Lab 11-1
Analyze the malware found in Lab11-01.exe.
Questions and Short Answers
What does the malware drop to disk?
A: The malware extracts and drops the file msgina32.dll onto disk from a resource section named TGAD.
How does the malware achieve persistence?
A: The malware installs msgina32.dll as a GINA DLL by adding it to the registry location
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GinaDLL, which causes the DLL to be loaded after system reboot.How does the malware steal user credentials?
A: The malware steals user credentials by performing GINA interception. The msgina32.dll file is able to intercept all user credentials submitted to the system for authentication.
What does the malware do with stolen credentials?
A: The malware logs stolen credentials to
%SystemRoot%\System32\msutil32.sys. The username, domain, and password are logged to the file with a timestamp.How can you use this malware to get user credentials from your test environment?
A: Once the malware is dropped and installed, there must be a system reboot for the GINA interception to begin. The malware logs credentials only when the user logs out, so log out and back in to see your credentials in the log file.
Detailed Analysis
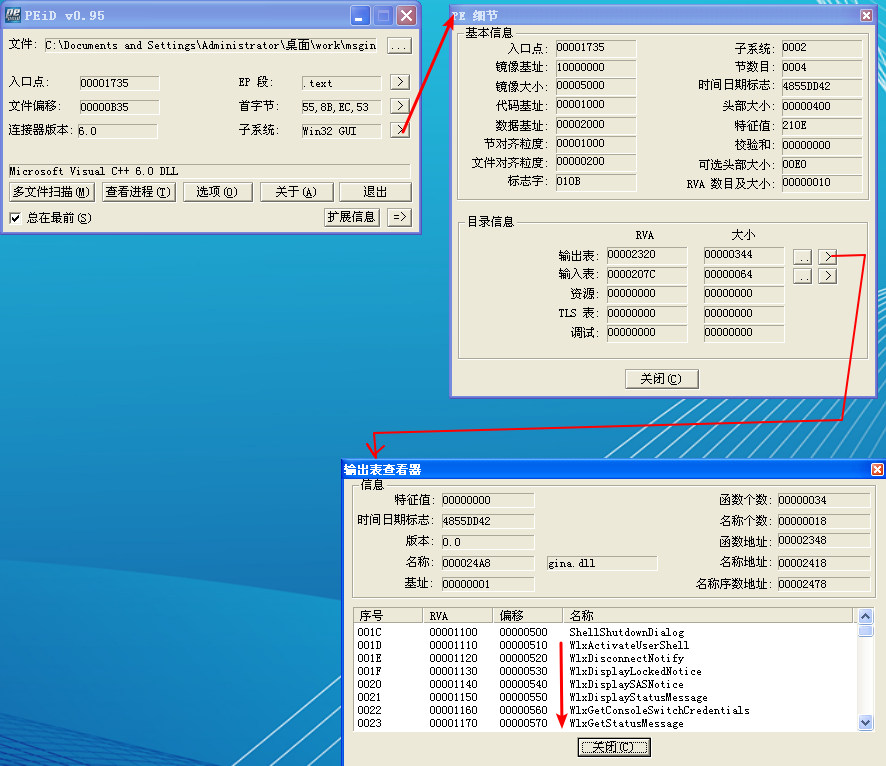
Beginning with basic static analysis, we see the strings GinaDLL and SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon, which lead us to suspect that this might be GINA interception malware. Examining the imports, we see functions for manipulating the registry and extracting a resource section. Because we see resource extraction import functions, we examine the file structure by loading Lab11-01.exe into PEview, as shown in Figure 11-1L.
