Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十五章:第一人称摄像机和动态索引
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十五章:第一人称摄像机和动态索引
代码工程地址:
https://github.com/jiabaodan/Direct12BookReadingNotes
学习目标
- 回顾视景坐标系变换的数学算法;
- 熟悉第一人称摄像机的功能;
- 实现第一人称摄像机;
- 理解如何动态索引一组纹理。
1 回顾视景坐标系变换

如果QW = (Qx, Qy, Qz, 1), uW = (ux, uy, uz, 0), vW = (vx, vy, vz, 0)并且wW = (wx, wy, wz, 0)。根据第三章4.3节,我们可以知道从视景坐标系变化到世界坐标系的变换矩阵为:

根据第三章4.5节,我们需要的是它的逆矩阵。因为世界坐标系和视景坐标系只变换位置和旋转,所以:
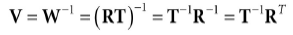
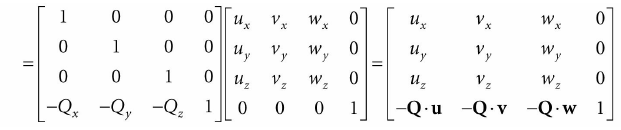
所以视景坐标系变换矩阵为:
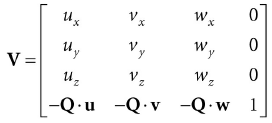
2 摄像机类
为了封装摄像机相关的代码,我们封装和实现了一个Camera类。它的数据主要分为下面几类:位置,右向,向上的向量和看向的向量;原点,视景坐标系在世界坐标系下的xyz轴:
class Camera{public:Camera();˜Camera();// Get/Set world camera position.DirectX::XMVECTOR GetPosition()const;DirectX::XMFLOAT3 GetPosition3f()const;void SetPosition(float x, float y, float z);void SetPosition(const DirectX::XMFLOAT3& v);// Get camera basis vectors.DirectX::XMVECTOR GetRight()const;DirectX::XMFLOAT3 GetRight3f()const;DirectX::XMVECTOR GetUp()const;DirectX::XMFLOAT3 GetUp3f()const;DirectX::XMVECTOR GetLook()const;DirectX::XMFLOAT3 GetLook3f()const;// Get frustum properties.float GetNearZ()const;float GetFarZ()const;float GetAspect()const;float GetFovY()const;float GetFovX()const;// Get near and far plane dimensions in view space coordinates.float GetNearWindowWidth()const;float GetNearWindowHeight()const;float GetFarWindowWidth()const;float GetFarWindowHeight()const;// Set frustum.void SetLens(float fovY, float aspect, float zn, float zf);// Define camera space via LookAt parameters.void LookAt(DirectX::FXMVECTOR pos,DirectX::FXMVECTOR target,DirectX::FXMVECTOR worldUp);void LookAt(const DirectX::XMFLOAT3& pos,const DirectX::XMFLOAT3& target,const DirectX::XMFLOAT3& up);// Get View/Proj matrices.DirectX::XMMATRIX GetView()const;DirectX::XMMATRIX GetProj()const;DirectX::XMFLOAT4X4 GetView4x4f()const;DirectX::XMFLOAT4X4 GetProj4x4f()const;// Strafe/Walk the camera a distance d.void Strafe(float d);void Walk(float d);// Rotate the camera.void Pitch(float angle);void RotateY(float angle);// After modifying camera position/orientation, call to rebuild the view matrix.void UpdateViewMatrix();private:// Camera coordinate system with coordinates relative to world space.DirectX::XMFLOAT3 mPosition = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f };DirectX::XMFLOAT3 mRight = { 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f };DirectX::XMFLOAT3 mUp = { 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f };DirectX::XMFLOAT3 mLook = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };// Cache frustum properties.float mNearZ = 0.0f;float mFarZ = 0.0f;float mAspect = 0.0f;float mFovY = 0.0f;float mNearWindowHeight = 0.0f;float mFarWindowHeight = 0.0f;bool mViewDirty = true;// Cache View/Proj matrices.DirectX::XMFLOAT4X4 mView = MathHelper::Identity4x4();DirectX::XMFLOAT4X4 mProj = MathHelper::Identity4x4();};
3 选择一些方法实现
3.1 返回XMVECTOR变量
我们提供了一些返回XMVECTOR变量的方法,这个只是为了方便:
