Wakeup Source框架设计与实现
Wakeup Source 为系统组件提供了投票机制,以便低功耗子系统判断当前是否可以进入休眠。
Wakeup Source(后简称:WS) 模块可与内核中的其他模块或者上层服务交互,并最终体现在对睡眠锁的控制上。
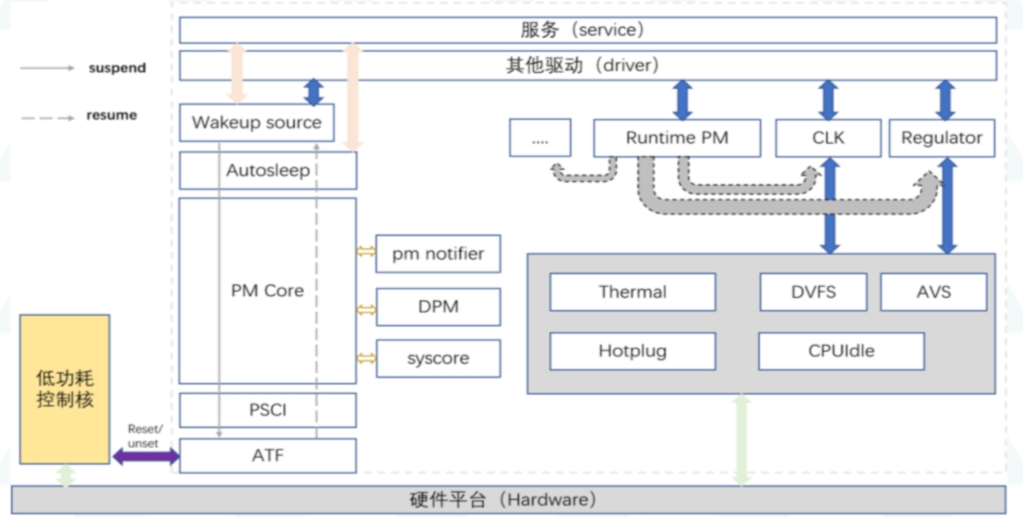
1. 模块功能说明
WS的处理逻辑基本上是围绕 combined_event_count 变量展开的,这个变量高16位记录系统已处理的所有的唤醒事件总数,低16位记录在处理中的唤醒事件总数。每次持锁时,处理中的唤醒事件记录(低16位)会加1;每次释放锁时,处理中的唤醒事件记录(低16位)会减1,同时已处理的唤醒事件记录(高16位)会加1。
对于每次系统能否进入休眠,通过判断是否有正在处理中的唤醒事件(低16位)来决定。该模块实现主要的功能:
- 持锁和释放锁
- 注册和注销锁
- 查询激活状态锁个数
2. 主要数据结构
2.1 wakeup_source 结构体
@include/linux/pm_wakeup.h
/**
* struct wakeup_source - Representation of wakeup sources
*
* @name: Name of the wakeup source
* @id: Wakeup source id
* @entry: Wakeup source list entry
* @lock: Wakeup source lock
* @wakeirq: Optional device specific wakeirq
* @timer: Wakeup timer list
* @timer_expires: Wakeup timer expiration
* @total_time: Total time this wakeup source has been active.
* @max_time: Maximum time this wakeup source has been continuously active.
* @last_time: Monotonic clock when the wakeup source's was touched last time.
* @prevent_sleep_time: Total time this source has been preventing autosleep.
* @event_count: Number of signaled wakeup events.
* @active_count: Number of times the wakeup source was activated.
* @relax_count: Number of times the wakeup source was deactivated.
* @expire_count: Number of times the wakeup source's timeout has expired.
* @wakeup_count: Number of times the wakeup source might abort suspend.
* @dev: Struct device for sysfs statistics about the wakeup source.
* @active: Status of the wakeup source.
* @autosleep_enabled: Autosleep is active, so update @prevent_sleep_time.