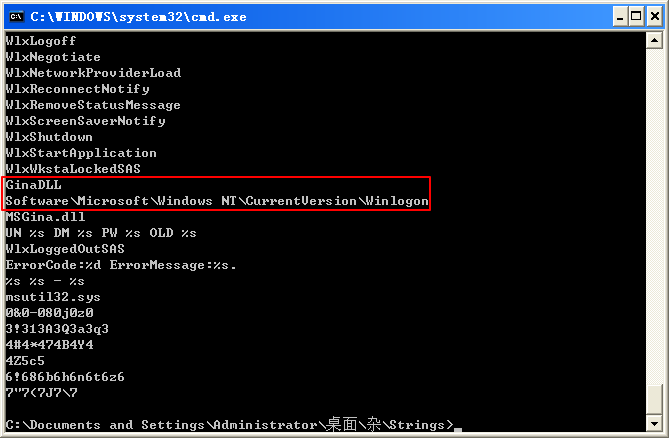
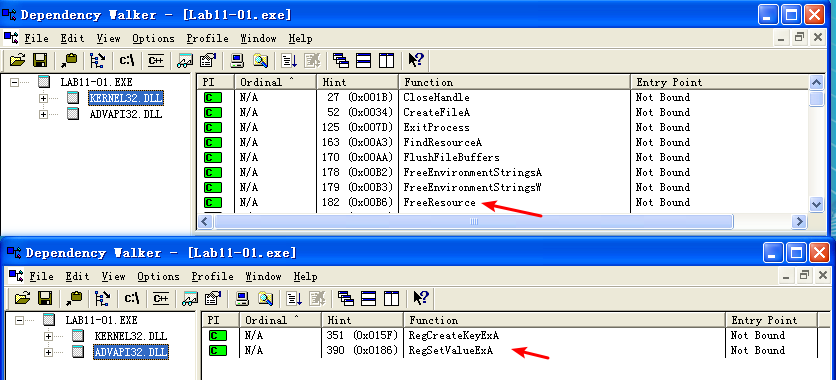
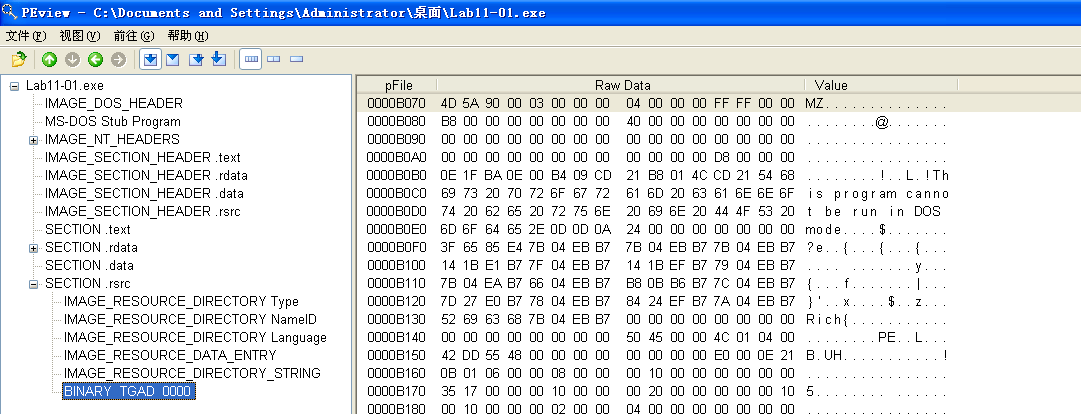
Figure 11-1L: Lab11-01.exe in PEview showing the TGAD resource section
Examining the PE file format, we see a resource section named TGAD. When we click that section in PEview, we see that TGAD contains an embedded PE file.
Next, we perform dynamic analysis and monitor the malware with procmon by setting a filter for Lab11-01.exe. When we launch the malware, we see that it creates a file named msgina32.dll on disk in the same directory from which the malware was launched. The malware inserts the path to msgina32.dll into the registry key HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\GinaDLL, so that the DLL will be loaded by Winlogon when the system reboots.
