java常用类与包装类--常用类正则表达式 String正则方法+Matcher+Pattern
0.java中的正则
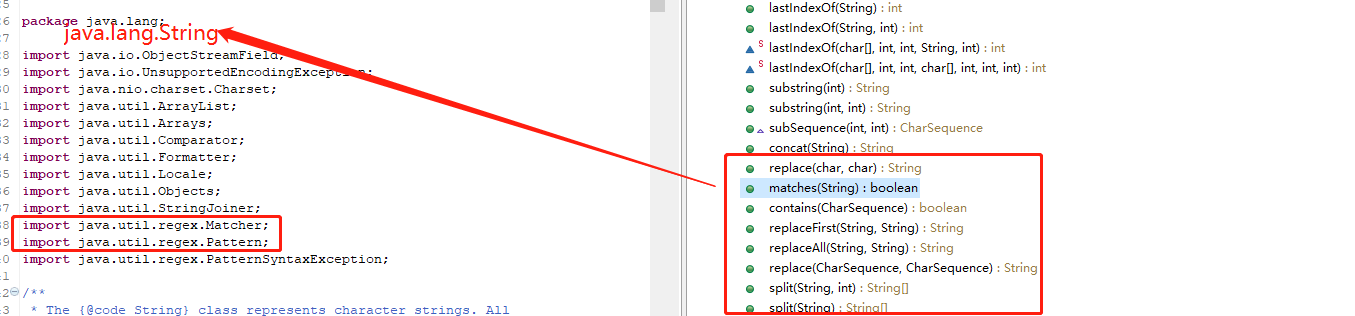
java 中的正则总共涉及三个类(或者说1个String类和一个regex包)
- java.lang.String
- java.util. Matcher
- java.util.Pattern
1.什么是正则表达式?
正则表达式是一种用来描述一定数量文本的模式。Regex代表Regular Express。我们使用一种自定义的模式来匹配一定数量的文本,并从中提取所需数据。
正则只和字符串相关了。
字符组:[字符组]
| [a-zA-Z] |
a 到 z 或 A 到 Z, 两头的字母包括在内(范围) |
| [a-d[m-p]] | a 到 d 或 m 到 p:[a-dm-p](并集) |
| [a-z&&[def]] | d、e 或 f(交集) |
| [a-z&&[^bc]] | a 到 z,除了 b 和 c:[ad-z](减去) |
| [a-z&&[^m-p]] | a 到 z,而非 m 到 p:[a-lq-z](减去) |
字符组案例
在同一个位置可能出现的各种字符组成了一个字符组,在正则表达式中用[]表示
字符分为很多类,比如数字、字母、标点等等。
假如你现在要求一个位置"只能出现一个数字",那么这个位置上的字符只能是0、1、2...9这10个数之一。
正则 |
待匹配字符 |
匹配 |
说明 |
[0123456789] |
8 |
True |
在一个字符组里枚举合法的所有字符,字符组里的任意一个字符 |
[0123456789] |
a |
False |
由于字符组中没有"a"字符,所以不能匹配 |
[0-9] |
7 |
True |
也可以用-表示范围,[0-9]就和[0123456789]是一个意思 |
[a-z] |
s |
True |
同样的如果要匹配所有的小写字母,直接用[a-z]就可以表示 |
[A-Z] |
B |
True |
[A-Z]就表示所有的大写字母 |
[0-9a-fA-F] |
e |
True |
可以匹配数字,大小写形式的a~f,用来验证十六进制字符 |
预定义字符:
元字符 |
匹配内容 |
| . | 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符 |
| \w | 匹配字母或数字或下划线 |
| \s | 匹配任意的空白符 |
| \d | 匹配数字 |
| \n | 匹配一个换行符 |
| \t | 匹配一个制表符 |
| \W |
匹配非字母或数字或下划线 |
| \D |
匹配非数字 |
| \S |
匹配非空白符 |
Logical 运算符
| Logical 运算符 | |
| XY | X 后跟 Y |
| X|Y | X 或 Y |
| (X) | X,作为捕获组 |
边界匹配器:
| 边界匹配器 | |
| ^ | 行的开头 |
| $ | 行的结尾 |
| \b | 单词边界 |
| \B | 非单词边界 |
| \A | 输入的开头 |
| \G | 上一个匹配的结尾 |
| \Z | 输入的结尾,仅用于最后的结束符(如果有的话) |
| \z | 输入的结尾 |
案例
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| 海. | 海燕海娇海东 | 海燕海娇海东 | 匹配所有"海."的字符 |
| ^海. | 海燕海娇海东 | 海燕 | 只从开头匹配"海." |
| 海.$ | 海燕海娇海东 | 海东 | 只匹配结尾的"海.$" |
量词:
| Greedy 数量词 | |
| X? | X,一次或一次也没有 |
| X* | X,零次或多次 |
| X+ | X,一次或多次 |
| X{n} | X,恰好 n 次 |
| X{n,} | X,至少 n 次 |
| X{n,m} | X,至少 n 次,但是不超过 m 次 |
| Reluctant 数量词 | |
| X?? | X,一次或一次也没有 |
| X*? | X,零次或多次 |
| X+? | X,一次或多次 |
| X{n}? | X,恰好 n 次 |
| X{n,}? | X,至少 n 次 |
| X{n,m}? | X,至少 n 次,但是不超过 m 次 |
| Possessive 数量词 | |
| X?+ | X,一次或一次也没有 |
| X*+ | X,零次或多次 |
| X++ | X,一次或多次 |
| X{n}+ | X,恰好 n 次 |
| X{n,}+ | X,至少 n 次 |
| X{n,m}+ | X,至少 n 次,但是不超过 m 次 |
量词案例
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| 李.? | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 |
李杰 |
?表示重复零次或一次,即只匹配"李"后面一个任意字符 |
| 李.* | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 |
*表示重复零次或多次,即匹配"李"后面0或多个任意字符 |
| 李.+ | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 |
+表示重复一次或多次,即只匹配"李"后面1个或多个任意字符 |
| 李.{1,2} | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 |
李杰和 |