*/
struct wakeup_source {
const char *name; //ws 名称
int id; //WS系统给本ws分配的ID
struct list_head entry; //用于把本ws节点维护到WS系统的全局链表中
spinlock_t lock;
struct wake_irq *wakeirq; //与本ws节点绑定的唤醒中断相关的结构体,用户可自行把指定中断与ws绑定
struct timer_list timer; //超时锁使用,如定义本ws为超时锁,指定在一定时间后释放锁
unsigned long timer_expires;//超时锁超时时间
ktime_t total_time; //本ws激活的总时长
ktime_t max_time; //在ws激活历史中,最长一次的激活时间
ktime_t last_time; //最后一次访问本ws的时间
ktime_t start_prevent_time; //本ws最近一次阻止autosleep进入休眠的时间戳
ktime_t prevent_sleep_time; //因本ws导致的阻止autosleep进入休眠的总时间
unsigned long event_count; //事件次数,本ws被持锁(不考虑是否已持锁),则加1并作记录
unsigned long active_count;//激活次数,本ws仅在首次持锁(激活)时加1(已持锁则不加1,锁释放后再次持锁则加1)
unsigned long relax_count; //释放次数,与 active_count 相对
unsigned long expire_count; //超时锁超时次数
unsigned long wakeup_count; //与event_count一样,但受events_check_enabled 使能标记控制
struct device *dev; //与本ws绑定的设备
bool active:1; //标记是否处于激活状态
bool autosleep_enabled:1; //标记是否使能autosleep
};
2.2 核心变量
2.2.1 combined_event_count 变量
static atomic_t combined_event_count = ATOMIC_INIT(0);
该变量是1个组合计数变量,高16位记录唤醒事件的总数,低16位记录正在处理中的唤醒事件的总数。系统根据低16位(正在处理中的唤醒事件)来判断是否可以进入休眠。
2.2.2 wakeup_sources 变量
static LIST_HEAD(wakeup_sources);
所有通过调用 wakeup_source_register()注册的ws全部维护在此链表中,以便系统进行维护。
2.3 主要函数分析
Wakeup Source 对外提供的主要接口:
wakeup_source_register()与wakeup_source_unregister()分别用于注册与注销一个ws__pm_stay_awake()与__pm_relax(),针对ws类型对象提供持锁与释放锁接口- (
device_set_wakeup_capable()+device_wakeup_enable()/device_wakeup_disable()/device_set_wakeup_enable())/device_init_wakeup()给设备配置是否支持唤醒以及注册/注销ws的接口 pm_stay_awake()与pm_relax(),针对device类型对象提供持锁与释放锁接口
2.3.1 wakeup_source_register()/wakeup_source_unregister() 接口
wakeup_source_register()函数为dev设备创建ws,并将创建的ws添加到全局链表wakeup_sources中,方便后续维护,并在sysfs系统中创建节点/sys/class/wakeup/wakeup<id>/,便于获取ws相关信息。
@drivers/base/power/wakeup.c
/**
* wakeup_source_register - Create wakeup source and add it to the list.
* @dev: Device this wakeup source is associated with (or NULL if virtual).
* @name: Name of the wakeup source to register.
