java中ThreadPool的介绍和使用
文章目录
java中ThreadPool的介绍和使用
Thread Pool简介
在Java中,threads是和系统的threads相对应的,用来处理一系列的系统资源。不管在windows和linux下面,能开启的线程个数都是有限的,如果你在java程序中无限制的创建thread,那么将会遇到无线程可创建的情况。
CPU的核数是有限的,如果同时有多个线程正在运行中,那么CPU将会根据线程的优先级进行轮循,给每个线程分配特定的CPU时间。所以线程也不是越多越好。
在java中,代表管理ThreadPool的接口有两个:ExecutorService和Executor。
我们运行线程的步骤一般是这样的:1. 创建一个ExecutorService。 2.将任务提交给ExecutorService。3.ExecutorService调度线程来运行任务。
画个图来表示:
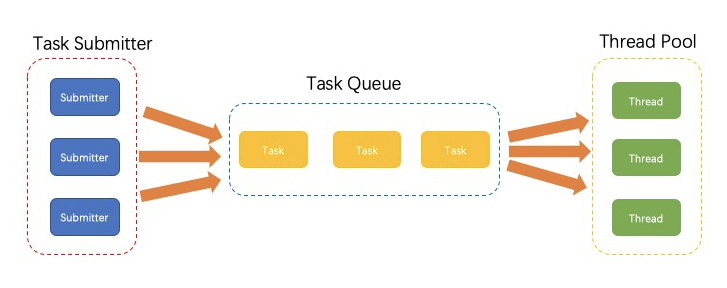
下面我讲一下,怎么在java中使用ThreadPool。
Executors, Executor 和 ExecutorService
Executors 提供了一系列简便的方法,来帮助我们创建ThreadPool。
Executor接口定义了一个方法:
public interface Executor {
/**
* Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
* may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
* thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation.
*
* @param command the runnable task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
* accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
void execute(Runnable command);
}
ExecutorService继承了Executor,提供了更多的线程池的操作。是对Executor的补充。
根据接口实现分离的原则,我们通常在java代码中使用ExecutorService或者Executor,而不是具体的实现类。
我们看下怎么通过Executors来创建一个Executor和ExecutorService:
Executor executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executor.execute(() -> log.info("in Executor"));
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.submit(()->log.info("in ExecutorService"));
executorService.shutdown();
关于ExecutorService的细节,我们这里就多讲了,感兴趣的朋友可以参考之前我写的ExecutorService的详细文章。
ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor是ExecutorService接口的一个实现,它可以为线程池添加更加精细的配置,具体而言它可以控制这三个参数:corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, 和 keepAliveTime。
PoolSize就是线程池里面的线程个数,corePoolSize表示的是线程池里面初始化和保持的最小的线程个数。
如果当前等待线程太多,可以设置maximumPoolSize来提供最大的线程池个数,从而线程池会创建更多的线程以供任务执行。
keepAliveTime是多余的线程未分配任务将会等待的时间。超出该时间,线程将会被线程池回收。
我们看下怎么创建一个ThreadPoolExecutor:
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
threadPoolExecutor.submit(()->log.info("submit through threadPoolExecutor"));
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
上面的例子中我们通过ThreadPoolExecutor的构造函数来创建ThreadPoolExecutor。
通常来说Executors已经内置了ThreadPoolExecutor的很多实现,我们来看下面的例子:
ThreadPoolExecutor executor1 =
(ThreadPoolExecutor) Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executor1.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return null;
});
executor1.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return null;
});
executor1.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return null;
});
log.info("executor1 poolsize {}",executor1.getPoolSize());
log.info("executor1 queuesize {}", executor1.getQueue().size());
executor1.shutdown();
上的例子中我们Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2)来创建一个ThreadPoolExecutor。
上面的例子中我们提交了3个task。但是我们pool size只有2。所以还有一个1个不能立刻被执行,需要在queue中等待。
我们再看一个例子:
ThreadPoolExecutor executor2 =
(ThreadPoolExecutor) Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executor2.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return null;
});
executor2.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return null;
});
executor2.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return null;
});
log.info("executor2 poolsize {}", executor2.getPoolSize());
log.info("executor2 queue size {}", executor2.getQueue().size());
executor2.shutdown();
上面的例子中我们使用Executors.newCachedThreadPool()来创建一个ThreadPoolExecutor。 运行之后我们可以看到poolsize是3,而queue size是0。这表明newCachedThreadPool会自动增加pool size。
如果thread在60秒钟之类没有被激活,则会被收回。
这里的Queue是一个SynchronousQueue,因为插入和取出基本上是同时进行的,所以这里的queue size基本都是0.