XMVECTOR Camera::GetPosition()const{return XMLoadFloat3(&mPosition);}XMFLOAT3 Camera::GetPosition3f()const{return mPosition;}
3.2 SetLens
我们通过SetLens函数来设置视锥体:
void Camera::SetLens(float fovY, float aspect, float zn, float zf){// cache propertiesmFovY = fovY;mAspect = aspect;mNearZ = zn;mFarZ = zf;mNearWindowHeight = 2.0f * mNearZ * tanf(0.5f*mFovY );mFarWindowHeight = 2.0f * mFarZ * tanf(0.5f*mFovY );XMMATRIX P = XMMatrixPerspectiveFovLH(mFovY, mAspect, mNearZ, mFarZ);XMStoreFloat4x4(&mProj, P);}
3.3 通过视锥体派生出来的数据
float Camera::GetFovX()const{float halfWidth = 0.5f*GetNearWindowWidth();return 2.0f*atan(halfWidth / mNearZ);}float Camera::GetNearWindowWidth()const{return mAspect * mNearWindowHeight;}float Camera::GetNearWindowHeight()const{return mNearWindowHeight;}float Camera::GetFarWindowWidth()const{return mAspect * mFarWindowHeight;}float Camera::GetFarWindowHeight()const{return mFarWindowHeight;}
3.4 变换摄像机
对于一个第一人称摄像机,如果无视碰撞检测,我们希望:
- 向看向的方向前进或者后退;
- 左右移动;
- 向上下旋转;
- 左右旋转。
void Camera::Walk(float d){// mPosition += d*mLookXMVECTOR s = XMVectorReplicate(d);XMVECTOR l = XMLoadFloat3(&mLook);XMVECTOR p = XMLoadFloat3(&mPosition);XMStoreFloat3(&mPosition, XMVectorMultiplyAdd(s, l, p));}void Camera::Strafe(float d){// mPosition += d*mRightXMVECTOR s = XMVectorReplicate(d);XMVECTOR r = XMLoadFloat3(&mRight);XMVECTOR p = XMLoadFloat3(&mPosition);XMStoreFloat3(&mPosition, XMVectorMultiplyAdd(s, r, p));}void Camera::Pitch(float angle){// Rotate up and look vector about the right vector.XMMATRIX R = XMMatrixRotationAxis(XMLoadFloat3(&mRight), angle);XMStoreFloat3(&mUp, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&R));XMStoreFloat3(&mLook, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&mLook), R));}void Camera::RotateY(float angle){// Rotate the basis vectors about the world yaxis.XMMATRIX R = XMMatrixRotationY(angle);XMStoreFloat3(&mRight, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&R));XMStoreFloat3(&mUp, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&mUp), R));XMStoreFloat3(&mLook, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&mLook), R));}
3.5 创建视景坐标系变换矩阵
UpdateViewMatrix函数的第一部分是重新标准正交化摄像机的向右,向上和看向的向量。因为经过变换后,由于数值问题可能导致它们不再标准正交;第二部分就是计算矩阵:
void Camera::UpdateViewMatrix(){if(mViewDirty){XMVECTOR R = XMLoadFloat3(&mRight);XMVECTOR U = XMLoadFloat3(&mUp);XMVECTOR L = XMLoadFloat3(&mLook);XMVECTOR P = XMLoadFloat3(&mPosition);// Keep camera’s axes orthogonal to each other and of unit length.L = XMVector3Normalize(L);U = XMVector3Normalize(XMVector3Cross(L, R));// U, L already ortho-normal, so no need to normalize cross product.R = XMVector3Cross(U, L);// Fill in the view matrix entries.float x = -XMVectorGetX(XMVector3Dot(P, R));float y = -XMVectorGetX(XMVector3Dot(P, U));float z = -XMVectorGetX(XMVector3Dot(P, L));XMStoreFloat3(&mRight, R);XMStoreFloat3(&mUp, U);XMStoreFloat3(&mLook, L);mView(0, 0) = mRight.x;mView(1, 0) = mRight.y;mView(2, 0) = mRight.z;mView(3, 0) = x;mView(0, 1) = mUp.x;mView(1, 1) = mUp.y;mView(2, 1) = mUp.z;mView(3, 1) = y;mView(0, 2) = mLook.x;mView(1, 2) = mLook.y;mView(2, 2) = mLook.z;mView(3, 2) = z;mView(0, 3) = 0.0f;mView(1, 3) = 0.0f;mView(2, 3) = 0.0f;mView(3, 3) = 1.0f;mViewDirty = false;}}