*/
struct wakeup_source *wakeup_source_register(struct device *dev,
const char *name)
{
struct wakeup_source *ws;
int ret;
ws = wakeup_source_create(name); //分配内存,设置ws的name和id
if (ws) {
if (!dev || device_is_registered(dev)) {
//在sysfs下为该ws创建dev, /sys/class/wakeup/wakeup<id>/
ret = wakeup_source_sysfs_add(dev, ws);
if (ret) {
wakeup_source_free(ws);
return NULL;
}
}
wakeup_source_add(ws); //设置超时回调函数并将ws添加到wakeup_sources链表
}
return ws;
}
@drivers/base/power/wakeup_stats.c
static struct device *wakeup_source_device_create(struct device *parent,
struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
struct device *dev = NULL;
int retval = -ENODEV;
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);
device_initialize(dev);
dev->devt = MKDEV(0, 0);
dev->class = wakeup_class; //ws dev挂于wakeup类
dev->parent = parent;
dev->groups = wakeup_source_groups;
dev->release = device_create_release;
dev_set_drvdata(dev, ws);
device_set_pm_not_required(dev);
retval = kobject_set_name(&dev->kobj, "wakeup%d", ws->id);
retval = device_add(dev);
return dev;
}
//ws dev存在的属性: /sys/class/wakeup/wakeup<id>/
static struct attribute *wakeup_source_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_name.attr, //RO, ws 名称
&dev_attr_active_count.attr, //RO, 激活次数
&dev_attr_event_count.attr, //RO, 持锁次数
&dev_attr_wakeup_count.attr, //RO, 同event_count,但受events_check_enabled使能标记
&dev_attr_expire_count.attr, //RO, 超时次数
&dev_attr_active_time_ms.attr, //RO, 如当前处于激活状态,显示已激活时间
&dev_attr_total_time_ms.attr, //RO, 总激活时间
&dev_attr_max_time_ms.attr, //RO, 最长激活时间
&dev_attr_last_change_ms.attr, //RO, 最近一次激活时的时间戳
&dev_attr_prevent_suspend_time_ms.attr, //RO, 阻止autosleep进入休眠的总时间
NULL,
};
ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(wakeup_source);
wakeup_source_unregister() 接口删除了已注册的ws,移除了sysfs系统中的节点并释放占用的系统资源。
@drivers/base/power/wakeup.c
void wakeup_source_unregister(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
if (ws) {
wakeup_source_remove(ws); //从wakeup_sources队列移除并删除其定时器
if (ws->dev)
wakeup_source_sysfs_remove(ws);//移除该ws在sysfs系统中的信息
wakeup_source_destroy(ws);
}
}
void wakeup_source_destroy(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
__pm_relax(ws); //释放该ws
wakeup_source_record(ws);//如果该ws被持锁过,则将其记录叠加到deleted_ws这个ws上
wakeup_source_free(ws);//释放内存资源
}
static struct wakeup_source deleted_ws = {//用于保存已移除ws的记录
.name = "deleted",
.lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(deleted_ws.lock),
};
static void wakeup_source_record(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
unsigned long flags;
spin_lock_irqsave(&deleted_ws.lock, flags);
if (ws->event_count) {//如果该ws被持锁过,则将记录都叠加到deleted_ws这个ws上
deleted_ws.total_time =
ktime_add(deleted_ws.total_time, ws->total_time);
deleted_ws.prevent_sleep_time =
ktime_add(deleted_ws.prevent_sleep_time,
ws->prevent_sleep_time);
deleted_ws.max_time =
ktime_compare(deleted_ws.max_time, ws->max_time) > 0 ?
deleted_ws.max_time : ws->max_time;
deleted_ws.event_count += ws->event_count;
deleted_ws.active_count += ws->active_count;
deleted_ws.relax_count += ws->relax_count;
deleted_ws.expire_count += ws->expire_count;
deleted_ws.wakeup_count += ws->wakeup_count;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&deleted_ws.lock, flags);
}
2.3.2 __pm_stay_awake()/__pm_relax() 接口
__pm_stay_awake() 用于上锁ws来阻止系统休眠。
@drivers/base/power/wakeup.c
void __pm_stay_awake(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
unsigned long flags;
if (!ws)
return;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ws->lock, flags);
wakeup_source_report_event(ws, false);//纪录该ws的信息
del_timer(&ws->timer);
ws->timer_expires = 0;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ws->lock, flags);
}
static void wakeup_source_report_event(struct wakeup_source *ws, bool hard)
{
ws->event_count++; //持锁次数加1
/* This is racy, but the counter is approximate anyway. */
if (events_check_enabled)
ws->wakeup_count++;