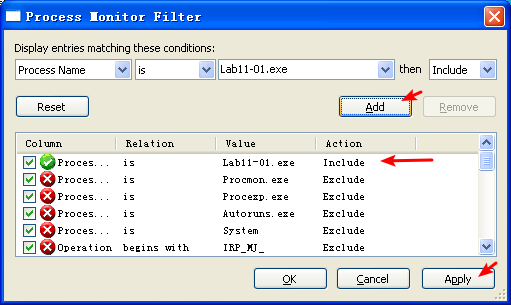
Lab11-01.exe 所在文件夹,在 Lab11-01.exe 执行前后对比:
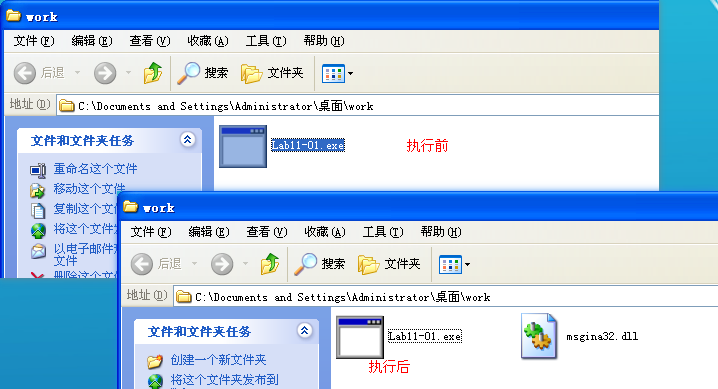
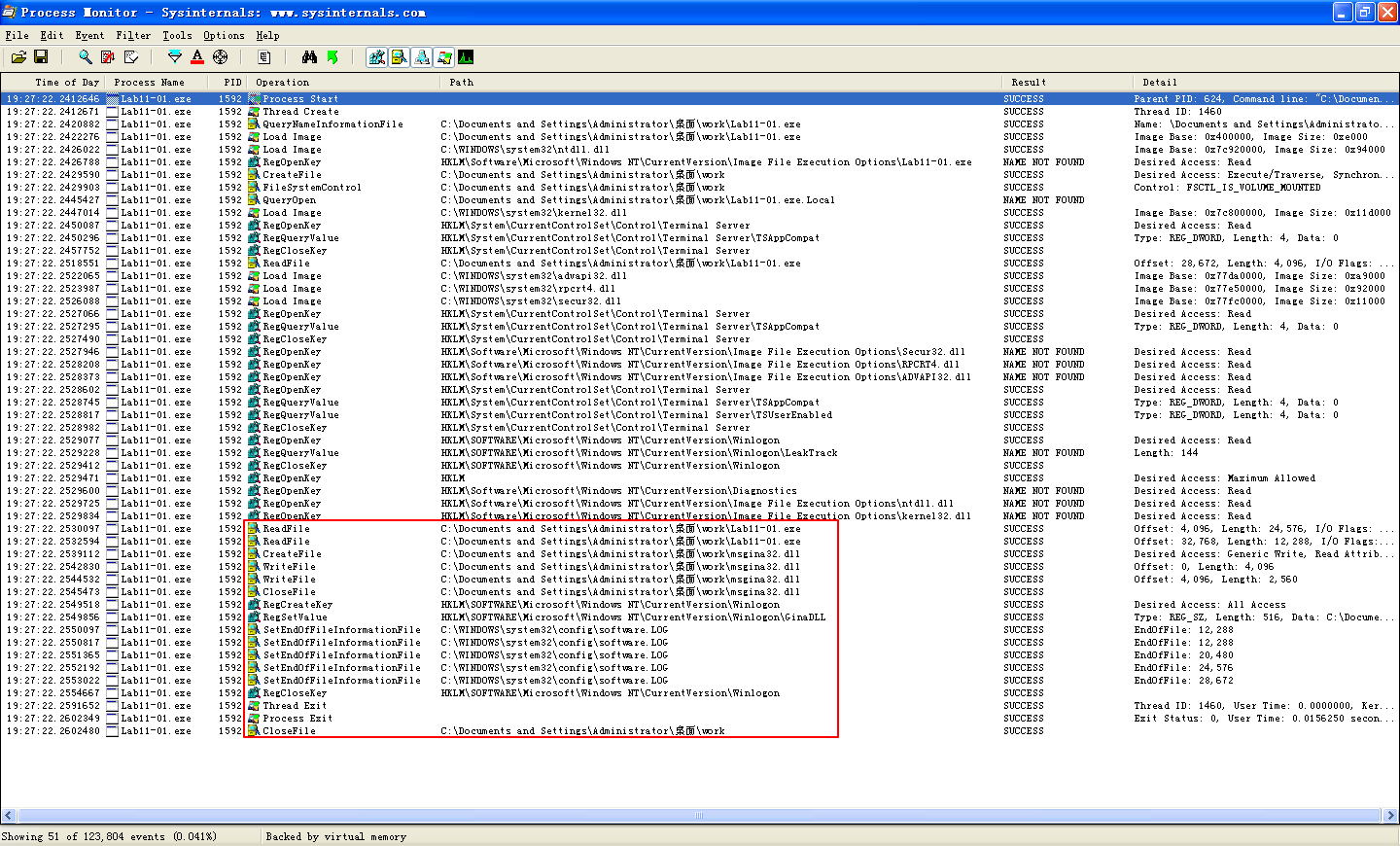

Extracting the TGAD resource section from Lab11-01.exe (using Resource Hacker) and comparing it to msgina32.dll, we find that the two are identical.
