王艳 201771010127《面向对象程序设计(java)》第八周学习总结
一:理论部分。
1.接口:Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多接口。(接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,它由常量和一组抽象方法组成)
1)通常,接口名称以able或ible结尾。
接口中不包括变量和有具体实现的方法。
2)声明方式:public interface 接口名 { }
扩展方法:public interface 接口1 extends 接口2{ }
3)接口中的所有常量必须是public static final,方法必须是public abstract。(系统默认的)
要将类声明为实现某个接口,需要使用关键字implements:class Employee implements Printable
4)接口不能构造接口对象,但可以声明接口变量以指向一个实现了该接口的类对象。、
5)接口与抽象类的区别:a.接口不能实现任何方法,而抽象类可以
b.一个类只能有一个父类,可以有多个接口
2.接口示例。
1)回调:它一种程序设计模式,可指出某个特定事件发生时程序应该采取的动作。
例如在java。swing包中有一个Timer类,可以使用它在达到给定时间间隔发出通告。
3.Comparator接口(java.util.*包中)的用途:处理字符串按长度进行排序的操作.
4.对象克隆:如果希望copy是一个新对象,它的初始状态与original相同,但是之后他们会有各自不同的状态,这是就可以使用clone方法。
1)clone方法是Object的一个protected方法,如果要调用clone方法,就需要覆盖clone()方法,并将属性设置为public。(在类的clone方法中,调用super.clone())
Object.clone()方法返回一个Object对象,必须进行强制类型转换才能得到需要的类型。
2)浅层拷贝:被拷贝对象的所有常量成员和基本类型属性都有与原来对象相同的拷贝值,而若成员域是一个对象,则被拷贝对象该对象域的对象引用仍然指向原来的对象。
深层拷贝:被拷贝对象的所有成员域都含有与原来对象相同的值,且对象域将指向被复制过的新对象,而不是原有对象被引用的对象。(要实现深拷贝,必须克隆类中所有的对象实例域。)
5.lambda表达式:本质上是一个匿名方法。
如public int add(intx,int y){return x+y};用lambda表达式表达为:lambda(int x,int y)->x+y;
6.函数式接口:只有一个方法的接口(标注:@FunctionalInterface)
二:实验部分。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握接口定义方法;
(2) 掌握实现接口类的定义要求;
(3) 掌握实现了接口类的使用要求;
(4) 掌握程序回调设计模式;
(5) 掌握Comparator接口用法;
(6) 掌握对象浅层拷贝与深层拷贝方法;
(7) 掌握Lambda表达式语法;
(8) 了解内部类的用途及语法要求。
2、程序测试。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第6章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行阅读教材214页-215页程序6-1、6-2,理解程序并分析程序运行结果;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握接口的实现用法;
l 掌握内置接口Compareable的用法。
程序如下:
import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates the use of the Comparable interface.
* @version 1.30 2004-02-27
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EmployeeSortTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Employee[] staff = new Employee[]; staff[] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", );
staff[] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", );
staff[] = new Employee("Tony Tester", ); Arrays.sort(staff);//调用Arrays类的sort方法(只有被static方法修饰了才可以这样调用) //输出所有employee对象的信息
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary());
}
}
用户自定义模块:
public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee>//实现接口类
{
private String name;
private double salary; public Employee(String name, double salary)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
} /**
* Compares employees by salary
* @param other another Employee object
* @return a negative value if this employee has a lower salary than
* otherObject, 0 if the salaries are the same, a positive value otherwise
*/
public int compareTo(Employee other)//比较Employee与其他对象的大小
{
return Double.compare(salary, other.salary);//调用double的compare方法
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

测试程序2:
l 编辑、编译、调试以下程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序:
interface A//接口A
{
double g=9.8;
void show( );
}
class C implements A//C实现接口A
{
public void show( )
{System.out.println("g="+g);}
}
class InterfaceTest
{
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
A a=new C( );
a.show( );
System.out.println("g="+C.g);//C实现了接口A,所以可以用C调用A中的变量
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材223页6-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 26行、36行代码参阅224页,详细内容涉及教材12章。
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握回调程序设计模式;
程序如下:
/**
@version 1.01 2015-05-12
@author Cay Horstmann
*/ import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer;
// to resolve conflict with java.util.Timer public class TimerTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ActionListener listener = new TimePrinter();//实现ActionListener类接口 //创建一个名为listener的timer数组
// 每十秒钟一次
Timer t = new Timer(, listener);//生成内置类对象
t.start();//调用t中的start方法 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");//窗口显示信息“Quit program?”
