第二十五篇 玩转数据结构——链表(Linked List)
- 我们之前实现的动态数组、栈、队列,底层都是依托静态数组,靠resize来解决固定容量的问题,而"链表"则是一种真正的动态数据结构,不需要处理固定容量的问题;
- 链表是最简单的动态数据结构;
- 学习链表有助于更深入的理解"引用"(或指针);
- 学习链表有助于更深入的理解"递归";
- 链表可以用来辅助组成其他数据结构;
- 数据存储在"节点"(Node)中;
- 链表的形象化解释如下图:
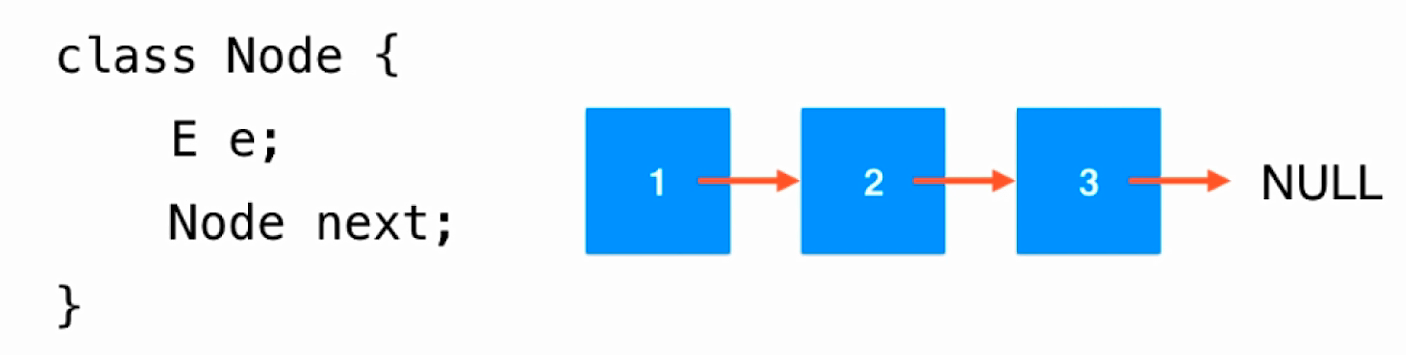
- 链表的优点在于,它是一种真正的动态数据结构,不需要处理固定容量问题;
- 链表的缺点在于,相较于数组,失去了随机访问的能力;
- 数组和链表的对比如下图所示:

- 实现链表的业务逻辑如下:
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next; //构造函数
public Node(E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
} //只传了参数e的构造函数
public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
} //不传递参数的构造函数
public Node() {
this(null, null);
} //方便打印测试
@Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
} private Node dummyHead;
private int size; //构造函数
public LinkedList() {
dummyHead = new Node(null, null); //虚拟头节点
size = 0;
} //获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize() {
return size;
} //判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
} //在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
//在链表中不是一个常用操作
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
} Node prev = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
} prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size++;
} //在链表头添加新元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(0, e);
} //在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e) {
add(size, e);
} //获取链表的index(0-based)位置的元素
//在链表中也不是一个常用操作
public E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
} Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.e;
} //获得链表的第一个元素
public E getFirst() {
return get(0);
} //获得链表的最后一个元素
public E getLast() {
return get(size - 1);
} //修改链表的index(0-based)位置的元素为e
//在链表中也不是一个常用操作
public void set(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
} Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.e = e;
} //查找链表中是否存在元素e
public boolean contains(E e) {
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.e.equals(e)) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
} //删除链表的index(0-based)位置的元素,并返回该元素
//在链表中也不是一个常用操作
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Illegal index.");
}
Node prev = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
}
Node retNode = prev.next;
prev.next = retNode.next;
retNode.next = null;
size--; return retNode.e;
} //删除链表中的第一个元素,并返回该元素
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
} //删除链表中的最后一个元素,并返回该元素
public E removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
} // 从链表中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){ Node prev = dummyHead;
while(prev.next != null){
if(prev.next.e.equals(e))
break;
prev = prev.next;
} if(prev.next != null){
Node delNode = prev.next;
prev.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
size --;
}