4 摄像机Demo注释
我们删除以前老的摄像机相关的变量mPhi, mTheta, mRadius, mView, 和mProj,添加新的变量:
Camera mCam;
然后在屏幕尺寸变化的时候,不再直接计算透视矩阵,而是SetLens:
void CameraApp::OnResize(){D3DApp::OnResize();mCamera.SetLens(0.25f*MathHelper::Pi, AspectRatio(), 1.0f, 1000.0f);}
在UpdateScene方法中:
void CameraApp::UpdateScene(float dt){if( GetAsyncKeyState(‘W’) & 0x8000 )mCamera.Walk(10.0f*dt);if( GetAsyncKeyState(‘S’) & 0x8000 )mCamera.Walk(-10.0f*dt);if( GetAsyncKeyState(‘A’) & 0x8000 )mCamera.Strafe(-10.0f*dt);if( GetAsyncKeyState(‘D’) & 0x8000 )mCamera.Strafe(10.0f*dt);
在OnMouseMove方法中:
void CameraAndDynamicIndexingApp::OnMouseMove(WPARAM btnState, int x, int y){if( (btnState & MK_LBUTTON) != 0 ){// Make each pixel correspond to a quarter of a degree.float dx = XMConvertToRadians(0.25f*static_cast<float>(x - mLastMousePos.x));float dy = XMConvertToRadians(0.25f*static_cast<float>(y - mLastMousePos.y));mCamera.Pitch(dy);mCamera.RotateY(dx);}mLastMousePos.x = x;mLastMousePos.y = y;}
最终,视景和透视投影矩阵可以通过摄像机实例访问:
mCamera.UpdateViewMatrix();XMMATRIX view = mCamera.View();XMMATRIX proj = mCamera.Proj();

5 动态索引
动态索引的思路非常简单,我们在着色器程序中动态索引一组资源,本Demo中,资源是一组纹理。索引可以通过多种方法定义:
- 可以是常量缓冲中的一个元素;
- 可以是一个系统ID:SV_PrimitiveID, SV_VertexID, SV_DispatchThreadID, or SV_InstanceID;
- 可以是通过计算得到的结果;
- 可以是纹理中的值;
- 可以是顶点结构中的组件。
下面是一个常量缓冲中的索引例子:
cbuffer cbPerDrawIndex : register(b0){int gDiffuseTexIndex;};Texture2D gDiffuseMap[4] : register(t0);float4 texValue = gDiffuseMap[gDiffuseTexIndex].Sample(gsamLinearWrap, pin.TexC);
对于当前Demo,我们的目标是:最小化我们每帧设置的descriptors的数量。我们设置物体的常量缓冲,材质常量缓冲和和漫反射问题贴图。最小化descriptors可以让我们的根签名更小,这代表每个绘制调用造成更少的性能开销;并且这个技术对实例化技术非常有用(下章讲解),我们的策略如下:
- 创建一个结构化缓冲保存所有的材质数据;
- 在物体常量缓冲中添加一个MaterialIndex值来指定使用的材质的索引;
- 绑定所有SRV descriptors每帧一次(之前每个渲染物体绑定一次);
- 在材质数据中添加DiffuseMapIndex值来指定使用的纹理贴图。
根据上面的设置,我们只需要对每个渲染物体设置逐物体的常量缓冲。然后使用MaterialIndex来匹配材质,使用DiffuseMapIndex来匹配纹理。
struct MaterialData{DirectX::XMFLOAT4 DiffuseAlbedo = { 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f };DirectX::XMFLOAT3 FresnelR0 = { 0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f };float Roughness = 64.0f;// Used in texture mapping.DirectX::XMFLOAT4X4 MatTransform = MathHelper::Identity4x4();UINT DiffuseMapIndex = 0;UINT MaterialPad0;UINT MaterialPad1;UINT MaterialPad2;};MaterialBuffer = std::make_unique<UploadBuffer<MaterialData>>(device, materialCount, false);
然后根据着色器,更新根签名:
CD3DX12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE texTable;texTable.Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_SRV, 4, 0, 0);// Root parameter can be a table, root descriptor or root constants.CD3DX12_ROOT_PARAMETER slotRootParameter[4];// Perfomance TIP: Order from most frequent to least frequent.slotRootParameter[0].InitAsConstantBufferView(0);slotRootParameter[1].InitAsConstantBufferView(1);slotRootParameter[2].InitAsShaderResourceView(0, 1);slotRootParameter[3].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &texTable, D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);auto staticSamplers = GetStaticSamplers();// A root signature is an array of root parameters.CD3DX12_ROOT_SIGNATURE_DESC rootSigDesc(4,slotRootParameter,(UINT)staticSamplers.size(),staticSamplers.data(),D3D12_ROOT_SIGNATURE_FLAG_ALLOW_INPUT_ASSEMBLER_INPUT_
