【集合系列】- 深入浅出分析LinkedHashMap
作者:炸鸡可乐
原文出处:www.pzblog.cn
一、摘要
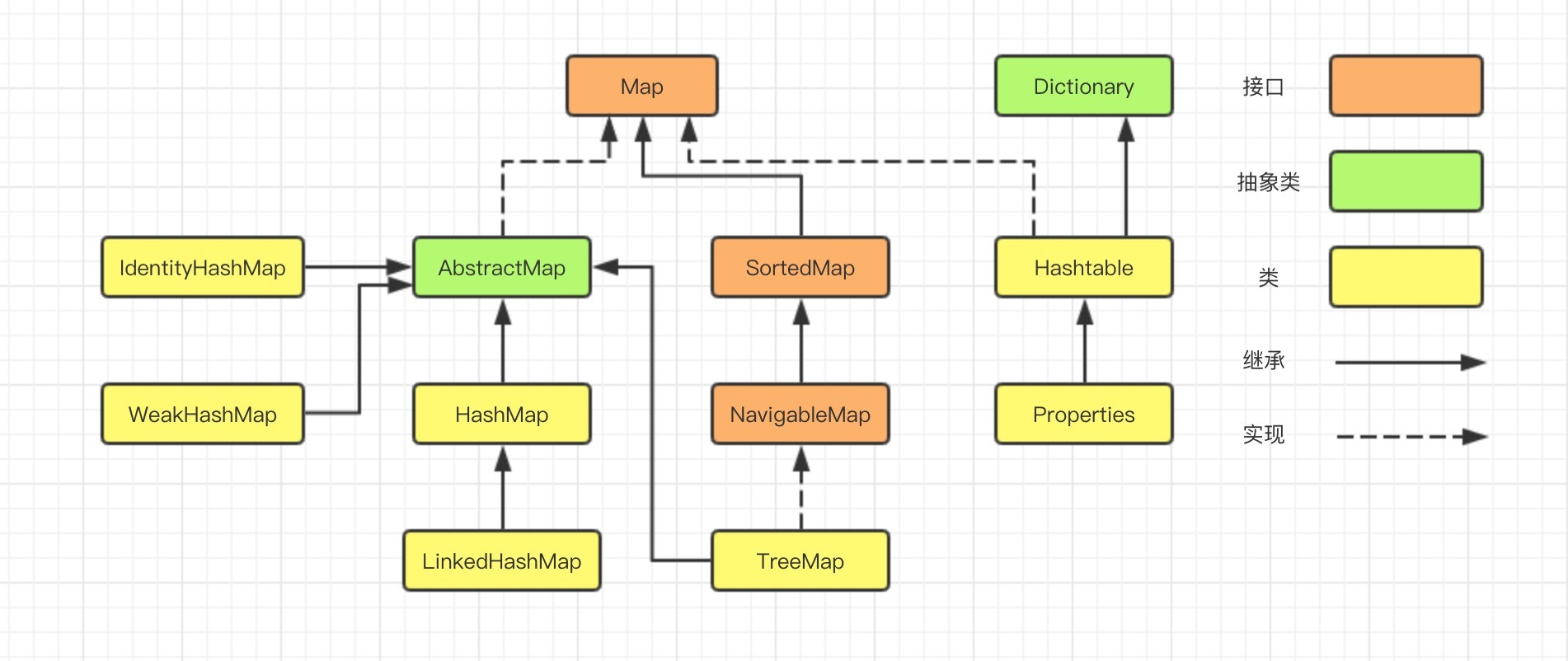
在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map的实现类有HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、IdentityHashMap、WeakHashMap、Hashtable、Properties等等。
本文主要从数据结构和算法层面,探讨LinkedHashMap的实现。
二、简介
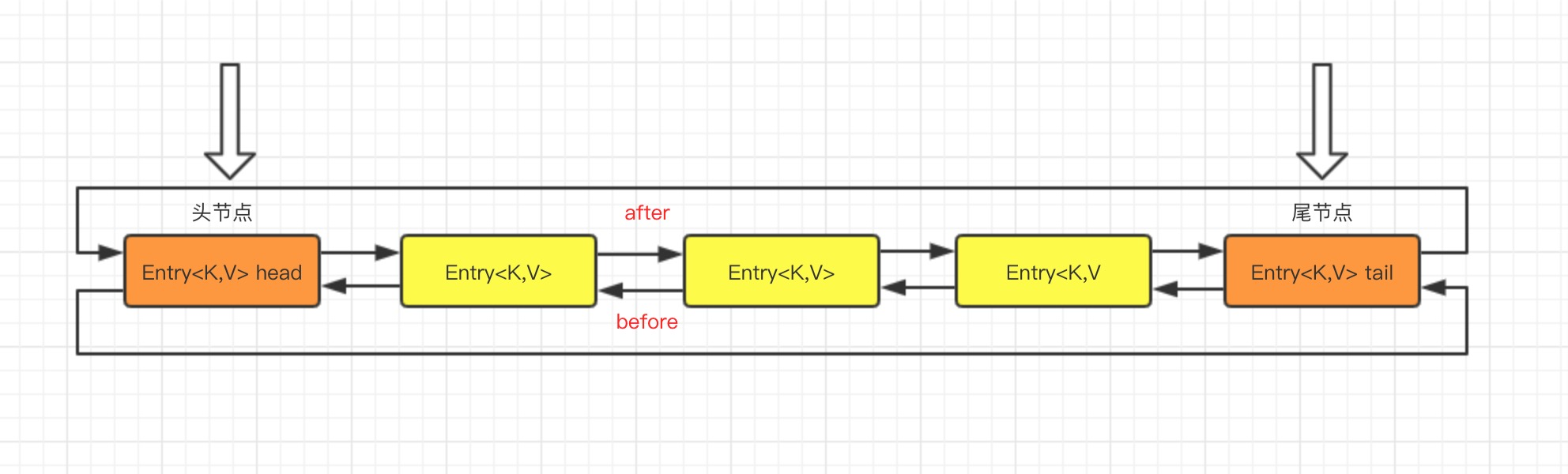
LinkedHashMap可以认为是HashMap+LinkedList,它既使用HashMap操作数据结构,又使用LinkedList维护插入元素的先后顺序,内部采用双向链表(doubly-linked list)的形式将所有元素( entry )连接起来。
LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,允许放入key为null的元素,也允许插入value为null的元素。从名字上可以看出该容器是LinkedList和HashMap的混合体,也就是说它同时满足HashMap和LinkedList的某些特性,可将LinkedHashMap看作采用Linked list增强的HashMap。
打开 LinkedHashMap 源码,可以看到主要三个核心属性:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>{
/**双向链表的头节点*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**双向链表的尾节点*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
/**
* 1、如果accessOrder为true的话,则会把访问过的元素放在链表后面,放置顺序是访问的顺序
* 2、如果accessOrder为false的话,则按插入顺序来遍历
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
}
LinkedHashMap 在初始化阶段,默认按插入顺序来遍历
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
