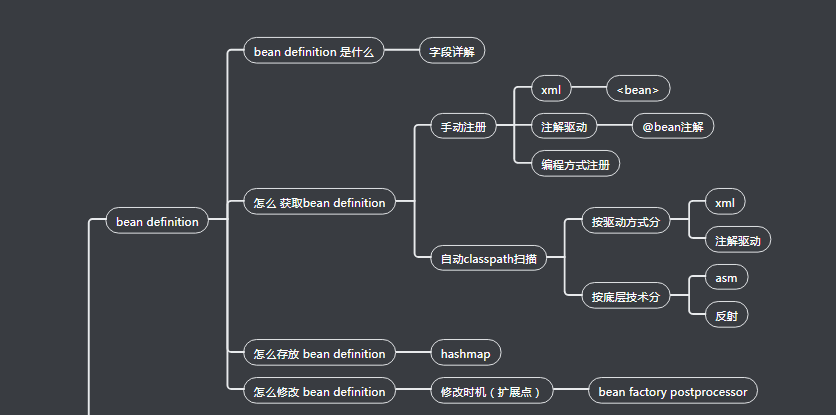
思维导图完整链接:https://www.processon.com/view/link/5deeefdee4b0e2c298aa5596
我大概的讲解思路也会是上面那样,从上到下,每个点细细地讲。
正文
bean definition是什么
闲言少叙,进入正题。第一讲,先说说bean definition吧,这个东西,实在太重要了,核心的存储结构啊。
大家可以再想一想,spring 当初刚出来的时候,主打的是ioc容器,容器里装了啥呢,bean啊!bean是什么呢?
恩。。。我也不知道是啥,反正spring里拿出来的就是bean。
行,那bean有什么特征吗?
哦,bean是一个对象,有名字,有class类型,有scope(单例、prototype那些),有role(属于应用的bean、还是spring框架的bean),有是否延迟初始化(lazy-init),有它依赖的其他bean,如果这个bean不好造(不能直接反射生成的话),可能还有个工厂方法和工厂bean呢,哎,好像还说漏了,反正挺多的。
那是不是每个bean都有这些属性呢?
仔细想想,好像是的吧。
既然都有这些东西,那这个东西感觉像是个模板了,就像是最近写了年终总结,hr小姐姐就给我们发了模板,上面姓名啊、部门啊、职位啊、述职的基本格式啊,都是固定的,我们只要拿来,填上自己的信息就行了,那我们是不是可以抽象一下,搞个class啊,比如下面这样:
package com.learn;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class SpringDefinition {
/**
* bean class名
*/
String beanClassName;
/**
* 工厂bean的名称
*/
String factoryBeanName;
/**
* 工厂方法的名称
*/
String factoryMethodName;
/**
* singleton/prototype等
*/
String scope;
/**
* 是否延迟初始化
*/
boolean isLazyInit;
/**
* 依赖的bean
*/
String[] dependsOn;
/**
* bean的角色,比如:1:框架;2:应用
*/
int role;
/**
* 是否为主候选bean
*/
boolean primary;
...其他属性
}
实话说,是可以的,一些简单的,轻量级ioc容器就是这么玩的,但是spring作为优秀代码的代表,肯定不能这么low,接口的抽象性要好得多,方便我们替换不同的实现,该用接口来抽象,肯定要抽象为接口。
下边我们就看看该接口,先看接口的描述:
* A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values,
* constructor argument values, and further information supplied by
* concrete implementations.
*
* <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} such as {@link PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer}
* to introspect and modify property values and other bean metadata.
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 19.03.2004
这里说的是,bean definition描述一个bean实例的各种属性,尤其声明了:这是一个最小化接口,主要目的是允许bean factory后置处理器,对bean property和其他元数据进行修改。而且,这是2004年的接口,可想而知,是多么核心的api了。
再看看具体定义的方法,更好理解:
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
String getParentName();
/**
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
void setParentName(String parentName);
/**
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
*/
String getBeanClassName();
/**
* Override the bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
*/
void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName);
/**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
String getFactoryBeanName();
/**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(String factoryBeanName);
/**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
String getFactoryMethodName();
/**
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* @param factoryMethodName static factory method name,
* or {@code null} if normal constructor creation should be used
* @see #getBeanClassName()
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(String factoryMethodName);
/**
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
String getScope();
/**
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(String scope);
/**
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
boolean isLazyInit();
/**
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
/**
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
String[] getDependsOn();
/**
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
*/
void setDependsOn(String[] dependsOn);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* If this value is true for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
boolean isPrimary();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is true for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
/**
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
/**
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton();
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype();
/**
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
*/
boolean isAbstract();
/**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides tools with an indication of the importance of a particular
* {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
*/
int getRole();
/**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
String getDescription();
/**
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
String getResourceDescription();
/**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
大家仔细看看,是不是其实和我们定义的class差不多呢,主要都是一些get/set方法。里面的字段呢,下一讲我们详细讲解一下,会结合一些融会贯通的地方。
bean definition接口的实现有哪些
然后我们看看这个接口有哪些实现吧?
