sping ioc 源码分析(二)-- refresh()方法分析
测试环境代码:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.yang.xiao.hui.ioc")
@Conditional(MyCondition.class)
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
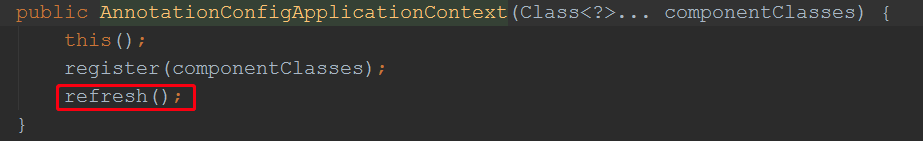
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(App.class); }
}
debug调试启动过程:本次主要分析refresh()方法:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { //该方法是spring ioc的核心,下面我们主要分析每一个方法
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();//1 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();//2 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);//3 try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);//4 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);//5 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);//6 // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();//7 // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();//8 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();//9 // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();//10 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);//11 // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();//12
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
1. prepareRefresh(); // Prepare this context for refreshing. 为调用后续的方法进行准备工作
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); //记录一下启动时间,是一个时间戳
this.closed.set(false); //将applicationContext状态设置非关闭
this.active.set(true); //将applicationContext状态设置已激活
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources(); //这个是留给子类去实现的,目前没做任何东东
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); //这里做了2个工作,一个是创建一个环境对象StandardEnvironment,另一个是校验必须的属性是否在环境变量中存在,不存在就抛异常MissingRequiredPropertiesException
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) { //会尽量这里,默认是空
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);//applicationListeners 为空集合
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear(); //重新设置applicationListeners内容
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>(); //收集早期的事件,一旦事件派发器可以使用,就派发这些事件
}
小结:prepareRefresh() 主要是为刷新工作做了些准备:设置context的状态,创建环境对象,初始化一些早期的事件监听器和事件
2.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
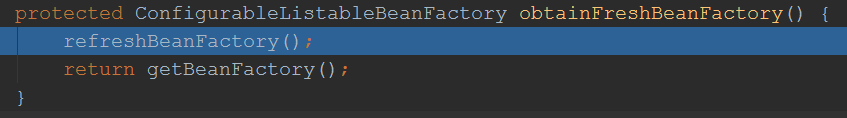
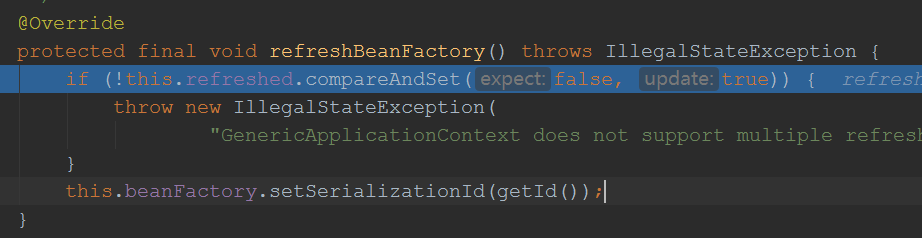

小结:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 方法作用是:刷新bean工厂,并将并工厂返回去,这个bean工厂是在GenericApplicationContext的构造方法进行初始化的

3.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); //Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 对beanFactory做一些初始化操作
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc. //设置类加载器,表达式解析器,资源相关的处理器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks. //添加了一个后者处理器,添加忽略接口,这个忽略接口的本意我还不知道,并非是说你使用@Autowired注入这些接口,就会被忽略
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
//下面这些resolvabelDependency的意思是,我要注入一个接口作为属性,如果该接口有很多实现类,此时不知道注入哪一个实现类,通过下面的方法可以指定要注入的对象,例如BeanFactory有很多实现类
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners. //这里新增了一个后置处理器,用于检测内部的的ApplicationListener
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
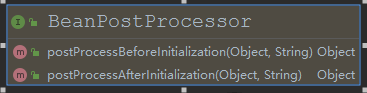
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found. //这个是用于类加载阶段进行AOP切入,而我们平时用的cglib或jdk动态代理是运行期切入
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans. //向容器中注册了3个环境相关的bean
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
prepareBeanFactory 新增了2个后置处理器:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 该后置处理器是处理实现Aware接口的bean的对应属性赋值:
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { //在bean 的init方法调用前执行
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null &&
(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); //执行对应的Aware属性赋值
}