LinkedHashMap 采用的 Hash 算法和 HashMap 相同,不同的是,它重新定义了数组中保存的元素Entry,该Entry除了保存当前对象的引用外,还保存了其上一个元素before和下一个元素after的引用,从而在哈希表的基础上又构成了双向链接列表。
源码如下:
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
//before指的是链表前驱节点,after指的是链表后驱节点
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
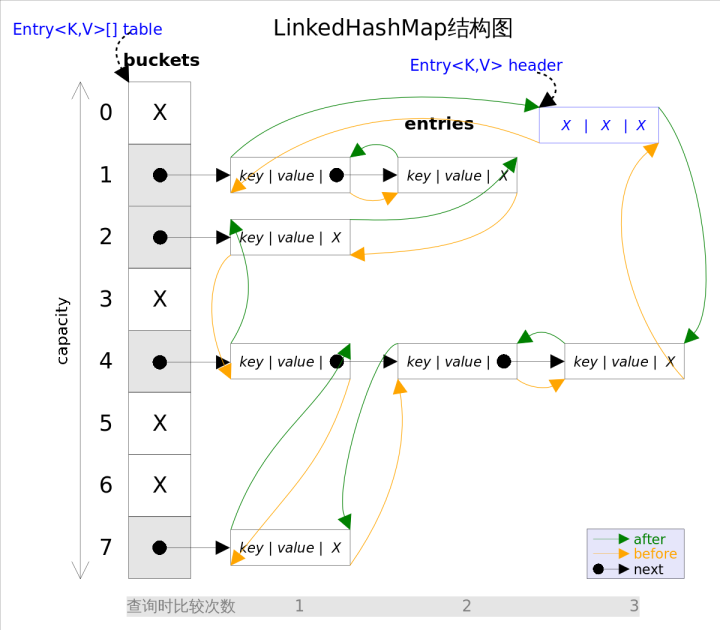
可以直观的看出,双向链表头部插入的数据为链表的入口,迭代器遍历方向是从链表的头部开始到链表尾部结束。
除了可以保迭代历顺序,这种结构还有一个好处:迭代LinkedHashMap时不需要像HashMap那样遍历整个table,而只需要直接遍历header指向的双向链表即可,也就是说LinkedHashMap的迭代时间就只跟entry的个数相关,而跟table的大小无关。
三、常用方法介绍
3.1、get方法
get方法根据指定的key值返回对应的value。该方法跟HashMap.get()方法的流程几乎完全一样,默认按照插入顺序遍历。
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
如果accessOrder为true的话,会把访问过的元素放在链表后面,放置顺序是访问的顺序
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
测试用例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//accessOrder默认为false
Map<String, String> accessOrderFalse = new LinkedHashMap<>();
accessOrderFalse.put("1","1");
accessOrderFalse.put("2","2");
accessOrderFalse.put("3","3");
accessOrderFalse.put("4","4");
System.out.println("acessOrderFalse:"+accessOrderFalse.toString());
//accessOrder设置为true
Map<String, String> accessOrderTrue = new LinkedHashMap<>(16, 0.75f, true);
accessOrderTrue.put("1","1");