可以看到,这里有两个是我标红了,因为他们特殊,特殊在他们不属于spring-beans包,而是在spring-context包里。后边遇到了我们再单说,这里存疑。
再来看看这个接口的继承图:
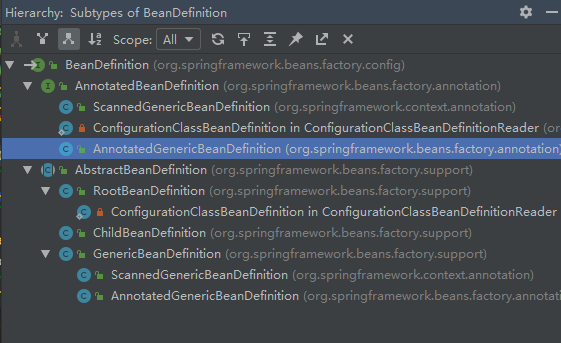
可以获取注解信息的子接口AnnotatedBeanDefinition
我们看到,这个接口有一个子接口,是AnnotatedBeanDefinition。这个接口定义如下:
/**
* Extended {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition}
* interface that exposes {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata}
* about its bean class - without requiring the class to be loaded yet.
* 这个接口扩展了BeanDefinition,可以获得bean definition中的bean class上的注解元数据。
* 举个例子,假设我们用@controller标注了某个类,那这里就能获取到@controller这个注解里面的信息
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.5
* @see AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata
*/
public interface AnnotatedBeanDefinition extends BeanDefinition {
/**
* Obtain the annotation metadata (as well as basic class metadata)
* for this bean definition's bean class.
* @return the annotation metadata object (never {@code null})
*/
AnnotationMetadata getMetadata();
}
可以想一想有什么用,这个接口能取到bean definition中对应bean class上标注的注解元数据。
比如下面的controller举例:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
/**
* The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
* to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component.
* @return the suggested component name, if any
*/
String value() default "";
}
那这个AnnotatedBeanDefinition就能取到controller中的value字段的值。
我这里也写了个简单的例子,如下:
@Component("testService")
public class HelloWorldService {
}
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory =
(DefaultListableBeanFactory) applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory();
// 获取bean definition,然后获取其注解元数据
AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("testService");
AnnotationMetadata metadata = annotatedBeanDefinition.getMetadata();
Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes("org.springframework.stereotype.Component");
log.info("annotationAttributes:{}",annotationAttributes);
}
我这边打印出来就是:
信息: annotationAttributes:{value=testService}
代码在
接口下的实现类
仔细看了两个接口 AnnotatedBeanDefinition和BeanDefinition,其实实现类都是差不多那几个。

基本上org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition充当了基本的实现,基本上,该实现的方法都实现了,除了一个:
/**
* Clone this bean definition.
* To be implemented by concrete subclasses.
* @return the cloned bean definition object
*/
public abstract AbstractBeanDefinition cloneBeanDefinition();
赶紧这个方法,对我们分析也没多大帮助,暂时跳过即可。
再看看org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition,感觉很重要,我们看看:
public class GenericBeanDefinition extends AbstractBeanDefinition {
private String parentName;
/**
* 这里有点意思,类似于builder模式,先生成一个实例,再自己各种set方法设置相关属性
*
* Create a new GenericBeanDefinition, to be configured through its bean
* properties and configuration methods.
* @see #setBeanClass
* @see #setBeanClassName
* @see #setScope
* @see #setAutowireMode
* @see #setDependencyCheck
* @see #setConstructorArgumentValues
* @see #setPropertyValues
*/
public GenericBeanDefinition() {
super();
}
...
@Override
public AbstractBeanDefinition cloneBeanDefinition() {
return new GenericBeanDefinition(this);
}
}
ok,都这么简单的话,就再看两个,spring beans包中的org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition:
public class AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition {
private final AnnotationMetadata metadata;
/**
* Create a new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition for the given bean class.
* @param beanClass the loaded bean class
*/
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(Class<?> beanClass) {
setBeanClass(beanClass);
this.metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(beanClass, true);
}
/**
* Create a new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition for the given annotation metadata,
* allowing for ASM-based processing and avoidance of early loading of the bean class.
* Note that this constructor is functionally equivalent to
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.ScannedGenericBeanDefinition
* ScannedGenericBeanDefinition}, however the semantics of the latter indicate that
* a bean was discovered specifically via component-scanning as opposed to other
* means.
* @param metadata the annotation metadata for the bean class in question
* @since 3.1.1
*/
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
Assert.notNull(metadata, "AnnotationMetadata must not be null");
setBeanClassName(metadata.getClassName());
this.metadata = metadata;
}
public final AnnotationMetadata getMetadata() {
return this.metadata;
}
}
很简单,就是多了获取bean class的注解的功能。
再看这个呢,
/**
* Extension of the {@link GenericBeanDefinition}
* class, based on an ASM ClassReader, with support for annotation metadata exposed
* through the {@link AnnotatedBeanDefinition} interface.
*
* <p>This class does <i>not</i> load the bean {@code Class} early.