{1,2}匹配1到2次任意字符
|
注意:前面的*,+,?等都是贪婪匹配,也就是尽可能匹配,后面加?号使其变成惰性匹配
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| 李.*? | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 | 李 李 李 |
惰性匹配 |
贪婪匹配详解
贪婪匹配:在满足匹配时,匹配尽可能长的字符串,默认情况下,采用贪婪匹配
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| <.*> |
<script>...<script> |
<script>...<script> |
默认为贪婪匹配模式,会匹配尽量长的字符串 |
| <.*?> | r'\d' |
<script> |
加上?为将贪婪匹配模式转为非贪婪匹配模式,会匹配尽量短的字符串 |
几个常用的非贪婪匹配Pattern
*? 重复任意次,但尽可能少重复
+? 重复1次或更多次,但尽可能少重复
?? 重复0次或1次,但尽可能少重复
{n,m}? 重复n到m次,但尽可能少重复
{n,}? 重复n次以上,但尽可能少重复
.*?的用法
. 是任意字符
* 是取 0 至 无限长度
? 是非贪婪模式。
何在一起就是 取尽量少的任意字符,一般不会这么单独写,他大多用在:
.*?x 就是取前面任意长度的字符,直到一个x出现
字符集[][^]案例
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| 李[杰莲英二棍子]* | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 |
李杰 |
表示匹配"李"字后面[杰莲英二棍子]的字符任意次 |
| 李[^和]* | 李杰和李莲英和李二棍子 |
李杰 |
表示匹配一个不是"和"的字符任意次 |
| [\d] | 456bdha3 |
4 |
表示匹配任意一个数字,匹配到4个结果 |
| [\d]+ | 456bdha3 |
456 |
表示匹配任意个数字,匹配到2个结果 |
分组 () 与 或 |[^]案例
身份证号码是一个长度为15或18个字符的字符串,如果是15位则全部由数字组成,首位不能为0;如果是18位,则前17位全部是数字,末位可能是数字或x,下面我们尝试用正则来表示:
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| ^[1-9]\d{13,16}[0-9x]$ | 110101198001017032 |
110101198001017032 |
表示可以匹配一个正确的身份证号 |
| ^[1-9]\d{13,16}[0-9x]$ | 1101011980010170 |
1101011980010170 |
表示也可以匹配这串数字,但这并不是一个正确的身份证号码,它是一个16位的数字 |
| ^[1-9]\d{14}(\d{2}[0-9x])?$ | 1101011980010170 |
False |
现在不会匹配错误的身份证号了 |
| ^([1-9]\d{16}[0-9x]|[1-9]\d{14})$ | 110105199812067023 |
110105199812067023 |
表示先匹配[1-9]\d{16}[0-9x]如果没有匹配上就匹配[1-9]\d{14}
|
转义符 \
在正则表达式中,有很多有特殊意义的是元字符,比如\n和\s等,如果要在正则中匹配正常的"\n"而不是"换行符"就需要对"\"进行转义,变成'\\'。
在python中,无论是正则表达式,还是待匹配的内容,都是以字符串的形式出现的,在字符串中\也有特殊的含义,本身还需要转义。所以如果匹配一次"\n",字符串中要写成'\\n',那么正则里就要写成"\\\\n",这样就太麻烦了。这个时候我们就用到了r'\n'这个概念,此时的正则是r'\\n'就可以了。
| 正则 | 待匹配字符 | 匹配 结果 |
说明 |
| \n | \n | False |
因为在正则表达式中\是有特殊意义的字符,所以要匹配\n本身,用表达式\n无法匹配 |
| \\n | \n | True |
转义\之后变成\\,即可匹配 |
| "\\\\n" | '\\n' | True |
如果在python中,字符串中的'\'也需要转义,所以每一个字符串'\'又需要转义一次 |
| r'\\n' | r'\n' | True |
在字符串之前加r,让整个字符串不转义 |
2.java中的String正则方法
public boolean matches(String regex) {
return Pattern.matches(regex, this);
}
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceAll(replacement);
}
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) {
/* fastpath if the regex is a
(1)one-char String and this character is not one of the
RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\\", or
(2)two-char String and the first char is the backslash and
the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter.