accessOrderTrue.put("2","2");
accessOrderTrue.put("3","3");
accessOrderTrue.put("4","4");
accessOrderTrue.get("2");//获取键2
accessOrderTrue.get("3");//获取键3
System.out.println("accessOrderTrue:"+accessOrderTrue.toString());
}
输出结果:
acessOrderFalse:{1=1, 2=2, 3=3, 4=4}
accessOrderTrue:{1=1, 4=4, 2=2, 3=3}
3.2、put方法
put(K key, V value)方法是将指定的key, value对添加到map里。该方法首先会调用HashMap的插入方法,同样对map做一次查找,看是否包含该元素,如果已经包含则直接返回,查找过程类似于get()方法;如果没有找到,将元素插入集合。
/**HashMap 中实现*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
LinkedHashMap 中覆写的方法
// LinkedHashMap 中覆写
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
// 将 Entry 接在双向链表的尾部
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
// last 为 null,表明链表还未建立
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
// 将新节点 p 接在链表尾部
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
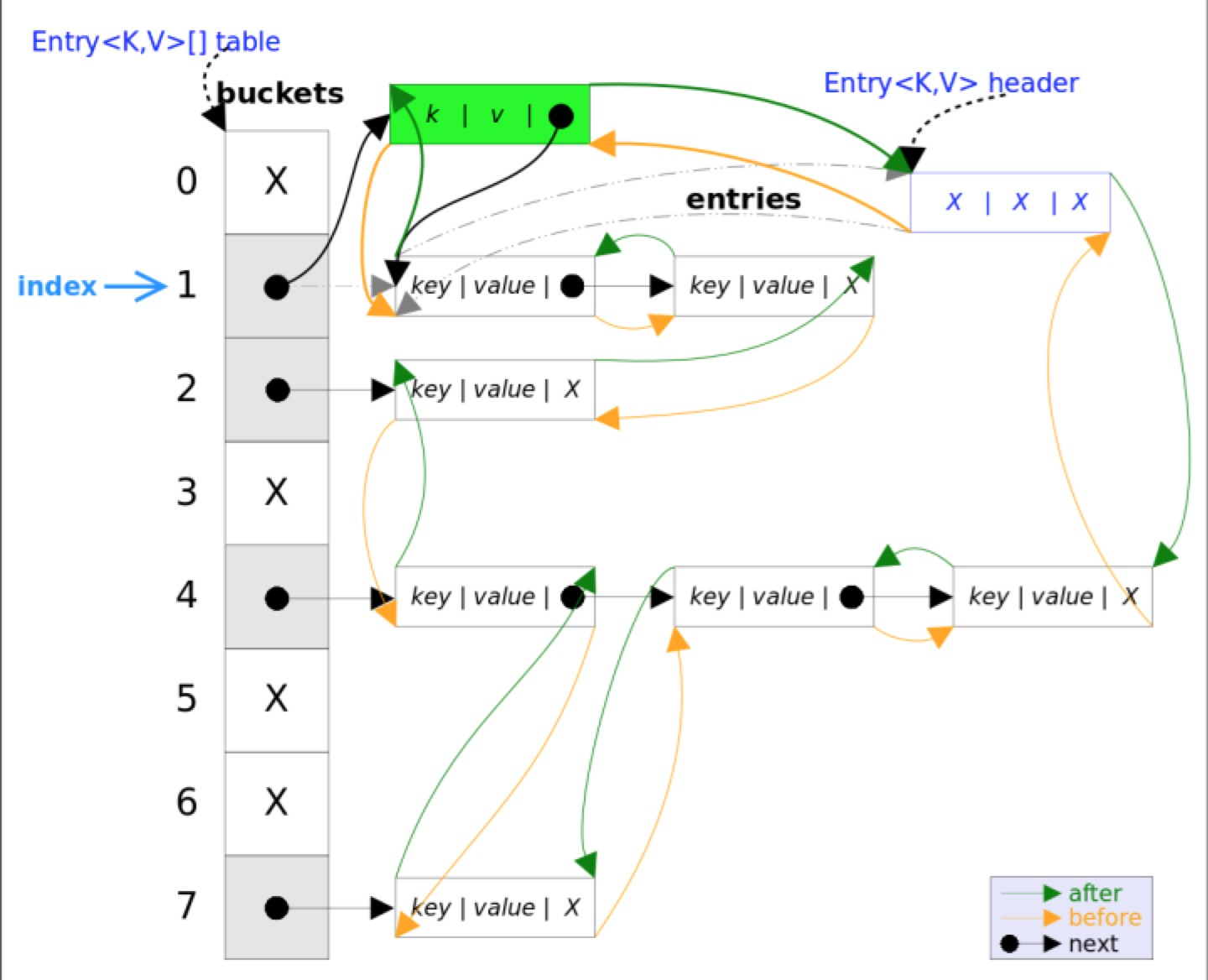
3.3、remove方法
remove(Object key)的作用是删除key值对应的entry,该方法实现逻辑主要以HashMap为主,首先找到key值对应的entry,然后删除该entry(修改链表的相应引用),查找过程跟get()方法类似,最后会调用 LinkedHashMap 中覆写的方法,将其删除!
/**HashMap 中实现*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode) {...}
else {
// 遍历单链表,寻找要删除的节点,并赋值给 node 变量