导出 Lab11-01.exe 中的 TGAD 资源节:
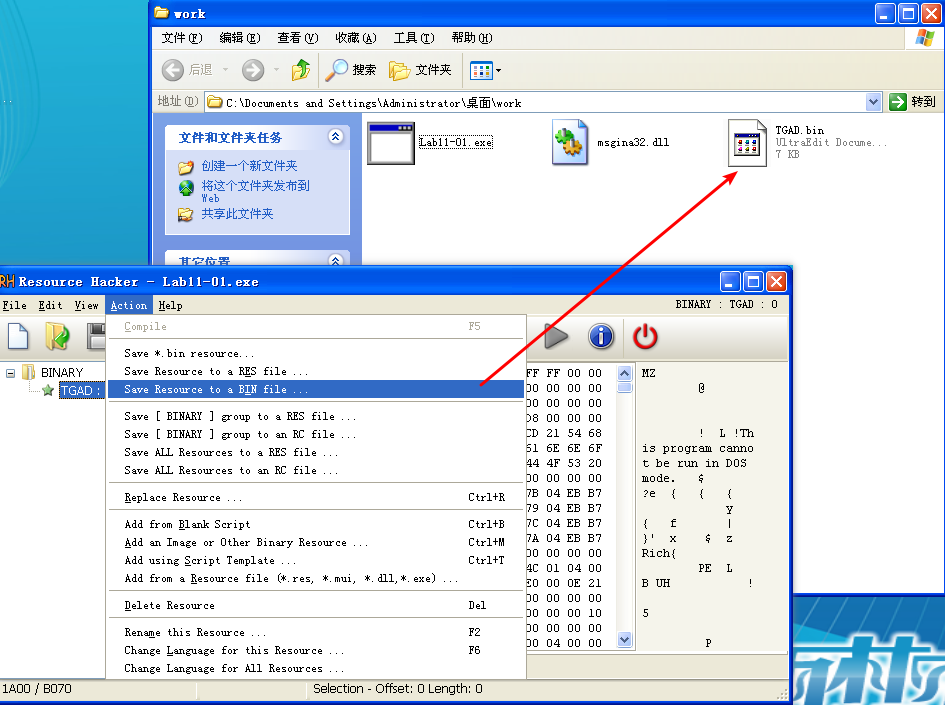
查 TGAD.bin 和 msgina32.dll 文件的 MD5:

它俩 MD5 相同,应该是同一文件。使用 PEview 查看也相同:
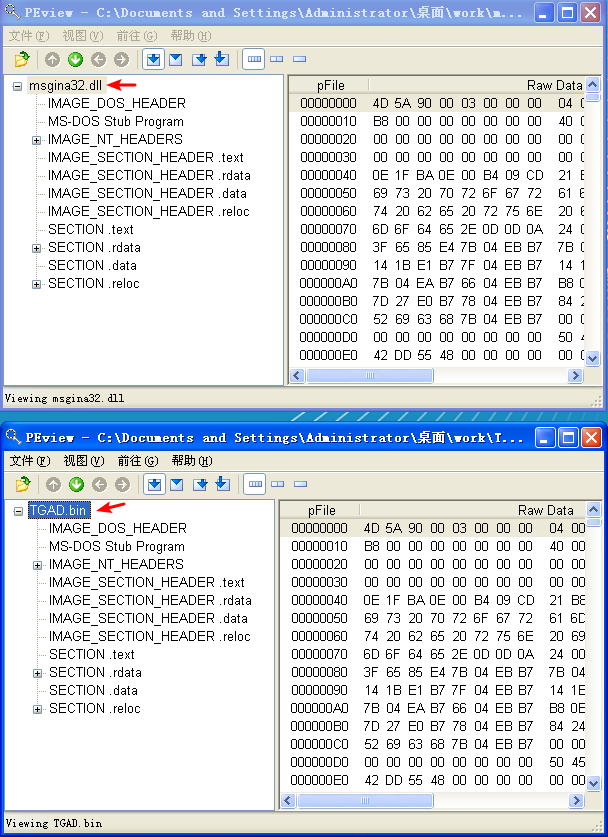
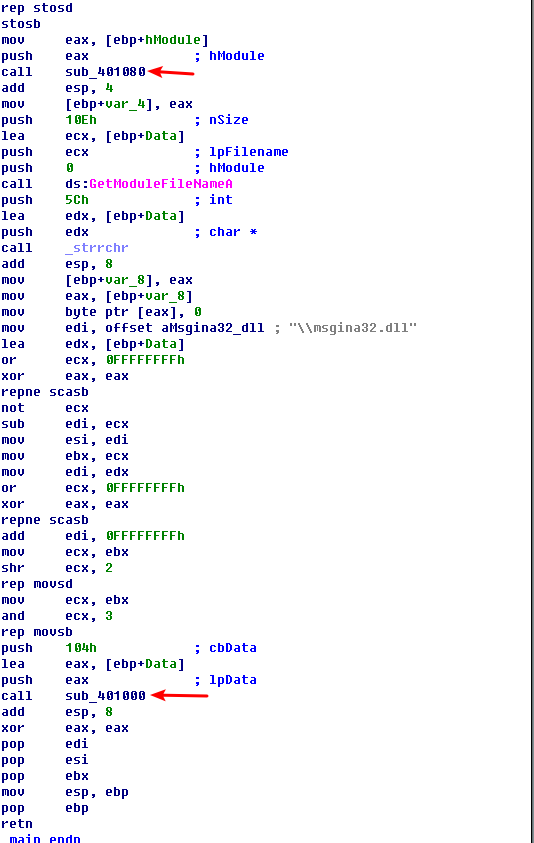
Next, we load Lab11-01.exe into IDA Pro to confirm our findings. We see that the main function calls two functions: sub_401080 (extracts the TGAD resource section to msgina32.dll) and sub_401000 (sets the GINA registry value). We conclude that Lab11-01.exe is an installer for msgina32.dll, which is loaded by Winlogon during system startup.
Analysis of msgina32.dll
We’ll begin our analysis of msgina32.dll by looking at the Strings output, as shown in Listing 11-1L.