} //方便打印测试
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// Node cur = dummyHead.next;
// while (cur != null) {
// res.append(cur + "->");
// cur = cur.next;
// }
for (Node cur = dummyHead.next; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
res.append(cur + "->");
}
res.append("NULL"); return res.toString();
}
}- 测试的业务逻辑如下:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
} linkedList.add(2, 666);
System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.remove(2);
System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeFirst();
System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeLast();
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}- 输出结果:
0->NULL
1->0->NULL
2->1->0->NULL
3->2->1->0->NULL
4->3->2->1->0->NULL
4->3->666->2->1->0->NULL
4->3->2->1->0->NULL
3->2->1->0->NULL
3->2->1->NULL
- 添加操作 O(n)
addLast(e) O(n)
addFirst(e) O(1)
add(index, e) O(n/2)=O(n)- 删除操作 O(n)
removeLase(e) O(n)
removeFirst(e) O(1)
remove(index, e) O(n/2)=O(n)- 修改操作 O(n)
set(index, e) O(n)
- 查找操作 O(n)
get(index) O(n)
contains(e) O(n)- 总体来说,链表的增、删、改、查的时间复杂度都是O(n)
- 如果我们只对链表的头进行添加和删除操作,那么时间复杂度是O(1),如果我们只查链表头的元素,那么时间复杂度也是O(1),满足这些条件的数据结构,我们很容易就会想到"栈",对于"栈"而言,遵循后进先出的原则,只对栈的一端,也就是"栈顶"进行操作,无论是添加、删除还是查看元素,都在栈顶进行。所以,我们就可以把链表头当作栈顶,用链表来作为栈的底层实现,来实现出一个栈。

- 链表栈的实现及测试的业务逻辑如下:
public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private LinkedList<E> list; //构造函数
public LinkedListStack() {
list = new LinkedList<>();
} //实现getSize方法
@Override
public int getSize() {
return list.getSize();
} //实现isEmpty方法
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return list.isEmpty();
} //实现push方法
@Override
public void push(E e) {
list.addFirst(e);
} //实现pop方法
@Override
public E pop() {
return list.removeFirst();
} //实现peek方法
@Override
public E peek() {
return list.getFirst();
} //方便打印测试
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Stack: top ");
res.append(list);
return res.toString();
} //测试
public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedListStack<Integer> stack = new LinkedListStack<>();
//测试入栈push
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
stack.push(i);
System.out.println(stack);
}
//测试出栈
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);
}
}- 输出结果:
Stack: top 0->NULL
Stack: top 1->0->NULL
Stack: top 2->1->0->NULL
Stack: top 3->2->1->0->NULL
Stack: top 4->3->2->1->0->NULL
Stack: top 3->2->1->0->NULL
- 测试的业务逻辑如下:
import java.util.Random; public class Main { //测试使用stack运行opCount个push和pop操作所需的时间,单位:秒
private static double testStack(Stack<Integer> stack, int opCount) { long startTime = System.nanoTime(); Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
stack.push(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
stack.pop();