System.exit();
}
} class TimePrinter implements ActionListener//用户自定义类:实现接口
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
System.out.println("At the tone, the time is " + new Date());
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();//返回Toolkit方法,借助Toolkit对象控制响铃
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
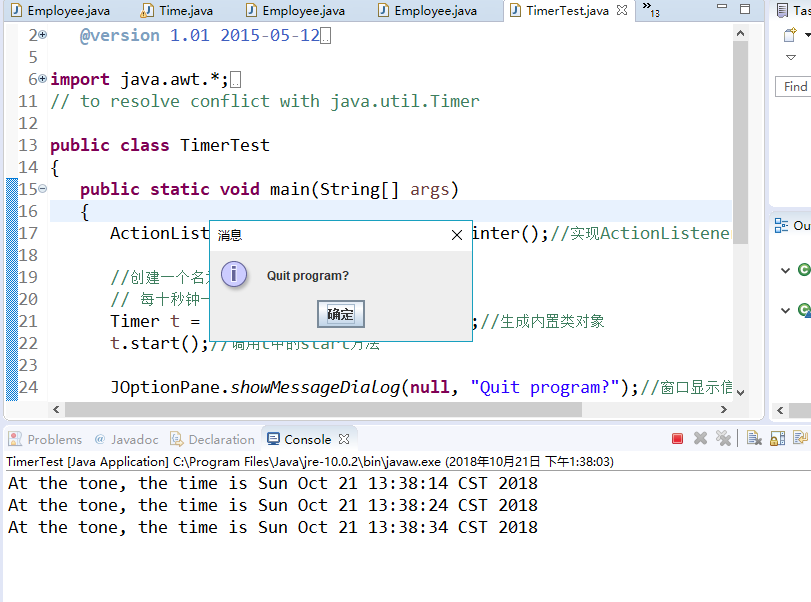
测试程序4:
调试运行教材229页-231页程序6-4、6-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
掌握对象克隆实现技术;
掌握浅拷贝和深拷贝的差别。
程序如下:
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar; public class Employee implements Cloneable
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private Date hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = new Date();
} public Employee clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
// 调用对象克隆
Employee cloned = (Employee) super.clone(); // 克隆易变字段
cloned.hireDay = (Date) hireDay.clone(); return cloned;
}//可能产生异常,放在try子句中 /**
* Set the hire day to a given date.
* @param year the year of the hire day
* @param month the month of the hire day
* @param day the day of the hire day
*/
public void setHireDay(int year, int month, int day)
{
Date newHireDay = new GregorianCalendar(year, month - , day).getTime(); // 实例字段突变
hireDay.setTime(newHireDay.getTime());
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
} public String toString()
{
return "Employee[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]";
}
}
/**
* This program demonstrates cloning.
* @version 1.10 2002-07-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class CloneTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try//try子句,后面是有可能会产生错误的代码
{
Employee original = new Employee("John Q. Public", );
original.setHireDay(, , );
Employee copy = original.clone();
copy.raiseSalary();
copy.setHireDay(, , );
System.out.println("original=" + original);
System.out.println("copy=" + copy);
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException e)//没有实现cloneable接口,抛出一个异常
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
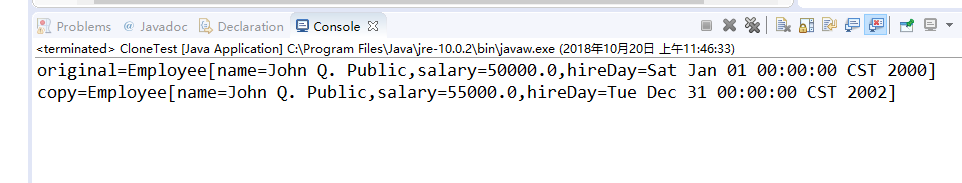
实验2: 导入第6章示例程序6-6,学习Lambda表达式用法。
l 调试运行教材233页-234页程序6-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
将27-29行代码与教材223页程序对比,将27-29行代码与此程序对比,体会Lambda表达式的优点。
程序如下:
import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer; /**
* This program demonstrates the use of lambda expressions.