Listing 11-1L: Strings output of msgina32.dll
The strings in this listing contain what appears to be a log message at \({\color{red}1}\), which could be used to log user credentials if this is GINA interception malware. The string msutil32.sys is interesting, and we will determine its significance later in the lab.
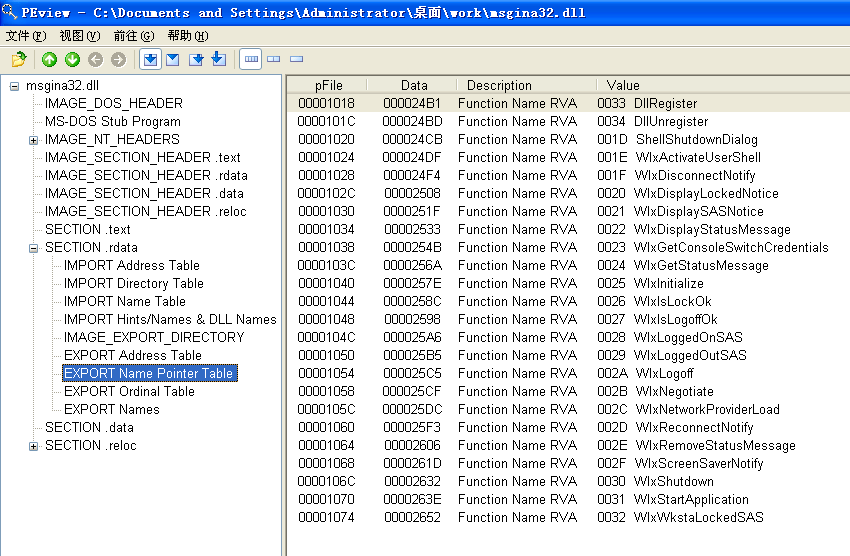
Examining msgina32.dll’s exports, we see many functions that begin with the prefix Wlx. Recall from Chapter 11 that GINA interception malware must contain all of these DLL exports because they are required by GINA. We’ll analyze each of these functions in IDA Pro.