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
prepareBeanFactory 新增的另一个后置处理器ApplicationListenerDetector用于检测某个单例的bean是否是监听器
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { //这个是init()方法执行后处理的
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) { //判断指定的bean是否监听器
// potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName); //获取指定的bean是否单例
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
// singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean); //收集监听器
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
// inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}
小结: prepareBeanFactory方法主要给beanFactory 设置了类加载器,环境相关的bean,2个后置处理器,以及一些忽略接口和可提前解析的接口
4. postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.这个是留给子类去实现的

子类可以重写该方法,在beanFactory标准初始化后(方法3是对其进行初始化),对其进行修改,所有的bean定义信息都被加载,但还没有bean被实例化,这个方法也允许,往beanFactory中添加特殊的后置处理器
5.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 按顺序执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的相应方法,在此我们分析下BeanFactoryPostProcessor,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor 三者区别
先看BeanFactoryPostProcessor,允许我们对beanFactory做一些修改,例如新增或者覆盖一些属性,甚至更早的初始化一些bean
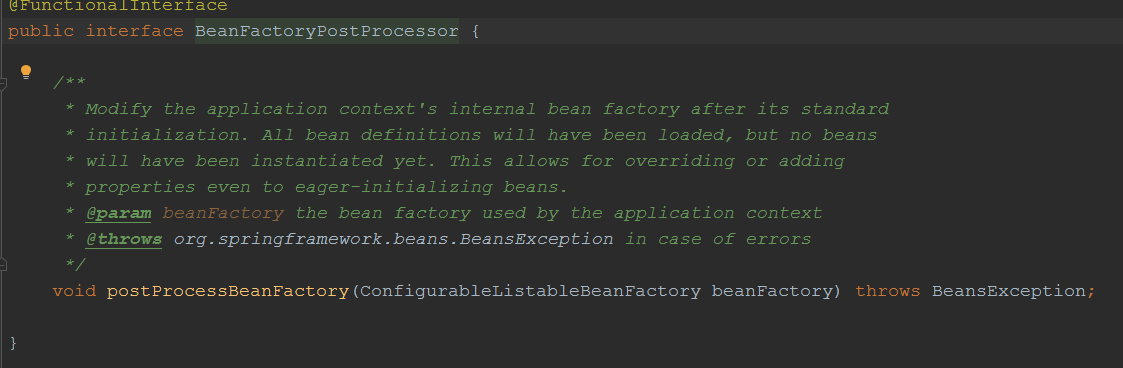
在这一步里,调用了一个核心的类ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,将@component等注解标注的类定义信息扫描到ioc容器中了,具体参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yangxiaohui227/p/13431628.html
接着我们看:BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 它继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,提供了一个方法,给我可以修改Bean的定义信息机会,例如将一个A类的BeanDefinition的类属性改成B类
最后我们看看BeanPostProcessor,这个是用于普通bean的生命周期逻辑处理,例如,init()方法执行前后
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);//针对的是下BeanFactoryPostProcessor,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
对于一组PostProcessors,他们执行需要一个顺序,这里就会涉及到PriorityOrdered 和Ordered接口,所以执行的顺序是,实现PriorityOrdered-->实现Ordered--》普通的,而BeanFactoryPostProcessor,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
的执行顺序是先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,然后再到BeanFactoryPostProcessor,有了上面的知识,我们开始分析源码:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. 优先执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();//已经执行过的处理器,防止重复执行 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); //普通的beanFactory后置处理器
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();//收集BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { //参数传过来的
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); //如果是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor就直接执行
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); //如果是普通的就收集
}
} // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); //当前需要执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor // First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. //首先是执行实现PriorityOrdered的后置处理器
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); //排序
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);//收集起来
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); //遍历调用
currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); //清空当前已经执行过的后置处理器集合 // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. //同样的方式处理实现Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. //最后处理没有实现PriorityOrdered或者Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
} // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); //因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,所以这里是执行后者的方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans //
//前面执行完所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,剩下要执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法,也要分实现PriorityOrdered,实现Ordered,和没有实现这2者的情况
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
} // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.执行实现PriorityOrdered
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. 执行实现Ordered接口的
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. 执行没有实现order接口的
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
小结:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors的逻辑是分组,并按照不同的顺序执行BeanFactoryPostProcessors
6. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);//注册BeanPostProcessors用于后面拦截Bean的创建过程
这里的逻辑是,获取所有的BeanPostProcessors,然后也跟方法5一样,分优先级,实现PriorityOrdered->internal->实现Ordered接口->普通的
之后按顺序将它们存到:DefaultListableBeanFactory 父类的一个集合中:List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
具体源码:

public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); //获取所有的BeanPostProcessor // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; //这里加1是因为下面添加了一个BeanPostProcessorChecker
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
//分组处理,分成4组
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
} // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
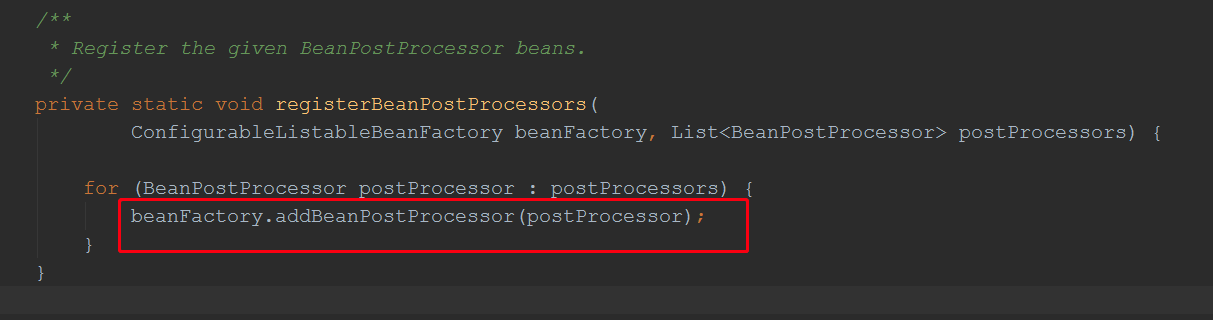
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); //排序
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); //保存到容器 // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. //处理Ordered
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); //排序
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); //注册到beanFactory // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); //排序
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); //这里重新添加了这个ApplicationListenerDetector,是为了让它排在最后
}
我们看看注册方法:

7.initMessageSource(); // Initialize message source for this context. 初始化专门处理国际化的bean
protected void initMessageSource() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) { //先判断容器中有没对应的bean
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());//设置父容器的MessageSource
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource(); //容器中不存在,就新创建一个,然再将其放到ioc中
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}
小结,上面仅仅是向容器中注入了一个message bean
8.initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // 初始化事件派发器,该对象存有一个list,值的内容是监听器,里面还有个发布事件的方法,发布事件时,遍历监听器,调用每个监听器去处理该事件
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { //容器中已存在就直接获取
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);//容器中不存在就创建
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
9.onRefresh(); 该方法是留给子类实现,在springboot内嵌tomcat的实现原理中,就是在该方法进行初始化tomcat容器的
10.registerListeners(); //主要逻辑是添加监听器到事件派发器中,然后派发事件
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); //将已存在的监听器加到事件派发器中
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);//从容器中获取所有的监听器
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);////将已存在的监听器加到事件派发器中
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; //获取所有早期的事件
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);//派发事件
}
}
}
11.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);//完成所有的非懒加载的类实例化,这里是核心,请参考另一篇博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yangxiaohui227/p/13438849.html
12.finishRefresh();//完成刷新,发布相关的事件
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches(); //清除缓存
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor(); //初始化LifecycleProcessor
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();//调用LifecycleProcessor的OnRefresh()方法
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));//派发上下文刷新事件
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); //MBean 不清楚啥作用
}
至此,启动核心源码分析完毕
sping ioc 源码分析(二)-- refresh()方法分析的更多相关文章
- sping ioc 源码分析(一)-- register(componentClasses) 方法
一.测试环境的搭建: public class Apple { } @Component public class MyComponet { } public class MyCondition im ...