* @version 1.0 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class LambdaTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] planets = new String[] { "Mercury", "Venus", "Earth", "Mars",
"Jupiter", "Saturn", "Uranus", "Neptune" };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
System.out.println("Sorted in dictionary order:");
Arrays.sort(planets);//调用Arrays类的sort方法
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
System.out.println("Sorted by length:");
Arrays.sort(planets, (first, second) -> first.length() - second.length());//lambda表达式
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets)); Timer t = new Timer(, event ->
System.out.println("The time is " + new Date()));
t.start(); // keep program running until user selects "Ok"
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");//窗口显示信息“Quit program?”
System.exit();
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

注:以下实验课后完成
实验3: 编程练习
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
程序如下:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Test{ private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist1;
public static void main(String[] args) { Personlist1 = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\lenovo\\Documents\\身份证"); try {
FileInputStream F = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(F));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String id = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String place =linescanner.nextLine();
Person Person = new Person();
Person.setname(name);
Person.setid(id);
Person.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
Person.setage(a);
Person.setbirthplace(place);
Personlist1.add(Person); }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("查找不到信息");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("信息读取有误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("1:按姓名字典序输出人员信息;");
System.out.println("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息;");
System.out.println("3.输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地");
System.out.println("4:按省份找你的同乡;");
System.out.println("5:退出");
int type = scanner.nextInt();
switch (type) {
case :
Collections.sort(Personlist1);
System.out.println(Personlist1.toString());
break;
case : int max=,min=;int j,k1 = ,k2=;
for(int i=;i<Personlist1.size();i++)
{
j=Personlist1.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
} }
System.out.println("年龄最大:"+Personlist1.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:"+Personlist1.get(k2));
break;
case :
System.out.println("place?");
String find = scanner.next();
String place=find.substring(,);
String place2=find.substring(,);
for (int i = ; i <Personlist1.size(); i++)
{
if(Personlist1.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(,).equals(place))
{
System.out.println("你的同乡:"+Personlist1.get(i));
}
} break;
case :
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int close=ageclose(yourage);
int d_value=yourage-Personlist1.get(close).getage();
System.out.println(""+Personlist1.get(close)); break;
case :
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("再见!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
}
}
public static int ageclose(int age) {
int m=;
int max=;
int d_value=;
int k=;
for (int i = ; i < Personlist1.size(); i++)
{
d_value=Personlist1.get(i).getage()-age;
if(d_value<) d_value=-d_value;
if (d_value<max)
{
max=d_value;
k=i;
} } return k; }
}
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private String id;
private int age;
private String sex;
private String birthplace;
public String getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getid() {
return id;
}
public void setid(String id) {
this.id= id;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex;
}
public void setsex(String sex) {
this.sex= sex;
}
public String getbirthplace() {
return birthplace;
}
public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) {
this.birthplace= birthplace;
}
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getname());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+id+"\t";
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
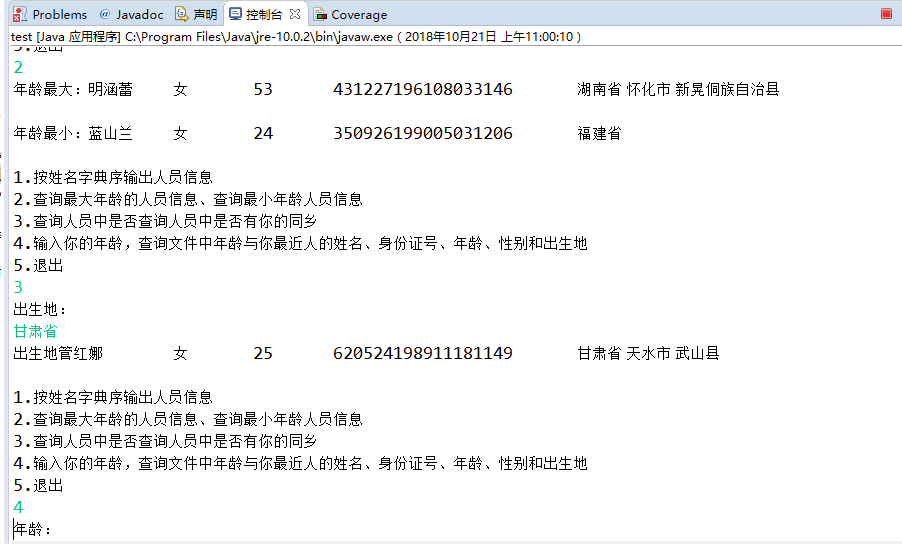

实验4:内部类语法验证实验
实验程序1:
l 编辑、调试运行教材246页-247页程序6-7,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解内部类的基本用法。
程序如下:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer; /**
* This program demonstrates the use of inner classes.