We begin by loading the malware into IDA Pro and analyzing DllMain, as shown in Listing 11-2L.

Listing 11-2L: DllMain of msgina32.dll getting a handle to msgina.dll
As shown in the Listing 11-2L, DllMain first checks the fdwReason argument at \({\color{red}1}\). This is an argument passed in to indicate why the DLL entry-point function is being called. The malware checks for DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, which is called when a process is starting up or when LoadLibrary is used to load the DLL. If this particular DllMain is called during a DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, the code beginning at \({\color{red}2}\) is called. This code gets a handle to msgina.dll in the Windows system directory via the call to LoadLibraryW at \({\color{red}3}\).
NOTE
msgina.dll is the Windows DLL that implements GINA, whereas msgina32.dll is the malware author’s GINA interception DLL. The name msgina32 is designed to deceive.
The malware saves the handle in a global variable that IDA Pro has named hModule at \({\color{red}4}\). The use of this variable allows the DLL’s exports to properly call functions in the msgina.dll Windows DLL. Since msgina32.dll is intercepting communication between Winlogon and msgina.dll, it must properly call the functions in msgina.dll so that the system will continue to operate normally.
Next, we analyze each export function. We begin with WlxLoggedOnSAS, as shown in Listing 11-3L.

Listing 11-3L: WlxLoggedOnSAS export just passing through to msgina.dll
The WlxLoggedOnSAS export is short and simply passes through to the true WlxLoggedOnSAS contained in msgina.dll. There are now two WlxLoggedOnSAS functions: the version in Listing 11-3L in msgina32.dll and the original in msgina.dll. The function in Listing 11-3L begins by passing the string WlxLoggedOnSAS to sub_10001000 and then jumps to the result. The sub_10001000 function uses the hModule handle (to msgina.dll) and the string passed in (in this case, WlxLoggedOnSAS) to use GetProcAddress to resolve a function in msgina.dll. The malware doesn’t call the function; it simply resolves the address of WlxLoggedOnSAS in msgina.dll and jumps to the function, as seen at \({\color{red}1}\). By jumping and not calling WlxLoggedOnSAS, this code will not set up a stack frame or push a return address onto the stack. When WlxLoggedOnSAS in msgina.dll is called, it will return execution directly to Winlogon because the return address on the stack is the same as what was on the stack when the code in Listing 11-3L is called.
If we continue analyzing the other exports, we see that most operate like WlxLoggedOnSAS (they are pass-through functions), except for WlxLoggedOutSAS, which contains some extra code. (WlxLoggedOutSAS is called when the user logs out of the system.)
The export begins by resolving WlxLoggedOutSAS within msgina.dll using GetProcAddress and then calling it. The export also contains the code shown in Listing 11-4L.

Listing 11-4L: WlxLoggedOutSAS calling the credential logging function sub_10001570
The code in Listing 11-4L passes a bunch of arguments and a format string at \({\color{red}1}\). This string is passed to sub_10001570, which is called at \({\color{red}2}\).
It seems like sub_10001570 may be the logging function for stolen credentials, so let’s examine it to see what it does. Listing 11-5L shows the logging code contained in sub_10001570.