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode) {...}
// 将要删除的节点从单链表中移除
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node); // 调用删除回调方法进行后续操作
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
LinkedHashMap 中覆写的 afterNodeRemoval 方法
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
// 将 p 节点的前驱后后继引用置空
p.before = p.after = null;
// b 为 null,表明 p 是头节点
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
// a 为 null,表明 p 是尾节点
if (a == null)
tail = b;
else
a.before = b;
}

四、总结
LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,所有大部分功能特性基本相同,二者唯一的区别是 LinkedHashMap 在HashMap的基础上,采用双向链表(doubly-linked list)的形式将所有 entry 连接起来,这样是为保证元素的迭代顺序跟插入顺序相同。
主体部分跟HashMap完全一样,多了header指向双向链表的头部,tail指向双向链表的尾部,默认双向链表的迭代顺序就是entry的插入顺序。
五、参考
1、JDK1.7&JDK1.8 源码
2、博客园 - CarpenterLee - Java集合框架源码剖析LinkedHashMap
【集合系列】- 深入浅出分析LinkedHashMap的更多相关文章
- 【Java集合系列六】LinkedHashMap解析
2017-08-14 16:30:10 1.简介 LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap,能保证迭代顺序,支持其他Map可选的操作.采用双向链表存储元素,默认的迭代序是插入序.重复插入一个已经 ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出的分析 Set集合
一.摘要 关于 Set 接口,在实际开发中,其实很少用到,但是如果你出去面试,它可能依然是一个绕不开的话题. 言归正传,废话咱们也不多说了,相信使用过 Set 集合类的朋友都知道,Set集合的特点主要 ...