} long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
} public static void main(String[] args){
int opCount = 10000; ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack<>();
double time1 = testStack(arrayStack,opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayStack, time: " + time1 + " s"); LinkedListStack<Integer> linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack<>();
double time2 = testStack(linkedListStack,opCount);
System.out.println("LinkedListStack, time: " + time2 + " s"); // 这二者的时间比较很复杂,ArrayStack会在扩容和缩容操作上面耗费时间,LinkedListStack则会在创建新的Node上面耗费时间
}
}- 这两种栈的时间复杂度基本处于相同的水平
- 链表队列的实现及测试的业务逻辑如下
public class LinkListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> { private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next; public Node(E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
} public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
} public Node() {
this(null, null);
} @Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
} private Node head, tail;
private int size; public LinkListQueue() {
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
} //实现getSize
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
} //实现isEmpty
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
} //实现enqueue
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
if (tail == null) {
tail = new Node(e);
head = tail;
} else {
tail.next = new Node(e);
tail = tail.next;
}
size++;
} //实现dequeue
@Override
public E dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
}
Node retNode = head;
head = head.next;
retNode.next = null;
if (head == null) {
tail = null;
}
size--;
return retNode.e;
} //实现getFront
public E getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
}
return head.e;
} //方便打印测试
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: front "); Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
res.append(cur + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
} //测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkListQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue); if (i % 3 == 2) {
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}- 输出结果:
Queue: front 0->NULL
Queue: front 0->1->NULL
Queue: front 0->1->2->NULL
Queue: front 1->2->NULL
Queue: front 1->2->3->NULL
Queue: front 1->2->3->4->NULL
Queue: front 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Queue: front 2->3->4->5->NULL
- 测试的业务逻辑如下:
import java.util.Random; public class Main { // 测试使用q运行opCount个enqueue和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime(); Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
q.dequeue();
} long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 100000; ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>();