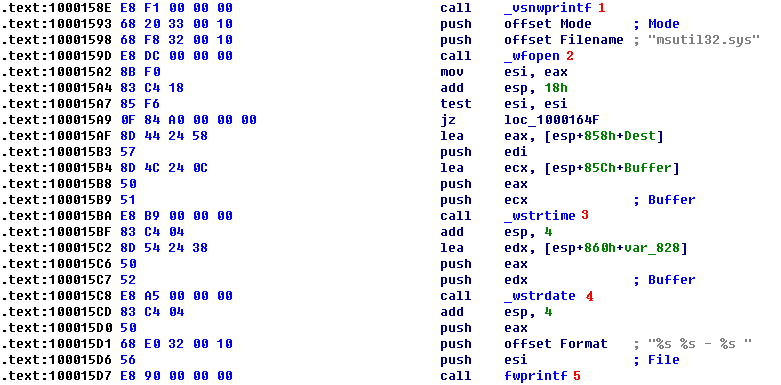
Listing 11-5L: The credential-logging function logging to msutil32.sys
The call to vsnwprintf at \({\color{red}1}\) fills in the format string passed in by the WlxLoggedOutSAS export. Next, the malware opens the file msutil32.sys at \({\color{red}2}\), which is created inside C:\Windows\System32\ since that is where Winlogon resides (and msgina32.dll is running in the Winlogon process). At \({\color{red}3}\) and \({\color{red}4}\), the date and time are recorded, and the information is logged at \({\color{red}5}\). You should now realize that msutil32.sys is used to store logged credentials and that it is not a driver, although its name suggests that it is.
We force the malware to log credentials by running Lab11-01.exe, rebooting the machine, and then logging in and out of the system. The following is an example of the data contained in a log file created by this malware:
重启刚刚运行过 Lab11-1.exe 的主机,再注销用户,再登录,在 C:\Windows\System32\ 目录下,查看 msutil32.sys 文件内容:
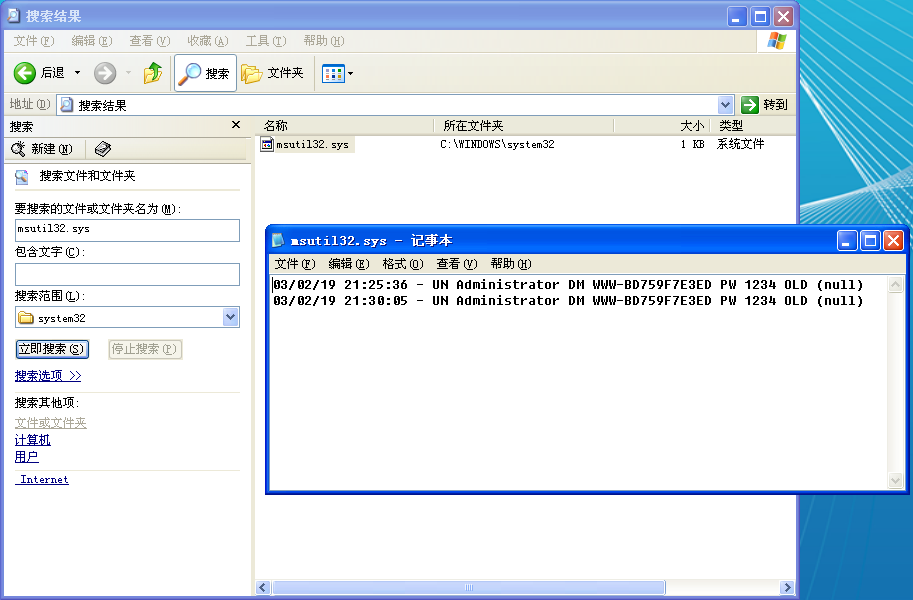
The usernames are Administrator, it password is 1234, and the domain is WWW-BD759F7E3ED.
Summary
Lab 11-1 is a GINA interceptor installer. The malware drops a DLL on the system and installs it to steal user credentials, beginning after system reboot. Once the GINA interceptor DLL is installed and running, it logs credentials to msutil32.sys when a user logs out of the system.
Preference
PRACTICAL MALWARE ANALYSIS: MALWARE BEHAVIOR(LAB 11-01)
Lab 11-1的更多相关文章
- RH033读书笔记(10)-Lab 11 Process Control
Lab 11 Process Control Sequence 1: Job Control 1. [student@stationX ~]$ su - 2. Begin some jobs in t ...