if (!ws->active) //ws还未激活情况下,激活ws
wakeup_source_activate(ws);
if (hard) //如果需要,可以强制阻止系统休眠
pm_system_wakeup();
}
static void wakeup_source_activate(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
unsigned int cec;
if (WARN_ONCE(wakeup_source_not_registered(ws),
"unregistered wakeup source\n"))
return;
ws->active = true;
ws->active_count++; //激活次数加1
ws->last_time = ktime_get(); //纪录最后操作该锁的时间戳
if (ws->autosleep_enabled) //如果autosleep已使能,则记录该ws阻止休眠时时间戳
ws->start_prevent_time = ws->last_time;
/* Increment the counter of events in progress. */
cec = atomic_inc_return(&combined_event_count); //combined_event_count低16位加1
trace_wakeup_source_activate(ws->name, cec);
}
__pm_relax() 用于将持有的睡眠锁释放掉,并在检测到combined_event_count低16位为0(表示当前没有在处理的ws)时会触发wakeup_count_wait_queue等待队列运行,如果工作队列满足睡眠条件,则继续进入睡眠流程,该机制是通过pm_get_wakeup_count()接口与autosleep配合使用的
@drivers/base/power/wakeup.c
void __pm_relax(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
unsigned long flags;
if (!ws)
return;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ws->lock, flags);
if (ws->active) //如果ws已激活,则去激活该ws
wakeup_source_deactivate(ws);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ws->lock, flags);
}
static void wakeup_source_deactivate(struct wakeup_source *ws)
{
unsigned int cnt, inpr, cec;
ktime_t duration;
ktime_t now;
ws->relax_count++; //释放次数加1
/*
* __pm_relax() may be called directly or from a timer function.
* If it is called directly right after the timer function has been
* started, but before the timer function calls __pm_relax(), it is
* possible that __pm_stay_awake() will be called in the meantime and
* will set ws->active. Then, ws->active may be cleared immediately
* by the __pm_relax() called from the timer function, but in such a
* case ws->relax_count will be different from ws->active_count.
*/
if (ws->relax_count != ws->active_count) {
ws->relax_count--; //未解决定时锁与主动调用释放锁并发操作时出现冲突做的处理
return;
}
ws->active = false;
now = ktime_get();
duration = ktime_sub(now, ws->last_time);
ws->total_time = ktime_add(ws->total_time, duration); //叠加总的持锁时间
if (ktime_to_ns(duration) > ktime_to_ns(ws->max_time))
ws->max_time = duration; //更新最长持锁时间
ws->last_time = now; //纪录最后操作该锁的时间戳
del_timer(&ws->timer);
ws->timer_expires = 0;
if (ws->autosleep_enabled)//如果autosleep已使能,更新该ws阻止系统休眠的时长
update_prevent_sleep_time(ws, now);
/*
* Increment the counter of registered wakeup events and decrement the
* couter of wakeup events in progress simultaneously.
*/
cec = atomic_add_return(MAX_IN_PROGRESS, &combined_event_count);//combined_event_count高16位加1
trace_wakeup_source_deactivate(ws->name, cec);
split_counters(&cnt, &inpr);//拆分出combined_event_count高16位和低16位
if (!inpr && waitqueue_active(&wakeup_count_wait_queue))//如果该ws已经无正在处理的唤醒事件,则通知PM core
wake_up(&wakeup_count_wait_queue);
}
注:同个ws连续使用多次__pm_stay_awake()或__pm_relax()只会增加/减少一次combined_event_count低16位(表示正在处理中的事件总数),只要__pm_relax()被调用就会释放锁。
2.3.3 pm_get_wakeup_count()接口
该函数主要是获取已处理的wakeup event数量(combined_event_count高16位)与正在处理的wakeup event数量是否为0(combined_event_count低16位)。
bool pm_get_wakeup_count(unsigned int *count, bool block)
{
unsigned int cnt, inpr;
if (block) {
DEFINE_WAIT(wait); //定义名为wait的等待队列入口
for (;;) {
prepare_to_wait(&wakeup_count_wait_queue, &wait,
TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); //准备 wakeup_count_wait_queue 等待队列
split_counters(&cnt, &inpr);
if (inpr == 0 || signal_pending(current))
break;
pm_print_active_wakeup_sources();
schedule(); //调度到其他线程
}
//__pm_relax() 里wake_up(&wakeup_count_wait_queue);会触发调度到此处
finish_wait(&wakeup_count_wait_queue, &wait);
}
split_counters(&cnt, &inpr);
*count = cnt;
return !inpr; //返回0表示有待处理事件,返回1表示无待处理事件
}
1.如果入参
block为0,则仅仅对入参count赋值当前已处理的wakeup event总数,并返回当前是否有待处理wakeup event(返回0表示有待处理事件,返回1表示无待处理事件)。
2.如果入参block为1,则需要一直等到待处理事件为0(combined_event_count低16位为0)或者当前挂起进程有事件需要处理时才退出。该处理分支的wait等待队列会在__pm_relax()满足睡眠条件时触发调度运行,即finish_wait().
