Word Embeddings: Encoding Lexical Semantics(译文)
词向量:编码词汇级别的信息
url:http://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/nlp/word_embeddings_tutorial.html?highlight=lookup
词嵌入
词嵌入是稠密向量,每个都代表了一个单词表里面的一个单词。NLP中每个Feature都是单词,但是怎么在电脑中表示单词呢??
ascii知识告诉我们每个单词是啥,没告诉我们是什么意思。还有就是,怎么融合这些表示呢?
第一步:通过one-hot编码。w=[0,0,1,0,0]。其中1是表示w的独一无二的维度。
但是缺点就是没有语义信息。正交表示就没有语义信息。
"出现在相似位置和相似语境中的单词具有语义相关性!"这就是分布式假设
例子
假设每个维度是代表某种属性(而不是one-hot中每种属性都是一个单词),那么通过在每个维度上各种属性的"调和",
就能够获取一个单词,相似的单词在某几个"属性上"类似,就会在向量空间距离变近。不相似的单词夹角就会很大。
避免了每个维度大量出现0(one-hot的缺陷)
那么问题就来了,每个维度代表什么属性怎么设计,太难了,就让神经网络自己设计,不需要程序员设计了。
为啥不让词嵌入作为模型参数呢??在训练中自己去更新!正是我们做的事情。
但是词嵌入可解释性不强,也就是说,训练出来,每个维度代表什么含义,不清楚。
但结果就是,近义词在潜在语义维度上确实相近,却难以解释。
总而言之,词嵌入是单词的语义解释。是高效的语义信息编码。
当然可以去"embedding"其他任何事情:词性标签,解析树。
特征嵌入的思想是这个领域的核心。
pytorch
通过PyTorch来进行Embedding。
类似于通过one-hot来对单词进行索引,我们要使用Embedding去给每个单词定义索引。
这是lookup table的关键所在。
这样,embedding被存入|V|*D的矩阵,D是embedding的维度,就比如单词的索引被存入矩阵的第i行。
在下面的代码中,单词到索引的映射是一个叫做word_to_ix的字典。
模块是nn.Embedding,参数是词汇表的size,和嵌入的维度
而且要注意,对于表的索引,使用torch.LongTensor,因为索引是整数,不是浮点数
CONTEXT_SIZE = 2
EMBEDDING_DIM = 10
# We will use Shakespeare Sonnet 2
test_sentence = """When forty winters shall besiege thy brow,
And dig deep trenches in thy beauty's field,
Thy youth's proud livery so gazed on now,
Will be a totter'd weed of small worth held:
Then being asked, where all thy beauty lies,
Where all the treasure of thy lusty days;
To say, within thine own deep sunken eyes,
Were an all-eating shame, and thriftless praise.
How much more praise deserv'd thy beauty's use,
If thou couldst answer 'This fair child of mine
Shall sum my count, and make my old excuse,'
Proving his beauty by succession thine!
This were to be new made when thou art old,
And see thy blood warm when thou feel'st it cold.""".split()
# we should tokenize the input, but we will ignore that for now
# build a list of tuples. Each tuple is ([ word_i-2, word_i-1 ], target word)
trigrams = [([test_sentence[i], test_sentence[i + 1]], test_sentence[i + 2])
for i in range(len(test_sentence) - 2)]
# print the first 3, just so you can see what they look like
print(trigrams[:3])
vocab = set(test_sentence)#得到单词的数量,编码的基础
word_to_ix = {word: i for i, word in enumerate(vocab)}#首先对单词进行最简单的编码
class NGramLanguageModeler(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, context_size):
super(NGramLanguageModeler, self).__init__()
self.embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)#其实就是词嵌入矩阵而已
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(context_size * embedding_dim, 128)#由于是利用前面两个词进行预测的,因此需要将得到的单词拼接起来,其实也可以加和,求平均什么的
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(128, vocab_size)#去分类
def forward(self, inputs):
embeds = self.embeddings(inputs).view((1, -1))#通过嵌入矩阵并且合并
out = F.relu(self.linear1(embeds))
out = self.linear2(out)
log_probs = F.log_softmax(out)
return log_probs
losses = []
loss_function = nn.NLLLoss()
model = NGramLanguageModeler(len(vocab), EMBEDDING_DIM, CONTEXT_SIZE)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(10):
total_loss = torch.Tensor([0])
for context, target in trigrams:
# Step 1. Prepare the inputs to be passed to the model (i.e, turn the words
# into integer indices and wrap them in variables)
context_idxs = [word_to_ix[w] for w in context]
context_var = autograd.Variable(torch.LongTensor(context_idxs))
# Step 2. Recall that torch *accumulates* gradients. Before passing in a
# new instance, you need to zero out the gradients from the old
# instance
model.zero_grad()
# Step 3. Run the forward pass, getting log probabilities over next
# words
log_probs = model(context_var)
# Step 4. Compute your loss function. (Again, Torch wants the target
# word wrapped in a variable)
loss = loss_function(log_probs, autograd.Variable(
torch.LongTensor([word_to_ix[target]])))
# Step 5. Do the backward pass and update the gradient
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.data
losses.append(total_loss)
print(losses) # The loss decreased every iteration over the training data!