*/
char ch = 0;
if (((regex.value.length == 1 &&
".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) ||
(regex.length() == 2 &&
regex.charAt(0) == '\\' &&
(((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) &&
(ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE ||
ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE))
{
int off = 0;
int next = 0;
boolean limited = limit > 0;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) {
if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) {
list.add(substring(off, next));
off = next + 1;
} else { // last one
//assert (list.size() == limit - 1);
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
off = value.length;
break;
}
}
// If no match was found, return this
if (off == 0)
return new String[]{this};
// Add remaining segment
if (!limited || list.size() < limit)
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
// Construct result
int resultSize = list.size();
if (limit == 0) {
while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0) {
resultSize--;
}
}
String[] result = new String[resultSize];
return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result);
}
return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit);
}
public String[] split(String regex) {
return split(regex, 0);
}
2.1对String的matches方法解析
源码解析:
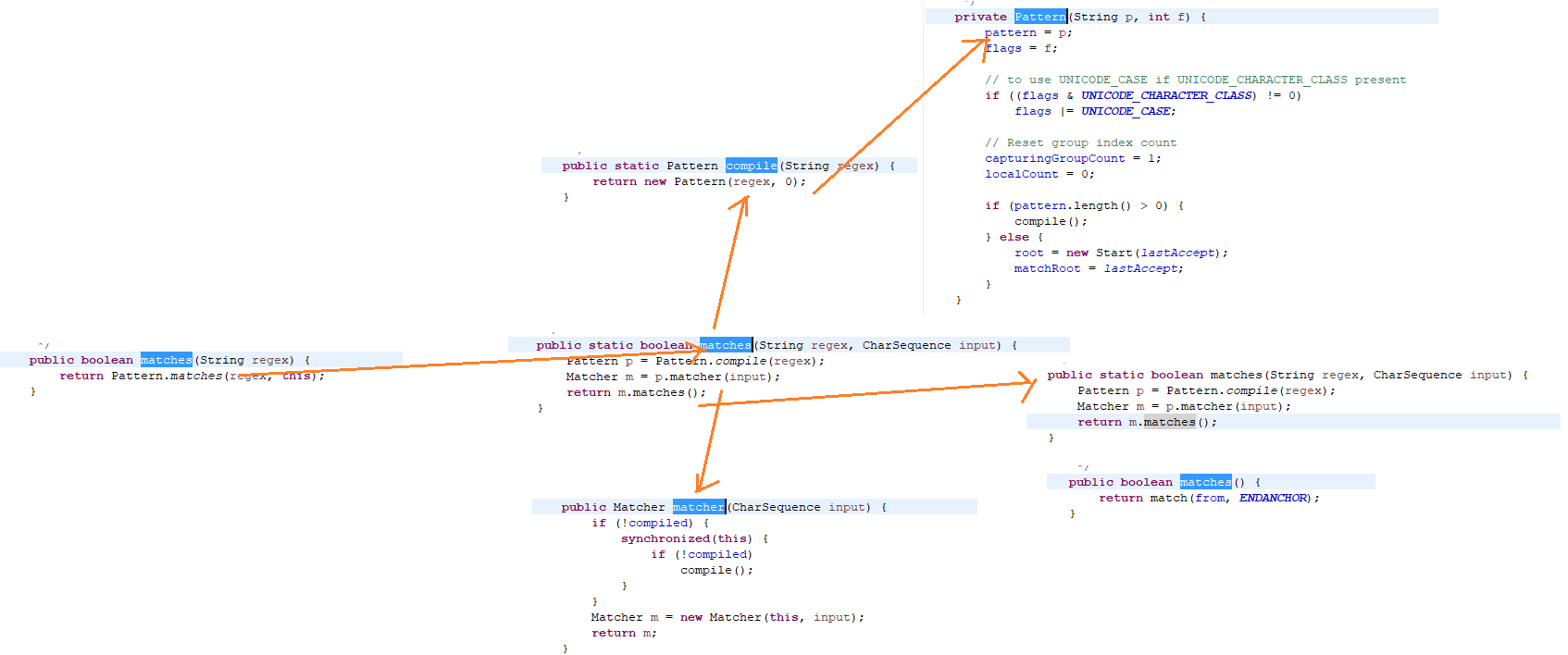
案例:
/*
* 匹配手机号
*
* 13012345678
* 13112345678
* 13212345678
* 130123456780
* 13513234567
*
*
* 要130 135开头的.
* 1.130/135开头
* 2.都是数字
* 3.长度11位
*
*
*/
public class RegexDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.println("输入一个手机号:");
String num = sc.next();
System.out.println(check(num));
} }
//判断一个字符串是否是130,135手机号
public static boolean check(String num){
//定义模式:正则表达式(带特殊符号的字符串)
String pattern = "13[05][0-9]{8}";
return num.matches(pattern); } }
匹配手机号
3 java之Pattern类详解
在JDK 1.4中,Java增加了对正则表达式的支持。
java与正则相关的工具主要在java.util.regex包中;此包中主要有两个类:Pattern、Matcher。
Pattern
声明:public final class Pattern implements java.io.Serializable
Pattern类有final 修饰,可知他不能被子类继承。
含义:模式类,正则表达式的编译表示形式。
注意:此类的实例是不可变的,可供多个并发线程安全使用。
字段:
public static final int UNIX_LINES = 0x01; /**
* 启用不区分大小写的匹配。*/
public static final int CASE_INSENSITIVE = 0x02; /**
* 模式中允许空白和注释。
*/
public static final int COMMENTS = 0x04; /**
* 启用多行模式。
*/
public static final int MULTILINE = 0x08; /**
* 启用模式的字面值解析。*/
public static final int LITERAL = 0x10; /**
* 启用 dotall 模式。
*/
public static final int DOTALL = 0x20; /**
* 启用 Unicode 感知的大小写折叠。*/
public static final int UNICODE_CASE = 0x40; /**
* 启用规范等价。
*/
public static final int CANON_EQ = 0x80;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5073258162644648461L; /**
* The original regular-expression pattern string.
*/
private String pattern; /**
* The original pattern flags.
*/
private int flags; /**
* Boolean indicating this Pattern is compiled; this is necessary in order
* to lazily compile deserialized Patterns.
*/
private transient volatile boolean compiled = false; /**
* The normalized pattern string.
*/
private transient String normalizedPattern; /**
* The starting point of state machine for the find operation. This allows
* a match to start anywhere in the input.
*/
transient Node root; /**
* The root of object tree for a match operation. The pattern is matched
* at the beginning. This may include a find that uses BnM or a First
* node.
*/
transient Node matchRoot; /**
* Temporary storage used by parsing pattern slice.
*/
transient int[] buffer; /**
* Temporary storage used while parsing group references.