2.3.4 pm_wakeup_pending() 接口
该函数的功能是确认当前是否满足休眠条件,返回true表示可以休眠,false表示不可休眠。
bool pm_wakeup_pending(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
bool ret = false;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&events_lock, flags);
if (events_check_enabled) {
unsigned int cnt, inpr;
split_counters(&cnt, &inpr);
ret = (cnt != saved_count || inpr > 0);
events_check_enabled = !ret;
}
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&events_lock, flags);
if (ret) {
pm_pr_dbg("Wakeup pending, aborting suspend\n");
pm_print_active_wakeup_sources();
}
return ret || atomic_read(&pm_abort_suspend) > 0;
}
判断允许休眠的依据:
1.已处理的wakeup event数量与已记录的数量(saved_count)一致,且
2.待处理的wakeup event数量为0,且
3.原子量pm_abort_suspend为0(该值大于0表示睡眠流程中出现了唤醒中断或事件,唤醒事件通过调用pm_system_wakeup()来给pm_abort_suspend加1操作。)
2.3.5 device与wakeup_source关联处理的接口
kernel抽象出的device数据结构存放着power manager相关的信息,其中就存放着wakeup source数据结构,如下:
//代码格式错误,仅为呈现数据结构,请忽略格式。
struct device {
// @power: For device power management.
struct dev_pm_info power {
unsigned int can_wakeup:1; //需置1才允许使用wakeup source
struct wakeup_source *wakeup;
};
};
wakeup source框架中为此提供了大量相关的接口直接操作某个dev的ws,接口如下:
int device_wakeup_enable(struct device *dev):注册设备的wakeup source
1.以dev名注册个ws,并指定该ws dev的parent为当前dev
2.将注册的ws关联到dev->power.wakeup,如果存在wakeirq,也会一起绑定到该ws上。int device_wakeup_disable(struct device *dev):注销设备的wakeup source
1.取消已注册的ws与dev->power.wakeup的关联
2.注销wsvoid device_set_wakeup_capable(struct device *dev, bool capable):设置设备是否支持wakeup source
1.设置dev->power.can_wakeup
2.如果设备支持wakeup,则为其创建属性文件(位于/sys/devices/<dev_name>/power/下);如果设备不支持wakeup,则不会移除相关属性文件。
static struct attribute *wakeup_attrs[] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
&dev_attr_wakeup.attr, //RW,可写入enabled/disabled动态配置是否支持wakeup
&dev_attr_wakeup_count.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的wakeup_count
&dev_attr_wakeup_active_count.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的active_count