* @version 1.11 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class InnerClassTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TalkingClock clock = new TalkingClock(, true);
clock.start(); // keep program running until user selects "Ok"
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
System.exit();
}
} /**
* A clock that prints the time in regular intervals.
*/
class TalkingClock
{
private int interval;
private boolean beep; /**
* Constructs a talking clock
* @param interval the interval between messages (in milliseconds)
* @param beep true if the clock should beep
*/
public TalkingClock(int interval, boolean beep)
{
this.interval = interval;
this.beep = beep;
} /**
* Starts the clock.
*/
public void start()
{
ActionListener listener = new TimePrinter();
Timer t = new Timer(interval, listener);
t.start();
} public class TimePrinter implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
System.out.println("At the tone, the time is " + new Date());
if (beep) Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
}
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
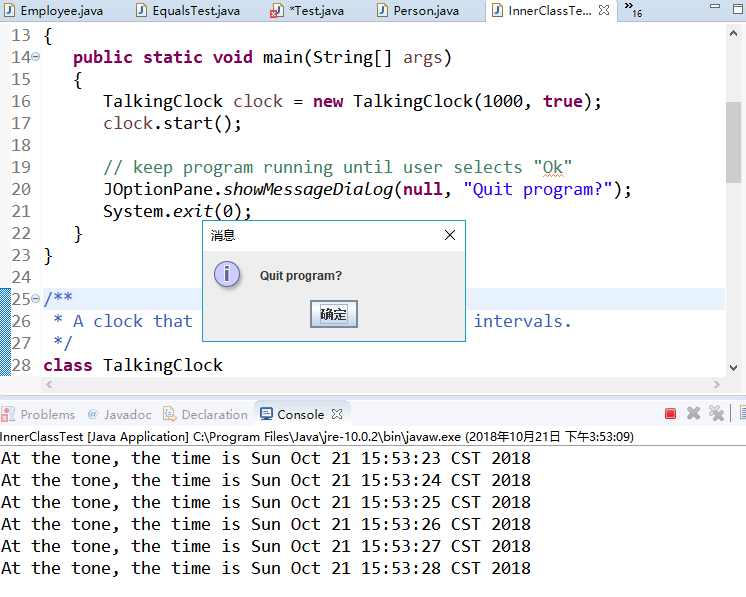
实验程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材254页程序6-8,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
了解匿名内部类的用法。
程序如下:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer; /**
* This program demonstrates anonymous inner classes.
* @version 1.11 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class AnonymousInnerClassTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TalkingClock clock = new TalkingClock();
clock.start(, true); // keep program running until user selects "Ok"
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
System.exit();
}
} /**
* A clock that prints the time in regular intervals.
*/
class TalkingClock
{
/**
* Starts the clock.
* @param interval the interval between messages (in milliseconds)
* @param beep true if the clock should beep
*/
public void start(int interval, boolean beep)
{
ActionListener listener = new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
System.out.println("At the tone, the time is " + new Date());
if (beep) Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
}
};
Timer t = new Timer(interval, listener);
t.start();
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

实验程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材257页-258页程序6-9,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解静态内部类的用法。
程序如下:
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of static inner classes.