*/
transient GroupHead[] groupNodes; /**
* Temporary null terminated code point array used by pattern compiling.
*/
private transient int[] temp; /**
* The number of capturing groups in this Pattern. Used by matchers to
* allocate storage needed to perform a match.此模式中的捕获组的数目。
*/
transient int capturingGroupCount; /**
* The local variable count used by parsing tree. Used by matchers to
* allocate storage needed to perform a match.
*/
transient int localCount; /**
* Index into the pattern string that keeps track of how much has been
* parsed.
*/
private transient int cursor; /**
* Holds the length of the pattern string.
*/
private transient int patternLength;
成员变量
组和捕获
捕获组可以通过从左到右计算其开括号来编号。
在表达式 ((A)(B(C))) 中,存在四个组:
| 1 | ABC |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | BC |
| 4 | C |
组零始终代表整个表达式。
构造器:
构造器是私有的,可知不能通过new创建Pattern对象。
private Pattern(String p, int f) {
pattern = p;
flags = f;
// Reset group index count
capturingGroupCount = 1;
localCount = 0;
if (pattern.length() > 0) {
compile();
} else {
root = new Start(lastAccept);
matchRoot = lastAccept;
}
}
如何得到Pattern类的实例?
查阅所有方法后发现:
public static Pattern compile(String regex) {
return new Pattern(regex, 0);
}
public static Pattern compile(String regex, int flags) {
return new Pattern(regex, flags);
}
可知是通过Pattern调用静态方法compile返回Pattern实例。
其他部分方法:
1、public Matcher matcher(CharSequence input)
创建匹配给定输入与此模式的匹配器,返回此模式的新匹配器。
public Matcher matcher(CharSequence input) {
if (!compiled) {
synchronized(this) {
if (!compiled)
compile();
}
}
Matcher m = new Matcher(this, input);
return m;
}
2、public static boolean matches(String regex,CharSequence input)
编译给定正则表达式并尝试将给定输入与其匹配。
public static boolean matches(String regex, CharSequence input) {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
return m.matches();
}
测试:
代码1(参考JDK API 1.6例子):
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("a*b")
Matcher m = p.matcher("aaaaab")
boolean b = m.matches()
System.out.println(b);// true
代码2:
System.out.println(Pattern.matches("a*b", "aaaaab"));// true
查阅matcher和matches方法可知matches自动做了一些处理,代码2可视为代码1的简化,他们是等效的。
如果要多次使用一种模式,编译一次后重用此模式比每次都调用此方法效率更高。
3、public String[] split(CharSequence input) 和 public String[] split(CharSequence input, int limit)
input:要拆分的字符序列;
limit:结果阈值;
根据指定模式拆分输入序列。
limit参数作用:
limit参数控制应用模式的次数,从而影响结果数组的长度。
如果 n 大于零,那么模式至多应用 n- 1 次,数组的长度不大于 n,并且数组的最后条目将包含除最后的匹配定界符之外的所有输入。
如果 n 非正,那么将应用模式的次数不受限制,并且数组可以为任意长度。
如果 n 为零,那么应用模式的次数不受限制,数组可以为任意长度,并且将丢弃尾部空字符串。
查看split(CharSequence input) 源码:
public String[] split(CharSequence input) {
return split(input, 0);
}
可知split(CharSequence input)实际调用了split(CharSequence input, int limit);以下只讨论split(CharSequence input, int limit)。
假设:
若input="boo:and:foo",匹配符为"o",可知模式最多可应用4次,数组的长度最大为5;
1、当limit=-2时,应用模式的次数不受限制且数组可以为任意长度;推测模式应用4次,数组的长度为5,数组为{"b","",":and:f","",""};
2、当limit=2时,模式至多应用1次,数组的长度不大于 2,且第二个元素包含除最后的匹配定界符之外的所有输入;推测模式应用1次,数组的长度为2,数组为{"b","o:and:foo"};
3、当limit=7时,模式至多应用6次,数组的长度不大于 7;推测模式应用4次,数组的长度为5,数组为{"b","",":and:f","",""};
4、当limit=0时,应用模式的次数不受限制,数组可以为任意长度,并且将丢弃尾部空字符串;推测模式应用4次,数组的长度为3,数组为{"b","",":and:f"}。
代码验证:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = null;
CharSequence input = "boo:and:foo";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("o");
arr = p.split(input, -2);
System.out.println(printArr(arr));// {"b","",":and:f","",""},共有5个元素
arr = p.split(input, 2);
System.out.println(printArr(arr));// {"b","o:and:foo"},共有2个元素
arr = p.split(input, 7);
System.out.println(printArr(arr));// {"b","",":and:f","",""},共有5个元素
arr = p.split(input, 0);
System.out.println(printArr(arr));// {"b","",":and:f"},共有3个元素
}
// 打印String数组
public static String printArr(String[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("{");
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
sb.append("\"").append(arr[i]).append("\"");
if (i != length - 1)
sb.append(",");
}
sb.append("}").append(",共有" + length + "个元素");
return sb.toString();
}
代码验证
输出结果与以上猜测结果一致。
4、toString()和pattern()
两个方法代码一样,都是返回此模式的字符串表示形式。
public String toString() {
return pattern;
}
public String pattern() {
return pattern;
}
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\d+");
System.out.println(p.toString());// 输出\d+
System.out.println(p.pattern());// 输出\d+
5、public int flags()
返回此模式的匹配标志。
public int flags() {
return flags;
}
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("a+", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
System.out.println(p.flags());//
查阅Pattern源代码:
public static final int CASE_INSENSITIVE = 0x02;
可知CASE_INSENSITIVE =2;所以测试输出2。
3.java之Matcher类详解
声明:public final class Matcher extends Objectimplements MatchResult
Matcher 类有final 修饰,可知他不能被子类继承。
含义:匹配器类,通过解释 Pattern 对 character sequence 执行匹配操作的引擎。
注意:此类的实例用于多个并发线程是不安全的。
字段:
/**
* The Pattern object that created this Matcher.创建此对象的模式匹配。
*/
Pattern parentPattern; /**
* The storage used by groups. They may contain invalid values if
* a group was skipped during the matching.组使用的存储。如果在匹配过程中跳过一个组,它们可能包含无效的值。
*/
int[] groups; /**
* The range within the sequence that is to be matched. Anchors
* will match at these "hard" boundaries. Changing the region
* changes these values.要匹配的序列中的范围。
*/
int from, to; /**
* Lookbehind uses this value to ensure that the subexpression
* match ends at the point where the lookbehind was encountered.