double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + " s"); LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>();
double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + " s"); LinkListQueue<Integer> linkListQueue = new LinkListQueue<>();
double time3 = testQueue(linkListQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LinkListQueue, time: " + time3 + " s"); }
}- 输出结果:
ArrayQueue, time: 3.069366801 s
LoopQueue, time: 0.010702659 s
LinkListQueue, time: 0.007079073 s
- 不使用dummyHead的实现方法
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while (head != null && head.val == val) {
//head = head.next;
ListNode delNode = head;
head = head.next;
delNode.next = null;
} if (head == null) {
return null;
} ListNode prev = head;
while (prev.next != null) {
if (prev.next.val == val) {
//prev.next = prev.next.next;
ListNode delNode = prev.next;
prev.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
} else {
prev = prev.next;
}
} return head;
}
}- 使用dummyHead的实现方法:
class Solution2 {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead.next = head; ListNode prev = dummyHead;
while (prev.next != null) {
if (prev.next.val == val) {
//prev.next = prev.next.next;
ListNode delNode = prev.next;
prev.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
} else {
prev = prev.next;
}
} return dummyHead.next;
}
}
- 使用dummyHead之后,代码变得更加简洁
- 从本质上讲,递归,就是将原来的问题转化为更小的同一个问题;
- 递归举例,数组求和:
Sum(arr[0...n-1]) = arr[0] + Sum(arr[1...n-1]) <-- 转化为更小的同一个问题
Sum(arr[1...n-1]) = arr[1] + Sum(arr[2...n-1]) <-- 转化为更小的同一个问题
......
Sum(arr[n-1...n-1]) = arr[n-1] + Sum([]) <-- 最基本的问题- 代码简单实现:
public class Sum {
public static int sum(int[] arr) {
return sum(arr, 0);
} //计算arr[l...n)这个区间内所有数的和
private static int sum(int[] arr, int l) {
if (l == arr.length) { // <-- 求解最基本问题
return 0;
}
return arr[l] + sum(arr, l + 1); // <-- 将原问题简化为更小的问题
} //测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8};
System.out.println(sum(arr));
}
}
- 通过下图,很容易理解为什么链表具有天然的递归性

- 用递归的思想解决删除链表中的节点的问题,原理示意图:
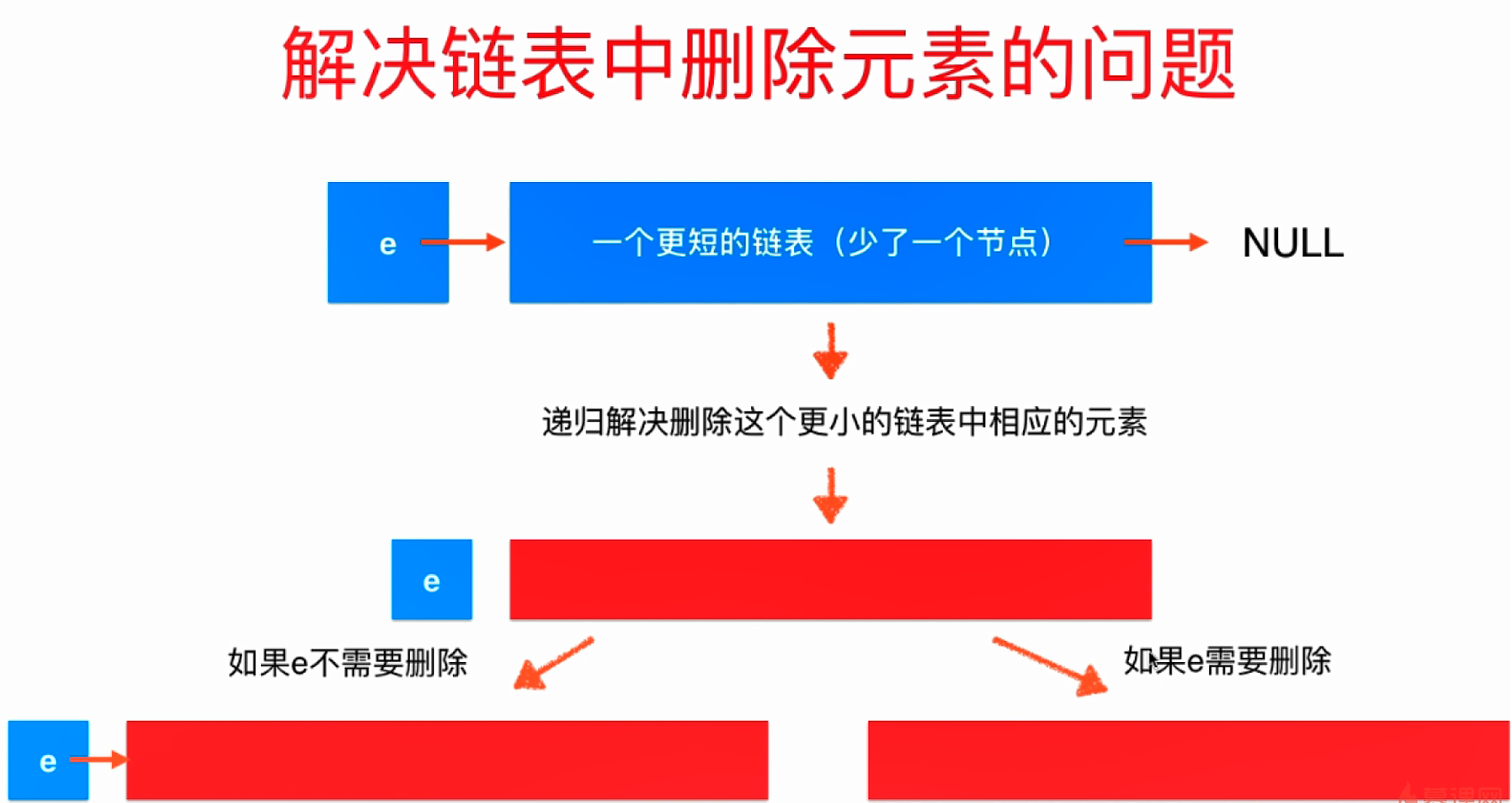
- 用递归实现删除链表中所有包含指定元素的节点的业务逻辑:
class Solution3 { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
} head.next = removeElements(head.next, val); //return head.val == val ? head.next : head;
if (head.val == val) {
return head.next;
} else {
return head;
}
}
}
第二十五篇 玩转数据结构——链表(Linked List)的更多相关文章
- 第二十八篇 玩转数据结构——堆(Heap)和有优先队列(Priority Queue)
1.. 优先队列(Priority Queue) 优先队列与普通队列的区别:普通队列遵循先进先出的原则:优先队列的出队顺序与入队顺序无关,与优先级相关. 优先队列可以使用队列的接口,只是在 ...
- 第二十六篇 玩转数据结构——二分搜索树(Binary Search Tree)
1.. 二叉树 跟链表一样,二叉树也是一种动态数据结构,即,不需要在创建时指定大小. 跟链表不同的是,二叉树中的每个节点,除了要存放元素e,它还有两个指向其它节点的引用,分别用Node l ...
- 第二十四篇 玩转数据结构——队列(Queue)
1.. 队列基础 队列也是一种线性结构: 相比数组,队列所对应的操作数是队列的子集: 队列只允许从一端(队尾)添加元素,从另一端(队首)取出元素: 队列的形象化描述如下图: 队列是一种先进 ...