现在,绘制任何渲染物体之前,我们可以绑定所有材质和纹理SRV每帧一次:
void CameraAndDynamicIndexingApp::Draw(const GameTimer& gt){…auto passCB = mCurrFrameResource->PassCB->Resource();mCommandList->SetGraphicsRootConstantBufferView(1, passCB->GetGPUVirtualAddress());// Bind all the materials used in this scene. For structured buffers,// we can bypass the heap and set as a root descriptor.auto matBuffer = mCurrFrameResource->MaterialBuffer->Resource();mCommandList->SetGraphicsRootShaderResourceView(2, matBuffer->GetGPUVirtualAddress());// Bind all the textures used in this scene. Observe// that we only have to specify the first descriptor in the table.// The root signature knows how many descriptors are expected in the table.mCommandList->SetGraphicsRootDescriptorTable(3,mSrvDescriptorHeap->GetGPUDescriptorHandleForHeapStart());DrawRenderItems(mCommandList.Get(), mOpaqueRitems);…}void CameraAndDynamicIndexingApp::DrawRenderItems(ID3D12GraphicsCommandList* cmdList,const std::vector<RenderItem*>& ritems){…// For each render item…for(size_t i = 0; i < ritems.size(); ++i){auto ri = ritems[i];…cmdList->SetGraphicsRootConstantBufferView(0, objCBAddress);cmdList->DrawIndexedInstanced(ri->IndexCount, 1,ri->StartIndexLocation, ri- >BaseVertexLocation, 0);}}
然后更新ObjectConstants结构(已经添加并更新MaterialIndex):
// UpdateObjectCBs…ObjectConstants objConstants;XMStoreFloat4x4(&objConstants.World, XMMatrixTranspose(world));XMStoreFloat4x4(&objConstants.TexTransform, XMMatrixTranspose(texTransform));**objConstants.MaterialIndex = e->Mat->MatCBIndex;**
着色器代码更新:
// Include structures and functions for lighting.#include “LightingUtil.hlsl”struct MaterialData{float4 DiffuseAlbedo;float3 FresnelR0;float Roughness;float4x4 MatTransform;uint DiffuseMapIndex;uint MatPad0;uint MatPad1;uint MatPad2;};// An array of textures, which is only supported in shader model 5.1+. Unlike// Texture2DArray, the textures in this array can be different sizes and// formats, making it more flexible than texture arrays.Texture2D gDiffuseMap[4] : register(t0);// Put in space1, so the texture array does not overlap with these resources.// The texture array will occupy registers t0, t1, …, t3 in space0.StructuredBuffer<MaterialData> gMaterialData : register(t0, space1);SamplerState gsamPointWrap : register(s0);SamplerState gsamPointClamp : register(s1);SamplerState gsamLinearWrap : register(s2);SamplerState gsamLinearClamp : register(s3);SamplerState gsamAnisotropicWrap : register(s4);SamplerState gsamAnisotropicClamp : register(s5);// Constant data that varies per frame.cbuffer cbPerObject : register(b0){float4x4 gWorld;float4x4 gTexTransform;uint gMaterialIndex;uint gObjPad0;uint gObjPad1;uint gObjPad2;};// Constant data that varies per material.cbuffer