*/
int lookbehindTo; /**
* The original string being matched.匹配的目的字符串。
*/
CharSequence text; /**
* Matcher state used by the last node. NOANCHOR is used when a
* match does not have to consume all of the input. ENDANCHOR is
* the mode used for matching all the input. NOANCHOR表示不必匹配所有的输入;ENDANCHOR表示必须匹配所有的输入。
*/
static final int ENDANCHOR = 1;
static final int NOANCHOR = 0;
int acceptMode = NOANCHOR; /**
* The range of string that last matched the pattern. If the last
* match failed then first is -1; last initially holds 0 then it
* holds the index of the end of the last match (which is where the
* next search starts).最后一个匹配模式的字符串的范围。
*/
int first = -1, last = 0; /**
* The end index of what matched in the last match operation.在最后一次匹配操作中匹配的结束索引。
*/
int oldLast = -1; /**
* The index of the last position appended in a substitution.追加在替换中的最后位置的索引。
*/
int lastAppendPosition = 0; /**
* Storage used by nodes to tell what repetition they are on in
* a pattern, and where groups begin. The nodes themselves are stateless,
* so they rely on this field to hold state during a match.
*/
int[] locals; /**
* Boolean indicating whether or not more input could change
* the results of the last match.
*
* If hitEnd is true, and a match was found, then more input
* might cause a different match to be found.
* If hitEnd is true and a match was not found, then more
* input could cause a match to be found.
* If hitEnd is false and a match was found, then more input
* will not change the match.
* If hitEnd is false and a match was not found, then more
* input will not cause a match to be found.
*/
boolean hitEnd; /**
* Boolean indicating whether or not more input could change
* a positive match into a negative one.
*
* If requireEnd is true, and a match was found, then more
* input could cause the match to be lost.
* If requireEnd is false and a match was found, then more
* input might change the match but the match won't be lost.
* If a match was not found, then requireEnd has no meaning.
*/
boolean requireEnd; /**
* If transparentBounds is true then the boundaries of this
* matcher's region are transparent to lookahead, lookbehind,
* and boundary matching constructs that try to see beyond them.
*/
boolean transparentBounds = false; /**
* If anchoringBounds is true then the boundaries of this
* matcher's region match anchors such as ^ and $.
*/
boolean anchoringBounds = true;
字段
构造器
Matcher() {
}
Matcher(Pattern parent, CharSequence text) {
this.parentPattern = parent;
this.text = text;
// Allocate state storage
int parentGroupCount = Math.max(parent.capturingGroupCount, 10);
groups = new int[parentGroupCount * 2];
locals = new int[parent.localCount];
// Put fields into initial states
reset();
}
构造器有包访问权限,可知不能在包外通过new创建Matcher对象。
如何在自定义的包中得到Matcher类的实例?
Matcher类中没有合适的方法,查阅Pattern类有:
public Matcher matcher(CharSequence input) {
if (!compiled) {
synchronized(this) {
if (!compiled)
compile();
}
}
Matcher m = new Matcher(this, input);
return m;
}
可知需要通过Pattern对象调用matcher方法来返回Matcher 类的实例。
对照Matcher构造器源码,可知构造器将Pattern对象的引用赋于Matcher中变量parentPattern,目标字符串赋于变量text;并创建了数组groups和locals 。
数组groups是组使用的存储。存储的是当前匹配的各捕获组的first和last信息。
groups[0]存储的是组零的first,groups[1]存储的是组零的last,groups[2]存储的是组1的first,groups[3]存储的是组1的last,依次类推。关于捕获组的信息请看java之Pattern类详解中的组和捕获。
初始化后状态表:(具体分析见以下reset()方法)
| 变量 | 类型 | 值 |
| first | int | -1 |
| last | int | 0 |
| oldLast | int | -1 |
| lastAppendPosition | int | 0 |
| from | int | 0 |
| to | int |
text.length() |
| groups |
int[] |
locals[i] = -1 |
| locals |
int[] |
locals[i] = -1 |
| parentPattern |
Pattern |
构造器传入的Pattern对象 |
| text |
CharSequence |
构造器传入的目标字符串 |
部分方法:
1、public String toString()
返回匹配器的字符串表示形式。包含可用于调试的信息的 Matcher 字符串表示形式。未指定确切格式。
源码:
public String toString() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("java.util.regex.Matcher");
sb.append("[pattern=" + pattern());
sb.append(" region=");
sb.append(regionStart() + "," + regionEnd());
sb.append(" lastmatch=");
if ((first >= 0) && (group() != null)) {
sb.append(group());
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
System.out.println(m);
打印:
java.util.regex.Matcher[pattern=(\w+)%(\d+) region=0,11 lastmatch=]
2、public Matcher reset()
重置匹配器。
public Matcher reset() {
first = -1;
last = 0;
oldLast = -1;
for(int i=0; i<groups.length; i++)
groups[i] = -1;
for(int i=0; i<locals.length; i++)
locals[i] = -1;
lastAppendPosition = 0;
from = 0;
to = getTextLength();
return this;
}
int getTextLength() {
return text.length();
}
可知reset()方法改变了变量first 、last 、oldLast、lastAppendPosition、from、to的值并将数组groups、locals初始化。
状态变化:
| 变量 | 类型 | 新值 |
| first | int | -1 |
| last | int | 0 |
| oldLast | int | -1 |
| lastAppendPosition | int | 0 |
| from | int | 0 |
| to | int |
text.length() |
| groups |
int[] |
locals[i] = -1 |
| locals |
int[] |
locals[i] = -1 |
测试1:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