- spring-boot-2.0.3启动源码篇二 - run方法(一)之SpringApplicationRunListener
前言 Springboot启动源码系列还只写了一篇,已经过去一周,又到了每周一更的时间了(是不是很熟悉?),大家有没有很期待了?我会尽量保证启动源码系列每周一更,争取不让大家每周的期望落空.一周之中可 ...
- Glide源码解析二---into方法
转载请标明出处,维权必究: https://www.cnblogs.com/tangZH/p/12543154.html Glide作为一个强大的图片加载框架,已经被android官方使用,所以,明白 ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(二)
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(二) 前言 上篇文章Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(一)简单分析了getBean()方法,还记得分析了什么吗?不记得了才 ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--容器实例化Bean的四种方法
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--实例化Bean的几种方法 前言 前面的文章Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(二)在讲解到bean真正通过那些方式实例化出来的时候,并没有继续分 ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(一)
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Bean实例化过程(一) 前言 上一篇文章Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Ioc容器注册BeanPostProcessor后置处理器以及事件消息处理已经完成了对 ...
- Spring IOC 源码分析
Spring 最重要的概念是 IOC 和 AOP,本篇文章其实就是要带领大家来分析下 Spring 的 IOC 容器.既然大家平时都要用到 Spring,怎么可以不好好了解 Spring 呢?阅读本文 ...
- Spring IoC 源码分析 (基于注解) 之 包扫描
在上篇文章Spring IoC 源码分析 (基于注解) 一我们分析到,我们通过AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类传入一个包路径启动Spring之后,会首先初始化包扫 ...
- Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Ioc的基础知识准备
Spring Ioc源码分析系列--Ioc的基础知识准备 本系列文章代码基于Spring Framework 5.2.x Ioc的概念 在Spring里,Ioc的定义为The IoC Containe ...
随机推荐
- javacv教程文档手册开发指南汇总篇
本章作为javacv技术栈系列文章汇总 前言 写了不少关于javacv的文章,不敢说精通 ,只能说对javacv很熟悉.虽然偶尔也提交pull request做做贡献,但是javacv包含的库实在太多 ...
- 超级码力编程赛带着6万奖金和1200件T恤向你跑来了~
炎炎夏日,总是感觉很疲劳,提不起一点精神怎么办?是时候参加一场比赛来唤醒你的激情了!阿里云超级码力在线编程大赛震撼携手全国数百所高校震撼来袭. 它来了,它来了,它带着60000现金和1200件T恤向你 ...
- 微信小程序入门教程
首先请看demo 很简单的静态js就可以实现一款小程序开发. js.json.html.css四个核心文件 序言 开始开发应用号之前,先看看官方公布的「小程序」教程吧!(以下内容来自微信官方公布的「小 ...
- Sql 注入----学习笔记2
转载自:http://blog.51cto.com/quiterr/1699964 sql注入 sql注入98年第一次出现在<phrack>54期上. 注入攻击有两个关键条件,第一是用户能 ...
- MockMvc编写单测
目录 MockMvc 注意点 code 待测试的controller 测试类 github MockMvc 注意点 1.通过spring上下文获取mockmvc对象 @BeforeEach publi ...
- Winform TextBox 数据绑定空值校验问题
问题: using System; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; public class Cost { /// <summary&g ...
- WebApi OAuth2身份认证
一.什么是OAuth OAuth是一个关于授权(Authorization)的开放网络标准,目前的版本是2.0版.注意是Authorization(授权),而不是Authentication(认证). ...
- mybatis-spring-boot-starter 1.3.0 操作实体类的SpringBoot例子
例程下载:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/xiandedanteng/gatling20200428-02.zip 需求:使用mybatis实现对hy_emp表的CRU ...
- 入门alibaba的EasyExcel
一.关于EasyExcel 1.什么是EasyExcel,有什么作用? EasyExcel是一个基于Java的简单.省内存的读写Excel的开源项目.在尽可能节约内存的情况下支持读写百M的Excel. ...
- Java 的各种内部类、Lambda表达式
内部类 内部类是指在一个外部类的内部再定义一个类.内部类的出现,再次打破了Java单继承的局限性. 内部类可以是静态 static 的,也可用 public,default,protected 和 p ...