cbPass : register(b1){float4x4 gView;float4x4 gInvView;float4x4 gProj;float4x4 gInvProj;float4x4 gViewProj;float4x4 gInvViewProj;float3 gEyePosW;float cbPerObjectPad1;float2 gRenderTargetSize;float2 gInvRenderTargetSize;float gNearZ;float gFarZ;float gTotalTime;float gDeltaTime;float4 gAmbientLight;// Indices [0, NUM_DIR_LIGHTS) are directional lights;// indices [NUM_DIR_LIGHTS, NUM_DIR_LIGHTS+NUM_POINT_LIGHTS) are point lights;// indices [NUM_DIR_LIGHTS+NUM_POINT_LIGHTS,//NUM_DIR_LIGHTS+NUM_POINT_LIGHT+NUM_SPOT_LIGHTS)// are spot lights for a maximum of MaxLights per object.Light gLights[MaxLights];};struct VertexIn{float3 PosL : POSITION;float3 NormalL : NORMAL;float2 TexC : TEXCOORD;};struct VertexOut{float4 PosH : SV_POSITION;float3 PosW : POSITION;float3 NormalW : NORMAL;float2 TexC : TEXCOORD;};VertexOut VS(VertexIn vin){VertexOut vout = (VertexOut)0.0f;// Fetch the material data.MaterialData matData = gMaterialData[gMaterialIndex];// Transform to world space.float4 posW = mul(float4(vin.PosL, 1.0f), gWorld);vout.PosW = posW.xyz;// Assumes nonuniform scaling; otherwise, need to use inverse-transpose// of world matrix.vout.NormalW = mul(vin.NormalL, (float3x3)gWorld);// Transform to homogeneous clip space.vout.PosH = mul(posW, gViewProj);// Output vertex attributes for interpolation across triangle.float4 texC = mul(float4(vin.TexC, 0.0f, 1.0f), gTexTransform);vout.TexC = mul(texC, matData.MatTransform).xy;return vout;}float4 PS(VertexOut pin) : SV_Target{// Fetch the material data.MaterialData matData = gMaterialData[gMaterialIndex];float4 diffuseAlbedo = matData.DiffuseAlbedo;float3 fresnelR0 = matData.FresnelR0;float roughness = matData.Roughness;uint diffuseTexIndex = matData.DiffuseMapIndex;// Dynamically look up the texture in the array.diffuseAlbedo *= gDiffuseMap[diffuseTexIndex].Sample(gsamLinearWrap, pin.TexC);// Interpolating normal can unnormalize it, so renormalize it.pin.NormalW = normalize(pin.NormalW);// Vector from point being lit to eye.float3 toEyeW = normalize(gEyePosW - pin.PosW);// Light terms.float4 ambient = gAmbientLight*diffuseAlbedo;Material mat = { diffuseAlbedo, fresnelR0, roughness };float4 directLight = ComputeDirectLighting(gLights, mat, pin.PosW, pin.NormalW, toEyeW);float4 litColor = ambient + directLight;// Common convention to take alpha from diffuse albedo.litColor.a = diffuseAlbedo.a;return litColor;}
为了总结本章,动态索引三个额外的用途如下:
- 合并使用不同纹理的网格到一个渲染项目,这样可以在同一个绘制调用中绘制它们。网格可以在顶点结构中保存texture/material属性;
- 一个rendering-pass中包含多个纹理(纹理有不同的大小和格式);
- 使用不用的纹理和材质实例化渲染项目,材质使用SV_InstanceID值作为索引。我们可以在下一章看到例子。
6 总结
- 我们通过摄像机的位置和方向来定义相机坐标系;
- 在相机类中添加透视投影矩阵;
- 添加前后左右移动,以及上下左右旋转;
- 动态索引是新的着色器5.1模型的功能,它可以让我们动态索引一组不同大小和格式的纹理。
7 练习
2、修改摄像机Demo,添加Roll函数,让相机可以围绕前向向量旋转(空战游戏中很有用):
Camera类添加代码:
void Roll(float angle); // 添加Rollvoid Camera::Roll(float angle){// Rotate up and look vector about the look vector.XMMATRIX R = XMMatrixRotationAxis(XMLoadFloat3(&mLook), angle);XMStoreFloat3(&mUp, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&mUp), R));XMStoreFloat3(&mRight, XMVector3TransformNormal(XMLoadFloat3(&mRight), R));mViewDirty = true;}