if (m.find()) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:0
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():ab%12
}
if (m.find()) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:6
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():cd%34
}
测试2:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
if (m.find()) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:0
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():ab%12
}
m.reset();
if (m.find()) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:0
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():ab%12
}
由测试1和测试2可知reset方法可将Matcher 对象状态初始化。
3、public Matcher reset(CharSequence input)
重置此具有新输入序列的匹配器。
public Matcher reset(CharSequence input) {
text = input;
return reset();
}
可知此方法在reset()方法的基础上改变了目标字符串的值。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
m.reset("ef%56-gh%78");
while (m.find()) {
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());
}
打印:
group():ef%56
group():gh%78
4、public Pattern pattern()
返回由此匹配器解释的模式。
源码:
public Pattern pattern() {
return parentPattern;
}
pattern()返回parentPattern,即构造器传入的Pattern对象。
5、public int groupCount()
返回此匹配器模式中的捕获组数。根据惯例,零组表示整个模式。它不包括在此计数中。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
System.out.println(m.groupCount());// 2
6、public String group()
返回当前查找而获得的与组匹配的所有子串内容。
查看group()源码:
public String group() {
return group(0);
}
可知group()实际调用了group(int group)方法,参数group为0。组零表示整个模式。
7、public String group(int group)
返回当前查找而获得的与组匹配的所有子串内容。
8、public int start()
返回当前匹配的子串的第一个字符在目标字符串中的索引位置 。
源码:
public int start() {
if (first < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("No match available");
return first;
}
可知start()方法返回的是匹配器的状态first。
9、public int start(int group)
返回当前匹配的指定组中的子串的第一个字符在目标字符串中的索引位置 。
10、public int end()
返回当前匹配的子串的最后一个字符的下一个位置在目标字符串中的索引位置 。
源码:
public int end() {
if (first < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("No match available");
return last;
}
可知end()方法返回的是匹配器的状态last。
11、public int end(int group)
返回当前匹配的的指定组中的子串的最后一个字符的下一个位置在目标字符串中的索引位置 。
12、public boolean find()
在目标字符串里查找下一个匹配子串。如果匹配成功,则可以通过 start、end 和 group 方法获取更多信息。
源码:
public boolean find() {
int nextSearchIndex = last;
if (nextSearchIndex == first)
nextSearchIndex++;
// If next search starts before region, start it at region
if (nextSearchIndex < from)
nextSearchIndex = from;
// If next search starts beyond region then it fails
if (nextSearchIndex > to) {
for (int i = 0; i < groups.length; i++)
groups[i] = -1;
return false;
}
return search(nextSearchIndex);
}
从源码中可知nextSearchIndex为下次查找匹配的开始位置;nextSearchIndex的值有三次判定:
1、last==first时,nextSearchIndex++;
2、nextSearchIndex<from时,nextSearchIndex=from;
3、nextSearchIndex>to时,return false;
可通过region(int start,int end)方法修改from和to,以此来影响下次查找匹配的开始位置。
注意:此方法会改变匹配器的状态:first、last和oldLast。
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
while (m.find()) {
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());
System.out.println("start():" + m.start());
System.out.println("end():" + m.end());
System.out.println("group(1):" + m.group(1));
System.out.println("start(1):" + m.start(1));
System.out.println("end(1):" + m.end(1));
System.out.println("group(2):" + m.group(2));
System.out.println("start(2):" + m.start(2));
System.out.println("end(2):" + m.end(2));
System.out.println();
}
打印:

group():ab%12
start():0
end():5
group(1):ab
start(1):0
end(1):2
group(2):12
start(2):3
end(2):5 group():cd%34
start():6
end():11
group(1):cd
start(1):6
end(1):8
group(2):34
start(2):9
end(2):11

可知find()方法匹配了两个子串:ab%12和cd%34;每个子串有2组。
13、public boolean find(int start)
重置此匹配器,然后尝试查找匹配该模式,从指定的位置开始查找下一个匹配的子串。如果匹配成功,则可以通过 start、end 和 group 方法获取更多信息。
注意:此方法会改变匹配器的转态。
源码:
public boolean find(int start) {
int limit = getTextLength();
if ((start < 0) || (start > limit))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal start index");
reset();
return search(start);
}
从源码可知此方法首先重置匹配器,然后搜索匹配,下次查找匹配的开始位置为指定的start参数。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
if (m.find(1)) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:1
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():b%12
}
if (m.find(0)) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:0
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():ab%12
}
if (m.find()) {
System.out.println("开始索引:" + m.start());// 开始索引:6
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());// group():cd%34
}
当有m.find(1)时,重置匹配器,从索引1处开始匹配,匹配的子串为“b%12”;
当有m.find(0)时,重置匹配器,从索引0处开始匹配,匹配的子串为“ab%12”;
当有m.find()时,并没有重置匹配器,从索引6处开始匹配,匹配的子串为“cd%34”;
14、public int regionStart()
报告此匹配器区域的开始索引。
源码:
public int regionStart() {
return from;
}
可知end()方法返回的是匹配器的状态from。
15、public int regionEnd()
报告此匹配器区域的结束索引(不包括)。
源码:
public int regionEnd() {
return to;
}
可知end()方法返回的是匹配器的状态to。
16、public Matcher region(int start,int end)
设置此匹配器的区域限制。重置匹配器,然后设置区域,使其从 start 参数指定的索引开始,到 end 参数指定的索引结束(不包括end索引处的字符)。
public Matcher region(int start, int end) {