- 【Java集合系列】目录
2017-07-29 13:49:40 一.Collection的全局继承关系 二.系列文章 [Java集合系列一]ArrayList解析 备注: 1.ArrayList本质上就是一个数组,所有对外提 ...
- Java集合系列[4]----LinkedHashMap源码分析
这篇文章我们开始分析LinkedHashMap的源码,LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,也就是说LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上扩展而来的,因此在看LinkedHas ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出的分析TreeMap
一.摘要 在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map的实现类有HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap.IdentityHashMap.WeakHashMap.Hashtable.Pro ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出的分析 Hashtable
一.摘要 在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map 的实现类有 HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap.IdentityHashMap.WeakHashMap.Hashtable.P ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出分析HashMap
一.摘要 在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map的实现类有HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap.IdentityHashMap.WeakHashMap.Hashtable.Pro ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出的分析IdentityHashMap
一.摘要 在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map 的实现类有 HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap.IdentityHashMap.WeakHashMap.Hashtable.P ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出的分析 WeakHashMap
一.摘要 在集合系列的第一章,咱们了解到,Map 的实现类有 HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap.IdentityHashMap.WeakHashMap.Hashtable.P ...
随机推荐
- Kubernetes快速入门
二.Kubernetes快速入门 (1)Kubernetes集群的部署方法及部署要点 (2)部署Kubernetes分布式集群 (3)kubectl使用基础 1.简介 kubectl就是API ser ...
- 像艺术家一样思考 Think Like an Artist
艺术家是如何获得灵感,如何找到自己的独特风格和主题的? 艺术家在绘画.写作.表演或歌唱前不会去征求谁的允许,而是随心而行 要想在数字时代获得满足感,我们需要变得有创造性 1.艺术家富有事业心 艺术家是 ...
- 机器学习回顾篇(7):决策树算法(ID3、C4.5)
.caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; } .label { border: 1px so ...
- Eclipse 创建 Maven 项目
本人也是新手小白,在创建 Maven 项目的时候几乎踩完了所有的坑.特此总结如下: 1.咱先选中 File -> New -> Maven Project 2.然后如下图 在这里说明 ...
- SQLMAP SSI注入错误解决
记一次SQL注入 目标地址:https://www.xxxx.com/ 之前补天提交过这个注入 后来貌似”修复了”(实际就是装了安全狗和过滤了一些关键字) 不过今天试了下 还是可以注入 可以看到已经 ...
- 对比 Git 与 SVN
一.Git vs SVN Git 和 SVN 孰优孰好,每个人有不同的体验. Git是分布式的,SVN是集中式的 这是 Git 和 SVN 最大的区别.若能掌握这个概念,两者区别基本搞懂大半.因为 G ...
- SpringBoot2.x--入门篇--01--HelloWorld
很多人说,学习springboot至少需要spring基础,servlet基础等等,笔者不敢苟同.凡是有一定java基础的人,都可以直接学习springboot,当学到原理和源码时,通过查缺补漏的方式 ...
- 初识mpvue
听说mpvue可以实现H5和小程序的同时开发 对使用过vue的选手几乎是0难度 忍不住搓搓小手手 看了文 唔~ 似乎不是很难的样子 然后实际上手操作了一下 老规矩:新建项目 npm install ...
- jmeter-操作mysql
1.下载mysql驱动并放至如下目录:E:\soft\apache-jmeter-5.1.1\lib\ext 2.添加JDBC Connection Configuration(线程组-配置元件-JD ...
- Java基础(三)对象与类
1.类的概念:类是构造对象的模板或蓝图.由类构造对象的过程称为创建类的实例. 2.封装的概念:封装(有时称为数据隐藏)是与对象有关的一个重要概念.对象中的数据称为实例域,操纵数据的过程称为方法.对于每 ...