&dev_attr_wakeup_abort_count.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的wakeup_count
&dev_attr_wakeup_expire_count.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的expire_count
&dev_attr_wakeup_active.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的active状态
&dev_attr_wakeup_total_time_ms.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的total_time
&dev_attr_wakeup_max_time_ms.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的max_time
&dev_attr_wakeup_last_time_ms.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的last_time
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_AUTOSLEEP
&dev_attr_wakeup_prevent_sleep_time_ms.attr, //RO, 读取该dev ws的prevent_sleep_time
#endif
#endif
NULL,
};
int device_init_wakeup(struct device *dev, bool enable):一步到位直接配置是否支持wakeup并且注册/注销ws
int device_init_wakeup(struct device *dev, bool enable)
{
int ret = 0;
if (enable) {
device_set_wakeup_capable(dev, true);
ret = device_wakeup_enable(dev);
} else {
device_wakeup_disable(dev);
device_set_wakeup_capable(dev, false);
}
return ret;
}
int device_set_wakeup_enable(struct device *dev, bool enable):设置设备是否能通过ws唤醒系统,注册/注销ws
int device_set_wakeup_enable(struct device *dev, bool enable)
{
return enable ? device_wakeup_enable(dev) : device_wakeup_disable(dev);
}
void pm_stay_awake(struct device *dev):持锁设备的ws,不让设备休眠,实际是调用__pm_stay_awake(dev->power.wakeup);实现void pm_relax(struct device *dev):释放设备的ws,允许设备休眠,实际是调用__pm_relax(dev->power.wakeup);实现
总结:
1.device_set_wakeup_capable()用于设置是否支持wakeup,并提供属性节点,便于调试
2.device_wakeup_enable()/device_wakeup_disable()/device_set_wakeup_enable()主要是注册/注销设备ws,需在device_set_wakeup_capable()为enabled的前提下才能使用。
3.device_init_wakeup()通常使用在默认支持wakeup的device上,在probe/remove时分别enable/disable。
4.pm_stay_awake()/pm_relax()主要是持有/释放ws锁,阻止/允许系统休眠
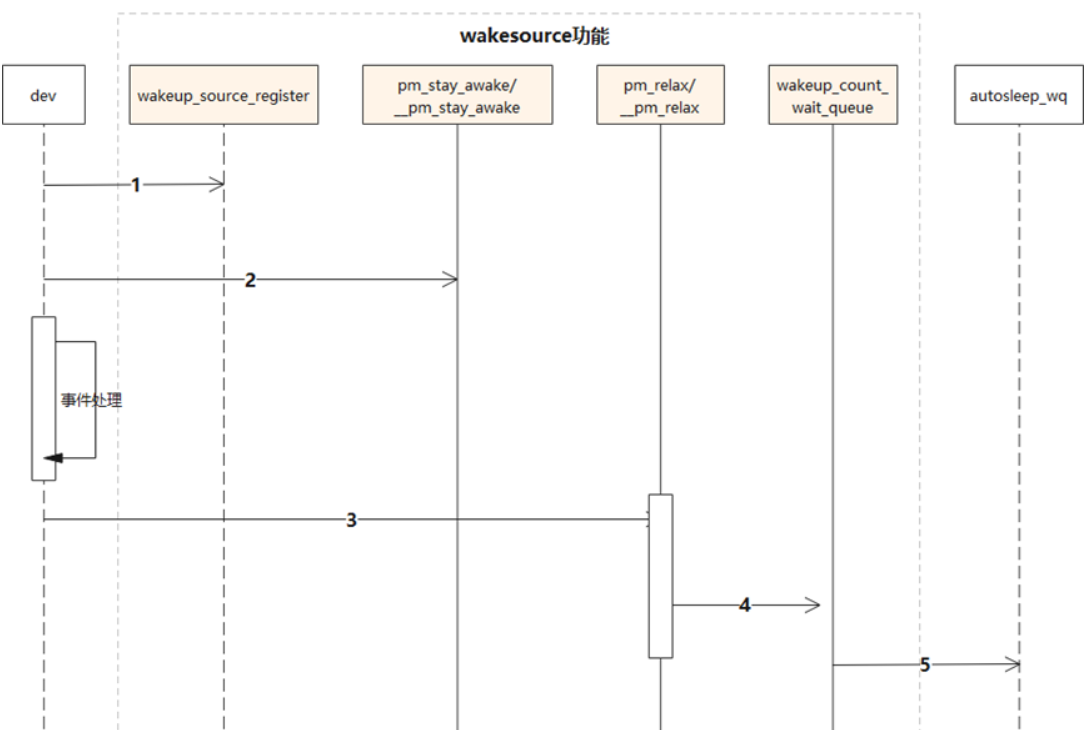
3. 主要工作时序
1)device或者其他需要上锁的模块调用device_init_wakeup()/wakeup_source_register()来注册ws
2)在处理业务时,为了防止系统进入睡眠流程,设备或模块可以通过调用pm_stay_awake()/__pm_stay_awake()来持锁ws阻止休眠