if ((start < 0) || (start > getTextLength()))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("start");
if ((end < 0) || (end > getTextLength()))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("end");
if (start > end)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
reset();
from = start;
to = end;
return this;
}
从源代码中可知region方法首先调用reset()重置,然后对from 和to赋值,来设置匹配的目的字符串的范围。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
m.region(0, 4);
while (m.find()) {
System.out.println("group():" + m.group());
System.out.println("regionStart():" + m.regionStart());
System.out.println("regionEnd():" + m.regionEnd());
}
打印:
group():ab%1
regionStart():0
regionEnd():4
17、public boolean lookingAt()
从目标字符串开始位置进行匹配。只有在有匹配且匹配的某一子串中包含目标字符串第一个字符的情况下才会返回true。
源码:
public boolean lookingAt() {
return match(from, NOANCHOR);
}
从源码中可知下次查找匹配的开始位置为from,可通过region(int start,int end)方法修改from的值。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
System.out.println(m.lookingAt());// true
m = p.matcher("%ab%12-cd%34");
System.out.println(m.lookingAt());// false
18、public boolean matches()
只有完全匹配时才会返回true。
源码:
public boolean matches() {
return match(from, ENDANCHOR);
}
对比上一个方法lookingAt(),从代码上看差别很小,调用的match方法只有一个参数不一样;lookingAt中使用的NOANCHOR,而matches中使用的ENDANCHOR。
NOANCHOR表示不必匹配所有的输入;ENDANCHOR表示必须匹配所有的输入。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("%ab%12");
System.out.println(m.matches());// false
m = p.matcher("ab%12%");
System.out.println(m.matches());// false
m = p.matcher("ab%12");
System.out.println(m.matches());// true
19、public Matcher appendReplacement(StringBuffer sb, String replacement)
将当前匹配子串替换为指定字符串,并将从上次匹配结束后到本次匹配结束后之间的字符串添加到一个StringBuffer对象中,最后返回其字符串表示形式。
注意:对于最后一次匹配,其后的字符串并没有添加入StringBuffer对象中,若需要这部分的内容需要使用appendTail方法。
20、public StringBuffer appendTail(StringBuffer sb)
将最后一次匹配工作后剩余的字符串添加到一个StringBuffer对象里。
源码:
public StringBuffer appendTail(StringBuffer sb) {
sb.append(getSubSequence(lastAppendPosition, getTextLength()).toString());
return sb;
}
查看源码有getSubSequence(lastAppendPosition, getTextLength()),即获取从lastAppendPosition索引处开始,到目的字符串结束索引处之间的子串。
lastAppendPosition为何值?
查阅Matcher类代码后,发现appendReplacement方法中有:
lastAppendPosition = last;
last即目前最后一次匹配结束后的索引。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("前ab%12中cd%34后");
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
while (m.find()) {
m.appendReplacement(s, "app");
}
System.out.println(s);// 前app中app
m.appendTail(s);
System.out.println(s);// 前app中app后
21、public StringreplaceAll(String replacement)
将匹配的子串用指定的字符串替换。
public String replaceAll(String replacement) {
reset();
boolean result = find();
if (result) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
do {
appendReplacement(sb, replacement);
result = find();
} while (result);
appendTail(sb);
return sb.toString();
}
return text.toString();
}
查看源码可知此方法首先重置匹配器,然后判断是否有匹配,若有,则创建StringBuffer 对象,然后循环调用appendReplacement方法进行替换,最后调用 appendTail方法并返回StringBuffer 对象的字符串形式。
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println(m.replaceAll("app"));// app-app
22、public String replaceFirst(String replacement)
将匹配的第一个子串用指定的字符串替换。
public String replaceFirst(String replacement) {
if (replacement == null)
throw new NullPointerException("replacement");
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
reset();
if (find())
appendReplacement(sb, replacement);
appendTail(sb);
return sb.toString();
}
查看源码可知此方法其实是 replaceAll方法的减配版本,只对第一次匹配做了替换。
测试:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(\\w+)%(\\d+)");
Matcher m = p.matcher("ab%12-cd%34");
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println(m.replaceFirst("app"));// app-cd%34
23、public Matcher usePattern(Pattern newPattern)
更改匹配器的匹配模式。
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("[a-z]+");
Matcher m = p.matcher("111aaa222");
System.out.println(piPei(m));// (模式[a-z]+):匹配子串:aaa;开始位置:3;结束位置:6;
m.usePattern(Pattern.compile("\\d+"));
System.out.println(piPei(m));// (模式\d+):匹配子串:222;开始位置:6;结束位置:9;
}
public static String piPei(Matcher m) {
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
while (m.find()) {
s.append("匹配子串:" + m.group() + ";");
s.append("开始位置:" + m.start() + ";");
s.append("结束位置:" + m.end() + ";");
}
if (s.length() == 0) {
s.append("没有匹配到!");
}
s.insert(0, "(模式" + m.pattern().pattern() + "):");
return s.toString();
}
可以看到更改匹配模式为"\\d+"后,只匹配到了"222",若需要匹配所有数字字符,应对匹配器初始化。
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("[a-z]+");
Matcher m = p.matcher("111aaa222");
System.out.println(piPei(m));// (模式[a-z]+):匹配子串:aaa;开始位置:3;结束位置:6;
m.usePattern(Pattern.compile("\\d+"));
m.reset();
System.out.println(piPei(m));// (模式\d+):匹配子串:111;开始位置:0;结束位置:3;匹配子串:222;开始位置:6;结束位置:9;
java常用类与包装类--常用类正则表达式 String正则方法+Matcher+Pattern的更多相关文章
- java常用类与包装类--常用类字符串String类、StringBuffer类、Stringbuilder类
1.String类 1.1String类的概念和储存结构: (1)字符串是一个比较特殊的对象,可以使用new,也可以不使用new来创建字符串对象 String s1 = new String(&quo ...
