第七章 android-UI组件
一、本章目录

二、用户界面概述
1,用户界面简介
(1)系统和用户之间进行信息交换的媒介
2,设计手机用户界面应解决的问题
(1)需要界面设计和逻辑代码完全分离(布局和逻辑代码分开放)
(2)根据不同型号手机的屏幕解析度,尺寸,纵横比各不相同,自动调增界面上部分的位置和尺寸,避免因为屏幕信息的变化出现显示错误
(3)能合理的利用较小的屏幕显示空间,构造符合人机交互规律的用户界面,避免出现凌乱,拥挤的用户界面
(4)Android已经解决了前两个问题,是用xml文件描述用户界面:资源文件独立保存在资源文件夹中;对界面用户的描述非常灵活,允许不明确定义界面元素的位置和尺寸,仅声明界面元素的相对位置和粗略的尺寸
3,Android用户界面框架
(1)Android用户界面框架采用了MVC模式
1)提供处理用户输入的控制器(Controller)
2)显示用户界面和图像的视图(View),以及保存数据和代码的模型(Model)
 _
_
M层:业务逻辑处理(例:数据库的存取操作,网络操作,复杂的算法,好耗时的任务都在M层处理)
V层:布局可以视为V层,显示Model层的数据结果
C层:在哪Android中,Activity处理用户交互问题,因此可以认为Activity是控制层,Activity读取V层的数据,控制用户输入,并向Model层发送数据请求
分析:
在MVC模式中我们发现,其实控制器Activity主要是起到解耦作用,将View视图和Model模型分离,虽然Activity起到交互作用,但是找Activity中有很多关于视图UI的显示代码,因此View视图和Activity控制器并不是完全分离的,也就是说一部分View视图和Contronller控制器Activity是绑定在一个类中的。
MVC的优点:
(1)耦合性低。所谓耦合性就是模块代码之间的关联程度。利用MVC框架使得View(视图)层和Model(模型)层可以很好的分离,这样就达到了解耦的目的,所以耦合性低,减少模块代码之间的相互影响。
(2)可扩展性好。由于耦合性低,添加需求,扩展代码就可以减少修改之前的代码,降低bug的出现率。
(3)模块职责划分明确。主要划分层M,V,C三个模块,利于代码的维护。
三、基本界面控件
1,界面控件简介
(1)Android中的界面控件分为定制控件和系统控件
1)定制控件:用户独立开发的控件,或通过继承并修改系统控件后所产生的心得控件。能够头为用户提供特殊的功能或与众不同的显示需求方式
2)系统控件:系统控件是Android系统提供给用户已经封装的用户界面,提供在应用程序开发过程中常见功能控件。系统控件更有利于帮助用户进行快速的开发,同时能够使Android系统中应用程序的界面保持一致性
(2)常见的系统控件:TextView,EditText,Button,ImagButton,checkbox,RadioButton,Spinner,ListView
2,TextView和EditText
TextView是一种用于显示字符串的控件
EditText则是用来输入和编辑字符串的控件
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv;
private EditText et;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
et=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.et);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="40dp"
android:text="hello:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>

3,Button和ImageView
Button是一种按钮控件,用户能够在该控件上点击,并后引发相应的事件处理函数
ImageButton用以实现能够显示图像功能的控件按钮
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<Button
android:text="btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/plane"/>
</LinearLayout>

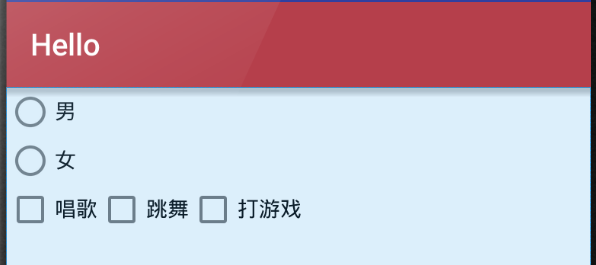
4,CheckBox和RadioButton
(1)CheckBox是一个同时可以选择多个选项的控件
(2)RadioButton则是仅可以选择一个选项的控件
(3)RadioGroup是RadioButton的承载体,程序运行时不可见,应用程序中可能包含一个或多个RadioGroup
(4)一个RadioGroup包含多个RadioButton,在每个RadioGroup中,用户仅能够选择其中一个RadioButton
***RadioButton必须配合RadioGroup使用***
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="男"/>
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="女"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="唱歌"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="跳舞"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="打游戏"/>
</LinearLayout>
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
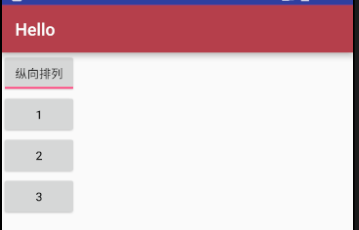
5,ToggleButton(状态开关按钮)
(1) ToggleButton有两种状态,开和关,通常用于切换程序中的某种状态。
(2) 常用属性:
1)android:checked 设置该按钮是否被选中
2)android:textOff 当按钮没被选中时显示的文本
3)android:textOn 当按钮被选中时显示的文本
关键代码:
这三行代码必须设置:
checked:默认的选中状态
textoff:关闭状态的文本信息
texton:开启状态的文本信息
android:checked="true"
android:textOff="横向排列"
android:textOn="纵向排列"
完整代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<ToggleButton
android:id="@+id/tb1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checked="true"
android:textOff="横向排列"
android:textOn="纵向排列"/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/bgtn1"
android:text="1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/bgtn2"
android:text="2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/bgtn3"
android:text="3"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.administrator.hello; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.ToggleButton; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ToggleButton tb;