3)当业务处理完成后,设备或模块可以调用pm_relax()/__pm_relax()来释放ws允许系统休眠
4)在__pm_relax()释放锁时,会检查当前是否有正在处理的持锁事件,如果没有,则触发wakeup_count_wait_queue
5)wakeup_count_wait_queue所在的pm_get_wakeup_count()接口会返回到autosleep的工作队列中继续走休眠流程
4. 调试节点
获取所有wakeup source信息节点:
cat /d/wakeup_sources
列出所有wakeup_source当前的信息,包括:name,active_count,event_count,wakeup_count,expire_count,active_since,total_time,max_time,last_change,prevent_suspend_time。
注:代码实现在@drivers/base/power/wakeup.c从wakeup类下获取某个ws的信息:
/sys/class/wakeup/wakeup<id>/
wakeup类下汇总了所有已注册的ws,该节点下存在属性:name, active_count, event_count, wakeup_count,expire_count, active_time_ms, total_time_ms, max_time_ms, last_change_ms, prevent_suspend_time_ms。
注:代码实现在@drivers/base/power/wakeup_stats.c从device节点下获取该设备的ws信息:
/sys/devices/<dev_name>/power/
该节点存在如下属性信息:wakeup(是否支持唤醒),wakeup_count, wakeup_active_count, wakeup_abort_count, wakeup_expire_count, wakeup_active, wakeup_total_time_ms, max_time_ms, last_time_ms, prevent_sleep_time_ms。
注:代码实现在@drivers/base/power/sysfs.c
注:本文是基于内核kernel-5.10展开。上述分析基于32位系统,若是64位系统,则combined_event_count会被拆分成2个32位分别来纪录唤醒事件的总数和正在处理中的唤醒事件的总数
Wakeup Source框架设计与实现的更多相关文章
- .NET框架设计(常被忽视的框架设计技巧)
阅读目录: 1.开篇介绍 2.元数据缓存池模式(在运行时构造元数据缓存池) 2.1.元数据设计模式(抽象出对数据的描述数据) 2.2.借助Dynamic来改变IOC.AOP动态绑定的问题 2.3.元数 ...
- .NET框架设计—常被忽视的框架设计技巧
阅读目录: 1.开篇介绍 2.元数据缓存池模式(在运行时构造元数据缓存池) 2.1.元数据设计模式(抽象出对数据的描述数据) 2.2.借助Dynamic来改变IOC.AOP动态绑定的问题 2.3.元数 ...
- 【STM32H7教程】第12章 STM32H7的HAL库框架设计学习
完整教程下载地址:http://forum.armfly.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=86980 第12章 STM32H7的HAL库框架设计学 ...
- 【ASP.NET Core快速入门】(六)配置的热更新、配置的框架设计
配置的热更新 什么是热更新:一般来说,我们创建的项目都无法做到热更新:即项目无需重启,修改配置文件后读取到的信息就是修改配置之后的 我们只需要吧项目中用到的IOptions改成IOptionsSnap ...
- 菜鸟入门【ASP.NET Core】6:配置的热更新、配置的框架设计
配置的热更新 什么是热更新:这个词听着有点熟悉,但到底是什么呢? 一般来说:创建的项目都无法做到热更新:即项目无需重启,修改配置文件后读取到的信息就是修改配置之后的 我们只需要吧项目中用到的IOpti ...
- .NET CORE 2.0小白笔记(五):配置的热更新、配置的框架设计
配置的热更新 什么是热更新:一般来说,我们创建的项目都无法做到热更新:即项目无需重启,修改配置文件后读取到的信息就是修改配置之后的 我们只需要吧项目中用到的IOptions改成IOptionsSnap ...