- Java中利用MessageFormat对象实现类似C# string.Format方法格式化
我们在写C#代码的时候常常会使用到string.Format("待格式化字符串{0},{1},....",参数1,参数2,...),来格式化字符串,特别是拼接字符的时候,这种方式使 ...
- Java基础之Java常用类--Object类,字符串相关类,包装类,日期相关类,数字相关类
Java是一种面向对象的语言,也就是将万事万物可以描述为对象,特点如下: 1.面向对象是常见的一种思考习惯,符合人们的思考习惯.2.面向对象的出现,将复杂的事情简单化.3.面向对象的出现,将之前过程中 ...
- Java中常用类(包装类扩展知识)
Java常用类有哪些? 八大基本数据类型的包装类 包装类均位于java.lang包中,包装类和基本数据类型的对应关系如下表: 基本数据类型 包装类 byte Byte boolean Boolean ...
- Java常用类:包装类,String,日期类,Math,File,枚举类
Java常用类:包装类,String,日期类,Math,File,枚举类
- java常用类,包装类,String类的理解和创建对象以及StringBuilder和StringBuffer之间的区别联系
一.包装类的分类: 1.黄色部分的父类为Number 继承关系: Boolean Character 其他六个基本数据类型 2.装箱和拆箱 理解:一个例子,其他的都相同 装箱:Integer inte ...
- JAVA基础--常用类 String,StringBuffer, 基础数据类型包装类, Math类, Enum类
字符串相关类: String, StringBuffer String类为不可变的字符序列 String s1="hello"; String s2="hello&quo ...
- Java SE核心之一:常用类,包装类,其他基本数据类型包装类。
在Java继承体系中,java.lang.Object类位于顶端(是所有对象的直接或间接父类).如果一个类没有写extends关键字声明其父类,则该类默认继承java.lang.Object类.Obj ...
- 3.1常用类(java学习笔记)包装类及日期类
一.包装类 java是一门面向对象的语言,秉承一切皆对象的思想. 可java中有一些基本数据类型并不是对象,有时可能需要将它们变为对象. 这时就需要用到我们的包装类了. 基本数据类型 包装类 int ...
随机推荐
- PyCharm安装+破解
PyCharm 是一款功能强大的 Python 编辑器,具有跨平台性,鉴于目前最新版 PyCharm 使用教程较少,为了节约时间,来介绍一下 PyCharm 在 Windows下是如何安装的. 这是 ...
- jmeter响应数据Unicode编码转换为汉字
2018-07-09 10:24:34 每次用jmeter做接口测试时,响应信息中文总是显示Unicode编码格式,每次都要在网上寻找这一段转换的代码,但是我发现在网上找这段代码有点麻烦,像我 ...
- cocos2dx基础篇(5) 按钮
这篇是直接复制的别人的,太多了,难得写... [本节内容] CCMenu.CCMenuItem其具体的六个子类 [菜单CCMenu] 菜单CCMenu是用来装载菜单按钮的图层,图层中的子节点只能够是菜 ...
- python学习之数据类型(dic)
3.8 字典 3.8.1 字典的介绍 字典(dict)是python中唯一的一个映射类型,它是以{ }括起来的键值对组成,在dict中key是唯一的.在保存的时候,根据key来计算出一个内存地址, ...
- 【Python开发】【神经网络与深度学习】网络爬虫之图片自动下载器
python爬虫实战--图片自动下载器 之前介绍了那么多基本知识[Python爬虫]入门知识(没看的赶紧去看)大家也估计手痒了.想要实际做个小东西来看看,毕竟: talk is cheap show ...
- 【神经网络与深度学习】【CUDA开发】【VS开发】Microsoft官方移植了Caffe配置过程说明
想在Windows平台使用Caffe,吭哧吭哧下载了半天第三方库,后来忽然发现Microsoft官方移植了Caffe,配置起来简直太省心了- 1. 从Microsoft官方Github上下载Caffe ...
- [转帖]linux学习问题总结
linux学习问题总结 https://www.cnblogs.com/chenfangzhi/p/10661946.html 学习作者的思路 目录 一.环境变量和普通变量的区别 二.rsyslog和 ...
- idea运行时 Process finished with exit code -1073741819 (0xC0000005)
问题描述: idea中启动项目报 Process finished with exit code -1073741819 (0xC0000005) ,如图所示: 问题解决: ...
- MySql MediumBlob——MySql的Bolb四种类型
MySQL中,BLOB是一个二进制大型对象,是一个可以存储大量数据的容器,它能容纳不同大小的数据.BLOB类型实际是个类型系列(TinyBlob.Blob.MediumBlob.LongBlob),除 ...
- CPU飙高,频繁GC,怎么排查?
处理过线上问题的同学基本上都会遇到系统突然运行缓慢,CPU 100%,以及Full GC次数过多的问题.当然,这些问题的最终导致的直观现象就是系统运行缓慢,并且有大量的报警. 本文主要针对系统运行缓慢 ...