- RH133读书笔记(11)-Lab 11 System Rescue and Troubleshooting
Lab 11 System Rescue and Troubleshooting Goal: To build skills in system rescue procedures. Estimate ...
- Lab 1-1
LABS The purpose of the labs is to give you an opportunity to practice the skills taught in the chap ...
- 第一章 Lab
关于Lab 教材恶意代码分析实战 课后练习恶意代码样本https://practicalmalwareanalysis.com或https://nostarch.com/malware.htm 以下是 ...
- 7 天玩转 ASP.NET MVC — 第 3 天
目录 第 1 天 第 2 天 第 3 天 第 4 天 第 5 天 第 6 天 第 7 天 0. 前言 我们假定你在开始学习时已经阅读了前两天的学习内容.在第 2 天我们完成了关于显示 Employee ...
- RAC之常用方法-----新手入门
年后换工作新入职,公司开发在使用RAC,之前居然一直没有了解过,独立开发的弊端,信息闭塞,而且自己也懒,这几天看了下RAC,确实很强大有木有. 什么是ARC 简单的说,RAC就是一个第三方库,他可以大 ...
- vmware目录2
http://www.globalknowledge.com/training/course.asp?pageid=9&courseid=17880&country=United+St ...
- 很好的vmware目录
http://www.globalknowledge.com/training/course.asp?pageid=9&courseid=18023&country=United+St ...
- 【转】Automated Testing Detail Test Plan
Automated Testing Detail Test PlanAutomated Testing DTP Overview This Automated Testing Detail Test ...
- Cygwin Run in the Windows(Simulation of UNIX)
Preface Environment Cygwin Run in the Windows(Simulation of UNIX) Resource Cygwin Install:http://cyg ...
随机推荐
- Ajax请求二进制流并在页面展示
后端代码: public void getIntegralQrcode(HttpServletResponse response, String token) throws BizException, ...
- RNA-seq标准化
你的 heatmap 可能用错数据了 (组间表达量标准化) http://www.genek.tv/article/24 RNA-seq的标准化方法罗列 https://www.jianshu.com ...
- 文本框defalutValue的使用
以下页面中的文本框的值无论怎么改变,点击“原始值”按钮始终会得到初始页面的时候的值,即“ffffffffffffff” <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <h ...
- pytorch使用不完全文档
1. 利用tensorboard看loss: tensorflow和pytorch环境是好的的话,链接中的logger.py拉到自己的工程里,train.py里添加相应代码,直接能用. 关于环境,小小 ...
- virtualenv的使用
virtualenv 是一个创建隔绝的Python环境的工具.在向服务器导入第三方库的时候特别有用. 1.首先,安装virtualenv pip install virtualenv 2.创建一个虚拟 ...
- tensorflow学习笔记2:c++程序静态链接tensorflow库加载模型文件
首先需要搞定tensorflow c++库,搜了一遍没有找到现成的包,于是下载tensorflow的源码开始编译: tensorflow的contrib中有一个makefile项目,极大的简化的接下来 ...
- 练手——用Python写的时间戳转换为北京时间的小工具
#北京时间需加上8小时bj = 8*3600 def time_stamp(times): #一天总秒数 nonDaySeconds = 24*3600 leapmonths = [ ...
- ROS机器人编程实践----琐碎知识点
amcl原理: amcl将激光传感器数据与从地图预估的传感器数据相比较,给出可能的位姿.如果传感器数据和某个候选位姿处的预测数据相同,amcl就会给这个位姿一个较高的概率,反之,就会降低这个概率.概率 ...
- keras用法
关于Keras的“层”(Layer) 所有的Keras层对象都有如下方法: layer.get_weights():返回层的权重(numpy array) layer.set_weights(weig ...
- 论使用HashMap优化双层For循环的实际性能
当需要对两个集合进行相互操作的时候,一般需要进行双层For循环,但我们知道双层For在数量越大的时候性能影响越大 这时候我们会想到的其中一种解决方法就是利用Hashmap在查找数据的高效上来优化双层F ...