- 第二十九篇 玩转数据结构——线段树(Segment Tree)
1.. 线段树引入 线段树也称为区间树 为什么要使用线段树:对于某些问题,我们只关心区间(线段) 经典的线段树问题:区间染色,有一面长度为n的墙,每次选择一段墙进行染色(染色允许覆盖),问 ...
- 第二十五篇:在SOUI中做事件分发处理
不同的SOUI控件可以产生不同的事件.SOUI系统中提供了两种事件处理方式:事件订阅 + 事件处理映射表(参见第八篇:SOUI中控件事件的响应) 事件订阅由于直接将事件及事件处理函数连接,不存在事件分 ...
- Python之路(第二十五篇) 面向对象初级:反射、内置方法
[TOC] 一.反射 反射的概念是由Smith在1982年首次提出的,主要是指程序可以访问.检测和修改它本身状态或行为的一种能力(自省).这一概念的提出很快引发了计算机科学领域关于应用反射性的研究.它 ...
- flask第二十五篇——控制语句
有兴趣的请加船长公众号:自动化测试实战 先和大家强调一个发邮件的问题 # coding: utf-8 import smtplib from email.mime.text import MIMETe ...
- 第二十五篇:使用 sigaction 函数实现可靠信号
前言 在前文中,讲述了一个可靠信号的示例.它分成几个步骤组成( 请参考前文 ).在 Linux 系统编程中,有个方法可以将这些步骤给集成起来,让我们使用起来更加的方便. 那就是调用 sigaction ...
- SpringBoot非官方教程 | 第二十五篇:2小时学会springboot
转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/61472783 本文出自方志朋的博客 一.什么是spring boot Takes an o ...
随机推荐
- 批量获取mysql数据库实例指定参数的值
需求:需要对比所有mysql数据库实例上面的指定参数配置情况,同时需要需要能看到如ip,端口,master or slave,毕竟主和从参数不一样还是有可能的. 说明:必须要有个数据库存储所有是数据库 ...
- 查找pod使用的物理目录位置
例子:找出当前pod挂载的是哪个物理目录 # 先查看pod web-0 的yaml文件 # kubectl get pod web-0 -o yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod ...
- 虚拟化技术xen的简介和安装
虚拟化技术的分类: 1,模拟:Emulation Qemu,PearPC,Bochs 2,完全虚拟化:Full Virtualization,Native Virtualization HVM ...
- 洛谷P1200 [USACO1.1]你的飞碟在这儿Your Ride Is Here
题目描述 众所周知,在每一个彗星后都有一只UFO.这些UFO时常来收集地球上的忠诚支持者.不幸的是,他们的飞碟每次出行都只能带上一组支持者.因此,他们要用一种聪明的方案让这些小组提前知道谁会被彗星带走 ...
- 天兔修改登录页的title
1.将 /opt/lampp/htdocs/lepus/application/views/login.php 文件中 第6行 <title><?php echo $this-> ...
- [Agc001A/At1979] BBQ Easy - 贪心
要准备N组食物, 他有2N的食材, 需要两两组成一个食物, 食物的价值是两食材中较小的那个. 问最大总价值是多少 ---------- 考虑到\(ans = (sum - delta)/2\),只需要 ...
- Maven2: Missing artifact but jars are in place
那是因为没有update project. 项目右键,maven-update project.
- Js Jquery 时间控件显示小时 分钟 秒
// ui.js 自带的datepicker 插件只能显示日期不能显示时分秒 使用dateTimePicker可以显示时间 效果图: 首先需要引用 js和css 注意 ui.js的顺序要在s ...
- MAC MAMP集成环境安装 PHP 扩展
MAC MAMP集成环境安装 PHP扩展 开发环境中,对于需要维护很多 WEB 站点,以及可能会使用到很多不同的 PHP 版本,集成环境比较好用,在MAC 上 MAMP 集成环境是比较好用的,但是在安 ...
- Java自学-Lambda 概念
Java Lambda 表达式概念 假设一个情景: 找出满足条件的Hero 从使用普通方法,匿名类,以及Lambda这几种方式,逐渐的引入Lambda的概念 步骤 1 : 普通方法 使用一个普通方法, ...