- 前端MVVM框架设计及实现
最近抽出点时间想弄个dom模块化的模板引擎,不过现在这种都是MVVM自带的,索性就想自己造轮子写一个简单的MVVM框架了 借鉴的自然还是从正美的Avalon开始了,我2013年写过一个关于MVC MV ...
- 前端MVVM框架设计及实现(二)
在前端MVVM框架设计及实现(一)中有一个博友提出一个看法: “html中使用mvvm徒增开发成本” 我想这位朋友要表达的意思应该是HTML定义了大量的语法标记,HTML中放入了太多的逻辑,从而增加了 ...
- JavaScript 框架设计
JavaScript 高级框架设计 在现在,jQuery等框架已经非常完美,以致于常常忽略了JavaScript原生开发,但是这是非常重要的. 所以,我打算写一个简单的框架,两个目的 熟练框架的思想 ...
- JavaScript 框架设计(二)
JavaScript 高级框架设计 (二) 上一篇,JavaScript高级框架设计(一)我们 实现了对tag标签的选择 下来我们实现对id的选择,即id选择器. 我们将上一篇的get命名为getTa ...
随机推荐
- 融合数据库生态:利用 EventBridge 构建 CDC 应用
简介: 近期,EventBridge 事件流已经支持了基于阿里云 DTS服务的 CDC 能力.本文将从 CDC.CDC 在 EventBridge 上的应用以及若干最佳实践场景等方面,为大家介绍如何利 ...
- 客户端单元测试实践——C++篇
简介: 我们团队在手淘中主要负责BehaviX模块,代码主要是一些逻辑功能,很少涉及到UI,为了减少双端不一致问题.提高性能,我们采用了将核心代码C++化的策略.由于团队项目偏底层,测试同学难以完全覆 ...
- 怀里橘猫柴犬,掌上代码江湖——对话阿里云 MVP郭旭东
简介: 跟郭旭东聊过之后,我对程序员的敬佩又多一分.这个92年的开发者,难能可贵地兼备朝气蓬勃的技术能量与长远深刻的行业洞见.独自承担DevOps平台从0到1的所有工作,我打趣说超级开发者不过如此,他 ...
- Linux系统诊断-内存基础
简介: Linux系统诊断-内存基础 1. 背景 谈及linux内存,很多时候,我们会关注free,top等基础命令.当系统遇到异常情况时,内存问题的根因追溯,现场诊断时,缺乏深层次的debug能力. ...
- [FAQ] FastAdmin epay 微信公众号支付 JSAPI 支付必须传 openid ?
使用 FastAdmin 的 epay 插件时,我们通过传不同的 method 决定支付方式. method=mp 时表示公众号支付,此时必须要 openid,但是插件里并没有说明如何获取. 其实这个 ...
- [FAQ] GoLand 需要手动开启代码补全吗 ?
使用 go mod download 下载模块到本地缓存中,之后 GoLand 就会根据输入自动代码提示. Other:[FAQ] Goland 始终没有包代码的提示 Link:https://www ...
- dotnet 6 数组拷贝性能对比
本文来对比多个不同的方法进行数组拷贝,和测试其性能 测试性能必须采用基准(标准)性能测试方法,否则测试结果不可信.在 dotnet 里面,可以采用 BenchmarkDotNet 进行性能测试.详细请 ...
- Docker的Portainer认识、安装、使用
一.认识 docker的图形化界面 Portainer 是一个轻量级的容器管理界面,可以让用户更轻松地管理 Docker 容器.镜像.网络和数据卷等.Portainer 提供了一个用户友好的 Web ...
- VSCode+VUE+ESLint以达到保存自动格式化
首先打开VSCode在.eslintrc.js中加入以下代码(不知道怎么找可以ctrl+shift+p进行搜索),添加 vscode 终端启动服务 // 添加⾃定义规则 'prettier/prett ...
- Solution Set - SAM
讲解一些 SAM 经典的应用.可以结合 字 符 串 全 家 桶 中 SAM 的部分食用. 洛谷P2408 求不同子串个数.在 SAM 中,所有结点是一个等价类,包含的字符串互不相同.结点 \(u\) ...