然后主App类中的RollAndBoxes::OnKeyboardInput函数中添加代码:
// 添加Rollif (GetAsyncKeyState('Q') & 0x8000)mCamera.Roll(3.0f*dt);if (GetAsyncKeyState('E') & 0x8000)mCamera.Roll(-3.0f*dt);

Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十五章:第一人称摄像机和动态索引的更多相关文章
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十二章:四元数(QUATERNIONS)
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十二章:四元数(QUATERNIONS) 学习目标 回顾复数,以及 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十九章:法线贴图
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十九章:法线贴图 学习目标 理解为什么需要法线贴图: 学习法线贴图如 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十六章:实例化和截头锥体裁切
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十六章:实例化和截头锥体裁切 代码工程地址: https://git ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十四章:曲面细分阶段
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十四章:曲面细分阶段 代码工程地址: https://github. ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十二章:几何着色器(The Geometry Shader)
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十二章:几何着色器(The Geometry Shader) 代码工 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十八章:立方体贴图
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十八章:立方体贴图 代码工程地址: https://github.c ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 全书总结
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 全书总结 本系列文章中可能有很多翻译有问题或者错误的地方:并且有些章节 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- Direct12优化
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- Direct12优化 第一章:向量代数 1.向量计算的时候,使用XMV ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十三章:角色动画
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十三章:角色动画 学习目标 熟悉蒙皮动画的术语: 学习网格层级变换 ...
随机推荐
- Redis学习笔记03-持久化
redis是一个内存型数据库,这就意味着,当主机重启或者宕机时,内存中的数据会被清空,redis可能会丢失数据.为了保存数据,实现数据持久化就必须要有一种机制,可以将redis数据库的数据保留在硬盘上 ...
- leetcode 847. Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes 无向连通图遍历最短路径
设计最短路径 用bfs 天然带最短路径 每一个状态是 当前的阶段 和已经访问过的节点 下面是正确但是超时的代码 class Solution: def shortestPathLength(self, ...
- 如何提高英语听力(内容摘自NECCS)+ 乘法表
乘法表 print('\n'.join([' '.join(['%s*%s=%-2s'%(y,x,x*y) for y in range(1,x+1)]) for x in range(1,10)]) ...
- Broken Keyboard UVA 11988 数组实现链表
这个构造十分巧妙,,,又学到一招,有点类似数组实现的邻接表 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <cstdi ...
- 使用Jedis操作Redis-使用Java语言在客户端操作---String类型
前提:需要引入Jedis的jar包. /** * 我的redis在Linux虚拟机Centos7中,192.168.222.129是我虚拟机的ip地址. */ private static Jedis ...
- 字符串无法分割 split无效: java split()使用“.” “\” "|" "*" "+"要转义
.是特殊字符 特殊字符需要转义. 改成split(“\\.”)
- el表达式 jsp页面取list的长度
方法1 ${cimlistForJsp.size()} 方法2,引入 <%@ taglib prefix="fn" uri="http://java.sun.com ...
- IO流10 --- 缓冲流(字节型)实现非文本文件的复制 --- 技术搬运工(尚硅谷)
字节型缓冲流,BufferedOutputStream默认缓冲区大小 8192字节byte,满了自动flush() @Test public void test6(){ File srcFile = ...
- Mac系统常用快捷键大全
苹果Mac系统常用快捷键有很多,但是很多童鞋对于这些mac快捷键都不是很熟悉,今天小编为大家整理了一份Mac系统常用快捷键大全,大家快收藏起来吧!平时在使用mac系统的时候可以提高不少工作效率哦! M ...
- Nginx负载均衡反向代理
http{ upstream test.com { server 118.118.66.88:8080; } server { listen 80; server_name www.test.com; ...