* It rather retrieves all relevant metadata from the ".class" file itself,
* parsed with the ASM ClassReader. It is functionally equivalent to
* {@link AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition#AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(AnnotationMetadata)}
* but distinguishes by type beans that have been <em>scanned</em> vs those that have
* been otherwise registered or detected by other means.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 2.5
* @see #getMetadata()
* @see #getBeanClassName()
* @see org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory
* @see AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class ScannedGenericBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition {
private final AnnotationMetadata metadata;
/**
* Create a new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition for the class that the
* given MetadataReader describes.
* @param metadataReader the MetadataReader for the scanned target class
*/
public ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
Assert.notNull(metadataReader, "MetadataReader must not be null");
this.metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
setBeanClassName(this.metadata.getClassName());
}
public final AnnotationMetadata getMetadata() {
return this.metadata;
}
}
我一开始,一眼看过去,感觉眼花了,差不多啊,但这个是在spring context包里,然后,可以看上面的注释,说是使用asm去获取注解信息。所以,这个和上面那个的差别是:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ScannedGenericBeanDefinition 位于spring-context,使用asm
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition 位于spring-beans,使用反射
再看看org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition(位于spring-beans),这个类下面只有一个子类,位于spring-context的
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition
这两个类,一看就比较特别,能看出来,和@configuration注解有莫大关系,这个我们放后面讲。
总结
本篇就先到这里,留了一些问题,放到后面(有些我也要查一下,哈哈)。下一讲继续。
曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot源码(六):Bean的创建详解
继续之前的项目: People加上无参构造方法: @Component public class People { // private User user; public People(){ Sys ...
- Spring Boot源码(四):Bean装配
为了演示Spring中对象是如何创建并放到spring容器中,这里新建一个maven项目: 其中pom.xm文件中只引入了一个依赖: <dependencies> <dependen ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 正 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 大 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 大 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(23)-- ASM又立功了,Spring原来是这么递归获取注解的元注解的
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 精尽Spring Boot源码分析 - 文章导读
该系列文章是笔者在学习 Spring Boot 过程中总结下来的,里面涉及到相关源码,可能对读者不太友好,请结合我的源码注释 Spring Boot 源码分析 GitHub 地址 进行阅读 Sprin ...
- Spring Boot源码(八):Spring AOP源码
关于spring aop的应用参见:Spring AOP-基于@AspectJ风格 spring在初始化容器时就会生成代理对象: 关于创建bean的源码参见:Spring Boot源码(六):Bean ...
随机推荐
- kubernetes的ingress-nginx
这是一篇学习记录.记录kubernetes集群中如何将jenkins服务通过域名接入外部.由于是测试环境,域名是自定义的,解析写在/etc/hosts和自己本地的hosts中. 部署图: 一.部署后端 ...
- nyoj 266-字符串逆序输出 (isdigit(), geline(cin, my_string))
266-字符串逆序输出 内存限制:64MB 时间限制:3000ms 特判: No 通过数:15 提交数:18 难度:0 题目描述: 给定一行字符,逆序输出此行(空格.数字不输出) 输入描述: 第一行是 ...
- (二十九)golang--map
map:是key-value数据结构,又称为字段或者关联数组,类似其它编程语言的集合: 基本语法:var 名称 map[键类型]值类型 key的类型可以是:bool.数字.string.指针.管道,还 ...
- 用户环境变量 shell变量 别名
常见用户环境变量: 环境变量 说明 LANG HOME LOGNAME 用户名 PATH SHELL PWD 查看环境变量用:env或者echo $LANG 设置用户环境变量:ex ...
- Win32 COM组件 x Android Service
有些书在介绍和讲解android的Service组件时,会使用后台服务一词,并且与运行在主线程的Activity相对.因为后台一词很容易误解,服务一直运行在后台?什么线程在运行?服务一直有条线程在运行 ...
- [转]shell 特殊字符
下面这篇博文对特殊字符总结的非常齐全.这里做一下mark.另外补充一些例子. https://blog.csdn.net/K346K346/article/details/51819236 假设我们定 ...
- JS三座大山再学习(三、异步和单线程)
本文已发布在西瓜君的个人博客,原文传送门 前言 写这一篇的时候,西瓜君查阅了很多资料和文章,但是相当多的文章写的都很简单,甚至互相之间有矛盾,这让我很困扰:同时也让我坚定了要写出一篇好的关于JS异步. ...
- Altium Designer 18 画keepout层与将keepout层转换成Mechanical1层的方法
画keepout的方法 先选中Keepout层:然后 右键->Place->Keepout->然后选择要画圆还是线 Keepout层一般只用来辅助Layout,不能作为PCB的外形结 ...
- python数据分析pandas中的DataFrame数据清洗
pandas中的DataFrame中的空数据处理方法: 方法一:直接删除 1.查看行或列是否有空格(以下的df为DataFrame类型,axis=0,代表列,axis=1代表行,以下的返回值都是行或列 ...
- Git之GitFlow工作流
一. GitFlow 介绍 1.1 什么是 GitFlow GitFlow 是一种 Git 工作流,它是团队成员遵守的一种代码管理方案 . 1.2 GitFlow 常用分支说明 分支名称 分支说明 P ...