private LinearLayout ll;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.table);
tb=(ToggleButton)findViewById(R.id.tb1);
ll=(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.ll);
tb.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
if(isChecked)
{
//1表示垂直布局
ll.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
tb.setChecked(true);
}
else
{
ll.setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);
tb.setChecked(false);
}
}
}); }
}

5,Spinner
6,ListView
(1) ListView是一种用于垂直显示的列表控件,如果显示内容过多,则会出现垂直滚动条
(2)ListView能够通过适配器将数据和自身绑定,在有限的屏幕上提供大量内容供用户选择,所以是经常使用的用户界面控件
(3)ListView支持点击事件处理,用户可以用少量的代码实现复杂的选择功能
(4)学会使用两种适配器:ArrayAdapter、SimpleAdapter
监听器:OnItemClickLister
(5)作用:Android系统中显示列表的控件,每一个ListView都可以包含多个列表项
(6)数据适配器:连接数据源和视图界面的桥梁
(7)实现步骤:新建数据源---新建适配器---添加数据源到适配器
1)新建数组适配器
arrayAdapter= new ArrayAdapter(Context,Resource,List);
参数信息(上下文信息,样式,数据源)
2)
A:ArrayAdapter
逻辑
package com.example.administrator.app1; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ListView lv;
private List<String> list;
private ArrayAdapter aa;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
lv=(ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv);
//新建数据源
list=new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<=20;i++)
{
list.add("listview子项"+i);
}
//新建适配器,将数据绑定到适配器
aa=new ArrayAdapter(MainActivity.this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,list);
//试图加载适配器
lv.setAdapter(aa); }
}
布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01"> <ListView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/lv"></ListView>
</LinearLayout>
布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/image"/> </LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.administrator.app2.MainActivity">
<GridView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/gv"
android:horizontalSpacing="4dp"
android:verticalSpacing="4dp"
android:numColumns="4"
> </GridView>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:id="@+id/iv" />
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.administrator.app2; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Adapter;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.GridView;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private GridView gv;
private ImageView iv;
private int[] imgs={R.drawable.e1,R.drawable.e2,R.drawable.e3,R.drawable.e4,R.drawable.e5,R.drawable.e6,R.drawable.e7,R.drawable.e8};
private List<Map<String,Object>> list;
private SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter;
private String[] str={"pics"};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
gv=(GridView)findViewById(R.id.gv);
iv=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.iv);
//定义事件源
list=new ArrayList<>(); for(int i=0;i<imgs.length;i++)
{
Map map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("pics",imgs[i]);
list.add(map);
}
//定义监听
simpleAdapter=new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this,list,R.layout.i,str,new int[]{R.id.image});
gv.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
gv.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
iv.setImageResource(imgs[position]);
}
});
//定义监听器
}
}
第七章 android-UI组件的更多相关文章
- Android UI组件----ListView列表控件详解
[声明] 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→ 生命壹号:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/ 文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/3 ...
- Laxcus大数据管理系统2.0(9)- 第七章 分布任务组件
第七章 分布任务组件 Laxcus 2.0版本的分布任务组件,是在1.x版本的基础上,重新整合中间件和分布计算技术,按照新增加的功能,设计的一套新的.分布状态下运行的数据计算组件和数据构建组件,以及依 ...