* @version 1.02 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class StaticInnerClassTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] d = new double[];
for (int i = ; i < d.length; i++)
d[i] = * Math.random();
ArrayAlg.Pair p = ArrayAlg.minmax(d);
System.out.println("min = " + p.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + p.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg
{
/**
* A pair of floating-point numbers
*/
public static class Pair
{
private double first;
private double second; /**
* Constructs a pair from two floating-point numbers
* @param f the first number
* @param s the second number
*/
public Pair(double f, double s)
{
first = f;
second = s;
} /**
* Returns the first number of the pair
* @return the first number
*/
public double getFirst()
{
return first;
} /**
* Returns the second number of the pair
* @return the second number
*/
public double getSecond()
{
return second;
}
} /**
* Computes both the minimum and the maximum of an array
* @param values an array of floating-point numbers
* @return a pair whose first element is the minimum and whose second element
* is the maximum
*/
public static Pair minmax(double[] values)
{
double min = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
double max = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
for (double v : values)
{
if (min > v) min = v;
if (max < v) max = v;
}
return new Pair(min, max);
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

实验总结:在本周的学习过程中,主要了解了接口,接口和继承在某些方面比较相似,但是接口又在继承的基础上发展了一些优点,克服了java单继承的缺点。在学习过程中,可能是因为接口并不是具体的类,它只是实现,所以感觉接口比继承抽象一些,不太容易理解。但通过这周的学习以及实验中对具体程序的运行,对接口有了一定的掌握。自己编写饰演的过程中,在之前的基础上有的接口等新内容,自己还是不能独立完成,在同学的帮助下才勉强完成了实验。在实验课上老师讲的克隆以及函数接口等,自己还没有太掌握,在之后的学习中,一定会继续深入学习。
王艳 201771010127《面向对象程序设计(java)》第八周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 20155321 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第八周学习总结
20155321 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第八周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 创建Logger对象 static Logger getLogger(String name ...
随机推荐
- JVM原理与深度调优(三)
jvm垃圾收集算法 1.引用计数算法每个对象有一个引用计数属性,新增一个引用时计数加1,引用释放时计数减1,计数为0时可以回收.此方法简单,无法解决对象相互循环引用的问题.还有一个问题是如何解决精准计 ...
- 事件总线功能库,Reface.EventBus 详细使用教程
Reface.AppStarter 中的事件总线功能是通过 Reface.EventBus 提供的. 参考文章 : Reface.AppStarter 框架初探 使用 Reface.EventBus ...
- solr7.4创建core,导入MySQL数据,中文分词
#solr版本:7.4.0 一.新建Core 进入安装目录下得server/solr/,创建一个文件夹,如:new_core 拷贝server/solr/configsets/_default/con ...
- 关于IE8上传文件的一些问题
问题1: IE8下上传完文件后,对后台返回的JSON格式的数据,浏览器提示了下载该文件. 原因是因为IE8还不支持'application/json"类型的响应. 解决方法将后台返回的JSO ...
- 简要理解CommonJS规范
写在前面: 一个文件就是一个模块. 另外本文中的示例代码需要在node.js环境中方可正常运行,否则将出现错误.事实上ES6已经出现了模块规范,如果使用ES6的模块规范是无需node.js环境的.因此 ...
- JavaScript实现选择排序
一.选择排序简介 **冒泡排序.插入排序.选择排序合称为简单排序.**下面是选择排序的思想: 假设有一个数组a,我们想象成有一个班级名叫a班,现在全班随意排成一排,排头的位置是a[0],排尾的位置是a ...
- Linked List-1
链表一直是面试的重点问题,恰好最近看到了Stanford的一篇材料,涵盖了链表的基础知识以及派生的各种问题. 第一篇主要是关于链表的基础知识. 一.基本结构 1.数组回顾 链表和数组都是用来存储一堆数 ...
- 程序员最喜欢用的在线IDE代码编译器,什么?你竟然不知道!
1.网址https://tech.io/snippet 支持 20+ 种编程语言,页面上没有杂七杂八的东西,非常简约,非常干净,另外,它上面的代码段还可以嵌入到网页之中. 2.网址 https://w ...
- ACM卡常处理办法(虽然我到现在没遇到)
今天做预流推送,一样的代码.别人500MS(OI选手)而我5S,百思不得其解,然后我知道了还有卡常这一说. 我们今天就来看一看吧: 1.循环展开: 在缓存和寄存器允许的情况下一条语句内大量的展开运算会 ...
- 使用Redis构建电商网站
涉及到的key: 1. login,hash结构,存储用户token与用户ID之间的映射. 2. recent_tokens,存储最近登陆用户token,zset结构 member: token,sc ...