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
还有个很常用的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,它继承自ThreadPoolExecutor, 并且实现了ScheduledExecutorService接口。
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
extends ThreadPoolExecutor
implements ScheduledExecutorService
我们看下怎么使用:
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
executor.schedule(() -> {
log.info("Hello World");
}, 500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
上面的例子中,我们定义了一个定时任务将会在500毫秒之后执行。
之前我们也讲到了ScheduledExecutorService还有两个非常常用的方法:
- scheduleAtFixedRate - 以开始时间为间隔。
- scheduleWithFixedDelay - 以结束时间为间隔。
CountDownLatch lock = new CountDownLatch(3);
ScheduledExecutorService executor2 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
ScheduledFuture<?> future = executor2.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
log.info("in ScheduledFuture");
lock.countDown();
}, 500, 100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
lock.await(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
future.cancel(true);
ForkJoinPool
ForkJoinPool是在java 7 中引入的新框架,我们将会在后面的文章中详细讲解。 这里做个简单的介绍。
ForkJoinPool主要用来生成大量的任务来做算法运算。如果用线程来做的话,会消耗大量的线程。但是在fork/join框架中就不会出现这个问题。
在fork/join中,任何task都可以生成大量的子task,然后通过使用join()等待子task结束。
这里我们举一个例子:
static class TreeNode {
int value;
Set<TreeNode> children;
TreeNode(int value, TreeNode... children) {
this.value = value;
this.children = Sets.newHashSet(children);
}
}
定义一个TreeNode,然后遍历所有的value,将其加起来:
public class CountingTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {
private final TreeNode node;
public CountingTask(TreeNode node) {
this.node = node;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
return node.value + node.children.stream()
.map(childNode -> new CountingTask(childNode).fork()).mapToInt(ForkJoinTask::join).sum();
}
}
下面是调用的代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(5,
new TreeNode(3), new TreeNode(2,
new TreeNode(2), new TreeNode(8)));
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = ForkJoinPool.commonPool();
int sum = forkJoinPool.invoke(new CountingTask(tree));
}
本文的例子请参考https://github.com/ddean2009/learn-java-concurrency/tree/master/threadPool
更多教程请参考 flydean的博客
java中ThreadPool的介绍和使用的更多相关文章
- 【转】java中Thread类方法介绍
原文: java中Thread类方法介绍 http://blog.csdn.net/seapeak007/article/details/53395609 这篇文章找时间分析一下!!!:http:// ...
- Java中包的介绍
包的介绍: 未命名包 命名包 可以避免类名重复 为了更好地组织类,Java 提供了包机制,用于区别类名的命名空间. 包的作用 1.把功能相似或相关的类或接口组织在同一个包中,方便类的查找和使用. 2. ...
- Java中BigDecimal类介绍及用法
Java中提供了大数字(超过16位有效位)的操作类,即 java.math.BinInteger 类和 java.math.BigDecimal 类,用于高精度计算. 其中 BigInteger 类是 ...
- Java中RunTime类介绍
Runtime 类代表着Java程序的运行时环境,每个Java程序都有一个Runtime实例,该类会被自动创建,我们可以通过Runtime.getRuntime() 方法来获取当前程序的Runtime ...
- Java中static关键字介绍
static关键字主要有两种作用: 第一,为某特定数据类型或对象分配单一的存储空间,而与创建对象的个数无关. 第二,实现某个方法或属性与类而不是对象关联在一起 具体而言,在Java语言中,static ...
- java中commons-beanutils的介绍
1. 概述 commons-beanutil开源库是apache组织的一个基础的开源库.为apache中很多类提供工具方法.学习它是学习其它开源库实现的基础. Commons-beanutil中包 ...
- java中commons-beanutils的介绍(转)
1. 概述 commons-beanutil开源库是apache组织的一个基础的开源库.为apache中很多类提供工具方法.学习它是学习其它开源库实现的基础. Commons-beanutil中包 ...
- 15、java中的内部类介绍
内部类顾名思义就是定义在类中的类,下面做一个简单介绍: 内部类的访问规则:1,内部类可以直接访问外部类中的成员,包括私有. 之所以可以直接访问外部类中的成员,是因为内部类中持有了一个外部类的引用,格式 ...
- Java基础(40):Java中的集合介绍---Collection与Map
集合类说明及区别Collection├List│├LinkedList│├ArrayList│└Vector│ └Stack└SetMap├Hashtable├HashMap└WeakHashMap ...
随机推荐
- flink 一分钟入门篇
1. 业务说:“…… bulabula……,这个需求很简单,怎么实现我不管?” 面对霸气侧漏的业务需求,由于没有大数据知识储备,咱心里没底,咱也不敢问,咱也不敢说,只能静下来默默储备.默默寻觅解决方案 ...
- ajax使用POST提交报错400
并非BadRequest!! 在用ajax访问登录接口的时候出现了这个错误,查阅得到使用Ajax的Post需要添加 contentType: "application/x-www-form- ...
- JDK12不包含JAXB-API
##用JDK12环境下 做EUREKA的的时候 报错如下 java.lang.TypeNotPresentException: Type javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext not ...
- Redis 练习(二)
需求: 为购物网站实现登录状态及浏览记录的维护 进入时检查 token 是否已登录 每次进入更新 token 最新进入时间 记录用户浏览的商品信息(最多 25 个) 定时检查 token 数量,如果超 ...
- 《综合》MMM集群
<综合>MMM集群 部署集群基础环境 MySQL-MMM架构部署 MySQL-MMM架构使用 1 部署集群基础环境 1.1 问题 本案例要求为MySQL集群准备基础环境,完成以下任务操作: ...
- time_wait 详解和解决方案
1. 产生原因 2. 导致问题 3. Nginx 3.1 长连接 4. 解决方案 5 .参考 产生原因 TCP 连接关闭时,会有 4 次通讯(四次挥手),来确认双方都停止收发数据了.如上图,主动关闭方 ...
- IO操作与IO模型
目录 一 .IO操作本质 二. IO模型 BIO – 阻塞模式I/O NIO – 非阻塞模式I/O IO Multiplexing - I/O多路复用模型 AIO – 异步I/O模型 三.同步I/O与 ...
- "斜体显示"组件:<i> —— 快应用组件库H-UI
 <import name="i" src="../Common/ui/h-ui/text/c_tag_i"></import> &l ...
- 012-C语言小游戏之推箱子
012-C语言小游戏之推箱子 一.创建游戏地图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #define ROWS 11 #define COLS 12 char ...
- 如何用 Python 绘制玫瑰图等常见疫情图
新冠疫情已经持续好几个月了,目前,我国疫情已经基本控制住了,而欧美国家正处于爆发期,我们会看到很多网站都提供了多种疫情统计图,今天我们使用 Python 的 pyecharts 框架来绘制一些比较常见 ...