- Android 高级UI设计笔记08:Android开发者常用的7款Android UI组件(转载)
Android开发是目前最热门的移动开发技术之一,随着开发者的不断努力和Android社区的进步,Android开发技术已经日趋成熟,当然,在Android开源社区中也涌现了很多不错的开源UI项目,它 ...
- Android群英传》读书笔记 (3) 第六章 Android绘图机制与处理技巧 + 第七章 Android动画机制与使用技巧
第六章 Android绘图机制与处理技巧 1.屏幕尺寸信息屏幕大小:屏幕对角线长度,单位“寸”:分辨率:手机屏幕像素点个数,例如720x1280分辨率:PPI(Pixels Per Inch):即DP ...
- 这是一个比较全的Android UI 组件
Android组件及UI框架大全 原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/smallnest/article/details/38658593 Android 是目前最流行的移动操作系统 ...
- Android UI组件学习
android.view.View类是全部UI组件的父类. 如果一些属性的内容本类找不到的时候一定要到父类之中进行查找. 所谓的学习组件的过程就是一个文档的查找过程. ※ Android之中所有的组件 ...
- 【ALearning】第四章 Android Layout组件布局(一)
在本章中,我们将Android学习组件布局.在前面的章节,我们也开始使用LinearLayout布局.然后我们在布局文件更加具体的学习和理解,会. Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完毕的,布局好 ...
- Android UI组件:布局管理器
为了更好的管理Android应用的用户界面中的组件,Android提供了布局管理器.通过使用布局管理器,Android应用的图形用户界面具有良好的平台无关性.通常,推荐使用布局管理器来管理组件的分布. ...
- Android UI组件----AppWidget控件入门详解
Widget引入 我们可以把Widget理解成放置在桌面上的小组件(挂件),有了Widget,我们可以很方便地直接在桌面上进行各种操作,例如播放音乐. 当我们长按桌面时,可以看到Widget选项,如下 ...
- Android UI 组件 » GifView
GifView 是一个为了解决android中现在没有直接显示gif的view,只能通过mediaplay来显示这个问题的项目,其用法和 ImageView一样,支持gif图片 使用方法: 1-把Gi ...
随机推荐
- linux备忘录-基本命令
基本命令 将命令分类为获取信息类,文件管理类,目录管理类,文本处理类,系统类,工具类. 获取信息类 uname # 输出所有信息 # 一行输出,空格分割 uname -a # 输出内核名称 uname ...
- Spring AOP的一个简单实现
针对学习笔记(六)中的购买以及退货代码,我们加入AOP框架,实现同样一个功能. 首先配置XML:service采用和之前一样的代码,只是没有通过实现接口来实现,而是直接一个实现类.transactio ...
- [poj] 2749 building roads
原题 2-SAT+二分答案! 最小的最大值,这肯定是二分答案.而我们要2-SATcheck是否在该情况下有可行解. 对于目前的答案limit,首先把爱和恨连边,然后我们n^2枚举每两个点通过判断距离来 ...
- BZOJ1296 [SCOI2009]粉刷匠 【dp】
题目 windy有 N 条木板需要被粉刷. 每条木板被分为 M 个格子. 每个格子要被刷成红色或蓝色. windy每次粉刷,只能选择一条木板上一段连续的格子,然后涂上一种颜色. 每个格子最多只能被粉刷 ...
- 在HTML网页上打印需要的内容
首先在head里面加入下面一段js代码: function preview(oper) { if (oper < 10) { bdhtml = window.document.body.inne ...
- vue后台项目
https://github.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin
- 内部类(inner class)的简单介绍
本文主要介绍内部类(inner class)的一些基本应用,将从内部类的分类角度,首先对每一个具体内部类进行介绍.主要包括普通的内部类[common inner class].局部内部类[local ...
- java算法(二) 快速排序
快速排序是一种交换排序. 快速排序由C. A. R. Hoare在1962年提出. 它的基本思想是:通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分:分割点左边都是比它小的数,右边都是比它大的数. 然后再 ...
- 生成 RSA 私钥及公钥
$ openssl # 进入 OpenSSL 程序 OpenSSL> genrsa -out rsa_private_key.pem 1024 # 生成私钥 OpenSSL> pkcs8 ...
- [从hzwer神犇那翻到的模拟赛题] 合唱队形
[问题描述] 学校要进行合唱比赛了,于是班主任小刘准备给大家排个队形. 他首先尝试排成m1行,发现最后多出来a1个同学:接着他尝试排成m2行,发现最后多出来a2个同学,……,他尝试了n种排队方案,但每 ...