总结
之前还是一直没有搞清词向量的本质,拿捏不定,其实词向量训练的方法很多,但本质的思想是类似的。就是设置一个查询表,也就是词嵌入矩阵。通过这个查询表,将原始稀疏的one-hot编码成稠密向量。而查询表需要通过训练得到,也就是网络中的参数。
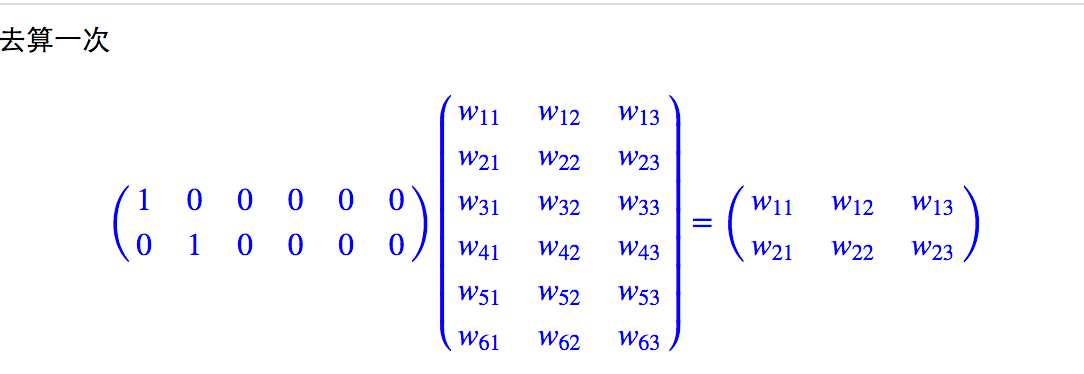
那么最终使用的就是这个权重矩阵的每行来表示对应位置的词向量,和原始的索引相乘只是一个查表的操作。
Word Embeddings: Encoding Lexical Semantics(译文)的更多相关文章
- Word Embeddings: Encoding Lexical Semantics
Word Embeddings: Encoding Lexical Semantics Getting Dense Word Embeddings Word Embeddings in Pytorch ...
- 翻译 | Improving Distributional Similarity with Lessons Learned from Word Embeddings
翻译 | Improving Distributional Similarity with Lessons Learned from Word Embeddings 叶娜老师说:"读懂论文的 ...
- [C5W2] Sequence Models - Natural Language Processing and Word Embeddings
第二周 自然语言处理与词嵌入(Natural Language Processing and Word Embeddings) 词汇表征(Word Representation) 上周我们学习了 RN ...
- deeplearning.ai 序列模型 Week 2 NLP & Word Embeddings
1. Word representation One-hot representation的缺点:把每个单词独立对待,导致对相关词的泛化能力不强.比如训练出“I want a glass of ora ...
- 论文阅读笔记 Word Embeddings A Survey
论文阅读笔记 Word Embeddings A Survey 收获 Word Embedding 的定义 dense, distributed, fixed-length word vectors, ...
- 课程五(Sequence Models),第二 周(Natural Language Processing & Word Embeddings) —— 1.Programming assignments:Operations on word vectors - Debiasing
Operations on word vectors Welcome to your first assignment of this week! Because word embeddings ar ...
- [IR] Word Embeddings
From: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pw187aaz49o Ref: http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/deta ...
- Word Embeddings
能够充分意识到W的这些属性不过是副产品而已是很重要的.我们没有尝试着让相似的词离得近.我们没想把类比编码进不同的向量里.我们想做的不过是一个简单的任务,比如预测一个句子是不是成立的.这些属性大概也就是 ...
- Papers of Word Embeddings
首先解释一下什么叫做embedding.举个例子:地图就是对于现实地理的embedding,现实的地理地形的信息其实远远超过三维 但是地图通过颜色和等高线等来最大化表现现实的地理信息. embeddi ...
随机推荐
- CPP 设计模式学习
源地址 https://www.ev0l.art/index.php/archives/20/ 备忘录模式 在一个类内部记录另一个类的快照状态的模式.可以再合适的时候跳回复用 设计备忘录的三大步骤: ...
- spring cloud 微服务之 -- 配置文件拆分之道
0-前言 在spring cloud微服务架构中,基本上每个拆分的微服务都会部署多个运行实例,这些运行实例,配置基本都是一样的,不同的是少数配置,比如端口,而这些不同的配置又是必不可少的 那我们怎么来 ...
- 关于Integer 和Double包装类创建对象时的底层解析
public void method1() { Integer i = new Integer(1); Integer j = new Integer(1); System.out.println(i ...
- 2018 东北地区大学生程序设计竞赛(ABEHIK)
HDU6500:Problem A. Game with string 题意: 给你一个字符串s以及它的m个子串的首尾位置,现在Alice和 Bob两个人轮流在任一子串的前面或者后面加1个字符,要求加 ...
- axios封装的拦截器的应用
axios拦截器 页面发送http请求,很多情况我们要对请求和其响应进行特定的处理:如果请求数非常多,单独对每一个请求进行处理会变得非常麻烦,程序的优雅性也会大打折扣.好在强大的axios为开发者 ...
- netcore使用IOptions
{ "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", " ...
- Java Linked集合的简单介绍和常用方法的使用
LinkedList的简单介绍 java.util.LinkedList 集合数据存储的结构是链表结构.LinkedList是一个双向链表在实际开发中,对一个集合元素的添加和删除,经常涉及到首尾操作, ...
- 一个由"2020年1月7日 京东出现的重大 Bug 漏洞"引起的思考...
2020年1月7日,京东由于优惠券设置错误,导致大量产品以0元或者超低价成交,并且发货.网传小家电被薅24万件,损失损失金额高达7000多万.很多网友表示收到货了,在网上晒出到货截图.下面为购买截图: ...
- Broken Necklace 坏掉的项链 USACO 模拟(易错)
1004: 1.1.4Broken Necklace 坏掉的项链 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB提交: 11 解决: 9[提交] [状态] [讨论版] [命题人:外部导入] 题目 ...
- C++ 排序引用的优化
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/83/B来源:牛客网 题目描述 第一次期中考终于结束啦!沃老师是个语文老师,他在评学生的作文成绩时,给每位学生的分数都是 ...
